热门标签
热门文章
- 1Python简单游戏代码_简单代码
- 2Android Studio--NDK编译C代码为.so文件,JNI调用
- 3计算机毕业设计之基于python的地震数据分析与可视化系统的设计与实现
- 4手机adb调试模式在那_手机数字密码忘了怎么办
- 5NLP基础概念
- 6Vscode远程服务器虚拟环境使用jupyter暨Jupyter远程访问_vscode远程jupyter
- 7javaEE -14(10000字 JavaScript入门 - 1)_javaee14
- 8大数据之 Hadoop 教程_hadoop教程
- 9AI绘画ComfyUI-插件-面部修复,快速入门安装使用!_comfui作图脸崩坏怎么修复
- 10GPT磁盘及ID号介绍_gpt分区id
当前位置: article > 正文
自动驾驶 PointNet++ 点云处理原理与代码实战 1(代码部分)_pointnet++代码
作者:小惠珠哦 | 2024-06-28 12:54:31
赞
踩
pointnet++代码
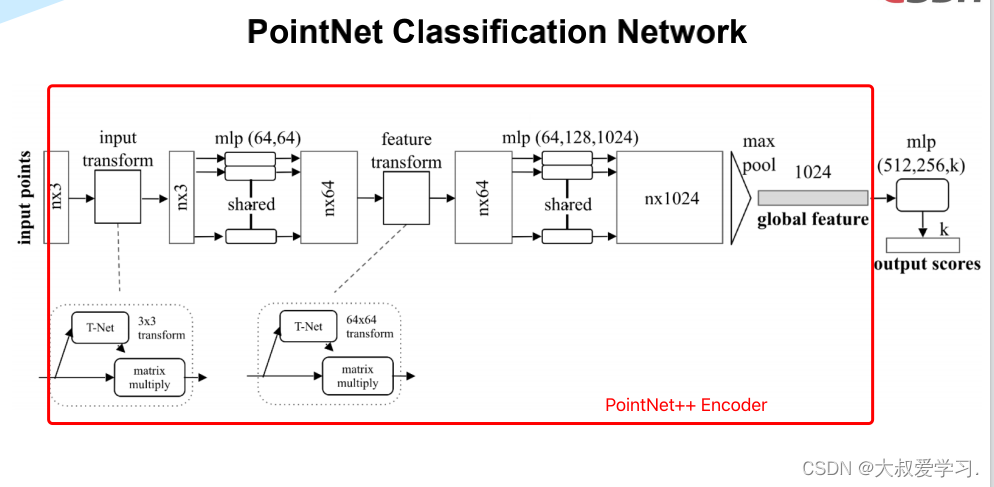
PointNet 模型代码详解
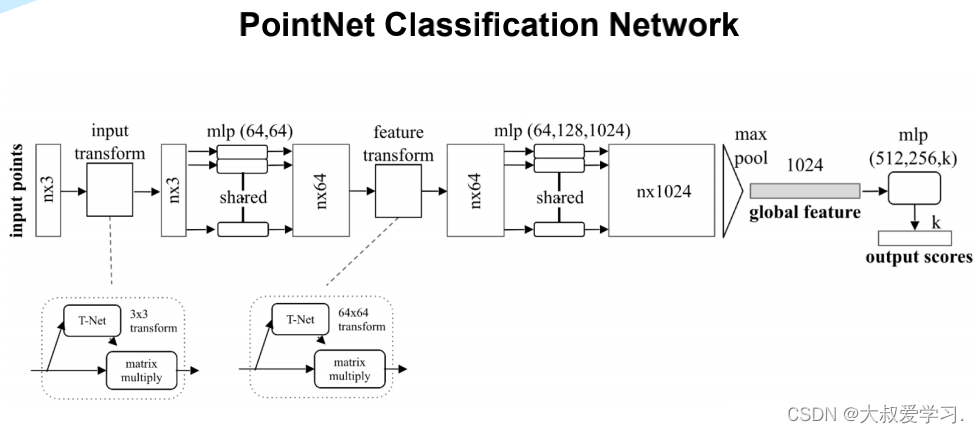
整个模型概览图
下面分部分的代码:
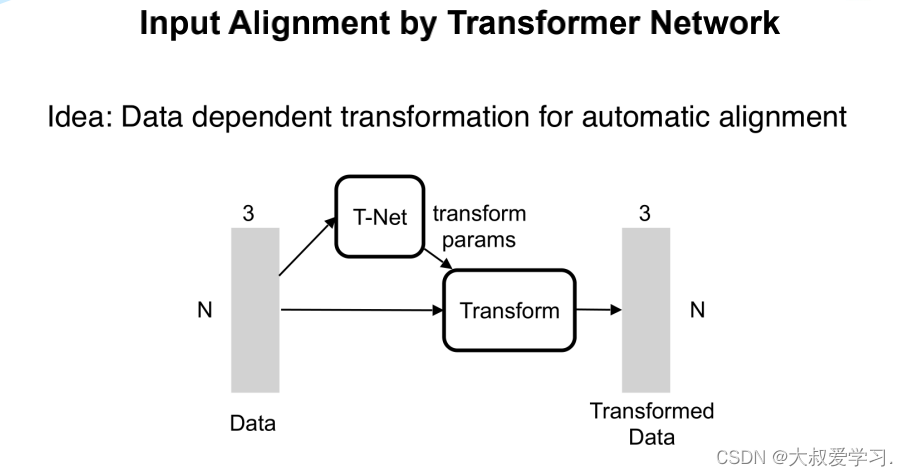
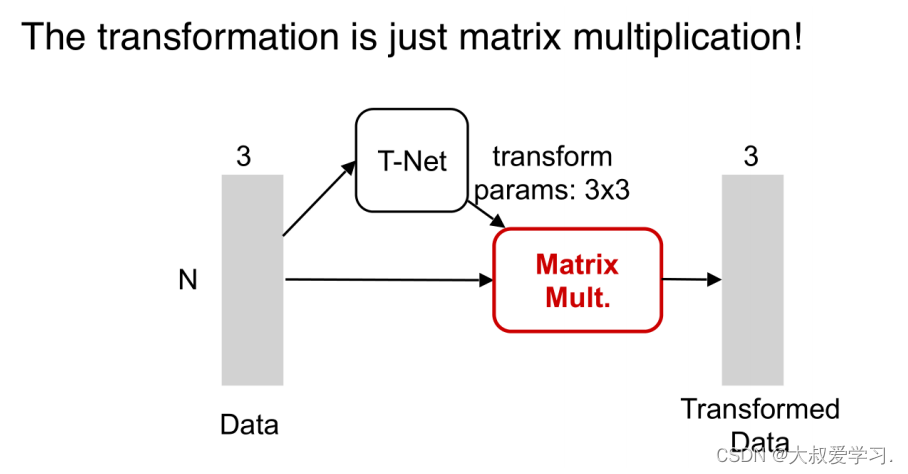
import torch.utils.data from torch.autograd import Variable import numpy as np import torch.nn.functional as F # STN3d: T-Net 3*3 transform # 类似一个mini-PointNet class STN3d(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel): super(STN3d, self).__init__() # torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True) self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(channel, 64, 1) self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1) self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 1024, 1) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 9) # 9=3*3 self.relu = nn.ReLU() self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024) self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512) self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256) def forward(self, x): batchsize = x.size()[0] x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x))) # Symmetric function: max pooling x = torch.max(x, 2, keepdim=True)[0] # x参数展平(拉直) x = x.view(-1, 1024) x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.fc1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.fc2(x))) x = self.fc3(x) # 展平的对角矩阵:np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]) iden = Variable(torch.from_numpy(np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]).astype(np.float32))).view(1, 9).repeat( batchsize, 1) if x.is_cuda: iden = iden.cuda() x = x + iden # affine transformation # 用view,转换成batchsize*3*3的数组 x = x.view(-1, 3, 3) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
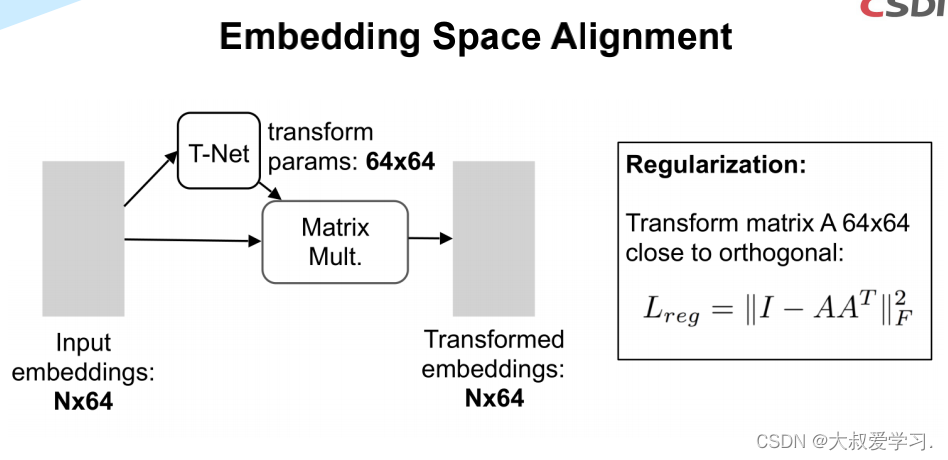
# STNkd: T-Net 64*64 transform,k默认是64 class STNkd(nn.Module): def __init__(self, k=64): super(STNkd, self).__init__() self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(k, 64, 1) self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1) self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 1024, 1) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, k * k) self.relu = nn.ReLU() self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024) self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512) self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256) self.k = k def forward(self, x): batchsize = x.size()[0] x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x))) # Symmetric function: max pooling x = torch.max(x, 2, keepdim=True)[0] # 参数拉直(展平) x = x.view(-1, 1024) x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.fc1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.fc2(x))) x = self.fc3(x) # 展平的对角矩阵 iden = Variable(torch.from_numpy(np.eye(self.k).flatten().astype(np.float32))).view(1, self.k * self.k).repeat( batchsize, 1) if x.is_cuda: iden = iden.cuda() x = x + iden # affine transformation x = x.view(-1, self.k, self.k) return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
# PointNet编码器 class PointNetEncoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, global_feat=True, feature_transform=False, channel=3): super(PointNetEncoder, self).