- 1一款专业的Mac系统清理软件CleanMyMac X 4.15.1破解版_cleanmymac 4.15.1
- 2java8新特性(2)-Lambda表达式_lambo表达式
- 32020-10-11《多重背包 单调队列优化》_第1行有2个整数n,m,表示物品的种类和背包的容积; 第2-n+1行,每行有3个整数vi,wi,p
- 4【LeetCode热题100】【技巧】下一个排列
- 5Altas 200 DK环境配置_atlas200dk
- 6宝塔面板mysql怎么用navicat 连接数据库呢,详细步骤_宝塔进服务器数据库
- 7简表报表配置以及ftl文件的一些功能_ftl文件中columnwidth设置
- 8什么?JS 异步原来还能这么处理?
- 9蓝桥杯单元测试专项练习Java版(单元测试4)(修正版)_请使用基本路径覆盖法 + 简单循环覆盖法的标准规则,对被测源代码 goods、goodsser
- 10git submodule 如何同步更新_git submodule update
7.Prism框架之对话框服务
赞
踩
一. 目标
- 1. 什么是Dialog?
- 2. 传统的Dialog如何实现?
- 3. Prism中Dialog实现方式
- 4. 使用Dialog实现一个异常信息弹出框
二. 技能介绍
① 什么是Dialog?
Dialog通常是一种特殊类型的窗口,用于和用户进行交互,一般是用来从用户那里接收数据,显示信息,或者是允许用户执行特定任务.窗口分为两种一种是模态窗口(Modal Window),一种是非模态窗口(Non-Modal WIndow)
-
模态窗口
模态窗口就是阻止和其他的控件进行交互的窗口,必须是处理完这个窗口之后,才能和其他的窗口进行交互,这个窗口脚模态窗口.一般用于比较重要的交互,比如保存文件,确认删除等.传统显示的是时候使用ShowDialog(),有返回值. -
非模态窗口
可以在不关闭这个窗口的情况下和其他的控件进行交互,一般适用于不需要立即决策或者响应的情况,如工具箱,提示信息等.传统显示的时候使用Show(),无返回值.
模态窗口的例子
namespace DialogSimple.ViewModels { public class MainWindowViewModel { public MainWindowViewModel() { ShowDialogCommand = new Command(DoShowDialog); } private void DoShowDialog(object modalType) { if (modalType is string modal) { switch (modal) { case "Modal": var modalDialog = new ModalDialog(); bool? result = modalDialog.ShowDialog(); if (result == true) { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("模态对话框返回值为true,执行保存操作!"); } else { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("模态对话框返回值为false,不执行保存操作!"); } break; } } } public Command ShowDialogCommand { get; private set; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
这里注意一个问题就是这里的result是一个窗口的返回值,为bool?类型,这个返回值是怎么返回的呢?
这个返回值是通过窗口的视图类中的一个
DialogResult属性,可以在事件处理的时候设置其返回值.
namespace DialogSimple { /// <summary> /// ModalDialog.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// </summary> public partial class ModalDialog : Window { public ModalDialog() { InitializeComponent(); } private void BtnOk_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { DialogResult = true; } private void BtnCancel_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { DialogResult = false; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
现在我有一个疑问,就是这里我们窗口的按钮实现的方式比较简单,如果比较复杂,比如按钮的处理逻辑放到对应的ViewModel中去处理的时候,这个时候是没有DialogResult属性呢,如果设置其返回值呢?注意事件本质上还是一个委托,其实可以当成是一个回调或者是钩子来使用.
namespace DialogSimple.ViewModels { public class ModalDialogViewModel { public event Action<bool>? RequestClose; public ModalDialogViewModel() { OkCommand = new Command(DoOkClick); CancelCommand = new Command(DoCancelClick); } private void DoCancelClick(object obj) { // 1. 处理其他逻辑 // 2. 调用窗口关闭事件,传递参数为false RequestClose?.Invoke(false); } private void DoOkClick(object obj) { // 1. 处理其他逻辑 // 2. 调用窗口关闭事件,传递参数为true RequestClose?.Invoke(true); } public Command OkCommand { get; private set; } public Command CancelCommand { get; private set; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
然后在UI程序中,去注册这个事件
namespace DialogSimple { /// <summary> /// ModalDialog.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// </summary> public partial class ModalDialog : Window { public ModalDialog() { InitializeComponent(); DataContext = new ModalDialogViewModel(); (DataContext as ModalDialogViewModel)!.RequestClose += ModalDialog_RequestClose; } private void ModalDialog_RequestClose(bool result) { DialogResult = result; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
这里有一个疑问就是为什么我没有关闭这个窗口,当我们点击确定和取消按钮的时候,窗口就关闭了呢,其实这里的原因是因为当在WPF应用中如果设置了DialogResult的属性之后,无论是设置的true还是false,它都会去关闭窗口
注意:
我们可能还记得
MVVM框架的设计原则,UI的逻辑一般都是在UI的模块代码中去完成,但是上面的弹窗部分是在ViewModel中实现的,并且在ViewModel中操作了UI视图的创建,这在实践上不是一个很好的实践,那么如何将这个创建弹窗的逻辑放到UI代码中去的也就是放到View中去呢,其中一种方式和上面的类似,就是通过事件.每次请求窗口的时候,调用事件,然后UI代码注册这个事件,完成对应的操作.
