- 1软件测试工程师--面试题_uftuif
- 2用Python 开发植物大战僵尸游戏_python中怎么做植物大战僵尸
- 3在MAC系统中使用mysql,出现mysql: command not found的情况_command not found: mysql
- 4【点云论文速读】6D位姿估计
- 5共识问题:区块链如何确认记账权?_区块链候选记账权
- 6python sys os time random模块_pycharm安装sys os time 模块
- 7Git重修系列 ------ Git的使用和常用命令总结
- 8uniapp tabBar角标问题_uniapp再tabbar上添加动态的数字角标
- 915个超实用Python文本处理案例分享,快点码住!_python关于文件经典例子
- 10auditd 用户审计详解
python+numpy实现DNN神经网络框架(底层原理)_python ndn
赞
踩
前言:
有什么写的不对的地方请大家在评论区指出来,我会及时改正,或是有什么疑问,我也会及时解答
1.开始架构之前我先简单介绍一下神经网络
网络结构是输入层->隐藏层->隐藏层->···->隐藏层->输出层,在每一层中,我会首先计算Z = np.dot(W,A) + b,这叫做【linear_forward】,然后再计算relu(Z) 或者 sigmoid(Z),这叫做【linear_activation_forward】,合并起来就是这一层的计算方法,所以每一层的计算都有这两个步骤,计算误差,然后就开始反向传播(计算出每一层w的导数),最后更新每一层参数信息
你也可以参照下图: 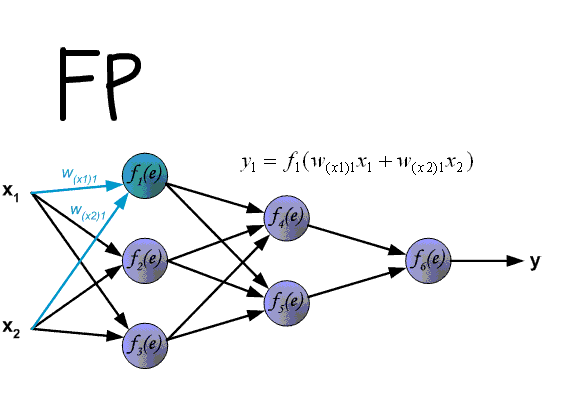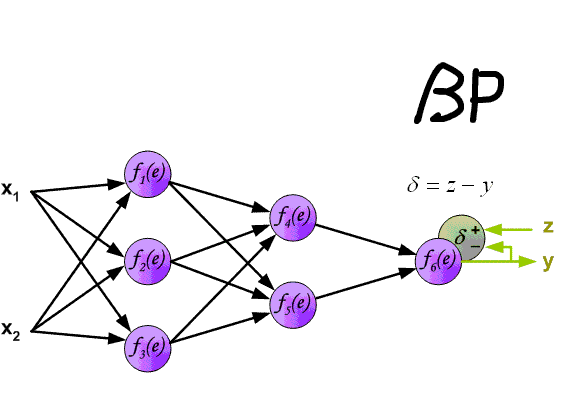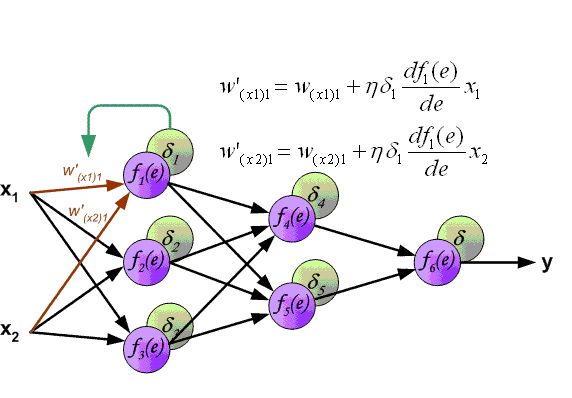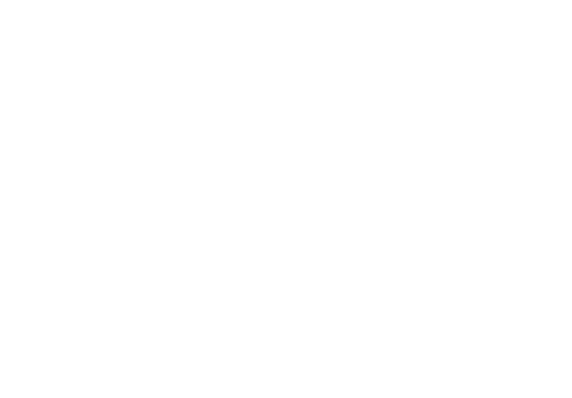
2.下面开始手写底层代码
2.1 初始化每一层的W,b
根据上的步骤我们先要把网络架构出来隐藏层层数,宽度,向前传输的公式是Z = np.dot(W,A) + b,我们根据这个公式定义矩阵和W,b,由公式np.dot(W,A) 得到W的形状就必须为(n,X.shape[0])n为该层的宽度,得到的节点结果就是(n,X.shape[1]),矩阵相加第一个维度要必须一样,所以b的形状就为(n,1),得到结果Z,Z经过激活函数变化后不会改变形状依然是(n,Xshape[1]),下一层隐藏层W形状就为(m,n)m为该层的宽度,b的形状为(m,1),依次类推,最后一层要和y的形状一样所以最后一个隐藏层的形状要为(Y.shape[0],上一层宽度),b的形状(Yshape[0],1),知道这样的规律后我们就可以写神经网络了
矩阵乘积如下图
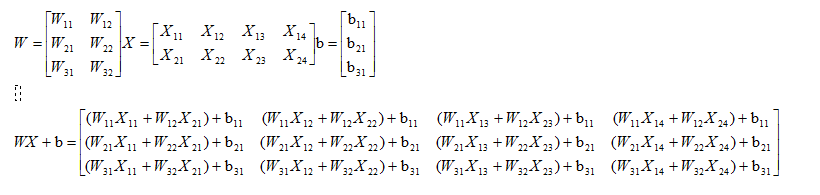
首先,我们创建一个列表来定义深度和宽度,列表的长度就是深度,列表里面的每一个值就是我们要定义的宽度
layers_dims = [X.shape[0],3,4,5,Y.shape[0]]这个列表的意思就是 有3个隐藏层,3,4,5分别代表每一个隐藏层的宽度,下面就开始初始化我们每一层的W和b值