__init__() self.stn = STN3d(channel) # STN3d: T-Net 3*3 transform self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(channel, 64, 1) self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1) self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 1024, 1) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024) self.global_feat = global_feat self.feature_transform = feature_transform if self.feature_transform: self.fstn = STNkd(k=64) # STNkd: T-Net 64*64 transform def forward(self, x): B, D, N = x.size() # batchsize,3(xyz坐标)或6(xyz坐标+法向量),1024(一个物体所取的点的数目) trans = self.stn(x) # STN3d T-Net x = x.transpose(2, 1) # 交换一个tensor的两个维度 if D >3 : x, feature = x.split(3,dim=2) # 对输入的点云进行输入转换(input transform) # input transform: 计算两个tensor的矩阵乘法 # bmm是两个三维张量相乘, 两个输入tensor维度是(b×n×m)和(b×m×p), # 第一维b代表batch size,输出为(b×n×p) x = torch.bmm(x, trans) if D > 3: x = torch.cat([x,feature],dim=2) x = x.transpose(2, 1) x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) # MLP if self.feature_transform: trans_feat = self.fstn(x) # STNkd T-Net x = x.transpose(2, 1) # 对输入的点云进行特征转换(feature transform) # feature transform: 计算两个tensor的矩阵乘法 x = torch.bmm(x, trans_feat) x = x.transpose(2, 1) else: trans_feat = None pointfeat = x # 局部特征 x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))) # MLP x = self.bn3(self.conv3(x)) # MLP x = torch.max(x, 2, keepdim=True)[0] # 最大池化得到全局特征 x = x.view(-1, 1024) # 展平 if self.global_feat: # 需要返回的是否是全局特征? return x, trans, trans_feat # 返回全局特征 else: x = x.view(-1, 1024, 1).repeat(1, 1, N) # 返回局部特征与全局特征的拼接 return torch.cat([x, pointfeat], 1), trans, trans_feat # 对特征转换矩阵做正则化: # constrain the feature transformation matrix to be close to orthogonal matrix def feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans): d = trans.size()[1] I = torch.eye(d)[None, :, :] # torch.eye(n, m=None, out=None) 返回一个2维张量,对角线位置全1,其它位置全0 if trans.is_cuda: I = I.cuda() # 正则化损失函数 loss = torch.mean(torch.norm(torch.bmm(trans, trans.transpose(2, 1) - I), dim=(1, 2))) return loss
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
PointNet++ 点云处理任务的代码
PointNet++ 物体形状分类代码
import torch.nn as nn import torch.utils.data import torch.nn.functional as F from pointnet import PointNetEncoder, feature_transform_reguliarzer class get_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, k=40, normal_channel=True): super(get_model, self).__init__() if normal_channel: channel = 6 else: channel = 3 self.feat = PointNetEncoder(global_feat=True, feature_transform=True, channel=channel) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, k) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.4) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256) self.relu = nn.ReLU() def forward(self, x): x, trans, trans_feat = self.feat(x) x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.fc1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.dropout(self.fc2(x)))) x = self.fc3(x) x = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) # 计算对数概率 return x, trans_feat class get_loss(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, mat_diff_loss_scale=0.001): super(get_loss, self).