namespace DialogSimple.ViewModels { public class MainWindowViewModel { public event Action<object>? RequestShowDialog; public MainWindowViewModel() { ShowDialogCommand = new Command(DoShowDialog); } private void DoShowDialog(object modalType) { if (modalType is string modal) { switch (modal) { case "Modal": RequestShowDialog?.Invoke("Modal"); break; } } } public Command ShowDialogCommand { get; private set; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
然后在View中去做具体的窗口弹出处理
public partial class MainWindow : Window { public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); DataContext = new MainWindowViewModel(); (DataContext as MainWindowViewModel)!.RequestShowDialog += MainWindow_RequestShowDialog; } private void MainWindow_RequestShowDialog(object obj) { if (obj is string windowType) { switch (windowType) { case "Modal": var result = new ModalDialog().ShowDialog(); if (result == true) { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("返回true,进行保存操作"); } else { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("返回false,取消保存操作"); } break; } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
非模态窗口的例子
非模态窗口就是把
ShowDialog换成Show()就OK了,并且非模态窗口是没有返回值的.
② Prism中Dialog的实现方式
Prism对话框Dialog的实现主要分为三步
- 1. 创建对话框(UserControl)
- 2. 注册对话框(并绑定其关联的ViewModel)
- 3. 使用IDialogService来显示对话框,如果有参数并传递参数
第一步: 创建对话框用户控件,注意这里只能是UserControl,不能是Window
<UserControl x:Class="PrismDialogSimple.Views.ModalDialog" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:PrismDialogSimple.Views" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignHeight="450" d:DesignWidth="800"> <Grid> <Grid> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition Height="50" /> <RowDefinition /> <RowDefinition Height="100" /> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <TextBlock Text="模态对话框演示" FontSize="16" Margin="10" HorizontalAlignment="Left" /> <TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="确认要进行保存吗" FontSize="18" HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" /> <StackPanel Grid.Row="2" HorizontalAlignment="Right" Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button Width="100" Height="30" Content="确定" Command="{Binding OkCommand}" CommandParameter="" /> <Button Width="100" Height="30" Content="取消" Command="{Binding CancelCommand}" CommandParameter="" Margin="10,0" /> </StackPanel> </Grid> </Grid> </UserControl>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
第二步:注册对话框
注意种类关联的
ViewModel,就是和对话框关联的ViewModel必须是实现了IDialogAware接口才可以.
namespace PrismDialogSimple.ViewModels { public class ModalDialogViewModel : BindableBase, IDialogAware { public string Title => throw new NotImplementedException(); public event Action<IDialogResult> RequestClose; public bool CanCloseDialog() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void OnDialogClosed() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void OnDialogOpened(IDialogParameters parameters) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
注册对话框的代码
protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
// 1. 注册导航视图和视图模型
containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<MainWindow, MainWindowViewModel>();
// 2. 注册对话框和对话框模型
containerRegistry.RegisterDialog<ModalDialog, ModalDialogViewModel>();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
第三步: 使用IDialogService显示对话框
在显示对话框之前,我们要把对话框的ViewModel中实现的那些接口来解释一下,并进行一些简单的实现,不然等下在弹出窗口的时候回报错.下面具体看看这个IDialogAware都实现了什么东西?
public class ModalDialogViewModel : BindableBase, IDialogAware { public string Title => throw new NotImplementedException(); public event Action<IDialogResult> RequestClose; public bool CanCloseDialog() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void OnDialogClosed() { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public void OnDialogOpened(IDialogParameters parameters) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- Title
我们首先要明白一点就是我们弹出的窗口是一个
UserContorl控件,它其实是在一个Window窗口中的,这个窗口呢是Prism框架来进行创建和管理的,这个窗口呢,绑定了一个标题,就是这个Title,所以如果你只是在初始化的时候就一个标题,那么就这样简单的赋值就行了,如果你想要在运行过程中更改这个标题,你还要实现它的通知属性才行.
private string title;
public string Title
{
get { return title; }
set
{
title = value;
RaisePropertyChanged();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- RequestClose()事件
用于从
ViewModel触发对话框的关闭.是的ViewModel能够控制视图的关闭,而不必依赖视图层的代码.