- def initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims):
- """
- 此函数是为了初始化多层网络参数而使用的函数。
- 参数:
- layers_dims - 包含我们网络中每个图层的节点数量的列表
- 返回:
- parameters - 包含参数“W1”,“b1”,...,“WL”,“bL”的字典:
- Wi - 权重矩阵,维度为(layers_dims [i],layers_dims [i-1])
- bi - 偏向量,维度为(layers_dims [i],1)
- """
- import numpy as np
- parameters={}
- L=len(layers_dims)
- for i in range(1,L):
- parameters["W"+str(i)]=np.random.normal(size=(layers_dims[i],layers_dims[i-1]))
- parameters["b"+str(i)]=np.zeros((layers_dims[i],1))
-
- return parameters
测试一下打印一下W,b的形状看一下对不对
- X = np.array([[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]])
- Y = np.array([[0,1]])
- layers_dims = [X.shape[0],3,4,5,Y.shape[0]]
- parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)
- L = len(layers_dims)
- for i in range(1,L):
- print("W",i,"shape:",parameters["W"+str(i)].shape)
- print("b",i,"shape:",parameters["b"+str(i)].shape)
-
- 打印结果为:
- W1 shape: (3, 2)
- b1 shape: (3, 1)
- W2 shape: (4, 3)
- b2 shape: (4, 1)
- W3 shape: (5, 4)
- b3 shape: (5, 1)
- W4 shape: (1, 5)
- b4 shape: (1, 1)
layers_dims大家可以自己改变数值,和长度
2.2 向前传播
向前传播我们从公式下手比较容易 每一层的的计算公式是一样的 Z= np.dot(W,A_prev) + b A是前一层的值,W,b是对应当前层的值,A=激活函数(Z) 计算出来的A就是当前层的值,根据公式写代码
激活函数公式入下图
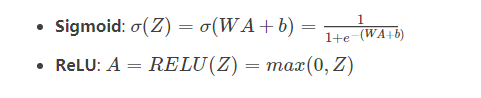
- def sigmoid(Z):
- return 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
-
-
- def linear_activation_forward(A_prev,W,b,activation):
- """
- 实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION 这一层的前向传播
- 参数:
- A_prev - 来自上一层(或输入层)的激活,维度为(上一层的节点数量,示例数)
- W - 权重矩阵,numpy数组,维度为(当前层的节点数量,前一层的大小)
- b - 偏向量,numpy阵列,维度为(当前层的节点数量,1)
- activation - 选择在此层中使用的激活函数名,字符串类型,【"sigmoid" | "relu"】
- 返回:
- A - 激活函数的输出,也称为激活后的值
- """
- Z = np.dot(W,A_prev)+b
- if activation == "relu":
- A = np.where(Z>0,Z,0)
- elif activation == "sigmoid":
- A = sigmoid(Z)
-
- return A
公式定义完了,就可以计算每一层的值一步一步的向前传播了,因为后面要向后传播求导,所以这里求出来的每一层的A我们都要记录一下
- def L_model_forward(X,parameters):
- """
- 实现[LINEAR-> RELU] *(L-1) - > LINEAR-> SIGMOID计算前向传播,也就是多层网络的前向传播,为后面每一层都执行LINEAR和ACTIVATION
- 参数:
- X - 数据,numpy数组,维度为(输入节点数量,示例数)
- parameters - initialize_parameters_deep()的输出
- 返回:
- AL - 最后的激活值
- caches - 包含参数“A1”,“A2”,...,“AL”,”的字典
- """
- A = X
- cache={}
- L = len(parameters) // 2
- for i in range(1,L):
- A = linear_activation_forward(A,parameters["W"+str(i)],parameters["b"+str(i)],"relu")
- cache["A"+str(i)]=A
- A = linear_activation_forward(A,parameters["W"+str(L)],parameters["b"+str(L)],"sigmoid")
- cache["A"+str(L)]=A
- return cache
2.3计算成本
我们已经把这模型的前向传播部分完成了,我们需要计算成本(误差),以确定它到底有没有在学习,成本的计算公式如下:
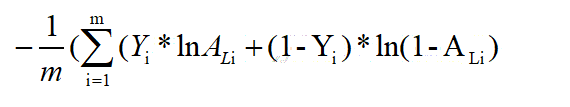
代码如下
- def compute_cost(AL,Y):
- """
- 成本函数。
- 参数:
- AL - 与标签预测相对应的概率向量,维度为(1,示例数量)
- Y - 标签向量(例如:如果不是猫,则为0,如果是猫则为1),维度为(1,数量)
- 返回:
- cost - 交叉熵成本
- """
- m = Y.shape[1]
- cost = -np.sum(np.multiply(np.log(AL),Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - AL), 1 - Y)) / m
-
- cost = np.squeeze(cost)
-
- return cost
2.4反向传播