__init__() self.mat_diff_loss_scale = mat_diff_loss_scale def forward(self, pred, target, trans_feat): # NLLLoss的输入是一个对数概率向量和一个目标标签. 它不会计算对数概率. # 适合网络的最后一层是log_softmax. # 损失函数 nn.CrossEntropyLoss()与NLLLoss()相同, 唯一的不同是它去做softmax. loss = F.nll_loss(pred, target) # 分类损失 mat_diff_loss = feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans_feat) #特征变换正则化损失 # 总的损失函数 total_loss = loss + mat_diff_loss * self.mat_diff_loss_scale return total_loss
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
PointNet++ 部件分割代码
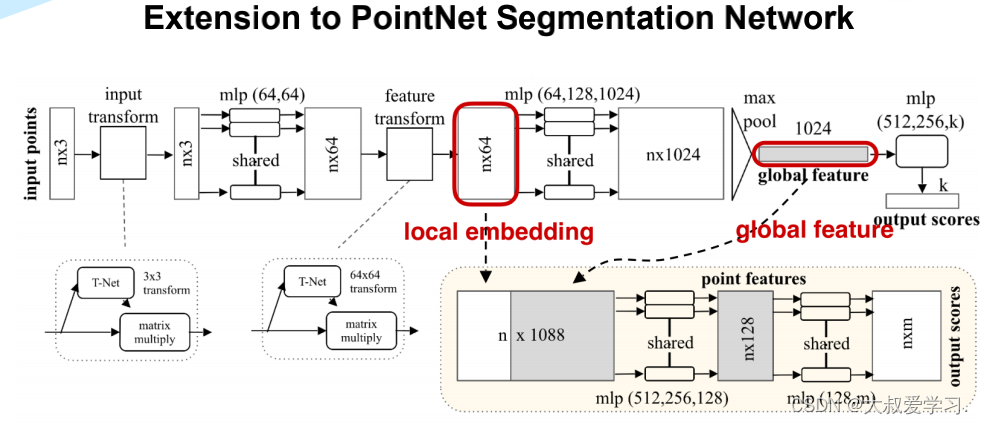
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.parallel import torch.utils.data import torch.nn.functional as F from pointnet import STN3d, STNkd, feature_transform_reguliarzer class get_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, part_num=50, normal_channel=True): super(get_model, self).__init__() if normal_channel: # 是否有法向量信息 channel = 6 else: channel = 3 self.part_num = part_num # 部件类别数量, ShapeNet中为50 self.stn = STN3d(channel) self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(channel, 64, 1) self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1) self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 128, 1) self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 512, 1) self.conv5 = torch.nn.Conv1d(512, 2048, 1) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512) self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(2048) self.fstn = STNkd(k=128) # 维度为128 self.convs1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(4944, 256, 1) self.convs2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 256, 1) self.convs3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 128, 1) self.convs4 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, part_num, 1) self.bns1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256) self.bns2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256) self.bns3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) def forward(self, point_cloud, label): B, D, N = point_cloud.size() trans = self.stn(point_cloud) point_cloud = point_cloud.transpose(2, 1) if D > 3: point_cloud, feature = point_cloud.split(3, dim=2) point_cloud = torch.bmm(point_cloud, trans) if D > 3: point_cloud = torch.cat([point_cloud, feature], dim=2) point_cloud = point_cloud.transpose(2, 1) out1 = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(point_cloud))) out2 = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(out1))) out3 = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(out2))) trans_feat = self.fstn(out3) x = out3.transpose(2, 1) net_transformed = torch.bmm(x, trans_feat) net_transformed = net_transformed.transpose(2, 1) out4 = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(net_transformed))) out5 = self.bn5(self.conv5(out4)) out_max = torch.max(out5, 2, keepdim=True)[0] # max后为2048个元素 out_max = out_max.view(-1, 2048) out_max = torch.cat([out_max,label.squeeze(1)],1) expand = out_max.view(-1, 2048+16, 1).repeat(1, 1, N) # 16个物体类别 concat = torch.cat([expand, out1, out2, out3, out4, out5], 1) # 局部特征与全局特征拼接 net = F.relu(self.bns1(self.convs1(concat))) net = F.relu(self.bns2(self.convs2(net))) net = F.relu(self.bns3(self.convs3(net))) net = self.convs4(net) net = net.transpose(2, 1).contiguous() net = F.log_softmax(net.view(-1, self.part_num), dim=-1) net = net.view(B, N, self.part_num) # [B, N, 50] return net, trans_feat class get_loss(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, mat_diff_loss_scale=0.001): super(get_loss, self).