这样做的好处就是保持了视图和业务逻辑的分离,符合MVVM设计原则.
- CanCloseDialog()方法
CanCloseDialog()方法用于确定对话框是否可以关闭.这可以基于某些判断,比如表单是否填写完毕或者是否满足特定的业务逻辑来控制对话框是否可以关闭.返回true表示可以关闭对话框,返回false表示不允许关闭对话框.
- OnDialogClosed()方法
关闭时调用,可以用于执行一些清理操作或者其他逻辑的地方,如资源释放或者状态重置.
- OnDialogOpened()方法
在对话框打开时调用,可以在这里处理对话框打开的初始化工作,如基于传入的参数设置初始状态或者加载数据.
关于对话框的返回值怎么传递的问题?当你需要从对话框返回数据到调用它的地方的时候,你可以在RequestClose事件时,传递一个
DialogResult实例,并通过DialogResult的构造函数或者属性来设置返回值.
private void DoCancel()
{
RequestClose?.Invoke(new DialogResult(ButtonResult.Cancel, null));
}
private void DoOk()
{
RequestClose?.Invoke(new DialogResult(ButtonResult.OK, null));
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
然后在弹出窗口的那里对结果进行获取,并进行判断
private void DoShowDialog(string modelType) { switch (modelType) { case "Modal": _dialogService.ShowDialog(nameof(ModalDialog), result => { if (result.Result == ButtonResult.OK) { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("点击了OK,进行保存操作."); } else { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("点击了取消,不进行保存操作."); } }); break; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
③ Dialog使用案例一 (修改器)
我们做一个案例,界面上有两个按钮,弹出来的是同一个弹窗,但是弹窗的功能稍微有点不同,一个是名称修改,一个是电话修改.这个案例不重要,主要是运用之前的知识. 修改之后,如果点击了确定按钮,要把这个新的数据返回给调用者,调用者那里显示这个新的值.
主界面操作按钮
<Window x:Class="DialogUsedSimple01.Views.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:prism="http://prismlibrary.com/" Title="{Binding Title}" Width="1000" Height="800" prism:ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel="True"> <Grid> <StackPanel Margin="50"> <Button Width="100" Height="35" Content="修改名称" Command="{Binding ModifyNameCommand}" /> <Button Width="100" Height="35" Content="修改电话" Command="{Binding ModifyPhoneCommand}" Margin="0,10" /> </StackPanel> </Grid> </Window>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
注册view和viewModel
namespace DialogUsedSimple01 { /// <summary> /// Interaction logic for App.xaml /// </summary> public partial class App { protected override Window CreateShell() { return Container.Resolve<MainWindow>(); } protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry) { // 1. 注册导航视图 containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<MainWindow, MainWindowViewModel>(); // 2.注册弹框 containerRegistry.RegisterDialog<DialogSimpleDemo, DialogSimpleViewModel>(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
弹框视图
<UserControl x:Class="DialogUsedSimple01.Views.DialogSimpleDemo" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DialogUsedSimple01.Views" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignHeight="450" d:DesignWidth="800" Width="500" Height="300"> <Grid> <StackPanel Margin="10" Orientation="Horizontal"> <Label Width="60" Height="30" Content="{Binding TextShow}" FontSize="16" VerticalAlignment="Center" /> <TextBox Width="200" Height="30" Text="{Binding TextInput}" Margin="10,0" VerticalContentAlignment="Center" /> </StackPanel> <StackPanel Margin="10" HorizontalAlignment="Right" VerticalAlignment="Bottom" Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button Width="100" Content="确认" Command="{Binding OkCommand}" /> <Button Width="100" Content="取消" Command="{Binding CancelCommand}" Margin="10,0" /> </StackPanel> </Grid> </UserControl>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
弹框视图对应的ViewModel
