- 1DFS递归之岛屿问题_岛屿问题如何处理无限递归
- 2FastDFS配置Nginx访问_fastdfs如何配置nginx访问
- 3配置基本的访问控制列表ACL【eNSP实现】_ensp访问控制列表
- 4gulimall技术栈笔记_gulimall异步笔记
- 5Pikachu靶场通关记录(详细)
- 6【华为OD】C卷真题:虚拟游戏理财 Java代码实现 【思路+代码】_华为od c卷 游戏理财
- 7深度学习(32)——CycleGAN(1)_cyclegan图像失真
- 8云、安全、网络三位一体,Akamai 推出大规模分布式边缘和云平台 Akamai Connected Cloud_akamai 安全
- 9Modbus驱动库—libmodbus驱动库的使用
- 10第八章 django_第8章django工具
【DETR】DETR训练VOC数据集/自己的数据集_pascal voc数据集转化成detr数据集
赞
踩
训练DETR
一、数据准备
DETR用的是COCO格式的数据集。
如果要用DETR训练自己的数据集,直接利用Labelimg标注成COCO格式。
1.如果是VOC数据集的话,要做一个格式转换。网上一大堆格式转换的代码都很乱,所以自己写了一个针对VOC数据集的转换。
更新:
2.针对yolo格式的数据集,转换成coco格式,可以参考我的github:yolo2coco
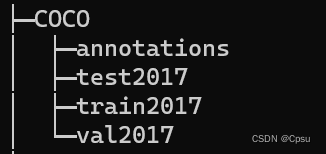
COCO数据集的格式类似这样,annotations文件夹里面有对应的train、val数据集的json文件。train2017则是训练集图片,其他同理。
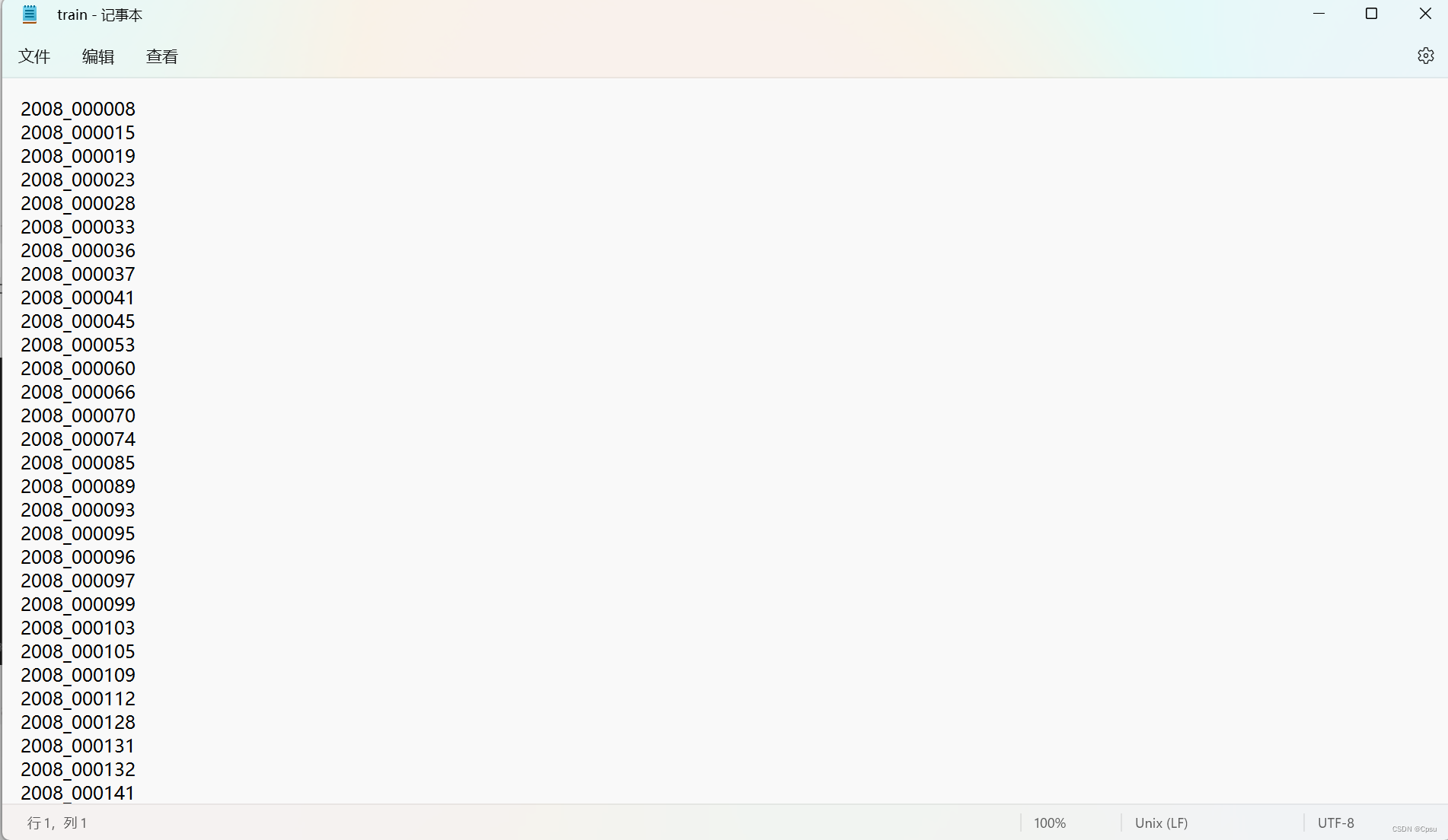
VOC数据集的存放方式是这样的,转换格式就是找出Main文件夹下用于目标检测的图片。

Main文件夹下有train.txt文件,记录了训练集的图片。val.txt记录了验证集的图片
只需要修改注释中的两个路径即可(创建文件夹时没有加判断语句严谨一点应该加上)。
import os import shutil import sys import json import glob import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET START_BOUNDING_BOX_ID = 1 # PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES = None # If necessary, pre-define category and its id PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES = {"aeroplane": 1, "bicycle": 2, "bird": 3, "boat": 4, "bottle": 5, "bus": 6, "car": 7, "cat": 8, "chair": 9, "cow": 10, "diningtable": 11, "dog": 12, "horse": 13, "motorbike": 14, "person": 15, "pottedplant": 16, "sheep": 17, "sofa": 18, "train": 19, "tvmonitor": 20} def get(root, name): vars = root.findall(name) return vars def get_and_check(root, name, length): vars = root.findall(name) if len(vars) == 0: raise ValueError("Can not find %s in %s." % (name, root.tag)) if length > 0 and len(vars) != length: raise ValueError( "The size of %s is supposed to be %d, but is %d." % (name, length, len(vars)) ) if