__init__() self.mat_diff_loss_scale = mat_diff_loss_scale def forward(self, pred, target, trans_feat): loss = F.nll_loss(pred, target) mat_diff_loss = feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans_feat) total_loss = loss + mat_diff_loss * self.mat_diff_loss_scale return total_loss
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
PointNet++ 语义分割代码
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.parallel import torch.utils.data import torch.nn.functional as F from pointnet import PointNetEncoder, feature_transform_reguliarzer class get_model(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_class, with_rgb=True): super(get_model, self).__init__() if with_rgb: channel = 6 else: channel = 3 self.k = num_class # 类别数 self.feat = PointNetEncoder(global_feat=False, feature_transform=True, channel=channel) # 注意:global_feat=False self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(1088, 512, 1) self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(512, 256, 1) self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 128, 1) self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, self.k, 1) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128) def forward(self, x): batchsize = x.size()[0] n_pts = x.size()[2] x, trans, trans_feat = self.feat(x) x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x))) x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x))) x = self.conv4(x) x = x.transpose(2,1).contiguous() x = F.log_softmax(x.view(-1,self.k), dim=-1) x = x.view(batchsize, n_pts, self.k) return x, trans_feat class get_loss(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, mat_diff_loss_scale=0.001): super(get_loss, self).__init__() self.mat_diff_loss_scale = mat_diff_loss_scale def forward(self, pred, target, trans_feat, weight): loss = F.nll_loss(pred, target, weight = weight) mat_diff_loss = feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans_feat) total_loss = loss + mat_diff_loss * self.mat_diff_loss_scale return total_loss if __name__ == '__main__': model = get_model(13, with_rgb=False) xyz = torch.rand(12, 3, 2048) (model(xyz))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
PointNet++ Util工具函数代码
Farthest Point Sample 最远点采样
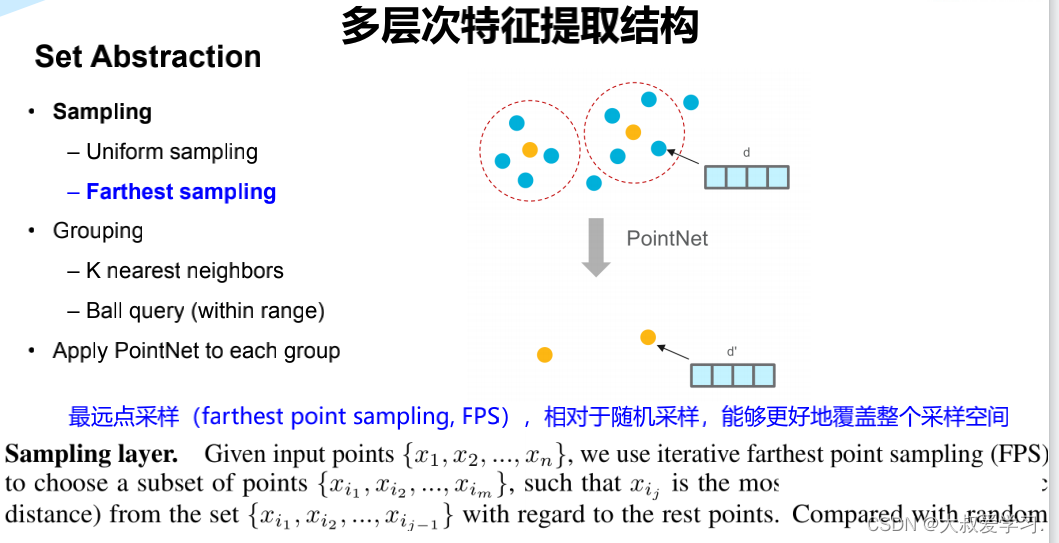
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from time import time import numpy as np def timeit(tag, t): print("{}: {}s".format(tag, time() - t)) return time() # 归一化点云,使用以centroid为中心的坐标,球半径为1 def pc_normalize(pc): l = pc.shape[0] centroid = np.mean(pc, axis=0) pc = pc - centroid m = np.max(np.sqrt(np.sum(pc**2, axis=1))) pc = pc / m return pc # square_distance函数用来在ball query过程中确定每一个点距离采样点的距离。 # 函数输入是两组点,N为第一组点src的个数,M为第二组点dst的个数,C为输入点的通道数(如果是xyz时C=3) # 函数返回的是两组点两两之间的欧几里德距离,即N×M的矩阵。 # 在训练中数据以Mini-Batch的形式输入,所以一个Batch数量的维度为B。 