namespace DialogUsedSimple01.ViewModels { public class DialogSimpleViewModel : BindableBase, IDialogAware { public DialogSimpleViewModel() { OkCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoOK); CancelCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoCancel); } private void DoCancel() { RequestClose?.Invoke(new DialogResult(ButtonResult.Cancel, new DialogParameters($"resVal={TextInput}"))); } private void DoOK() { RequestClose?.Invoke(new DialogResult(ButtonResult.OK, new DialogParameters($"resVal={TextInput}"))); } public DelegateCommand OkCommand { get; private set; } public DelegateCommand CancelCommand { get; private set; } private string title; public string Title { get { return title; } set { title = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } private string textShow; public string TextShow { get { return textShow; } set { textShow = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } private string textInput; public string TextInput { get { return textInput; } set { textInput = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } public event Action<IDialogResult> RequestClose; public bool CanCloseDialog() { return true; } public void OnDialogClosed() { } public void OnDialogOpened(IDialogParameters parameters) { var parameter = parameters.GetValue<string>("modifyType"); if (parameter == "Name") { Title = "名称修改器"; TextShow = "新名称:"; } else if (parameter == "Phone") { Title = "电话修改器"; TextShow = "新电话:"; } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
主视图对应的ViewModel
namespace DialogUsedSimple01.ViewModels { public class MainWindowViewModel : BindableBase { private IDialogService _dialogService; private string _title = "弹窗示例1"; public string Title { get { return _title; } set { SetProperty(ref _title, value); } } public MainWindowViewModel(IDialogService dialogService) { _dialogService = dialogService; ModifyNameCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoModifyName); ModifyPhoneCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoModifyPhone); } private void DoModifyPhone() { _dialogService.ShowDialog(nameof(DialogSimpleDemo), new DialogParameters($"modifyType=Phone"), result => { string newVal = result.Parameters.GetValue<string>("resVal"); if (result.Result == ButtonResult.OK) { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"确认成功,修改后的电话为:{newVal}"); } else { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"取消修改"); } }); } private void DoModifyName() { _dialogService.ShowDialog(nameof(DialogSimpleDemo), new DialogParameters($"modifyType=Name"), result => { string newVal = result.Parameters.GetValue<string>("resVal"); if (result.Result == ButtonResult.OK) { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"确认成功,修改后名字为: {newVal}"); } else { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"取消修改"); } }); } public DelegateCommand ModifyNameCommand { get; private set; } public DelegateCommand ModifyPhoneCommand { get; private set; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
④ Dialog使用案例2(异常显示窗口)
我们平时看到的异常,比如下面这些,都分别代表什么意思呢?
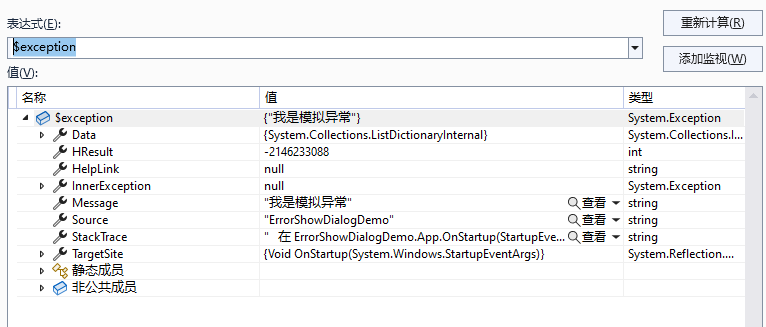
-
1. Data
-
类型:
IDictionary -
描述: 获取一个键值对集合,可以在其中添加自定义的异常处理信息.这使得你可以将额外的数据和异常对象关联,便于异常处理时获取更多的上下文信息.
-
2. HResult
-
类型:
int -
描述: 获取或者设置
HResult(一个由返回值标识的整数),它是一个从底层COM组件中映射过来的错误代码.通常是一个固定的很大的负数. -
3. HelpLink
-
类型:
string -
描述: 获取或者设置异常处理相关文档的链接地址或者
URI,通常是文件路径或者是网页路径,可以提供更多的异常相关的帮助 -
4. InnerException
-
类型:
Exception -
描述: 内部异常,也就是说异常是可以嵌套的,当我们在处理异常A的过程中,这个异常A是因为异常B导致的,也就是说抛出的异常A在异常B的
Catch逻辑里,那么我称最开始出现的异常B为异常A的内部异常,说白了就是我们捕获的时候可能最后只捕获了异常A,但是异常A发生的时候其实先发生了异常B,异常B就是异常A的内部异常.
try
{
string content= File.ReadAllText(filePath);
}
catch(BException ex)
{
throw new AException();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
上面的BException就是AException的内部异常.