length == 1: vars = vars[0] return vars def get_filename_as_int(filename): try: filename = filename.replace("\\", "/") filename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(filename))[0] return int(filename) except: raise ValueError( "Filename %s is supposed to be an integer." % (filename)) def get_categories(xml_files): """Generate category name to id mapping from a list of xml files. Arguments: xml_files {list} -- A list of xml file paths. Returns: dict -- category name to id mapping. """ classes_names = [] for xml_file in xml_files: tree = ET.parse(xml_file) root = tree.getroot() for member in root.findall("object"): classes_names.append(member[0].text) classes_names = list(set(classes_names)) classes_names.sort() return {name: i for i, name in enumerate(classes_names)} def convert(xml_files, json_file): json_dict = {"images": [], "type": "instances", "annotations": [], "categories": []} if PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES is not None: categories = PRE_DEFINE_CATEGORIES else: categories = get_categories(xml_files) bnd_id = START_BOUNDING_BOX_ID for xml_file in xml_files: tree = ET.parse(xml_file) root = tree.getroot() path = get(root, "path") if len(path) == 1: filename = os.path.basename(path[0].text) elif len(path) == 0: filename = get_and_check(root, "filename", 1).text else: raise ValueError("%d paths found in %s" % (len(path), xml_file)) # The filename must be a number image_id = get_filename_as_int(filename) size = get_and_check(root, "size", 1) width = int(get_and_check(size, "width", 1).text) height = int(get_and_check(size, "height", 1).text) image = { "file_name": filename, "height": height, "width": width, "id": image_id, } json_dict["images"].append(image) # Currently we do not support segmentation. # segmented = get_and_check(root, 'segmented', 1).text # assert segmented == '0' for obj in get(root, "object"): category = get_and_check(obj, "name", 1).text if category not in categories: new_id = len(categories) categories[category] = new_id category_id = categories[category] bndbox = get_and_check(obj, "bndbox", 1) xmin = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "xmin", 1).text) - 1 ymin = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "ymin", 1).text) - 1 xmax = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "xmax", 1).text) ymax = int(get_and_check(bndbox, "ymax", 1).text) assert xmax > xmin assert ymax > ymin o_width = abs(xmax - xmin) o_height = abs(ymax - ymin) ann = { "area": o_width * o_height, "iscrowd": 0, "image_id": image_id, "bbox": [xmin, ymin, o_width, o_height], "category_id": category_id, "id": bnd_id, "ignore": 0, "segmentation": [], } json_dict["annotations"].append(ann) bnd_id = bnd_id + 1 for cate, cid in categories.items(): cat = {"supercategory": "none", "id": cid, "name": cate} json_dict["categories"].append(cat) os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(json_file), exist_ok=True) json_fp = open(json_file, "w") json_str = json.dumps(json_dict) json_fp.write(json_str) json_fp.close() if __name__ == "__main__": # 只需修改以下两个路径 # VOC数据集根目录 voc_path = "VOC2012" # 保存coco格式数据集根目录 save_coco_path = "VOC2COCO" # VOC只分了训练集和验证集即train.txt和val.txt data_type_list = ["train", "val"] for data_type in data_type_list: os.makedirs(os.path.join(save_coco_path, data_type+"2017")) os.makedirs(os.path.join(save_coco_path, data_type+"_xml")) with open(os.path.join(voc_path, "ImageSets\Main", data_type+".txt"), "r") as f: txt_ls = f.readlines() txt_ls = [i.strip() for i in txt_ls] for i in os.listdir(os.path.join(voc_path, "JPEGImages")): if os.path.splitext(i)[0] in txt_ls: shutil.copy(os.path.join(voc_path, "JPEGImages", i), os.path.join(save_coco_path, data_type+"2017", i)) shutil.copy(os.path.join(voc_path, "Annotations", i[:-4]+".xml"), os.path.join( save_coco_path, data_type+"_xml", i[:-4]+".xml")) xml_path = os.path.join(save_coco_path, data_type+"_xml") xml_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(xml_path, "*.xml")) convert(xml_files, os.path.join(save_coco_path, "annotations", "instances_"+data_type+"2017.json")) shutil.rmtree(xml_path)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
结果如图所示,在voc2coco文件夹下有三个文件:

二、配置DETR
推荐使用命令行传递参数,这里修改
main.py只是为了说明参数的意义。
例如:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=8 --use_env main.py --coco_path /path/to/coco --output_dir ./output
对于
argparse命令行参数的传递有问题可以参考我的另一篇文章:argparse — 命令行选项、参数和子命令解析器详解
修改main.py文件中的参数、超参数:

这个最好不改,就设为coco。去修改models/detr.py 文件的num_classes(大概在三百多行)。这里作者也解释了num_classes其实并不是类别数,因为coco只有80类,因为coco的id是不连续的,coco数据集最大的ID是90,所以原论文时写的MAX ID +1 即91。对于我们自定义的和转化的VOC数据集num_classes就是类别数。
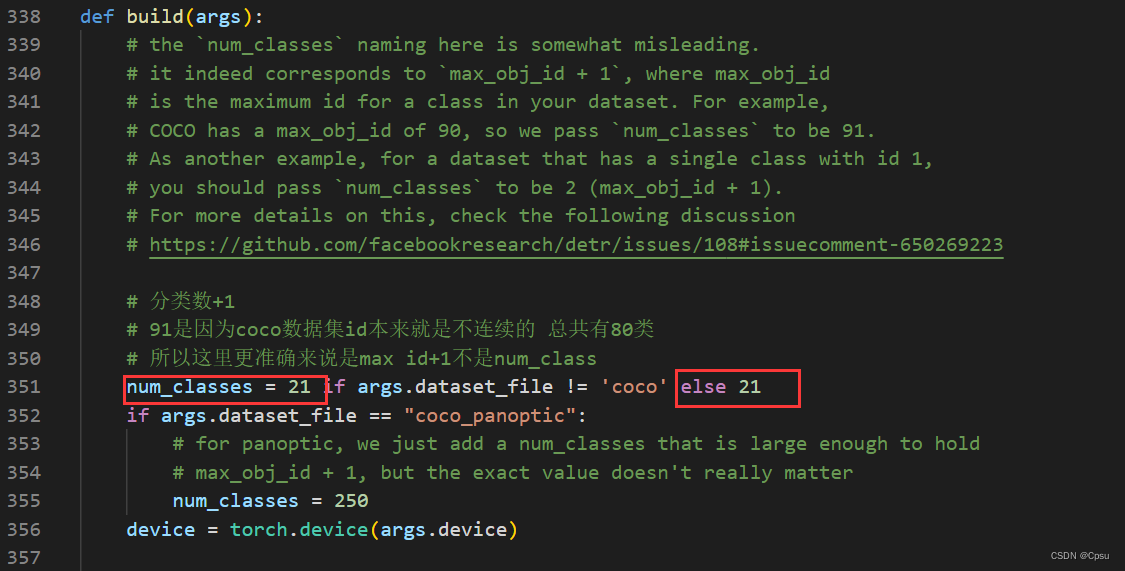

coco_path改成自己的coco路径。
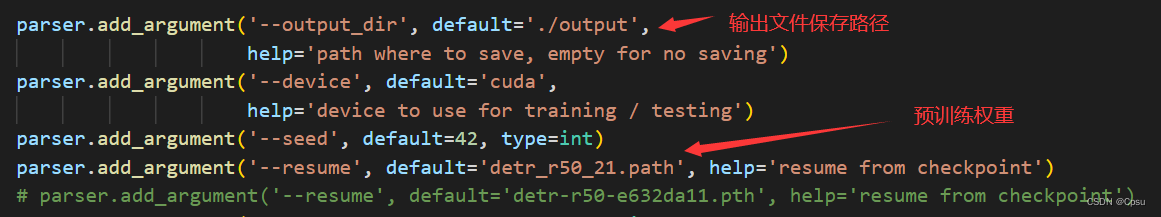
其中预训练权重需要修改一下,coco是80类,不能直接加载官方的模型。voc是20类。把num_classes改成21。传入得到的detr_r50_21.pth新的权重文件。
import torch
pretrained_weights=torch.load('detr-r50-e632da11.pth')
num_classes=21
pretrained_weights["model"]["class_embed.weight"].resize_(num_classes+1,256)
pretrained_weights["model"]["class_embed.bias"].resize_(num_classes+1)
torch.save(pretrained_weights,"detr_r50_%d.pth"%num_classes)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
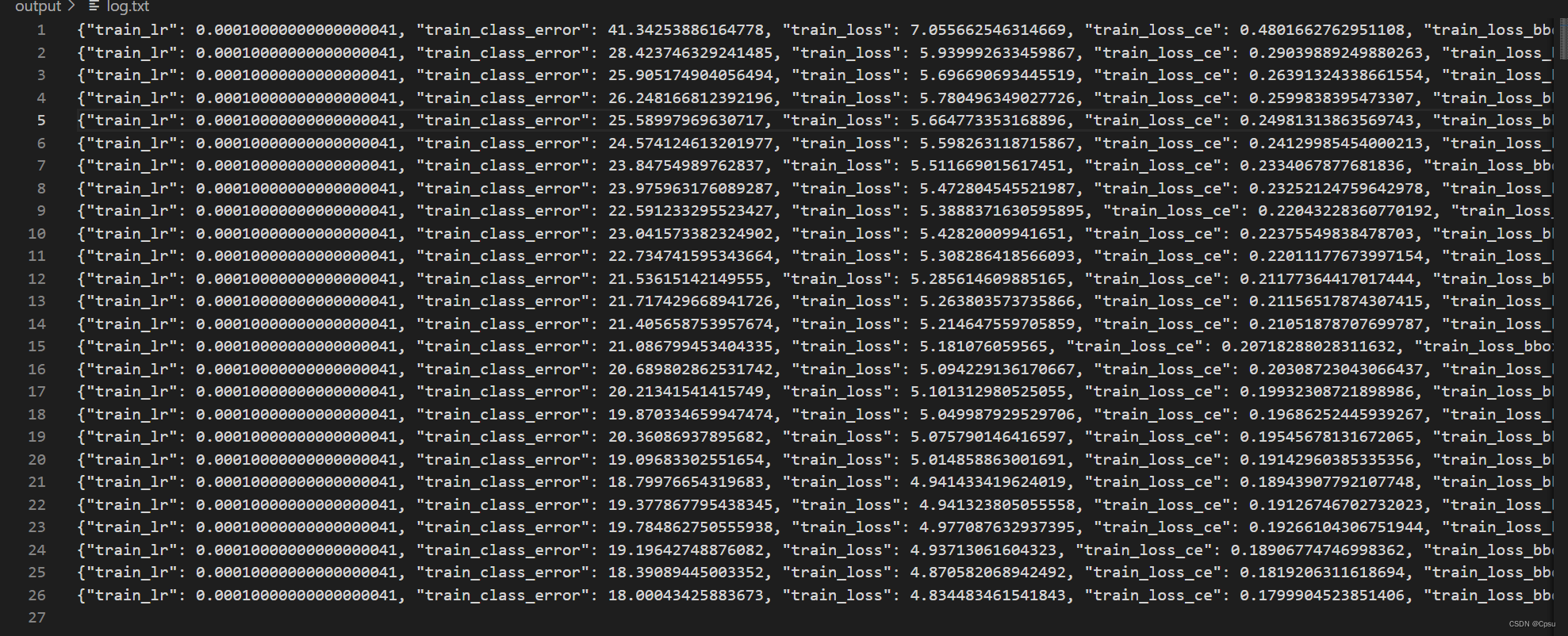
运行日志(特别难训练):
三、绘图
在util文件夹下有plot_utils.py文件,可以绘制损失和mAP曲线。
在plot_utils.py文件中加入代码运行即可:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 路径更换为保存输出的eval路径
# mAP曲线
files=list(Path("./outputs/eval").glob("*.pth"))
