- 1计算机专业毕业设计演示视频(论文+系统)_kaic
- 2SSM框架梳理(一)SpringMVC工作流程_ssm框架工作流程
- 3微信小程序(7):常用的表单组件_cursor-spacing
- 4001-Photoshop基础操作_ps软件基础
- 5unity游戏运行环境_Unity OTC参赛全纪录 | 1.搭建环境
- 6【HarmonyOS】API9沉浸式状态栏_鸿蒙api9 沉浸式状态栏
- 7LINUX内核升级-更新网卡驱动
- 8应用程序虚拟化初体验 App-V Management Server简单部署与配置
- 9鸿蒙开发-List组件_鸿蒙 横向list
- 10《Android移动开发基础案例教程》复习知识点_安卓移动开发基础案例教程期末
详解C++中的三种 继承(public, protected, private)_c++ public private protect继承
赞
踩
@TOCC++三种继承方式:
先看一张继承关系表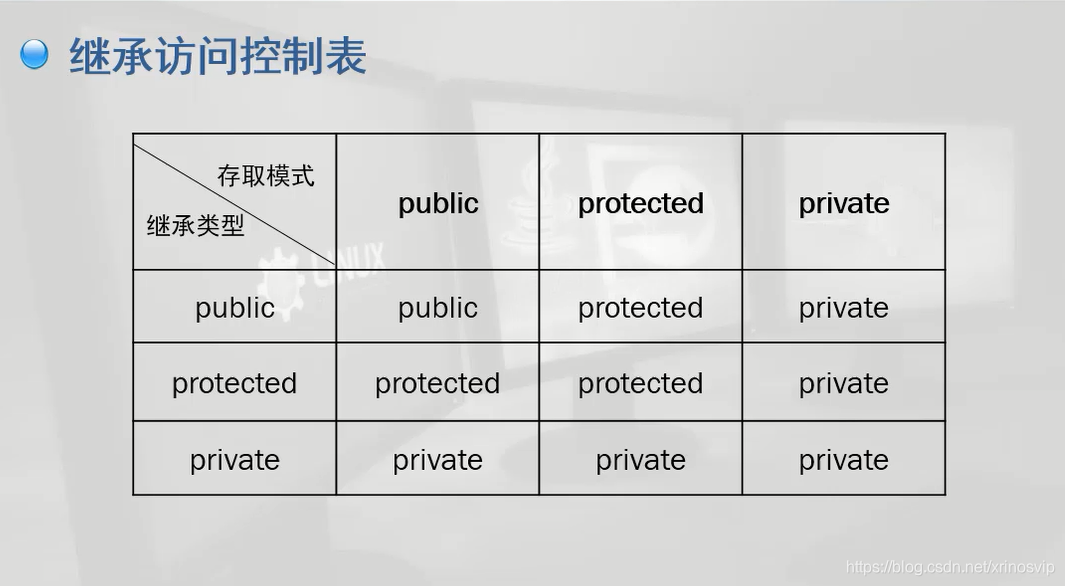
三种继承方式:
1.首先说明一点:类实例(即类对象)不能直接访问类的 private成员和protected成员,但是能直接访问类的public成员。
2.另外无论哪种继承方式,子类都不能直接访问父类的 private成员;但是能直接访问父类的 protected成员和public成员(注意:是子类,而不是类实例),并且能通过父类的protected成员函数和public成员函数间接访问父类的private成员;这句话强调了类与类之间通过继承方式的访问规则,而非类与实例之间的访问规则。
3.子类通过public方式继承父类,则父类中的public、protected和private属性的成员在 子类 中 依次 是 public、protected和private属性,即通过public继承并不会改变父类原来的数据属性。
4.子类通过protected方式继承父类,则父类中的public、protected和private属性的成员在 子类 中 依次 是 protected、protected和private属性,即通过protected继承原来父类中public属性降级为子类中的protected属性,其余父类属性在子类中不变。
5.子类通过private方式继承父类,则父类中的public、protected和private属性的成员在 子类 中 依次 是 private、private和private属性,即通过private继承原来父类中public属性降级为子类中的private属性,protected属性降级为子类中的private属性,其余父类属性在子类中不变。
注意: 其实父类的原属性并未改变,只是通过 继承关系被继承到子类中的父类成员的个别属性有所变化 ,即只是在子类中父类的个别成员属性降级了,原来父类的成员属性并未变。
code如下:
类声明的头文件 heritage.h
// // Created by ZP on 2021/7/28. // #ifndef HERITAGE_HERITAGE_H #define HERITAGE_HERITAGE_H class A{ private: int a; protected: int b; public: int c; A(int A, int B, int C); ~A(); void set(int val_a, int val_b, int val_c); int get_a() const; int get_b() const; int get_c() const; }; class B{ private: int x; protected: int y; public: int z; B(); ~B(); void set(int &val_x, int &val_y, int &val_z); int get_x() const; int get_y() const; int get_z() const; }; class C{ private: int u; protected: int v; public: explicit C(int U = 10, int V = 18); ~C(); void set(int val_u, int val_v); void set(int &val_u); int get_uv() const; }; // public heritage class D: public A{ private: int m_total; public: D(int v1, int v2, int v3): A(v1, v2, v3){ m_total= 0; } ~D()= default; inline int add() { // m_total = c + b + A::get_a(); // a is class A's private value. m_total = c + b + get_a(); return m_total; } }; // protected heritage class E: protected B{ private: int m_tesult; public: E(): B(){ m_tesult = 0; } ~E() = default; void get_xyz() const; // 要修改 B 的私有变量 x ,则要调用 B 类 的set方法或者声明一个类E的成员函数为类B的友元函数, 从而访问 private value. void set_xyz(int X, int Y, int Z); inline int mul(){ m_tesult = y * z * get_x(); // x is private value return m_tesult; } }; // private heritage class F: private C{ private: int m_result; public: F(int v1, int v2): C(v1, v2){ m_result = 0; } ~F() = default; void set_uv(int U, int V); inline int product(){ return get_uv(); } }; #endif //HERITAGE_HERITAGE_H
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
头文件heritage.h的实现代码 heritage.cpp