def square_distance(src, dst): """ Calculate Euclid distance between each two points. src^T * dst = xn * xm + yn * ym + zn * zm; sum(src^2, dim=-1) = xn*xn + yn*yn + zn*zn; sum(dst^2, dim=-1) = xm*xm + ym*ym + zm*zm; dist = (xn - xm)^2 + (yn - ym)^2 + (zn - zm)^2 = sum(src**2,dim=-1)+sum(dst**2,dim=-1)-2*src^T*dst Input: src: source points, [B, N, C] dst: target points, [B, M, C] Output: dist: per-point square distance, [B, N, M] """ B, N, _ = src.shape _, M, _ = dst.shape dist = -2 * torch.matmul(src, dst.permute(0, 2, 1)) dist += torch.sum(src ** 2, -1).view(B, N, 1) dist += torch.sum(dst ** 2, -1).view(B, 1, M) return dist # 按照输入的点云数据和索引返回索引的点云数据。 # 例如points为B×2048×3点云,idx为[5,666,1000,2000], # 则返回Batch中第5,666,1000,2000个点组成的B×4×3的点云集。 # 如果idx为一个[B,D1,...DN],则它会按照idx中的维度结构将其提取成[B,D1,...DN,C]。 def index_points(points, idx): """ Input: points: input points data, [B, N, C] idx: sample index data, [B, S] Return: new_points:, indexed points data, [B, S, C] """ device = points.device B = points.shape[0] view_shape = list(idx.shape) view_shape[1:] = [1] * (len(view_shape) - 1) repeat_shape = list(idx.shape) repeat_shape[0] = 1 batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(view_shape).repeat(repeat_shape) new_points = points[batch_indices, idx, :] return new_points # farthest_point_sample函数完成最远点采样: # 从一个输入点云中按照所需要的点的个数npoint采样出足够多的点, # 并且点与点之间的距离要足够远。 # 返回结果是npoint个采样点在原始点云中的索引。 def farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint): """ Input: xyz: pointcloud data, [B, N, 3] npoint: number of samples Return: centroids: sampled pointcloud index, [B, npoint] """ device = xyz.device B, N, C = xyz.shape # 初始化一个centroids矩阵,用于存储npoint个采样点的索引位置,大小为B×npoint # 其中B为BatchSize的个数 centroids = torch.zeros(B, npoint, dtype=torch.long).to(device) # distance矩阵(B×N)记录某个batch中所有点到某一个点的距离,初始化的值很大,后面会迭代更新 distance = torch.ones(B, N).to(device) * 1e10 # farthest表示当前最远的点,也是随机初始化,范围为0~N,初始化B个;每个batch都随机有一个初始最远点 farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device) # batch_indices初始化为0~(B-1)的数组 batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device) # 直到采样点达到npoint,否则进行如下迭代: for i in range(npoint): # 设当前的采样点centroids为当前的最远点farthest centroids[:, i] = farthest # 取出该中心点centroid的坐标 centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3) # 求出所有点到该centroid点的欧式距离,存在dist矩阵中 dist = torch.sum((xyz - centroid) ** 2, -1) # 建立一个mask,如果dist中的元素小于distance矩阵中保存的距离值,则更新distance中的对应值 # 随着迭代的继续,distance矩阵中的值会慢慢变小, # 其相当于记录着某个Batch中每个点距离所有已出现的采样点的最小距离 mask = dist < distance distance[mask] = dist[mask] # 从distance矩阵取出最远的点为farthest,继续下一轮迭代 farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1] return centroids
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
Ball Query 球查询
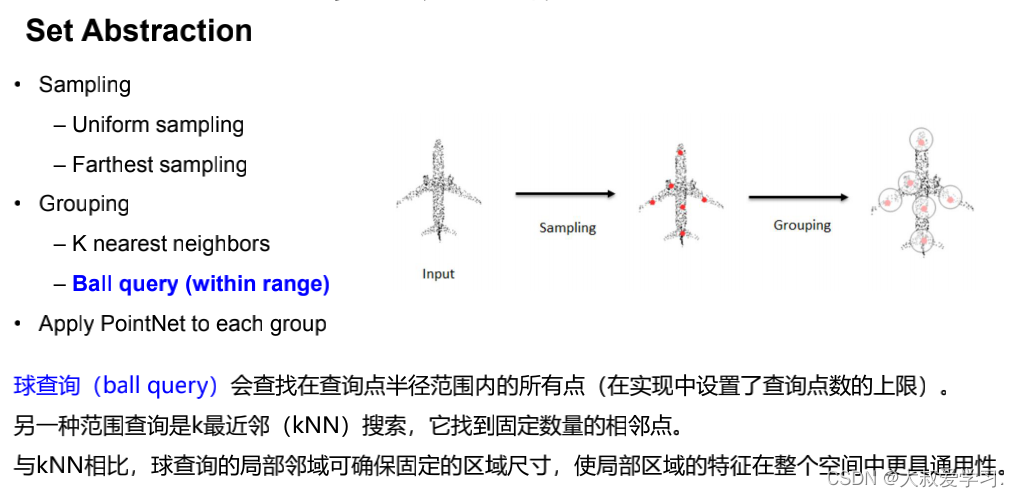
# query_ball_point函数用于寻找球形邻域中的点。 # 输入中radius为球形邻域的半径,nsample为每个邻域中要采样的点, # new_xyz为centroids点的数据,xyz为所有的点云数据 # 输出为每个样本的每个球形邻域的nsample个采样点集的索引[B,S,nsample] def query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz): """ Input: radius: local region radius nsample: max sample number in local region xyz: all points, [B, N, 3] new_xyz: query points, [B, S, 3] Return: group_idx: grouped points index, [B, S, nsample] """ device = xyz.device B, N, C = xyz.shape _, S, _ = new_xyz.shape group_idx = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(1, 1, N).repeat([B, S, 1]) # sqrdists: [B, S, N] 记录S个中心点(new_xyz)与所有点(xyz)之间的欧几里德距离 sqrdists = square_distance(new_xyz, xyz) # 找到所有距离大于radius^2的点,其group_idx直接置为N;其余的保留原来的值 group_idx[sqrdists > radius ** 2] = N # 做升序排列,前面大于radius^2的都是N,会是最大值,所以直接在剩下的点中取出前nsample个点 group_idx = group_idx.sort(dim=-1)[0][:, :, :nsample] # 考虑到有可能前nsample个点中也有被赋值为N的点(即球形区域内不足nsample个点), # 这种点需要舍弃,直接用第一个点来代替即可 # group_first: 实际就是把group_idx中的第一个点的值复制;为[B, S, K]的维度,便于后面的替换 group_first = group_idx[:, :, 0].view(B, S, 1).repeat([1, 1, nsample]) # 找到group_idx中值等于N的点 mask = group_idx == N # 将这些点的值替换为第一个点的值 group_idx[mask] = group_first[mask] return group_idx # S个group
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