plot_precision_recall(files)
plt.show()
# 路径更换为保存输出的路径
# 损失曲线
plot_logs(Path("./output"))
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
四、推理
训练完毕后我们会得到一个checkpoint.pth的文件,可以用自己训练得到的模型来推理图片,代码如下:
import numpy as np from models.detr import build from PIL import Image import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torch import torchvision.transforms as transforms torch.set_grad_enabled(False) COLORS = [[0.000, 0.447, 0.741], [0.850, 0.325, 0.098], [0.929, 0.694, 0.125], [0.494, 0.184, 0.556], [0.466, 0.674, 0.188], [0.301, 0.745, 0.933]] transform_input = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(800), transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]) def box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(x): x_c, y_c, w, h = x.unbind(1) b = [(x_c - 0.5 * w), (y_c - 0.5 * h), (x_c + 0.5 * w), (y_c + 0.5 * h)] return torch.stack(b, dim=1) def rescale_bboxes(out_bbox, size): img_w, img_h = size b = box_cxcywh_to_xyxy(out_bbox) b = b * torch.tensor([img_w, img_h, img_w, img_h], dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda") return b def plot_results(pil_img, prob, boxes, img_save_path): plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10)) plt.imshow(pil_img) ax = plt.gca() colors = COLORS * 100 for p, (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax), c in zip(prob, boxes.tolist(), colors): ax.add_patch(plt.Rectangle((xmin, ymin), xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin, fill=False, color=c, linewidth=3)) cl = p.argmax() text = f'{CLASSES[cl]}: {p[cl]:0.2f}' ax.text(xmin, ymin, text, fontsize=9, bbox=dict(facecolor='yellow', alpha=0.5)) plt.savefig(img_save_path) plt.axis('off') plt.show() def main(chenkpoint_path, img_path, img_save_path): args = torch.load(chenkpoint_path)['args'] model = build(args)[0] device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" model.to(device) # 加载模型参数 model_data = torch.load(chenkpoint_path)['model'] model.load_state_dict(model_data) model.eval() img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') size = img.size inputs = transform_input(img).unsqueeze(0) outputs = model(inputs.to(device)) # 这类最后[0, :, :-1]索引其实是把背景类筛选掉了 probs = outputs['pred_logits'].softmax(-1)[0, :, :-1] # 可修改阈值,只输出概率大于0.7的物体 keep = probs.max(-1).values > 0.7 bboxes_scaled = rescale_bboxes(outputs['pred_boxes'][0, keep], size) # 保存输出结果 ori_img = np.array(img) plot_results(ori_img, probs[keep], bboxes_scaled, img_save_path) if __name__ == "__main__": CLASSES = ['N/A', "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat", "bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair", "cow", "diningtable", "dog", "horse", "motorbike", "person", "pottedplant", "sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor", "background"] main(chenkpoint_path="checkpoint.pth", img_path="test.png", img_save_path="result2.png")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
几点说明:
1.CLASSES是我们数据集对应的类别名,注意自己标注的顺序一定写对。第一个类别是"N/A"既不是背景也不是前景,因为我们转换的数据集的索引是从1开始的,所以索引为0的类别就缺失了。背景类应该是索引最大的也就是第21类。其实上面的"background"我认为加上才是最严谨的。

2.chenkpoint_path:保存的权重文件
img_path:测试的图片路径
img_save_path:保存结果路径
3.可修改阈值,论文中默认只输出概率大于0.7的物体。
用VOC数据集训练的模型推理效果:
(VOC数据集中没有自行车一类所以识别不出来)

五、一些小bug
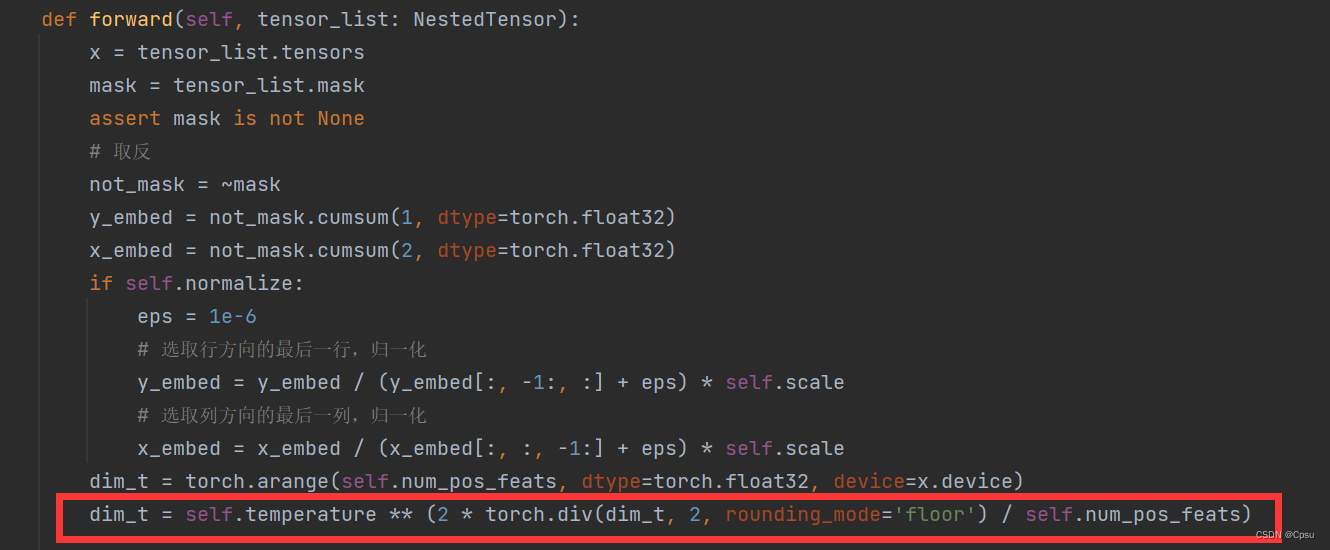
1.取整问题
UserWarning: floordiv is deprecated, and its behavior will change in a future version of pytorch. It currently rounds toward 0 (like the ‘trunc’ function NOT ‘floor’). This results in incorrect rounding for negative values. To keep the current behavior, use torch.div(a, b, rounding_mode=‘trunc’), or for actual floor division, use torch.div(a, b, rounding_mode=‘floor’).