// // Created by ZP on 2021/7/28. // #include <iostream> #include "heritage.h" using namespace std; // class A implement A::A(int A, int B, int C):a(A), b(B), c(C){ } A::~A() { } void A::set(int val_a, int val_b, int val_c) { this->a = val_a; this->b = val_b; this->c = val_c; } int A::get_a() const { return a; } int A::get_b() const { return b; } int A::get_c() const { return c; } // class B B::B() { x = 0; y = 1; z = 2; } B::~B() = default; void B::set(int &val_x, int &val_y, int &val_z) { this->x = val_x; this->y = val_y; this->z = val_z; } int B::get_x() const { return x; } int B::get_y() const { return y; } int B::get_z() const { return z; } // class C C::C(int U, int V): u(U), v(V) { } C::~C() = default; void C::set(int val_u, int val_v) { this->u = val_u; this->v = val_v; } void C::set(int &val_u) { this->u = val_u; } int C::get_uv() const { return u * v; } // class E void E::get_xyz() const { cout << "x: " << get_x() << "\ty: " << y << "\tz: " << z << endl; } void E::set_xyz(int X, int Y, int Z){ set(X, Y, Z); } // class F void F::set_uv(int U, int V) { v = V; // private heritage, 但是还是能在子类内部 直接使用 父类的 protected value set(U); // private heritage, 但是还是能在子类内部 直接使用 父类的 public function }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
主函数代码 main.cpp
// // Created by ZP on 2021/7/28. // #include <iostream> #include "heritage.h" using std::cout; using std::endl; int main(){ A a(100, 200, 300); cout << "a: " << a.get_a() << "\tb: " << a.get_b() << "\tc: " << a.get_c() << endl; // 实例a 能直接访问 类A 的 public value, 但是不能直接访问 protected and private 变量,要想访问,需通过成员函数访问 cout << "public c: \t" << a.c << endl; cout << endl; B b; cout << "x: " << b.get_x() << "\ty: " << b.get_y() << "\tc: " << b.get_z() << endl; cout << "public z: \t" << b.z << endl; // public value 破坏了 类的数据隐藏封装特性。 cout << endl; C c; cout << "u*v: " << c.get_uv()<< endl; cout << endl; // class D public heritage D d(10, 20, 30); cout << "d: " << d.get_a() << "\t" << d.get_b() << "\t" << d.get_c() << endl; cout << "d_total: " << d.add() << endl; d.set(12, 13, 14); cout << "d-set: " << d.get_a() << "\t" << d.get_b() << "\t" << d.get_c() << endl; cout << "d_total: " << d.add() << endl; cout << "d heritage class A's public c: \t" << d.c << endl; cout << endl; // class E protected heritage E e; e.get_xyz(); cout << "e_product: " << e.mul() << endl; e.set_xyz(1, 2, 3); e.get_xyz(); cout << "e_product: " << e.mul() << endl; // 实例 不能直接访问 heritage class 的 public value, 因为被继承的 public value 变成了 protected value。 // e.z cout << endl; F f(50, 100); // private u, protected v;public set函数 通过 private heritage 后,全部为 private, 类实例 不能 直接访问 // f.set(10, 10); // f.u; // f.v; cout << "f_product: " << f.product() << endl; f.set_uv(50, 50); cout << "f_product set_uv: " << f.product() << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
运行结果:
E:\programme\C_C++\CLion\C++\Exercise\heritage\cmake-build-debug\heritage.exe a: 100 b: 200 c: 300 public c: 300 x: 0 y: 1 c: 2 public z: 2 u*v: 180 d: 10 20 30 d_total: 60 d-set: 12 13 14 d_total: 39 d heritage class A's public c: 14 x: 0 y: 1 z: 2 e_product: 0 x: 1 y: 2 z: 3 e_product: 6 f_product: 5000 f_product set_uv: 2500 Process finished with exit code 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24