反向传播用于计算相对于参数的损失函数的梯度,下面就是求导了,我们一个一个的来求导,先是cost的导数:
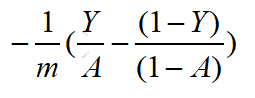
激活函数的导数 :
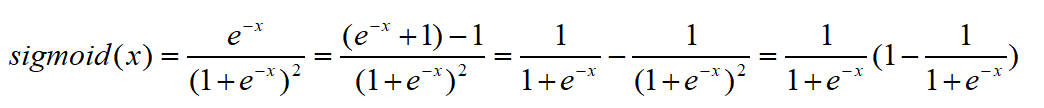
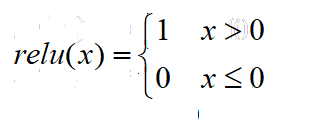
![]()
由上面的推导可得第一个倒数信息dZ:
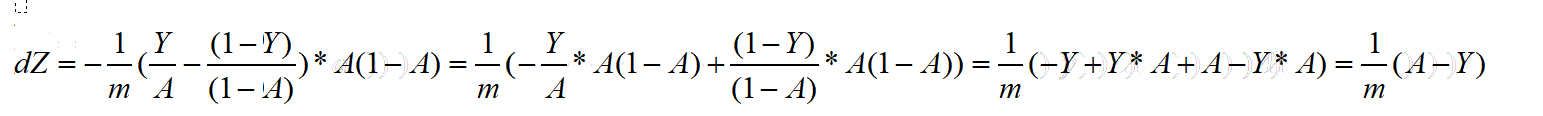
之前记录 的每个节点A值现在就要都用上了
A=WA(i-1)-b
dW=dZ*A
db=dZ
- def linear_activation_backward(X,parameters,cache):
- """
- 实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION层的后向传播。
- 参数:
- cache - 我们存储的用于有效计算反向传播的值的元组(值为linear_cache,activation_cache)
- activation - 要在此层中使用的激活函数名,字符串类型,【"sigmoid" | "relu"】
- 返回:
- dA_prev - 相对于激活(前一层i-1)的成本梯度值,与A_prev维度相同
- dW - 相对于W(当前层i)的成本梯度值,与W的维度相同
- db - 相对于b(当前层i)的成本梯度值,与b的维度相同
- """
- grads={}
- L=len(cache)
- dZ = cache["A"+str(L)] - Y
- for i in range(1,L):
- dW = (1 / m) * (np.dot(dZ, cache["A"+str(L-i)].T))
- db = (1 / m) * (np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True))
- dZ =(np.dot(parameters["W"+str(L-i+1)].T,dZ))*np.where(cache["A"+str(L-i)] > 0, 1, 0)
- grads["dW"+str(L-i)]=dW
- grads["db"+str(L-i)]=db
- dW = (1 / m) * (np.dot(dZ, X.T))
- db = (1 / m) * (np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True))
- grads["dW"+str(L-i-1)]=dW
- grads["db"+str(L-i-1)]=db
-
- return grads
2.5更新参数
我们把向前向后传播都完成了,现在我们就开始更新参数
- def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
- """
- 使用梯度下降更新参数
- 参数:
- parameters - 包含你的参数的字典
- grads - 包含梯度值的字典,是L_model_backward的输出
- 返回:
- parameters - 包含更新参数的字典
- 参数[“W”+ str(i)] = ...
- 参数[“b”+ str(i)] = ...