这时一个torch版本原因导致的一个函数问题,报了一个警告。
将models/position_encoding.py文件中的第44行改成如下形式即可。
2.num_class的设置问题
num_class的设置问题在github上有详细的讨论:num_class如何设置
引用作者原话:
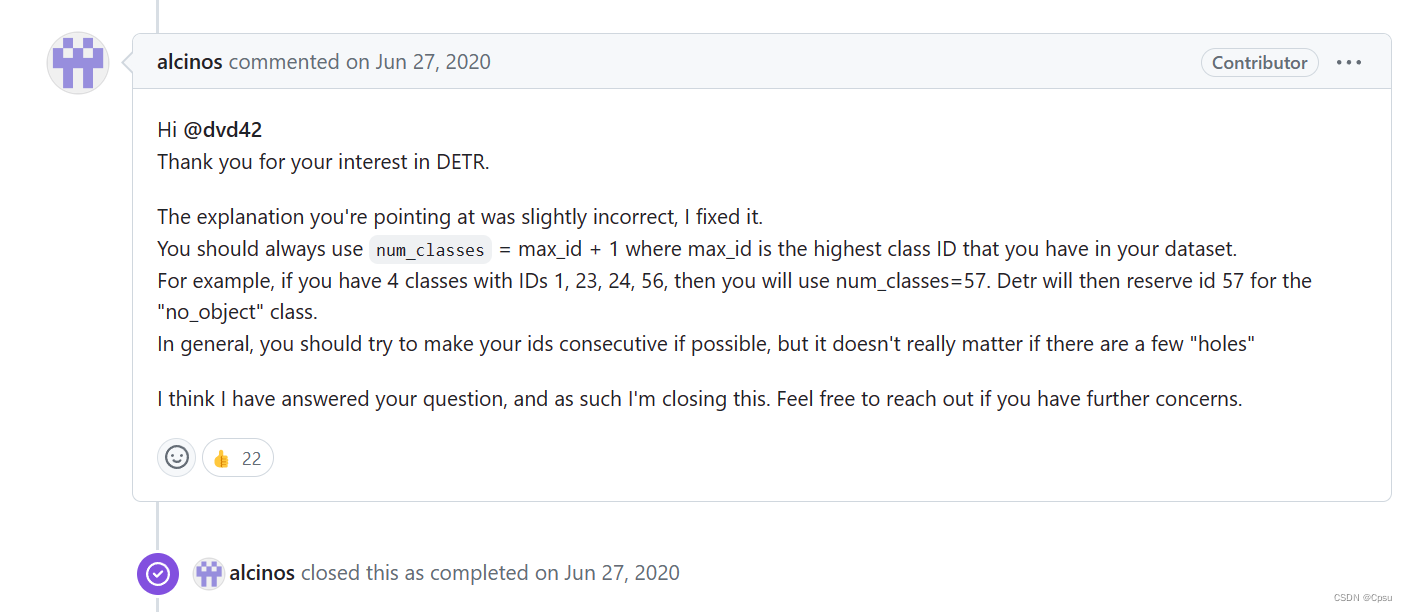
num_class应该设置为max_id+1,比如上面的voc2coco数据集,索引从1到20,那么num_class应该设置为20+1=21,索引为21的类为背景类,但是因为索引从1开始,所以把索引为0 的类设置为N/A,既不是背景也不是前景,应该是缺失类。