-
5. Message
-
类型: string
-
描述: 获取描述当前异常的消息.这是一个人类可以读取的错误描述,通常用于提示异常原因.
-
6. Source
-
类型:
string -
描述: 获取或者设置引发当前异常的应用程序或者对象的名称.默认情况下,这通常是引发异常的程序集的名称.
-
7. StackTrace
-
类型:
string -
描述: 获取调用堆栈上的当前发生异常的时候的方法调用序列包括异常发生的地方,对于调试和定位问题非常重要.
-
8. TargetSite
-
类型:
MethodBase -
描述: 获取引发当前异常的方法.这个返回一个
MethodBase对象,包含有关异常源头的方法的信息,如方法名,拥有类等.
个人想法
我现在是这样想的,当出现异常的时候,我首先是弹出一个框,这个框先弹出来的异常信息,上面有几个按钮,一个是查看详情,一个是打开打开异常日志目录,一个是关闭,点击查看详情的时候弹出一个框显示这个异常的详细信息,详细信息就是上面介绍的这些内容,这里要注意一点就是如果有内部异常,内部异常也要现实出来.然后这个详情页就只有两个按钮,一个是复制,一个是关闭
第一步: 创建异常显示页面,只显示异常的Message消息
<UserControl x:Class="ExceptionShowDialogDemo.Dialogs.ErrorShowDialog" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:ExceptionShowDialogDemo.Dialogs" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" xmlns:prism="http://prismlibrary.com/" mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignHeight="450" d:DesignWidth="800"> <!-- 设置Prism对话框所在窗口的全局属性 1) 窗口显示的区域,父窗口的中心 2) 窗口是否可以被用户调整大小,NoResize不可以 3) 窗口是否在任务栏中显示, False,不显示,一般模态窗口和一些简单的操作不显示在任务栏 4) 设置窗口的大小自动调整以适应其内容宽高 --> <prism:Dialog.WindowStyle> <Style TargetType="Window"> <Setter Property="prism:Dialog.WindowStartupLocation" Value="CenterOwner" /> <Setter Property="ResizeMode" Value="NoResize" /> <Setter Property="ShowInTaskbar" Value="False" /> <Setter Property="SizeToContent" Value="WidthAndHeight" /> </Style> </prism:Dialog.WindowStyle> <UserControl.Resources> <Style TargetType="Button"> <Setter Property="Height" Value="35" /> <Setter Property="VerticalContentAlignment" Value="Center" /> </Style> </UserControl.Resources> <DockPanel MinWidth="700" MinHeight="300" Background="#EEE" LastChildFill="False"> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <Label> <TextBlock Text="{Binding Message}" Foreground="#333" FontSize="16" TextWrapping="Wrap" /> </Label> </StackPanel> <StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Bottom" Margin="20" HorizontalAlignment="Right" Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button Width="100" Content="查看详情" Command="{Binding ViewDetailCommand}" /> <Button Width="100" Content="关闭" Command="{Binding CloseDialogCommand}" /> </StackPanel> </DockPanel> </UserControl>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
其对应的ViewModel
namespace ExceptionShowDialogDemo.ViewModels { public class ErrorShowDialogViewModel : BindableBase, IDialogAware { private readonly IDialogService _dialogService; public ErrorShowDialogViewModel(IDialogService dialogService) { _dialogService = dialogService; ViewDetailCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoViewDetail); OpenErrorDirCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoOpenErrorDir); CloseDialogCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoCloseDialog); } private void DoCloseDialog() { RequestClose?.Invoke(new DialogResult()); } private void DoOpenErrorDir() { } private void DoViewDetail() { DialogParameters parameters = new DialogParameters() { {"Title","异常详情页" }, {"Exception",ExceptionDetail } }; _dialogService.ShowDialog(nameof(ExceptionDetailDialog), parameters, result => { }); } public DelegateCommand ViewDetailCommand { get; private set; } public DelegateCommand OpenErrorDirCommand { get; private set; } public DelegateCommand CloseDialogCommand { get; private set; } private string title; public string Title { get { return title; } set { title = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } private string message; public string Message { get { return message; } set { message = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } public Exception ExceptionDetail { get; set; } public event Action<IDialogResult> RequestClose; public bool CanCloseDialog() { return true; } public void OnDialogClosed() { } public void OnDialogOpened(IDialogParameters parameters) { var title = parameters.GetValue<string>("Title"); var exception = parameters.GetValue<Exception>("Exception"); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(title) && exception != null) { Title = title; ExceptionDetail = exception; // 异常赋值 Message = exception.Message; } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