Sample and Group
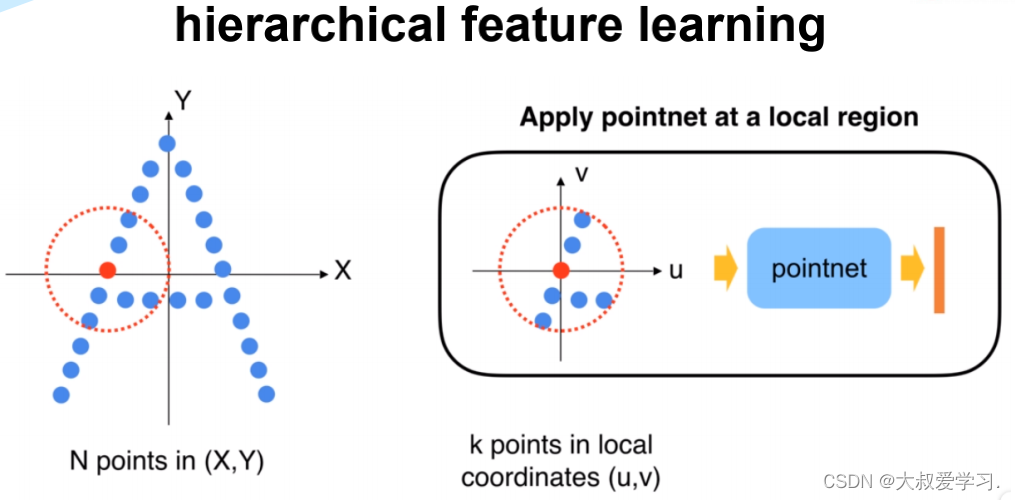
# Sampling + Grouping主要用于将整个点云分散成局部的group, # 对每一个group都可以用PointNet单独地提取局部的全局特征。 # Sampling + Grouping分成了sample_and_group和sample_and_group_all两个函数, # 其区别在于sample_and_group_all直接将所有点作为一个group。 # 例如: # 512 = npoint: points sampled in farthest point sampling # 0.2 = radius: search radius in local region # 32 = nsample: how many points in each local region def sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points, returnfps=False): """ Input: npoint: radius: nsample: xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3] points: input points data, [B, N, D] Return: new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3] new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3+D] """ B, N, C = xyz.shape S = npoint # 从原点云通过最远点采样挑出的采样点作为new_xyz: # 先用farthest_point_sample函数实现最远点采样得到采样点的索引, # 再通过index_points将这些点的从原始点中挑出来,作为new_xyz fps_idx = farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint) # [B, npoint, C] torch.cuda.empty_cache() new_xyz = index_points(xyz, fps_idx) # 中心点 torch.cuda.empty_cache() # idx:[B, npoint, nsample],代表npoint个球形区域中每个区域的nsample个采样点的索引 idx = query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz) torch.cuda.empty_cache() grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, idx) # [B, npoint, nsample, C] torch.cuda.empty_cache() # grouped_xyz减去采样点即中心值 grouped_xyz_norm = grouped_xyz - new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C) torch.cuda.empty_cache() # 如果每个点上有新的特征的维度,则拼接新的特征与旧的特征,否则直接返回旧的特征 # 注:用于拼接点特征数据和点坐标数据 if points is not None: grouped_points = index_points(points, idx) new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz_norm, grouped_points], dim=-1) # [B, npoint, nsample, C+D] else: new_points = grouped_xyz_norm if returnfps: return new_xyz, new_points, grouped_xyz, fps_idx else: return new_xyz, new_points # sample_and_group_all直接将所有点作为一个group; npoint=1 def sample_and_group_all(xyz, points): """ Input: xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3] points: input points data, [B, N, D] Return: new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, 1, 3] new_points: sampled points data, [B, 1, N, 3+D] """ device = xyz.device B, N, C = xyz.shape new_xyz = torch.zeros(B, 1, C).to(device) grouped_xyz = xyz.view(B, 1, N, C) if points is not None: new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz, points.view(B, 1, N, -1)], dim=-1) else: new_points = grouped_xyz return new_xyz, new_points
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
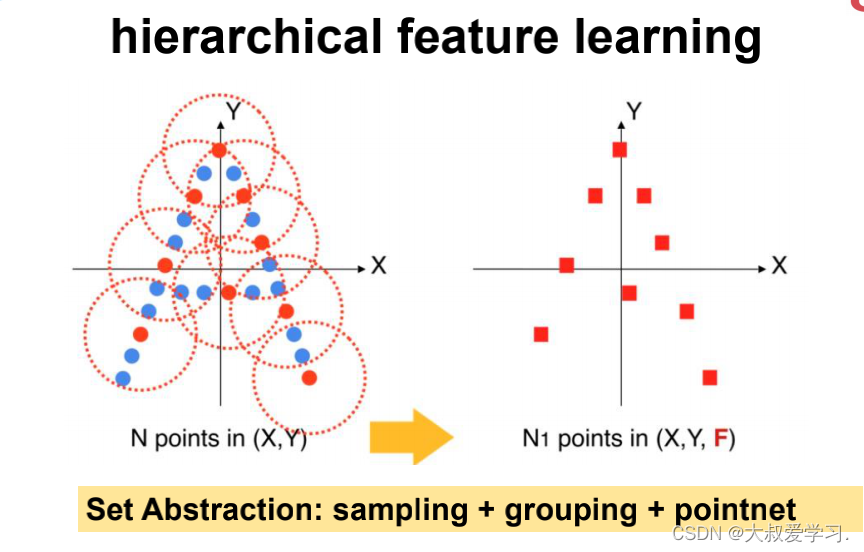
Set Abstraction