- """
- L = len(parameters) // 2 #整除
- for i in range(L):
- parameters["W" + str(i + 1)] = parameters["W" + str(i + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(i)]
- parameters["b" + str(i + 1)] = parameters["b" + str(i + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(i )]
-
- return parameters
3.已经全部推完了
我把它封装成了一个class
- #!usr/bin/env python
- #-*- coding:utf-8 _*-
-
- import numpy as np
-
-
- class Net(object):
-
- def __init__(self, X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate, num_iterations, num_display, num_learn_rate=None,
- learn_decline_rate=0.1,lambd=0.001):
-
- """
- X - 训练参数
- Y - 目标值
- layers_dims - 包含我们网络中每个图层的节点数量的列表 ,例如 [X.shape[0],3,5,Y.shape[0]] 两个隐藏层 宽度分别是3,5
- learning_rate - 学习率
- num_iterations - 迭代次数
- num_display - 每迭代多少次显示cost
- num_learn_rate - 每迭代多少次下降学习,默认None,不下降
- learn_decline_rate - 学习率下降比例 默认0.1
-
- lambd - 正则权重,默认0.001
- parameters - 包含参数“W1”,“b1”,...,“WL”,“bL”的字典:
- Wi - 权重矩阵,维度为(layers_dims [i],layers_dims [i-1])
- bi - 偏向量,维度为(layers_dims [i],1)
- caches - 包含参数 "A1","A2",...,"AL"的字典
- Ai - 每个节点值
- grads - 包含参数“dW1”,“db1”,...,“dWL”,“dbL”的字典:
- dWi - 相对于Wi的成本梯度值,与Wi的维度相同
- dbi - 相对于bi的成本梯度值,与bi的维度相同
- L - 网络结构的深度
- """
- self.X = X
- self.Y = Y
- self.m = self.Y.shape[1]
- self.learning_rate = learning_rate
- self.layers_dims = layers_dims
- self.L = len(self.layers_dims)
- self.num_iterations = num_iterations
- self.num_display = num_display
- self.num_learn_rate = num_learn_rate
- self.learn_decline_rate = learn_decline_rate
- self.parameters = {}
- self.cache = {}
- self.grads = {}
- self.cost = 0.0
- self.lambd = lambd
-
- def softmax(self,Z):
- Z = Z - np.max(Z)
- exp_Z = np.exp(Z)
- softmax_Z = exp_Z / np.sum(exp_Z)
- return softmax_Z
-
- def sigmoid(self, Z):
- return np.float32(1 / (1 + np.exp(-Z)))
-
- def initialize_parameters_deep(self):
- """
- 此函数是为了初始化多层网络参数而使用的函数。
- """
-
- for i in range(1, self.L):
- self.parameters["W" + str(i)] =np.float32 (np.random.normal(size=(self.layers_dims[i], self.layers_dims[i - 1])))
- self.parameters["b" + str(i)] =np.float32 (np.zeros((self.layers_dims[i], 1)))
-
- def linear_activation_forward(self, A_prev, W, b, activation):
- """
- 实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION 这一层的前向传播
- 参数:
- A_prev - 来自上一层(或输入层)的激活,维度为(上一层的节点数量,示例数)
- W - 权重矩阵,numpy数组,维度为(当前层的节点数量,前一层的大小)
- b - 偏向量,numpy阵列,维度为(当前层的节点数量,1)
- activation - 选择在此层中使用的激活函数名,字符串类型,【"sigmoid" | "relu"】
- 返回:
- A - 激活函数的输出,也称为激活后的值
- """
- Z = np.dot(W, A_prev) + b
- assert (Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
- if activation == "relu" :
- A = np.where(Z > 0, Z, 0)
- elif activation == "sigmoid" :
- A = self.sigmoid(Z)
- elif activation == "tanh" :
- A = np.tanh(Z)
- elif activation == "softmax" :
- A = self.softmax_x(Z)
- return A
-
- def L_model_forward(self):
- """
- 实现[LINEAR-> RELU] *(L-1) - > LINEAR-> SIGMOID计算前向传播,也就是多层网络的前向传播,为后面每一层都执行LINEAR和ACTIVATION
- """
- A = self.X
- for i in range(1, self.L - 1):
- A = self.linear_activation_forward(A, self.parameters["W" + str(i)], self.parameters["b" + str(i)], "relu")
- self.cache["A" + str(i)] = np.float32(A)
- A = self.linear_activation_forward(A, self.parameters["W" + str(self.L - 1)],
- self.parameters["b" + str(self.L - 1)], "softmax")
- self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)] = np.float32(A)
-
- def regularization_2(self):
- L2_regularization_cost = 0.0
- for i in range(1,self.L):
- L2_regularization_cost += np.nansum(np.square(self.parameters["W"+str(i)]))