注册和模拟异常代码app.cs中
namespace ExceptionShowDialogDemo { /// <summary> /// Interaction logic for App.xaml /// </summary> public partial class App { public App() { Startup += App_Startup; DispatcherUnhandledException += App_DispatcherUnhandledException; } private void App_DispatcherUnhandledException(object sender, DispatcherUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { var dialogService = Container.Resolve<IDialogService>(); DialogParameters parameters = new DialogParameters { { "Title", "未捕获异常提示框" }, { "Exception", e.Exception } }; dialogService.ShowDialog(nameof(ErrorShowDialog), parameters, result => { }); } private void App_Startup(object sender, StartupEventArgs e) { } protected override Window CreateShell() { return Container.Resolve<MainWindow>(); } protected override void OnStartup(StartupEventArgs e) { base.OnStartup(e); try { throw new ArgumentException("数据库操作异常"); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.Data.Add("DataBaseName", "TableA"); ex.Data.Add("HappenTime", DateAndTime.Now.ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); ex.HelpLink = "Https//www.baidu.com"; throw new Exception("外部异常", ex); } } protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry) { containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<MainWindow, MainWindowViewModel>(); containerRegistry.RegisterDialog<ErrorShowDialog, ErrorShowDialogViewModel>(); containerRegistry.RegisterDialog<ExceptionDetailDialog, ExceptionDetailDialogViewModel>(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
点击详情页弹出的另外一个详情页窗口
<UserControl x:Class="ExceptionShowDialogDemo.Dialogs.ExceptionDetailDialog" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:converter="clr-namespace:ExceptionShowDialogDemo.ValueConverters" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:ExceptionShowDialogDemo.Dialogs" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" xmlns:prism="http://prismlibrary.com/" mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignHeight="450" d:DesignWidth="800"> <prism:Dialog.WindowStyle> <Style TargetType="Window"> <Setter Property="prism:Dialog.WindowStartupLocation" Value="CenterOwner" /> <Setter Property="ResizeMode" Value="NoResize" /> <Setter Property="ShowInTaskbar" Value="False" /> <Setter Property="SizeToContent" Value="WidthAndHeight" /> </Style> </prism:Dialog.WindowStyle> <UserControl.Resources> <converter:GetTypeConverter x:Key="GetTypeConverter" /> <converter:NotNullConverter x:Key="NotNullConverter" /> <Style TargetType="Button"> <Setter Property="Height" Value="35" /> <Setter Property="Width" Value="100" /> <Setter Property="VerticalContentAlignment" Value="Center" /> </Style> </UserControl.Resources> <DockPanel MinWidth="700" MinHeight="300" Background="#EEE" LastChildFill="False"> <StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Top" Margin="10" Orientation="Horizontal"> <Label VerticalContentAlignment="Center"> <TextBlock Text="{Binding ExceptionShow.Message}" Foreground="#333" TextWrapping="Wrap" /> </Label> </StackPanel> <!-- Width = "*" 和 Width 什么都不写有什么区别? 1) Width = * 宽度占用剩余的部分,使用Width="*" 2) 如果什么都不写表示这个列的宽度会根据内容自动适应 --> <Grid Margin="10"> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="250" /> <ColumnDefinition Width="auto" /> <ColumnDefinition Width="*" /> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ListView Background="#EEE" Padding="5,0" ItemsSource="{Binding Exceptions}" SelectedValue="{Binding ExceptionSelected, Mode=TwoWay}"> <ListView.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <!-- 绑定当前上下文,其中的Bingding Path=. 