# PointNetSetAbstraction类实现普通的Set Abstraction: # 首先通过sample_and_group的操作形成局部group, # 然后对局部group中的每一个点做MLP操作,最后进行局部的最大池化,得到局部的全局特征。 class PointNetSetAbstraction(nn.Module): # 例如:npoint=128, radius=0.4, nsample=64, in_channel=128 + 3, mlp=[128, 128, 256], group_all=False # 128 = npoint: points sampled in farthest point sampling # 0.4 = radius: search radius in local region # 64 = nsample: how many points in each local region # [128, 128 ,256] = output size for MLP on each point def __init__(self, npoint, radius, nsample, in_channel, mlp, group_all): super(PointNetSetAbstraction, self).__init__() self.npoint = npoint self.radius = radius self.nsample = nsample self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList() self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList() last_channel = in_channel for out_channel in mlp: self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1)) self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)) last_channel = out_channel self.group_all = group_all def forward(self, xyz, points): """ Input: xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N] points: input points data, [B, D, N] Return: new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S] new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S] """ xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1) if points is not None: points = points.permute(0, 2, 1) # 形成局部的group if self.group_all: new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group_all(xyz, points) else: new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group(self.npoint, self.radius, self.nsample, xyz, points) # new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, C] # new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, C+D] new_points = new_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1) # [B, C+D, nsample,npoint] # 以下是pointnet操作: # 对局部group中的每一个点做MLP操作: # 利用1x1的2d的卷积相当于把每个group当成一个通道,共npoint个通道, # 对[C+D, nsample]的维度上做逐像素的卷积,结果相当于对单个C+D维度做1d的卷积 for i, conv in enumerate(self.mlp_convs): bn = self.mlp_bns[i] new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points))) # 最后进行局部的最大池化,得到局部的全局特征 new_points = torch.max(new_points, 2)[0] new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1) return new_xyz, new_points # PointNetSetAbstractionMSG类实现MSG方法的Set Abstraction: # 这里radius_list输入的是一个list,例如[0.1,0.2,0.4]; # 对于不同的半径做ball query,将不同半径下的点云特征保存在new_points_list中,最后再拼接到一起。 class PointNetSetAbstractionMsg(nn.Module): # 例如:128, [0.2, 0.4, 0.8], [32, 64, 128], 320, [[64, 64, 128], [128, 128, 256], [128, 128, 256]] def __init__(self, npoint, radius_list, nsample_list, in_channel, mlp_list): super(PointNetSetAbstractionMsg, self).__init__() self.npoint = npoint self.radius_list = radius_list self.nsample_list = nsample_list self.conv_blocks = nn.ModuleList() self.bn_blocks = nn.ModuleList() for i in range(len(mlp_list)): convs = nn.ModuleList() bns = nn.ModuleList() last_channel = in_channel + 3 for out_channel in mlp_list[i]: convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1)) bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)) last_channel = out_channel self.conv_blocks.append(convs) self.bn_blocks.append(bns) def forward(self, xyz, points): """ Input: xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N] points: input points data, [B, D, N] Return: new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S] new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S] """ xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1) if points is not None: points = points.permute(0, 2, 1) B, N, C = xyz.shape S = self.npoint # 最远点采样 new_xyz = index_points(xyz, farthest_point_sample(xyz, S)) # 