作者举例4个类别IDs分别为1,23,24,56那么num_class应该设置为57,索引为57的类为背景类。其中缺失索引值:0、2-22、25-55应该用N/A填充,都是缺失类。
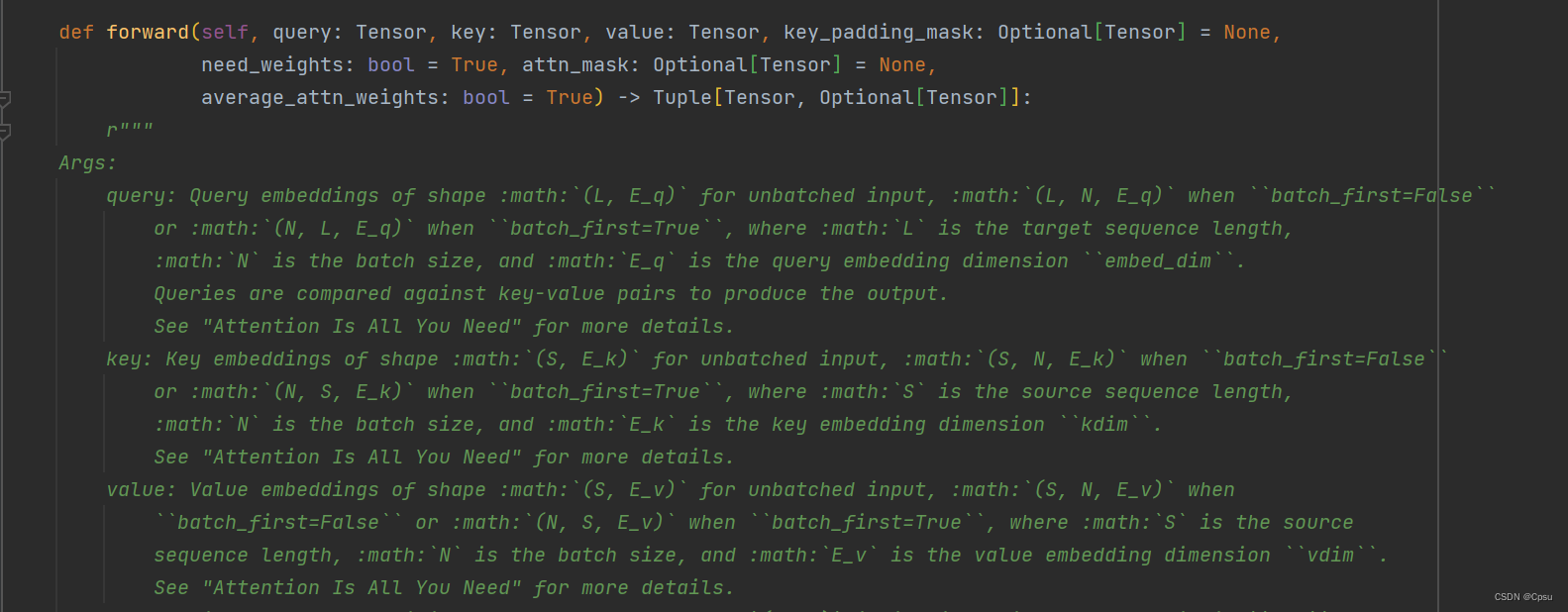
3.Encoder的输入为什么要把特征图的维度进行变换 (bs, c, hw) -> (hw, bs, c)?

这里只是一个小细节,当初发现这里和ViT等论文的Encoder输入不太一样,不明白为什么要多此一举进行维度变换。这里其实是pytorch中注意力实现的一个不同,在源码中的文档中写的很清楚,pytorch中的transformer实现有一个batch_first=False的参数,也就是默认传入的第一个维度不是batch_size,所以才要进行一个维度变换。