可以省略,直接写成Binding Convereter={StaticResource GetTypeConverter} --> <TextBlock Text="{Binding Path=., Mode=OneWay, Converter={StaticResource GetTypeConverter}}" /> </DataTemplate> </ListView.ItemTemplate> </ListView> <!-- Grid之间的分隔线 --> <GridSplitter Grid.Column="1" Width="2" Background="#888" Margin="10,0" /> <ScrollViewer Grid.Column="2" HorizontalScrollBarVisibility="Auto" TextBlock.FontSize="13" VerticalScrollBarVisibility="Hidden"> <StackPanel> <Label> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <TextBlock Text="{Binding ExceptionSelected, Converter={StaticResource GetTypeConverter}}" FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold" /> <TextBlock Text="(异常类型)" FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold" /> </StackPanel> </Label> <Label Content="Message(异常信息)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,5,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Message, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Message}" FontSize="12" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Message, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="Stack Trace(方法调用序列)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,5,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.StackTrace, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="{Binding ExceptionSelected.StackTrace}" Margin="0,5,0,0" /> <Label Content="Target Site(异常发生方法)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,5,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.TargetSite, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="{Binding ExceptionSelected.TargetSite}" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.TargetSite, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <!-- 每个Exception对象都有一个Data属性,这是一个IDictionary接口的实例,用于存储定义的键值数据. 如果你有一个数据库连接异常,你想知道是哪个数据库连接异常,你可以把这个信息添加到Data中去. --> <Label Content="Data(异常附加信息)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,5,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Data, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <ItemsControl ItemsSource="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Data}" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Data, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}"> <ItemsControl.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <Label> <TextBlock FontSize="12" FontStyle="Italic"> <Run Text="{Binding Key, Mode=OneWay}" /> <Run Text=" = " /> <Run Text="{Binding Value, Mode=OneWay}" /> </TextBlock> </Label> </DataTemplate> </ItemsControl.ItemTemplate> </ItemsControl> <!-- 获取或者设置导致错误的应用程序的名称,通常是引发异常的应用程序的名称 --> <Label Content="Source(异常程序集)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,5,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Source, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Source}" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.Source, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="Help Link(异常帮助链接)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,5,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.HelpLink, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="{Binding ExceptionSelected.HelpLink}" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.HelpLink, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="HResult(异常错误代码)" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="0,10,0,0" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.HResult, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> <Label Content="{Binding ExceptionSelected.HResult}" Visibility="{Binding ExceptionSelected.HResult, Converter={StaticResource NotNullConverter}}" /> </StackPanel> </ScrollViewer> </Grid> <StackPanel DockPanel.Dock="Bottom" Margin="10" HorizontalAlignment="Right" Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button Content="关闭" Command="{Binding CloseDialogCommand}" /> </StackPanel> </DockPanel> </UserControl>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
异常详情页对应的ViewModel