-
- return L2_regularization_cost
-
- def pre_model_forward(self, per_X):
- """
- 实现[LINEAR-> RELU] *(L-1) - > LINEAR-> SIGMOID计算前向传播,也就是多层网络的前向传播,为后面每一层都执行LINEAR和ACTIVATION
- """
- A = per_X
- for i in range(1, self.L - 1):
- A = self.linear_activation_forward(A, self.parameters["W" + str(i)], self.parameters["b" + str(i)], "relu")
- self.cache["A" + str(i)] = np.float32(A)
- A = self.linear_activation_forward(A, self.parameters["W" + str(self.L - 1)],
- self.parameters["b" + str(self.L - 1)], "sigmoid")
- self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)] = np.float32(A)
-
- def compute_cost(self):
- """
- 实施定义的成本函数。
- 返回:
- cost - 交叉熵成本
- """
-
- m = self.Y.shape[1]
- # self.cost = -np.sum(self.Y * np.log(self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)]) + (1 - self.Y) * np.log(1 - self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)])) / m
- self.cost = (-np.nansum(np.multiply(np.log(self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)]),self.Y)\
- + np.multiply(np.log(1 - self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)]), 1 - self.Y)) / m)
- self.cost = np.squeeze(self.cost)
- L2_regularization_cost = self.regularization_2()
- self.cost += self.lambd * L2_regularization_cost / (2*m)
- self.cost = np.float32(self.cost)
-
- def linear_activation_backward(self):
- """
- 实现LINEAR-> ACTIVATION层的后向传播。
- """
- m = self.Y.shape[1]
- dZ = self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)] - self.Y
- for i in range(1, self.L - 1):
- dW = (1 / self.m) * (np.dot(dZ, self.cache["A" + str(self.L - i - 1)].T)) \
- + ((self.lambd*self.parameters["W" + str(self.L - i )])/m)
- db = (1 / self.m) * (np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True))
- dZ = (np.dot(self.parameters["W" + str(self.L - i)].T, dZ)) * np.where( \
- self.cache["A" + str(self.L - i - 1)] > 0, 1, 0)
- self.grads["dW" + str(self.L - i - 1)] = np.float32(dW)
- self.grads["db" + str(self.L - i - 1)] = np.float32(db)
- dW = (1 / self.m) * (np.dot(dZ.astype(np.float32), self.X.T)) \
- + ((self.lambd*self.parameters["W" + str(self.L - i - 1)])/m)
- db = (1 / self.m) * (np.sum(dZ.astype(np.float32), axis=1, keepdims=True))
- self.grads["dW" + str(self.L - i - 2)] = np.float32(dW)
- self.grads["db" + str(self.L - i - 2)] = np.float32(db)
-
- def update_parameters(self):
- """
- 使用梯度下降更新参数
- """
- L = len(self.parameters) // 2 # 整除
- for i in range(L):
- self.parameters["W" + str(i + 1)] = self.parameters["W" + str(i + 1)].astype(np.float32) - self.learning_rate * self.grads[
- "dW" + str(i)]
- self.parameters["b" + str(i + 1)] = self.parameters["b" + str(i + 1)].astype(np.float32) - self.learning_rate * self.grads[
- "db" + str(i)]
-
- def run(self):
-
- self.initialize_parameters_deep()
-
- for j in range(self.num_iterations + 1):
- self.L_model_forward()
- self.compute_cost()
- self.linear_activation_backward()
- self.update_parameters()
-
- if self.num_learn_rate and j % self.num_learn_rate == 0 and j:
- print("当前学习率:",self.learning_rate)
- self.learning_rate -= np.multiply(self.learning_rate , self.learn_decline_rate)
- print("下降后学习率:",self.learning_rate)
-
-
- if j % self.num_display == 0:
- print("第", j, "次迭代,cost值为:" + str(self.cost))
-
- def predict(self, per_X):
- """
- 返回
- predictions - 我们模型预测的向量
- """
- self.pre_model_forward(per_X)
- self.predictions = np.round(self.cache["A" + str(self.L - 1)])
-
- return self.predictions
有什么不对的地方还请多多指正