将不同半径下的点云特征保存在new_points_list new_points_list = [] for i, radius in enumerate(self.radius_list): K = self.nsample_list[i] # query_ball_point函数用于寻找球形邻域中的点 group_idx = query_ball_point(radius, K, xyz, new_xyz) # 按照输入的点云数据和索引返回索引的点云数据 grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, group_idx) grouped_xyz -= new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C) if points is not None: grouped_points = index_points(points, group_idx) # 拼接点特征数据和点坐标数据 grouped_points = torch.cat([grouped_points, grouped_xyz], dim=-1) else: grouped_points = grouped_xyz grouped_points = grouped_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1) # [B, D, K, S] for j in range(len(self.conv_blocks[i])): conv = self.conv_blocks[i][j] bn = self.bn_blocks[i][j] grouped_points = F.relu(bn(conv(grouped_points))) # 最大池化,获得局部区域的全局特征 new_points = torch.max(grouped_points, 2)[0] # [B, D', S] new_points_list.append(new_points) # 不同半径下的点云特征的列表 new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1) # 拼接不同半径下的点云特征 new_points_concat = torch.cat(new_points_list, dim=1) return new_xyz, new_points_concat
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
分割中的 Feature Prepogation
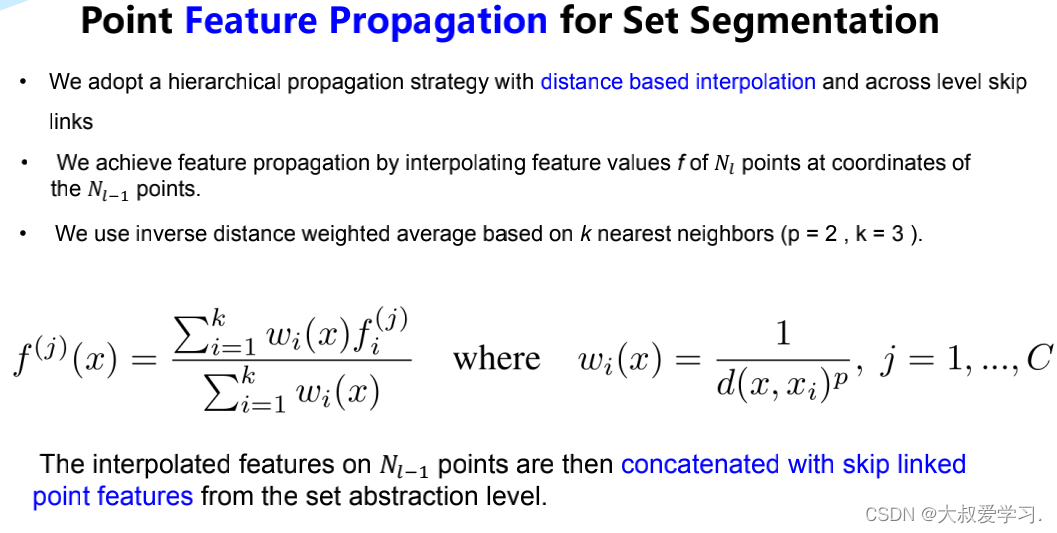
# Feature Propagation的实现主要通过线性差值和MLP完成。 # 当点的个数只有一个的时候,采用repeat直接复制成N个点; # 当点的个数大于一个的时候,采用线性差值的方式进行上采样, # 拼接上下采样对应点的SA层的特征,再对拼接后的每一个点都做一个MLP。 class PointNetFeaturePropagation(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channel, mlp): # 例如in_channel=384, mlp=[256, 128] super(PointNetFeaturePropagation, self).__init__() self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList() self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList() last_channel = in_channel for out_channel in mlp: self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv1d(last_channel, out_channel, 1)) self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channel)) last_channel = out_channel def forward(self, xyz1, xyz2, points1, points2): """ Input: xyz1: input points position data, [B, C, N] xyz2: sampled input points position data, [B, C, S] points1: input points data, [B, D, N] points2: input points data, [B, D, S] Return: new_points: upsampled points data, [B, D', N] # 上采样后的点 """ xyz1 = xyz1.permute(0, 2, 1) xyz2 = xyz2.permute(0, 2, 1) points2 = points2.permute(0, 2, 1) B, N, C = xyz1.shape _, S, _ = xyz2.shape if S == 1: # 当点的个数只有一个的时候,采用repeat直接复制成N个点 interpolated_points = points2.repeat(1, N, 1) else: # 当点的个数大于一个的时候,采用线性差值的方式进行上采样 dists = square_distance(xyz1, xyz2) dists, idx = dists.sort(dim=-1) dists, idx = dists[:, :, :3], idx[:, :, :3] # [B, N, 3] dist_recip = 1.0 / (dists + 1e-8) # 距离越远的点权重越小 norm = torch.sum(dist_recip, dim=2, keepdim=True) weight = dist_recip / norm # 对于每一个点的权重再做一个全局的归一化 # 获得插值点 interpolated_points = torch.sum(index_points(points2, idx) * weight.view(B, N, 3, 1), dim=2) if points1 is not None: points1 = points1.permute(0, 2, 1) # 拼接上下采样前对应点SA层的特征 new_points = torch.cat([points1, interpolated_points], dim=-1) else: new_points = interpolated_points new_points = new_points.permute(0, 2, 1) # 对拼接后每一个点都做一个MLP for i, conv in enumerate(self.mlp_convs): bn = self.mlp_bns[i] new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points))) return new_points
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小惠珠哦/article/detail/766032
推荐阅读
相关标签