namespace ExceptionShowDialogDemo.ViewModels { public class ExceptionDetailDialogViewModel : BindableBase, IDialogAware { public ExceptionDetailDialogViewModel() { CloseDialogCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoCloseDialog); } private void DoCloseDialog() { RequestClose?.Invoke(new DialogResult()); } public DelegateCommand CloseDialogCommand { get; private set; } private string title; public string Title { get { return title; } set { title = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } private Exception exceptionSelected; public Exception ExceptionSelected { get { return exceptionSelected; } set { exceptionSelected = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } /// <summary> /// 异常列表,包括发生异常的内部异常. /// </summary> private ObservableCollection<Exception> exceptions = new ObservableCollection<Exception>(); public ObservableCollection<Exception> Exceptions { get { return exceptions; } set { exceptions = value; RaisePropertyChanged(); } } public event Action<IDialogResult> RequestClose; public bool CanCloseDialog() { return true; } public void OnDialogClosed() { } public void OnDialogOpened(IDialogParameters parameters) { Exceptions.Clear(); var title = parameters.GetValue<string>("Title"); var exception = parameters.GetValue<Exception>("Exception"); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(title)) { Title = title; } while (exception != null) { Exceptions.Add(exception); // 当没有内部异常的时候exception.InnerException的返回值为null exception = exception.InnerException; } ExceptionSelected = Exceptions.FirstOrDefault(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
使用到的两个类型转换器
namespace ExceptionShowDialogDemo.ValueConverters { public class GetTypeConverter : IValueConverter { /// <summary> /// 当数据从绑定源(后台的一个数据模型)传递给绑定目标(例如一个控件)时,Converter方法会被调用. /// </summary> /// <param name="value">要转换的值(绑定的数据源)</param> /// <param name="targetType">转换的目标类型,UI控件属性承载的类型,比如Text和Content的目标类型就是string</param> /// <param name="parameter">一个可选参数,可以在XAML中提供,你可以使用这个参数来影响转换的行为</param> /// <param name="culture">用于转换的文化信息,用来进行一些区域特性的转换,例如日期和字符串</param> /// <returns></returns> public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture) { var res = value?.GetType() ?? targetType; // 如果value为null,就返回targetType,如果是textBox或者是textBlock就返回string return res; } // 当数据从绑定目标传递给绑定源的时候,就是从UI控件的值到后台的值的时候.ConvertBack会被调用. // 其实就是相当于控件上的值发生了变化,会调用这个方法,而我们使用了Bingding.DoNothing,表示不作转换 // 什么都不做. /// <summary> /// /// </summary> /// <param name="value">从绑定目标(UI控件)传递过来的值</param> /// <param name="targetType">绑定源的数据类型</param> /// <param name="parameter"></param> /// <param name="culture"></param> /// <returns></returns> public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture) { return Binding.DoNothing; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
namespace ExceptionShowDialogDemo.ValueConverters { public class NotNullConverter : IValueConverter { public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture) { bool res = value != null; switch (value) { case ICollection collection: res = collection.Count > 0; break; case string str: res = !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(str); break; case int i: res = i != 0; break; case double d: res = Math.Abs(d) > 0.00001; break; } // 看看是否需要 反转结果,根据paraeter的值来判读昂 if ((parameter is bool inverse || parameter is string s && bool.TryParse(s, out inverse)) && inverse) res = !res; if (targetType == typeof(Visibility)) return res ? Visibility.Visible : Visibility.Collapsed; return res; } public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture) { return Binding.DoNothing; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
最后实现的效果,出现异常的第一个弹窗
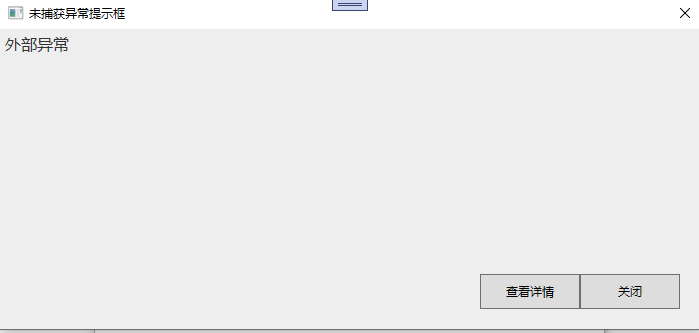
点击查看详情的弹窗
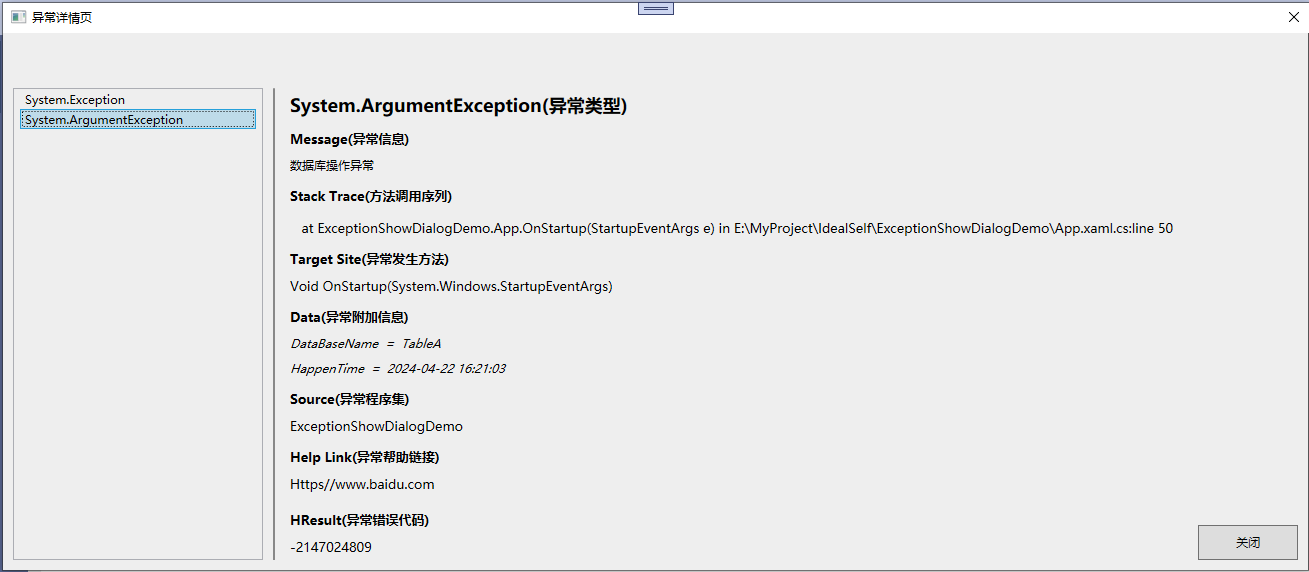
总结:
这个小案例还是用到了不少的知识点,但是还是有可以优化的地方,因为这里又在
ViewModel中操作了UI,最好的实践方式是将弹窗这里封装成为一个服务,然后在服务里操作窗口,后续再介绍



