- 1大流量 高并发系统之限流特技_限制一段时间内允许通过的流量 应用限流
- 2Git使用手册
- 3【精品毕设推荐】基于JSP的旅游网站设计与实现
- 4Cesium-基于JS的开源3D地图渲染引擎_cesiumjs 开源版
- 5subprocess—Python多进程模块_python subprocess
- 6Spring Boot中使用Redis和Lua脚本实现延时队列
- 7css基础篇 06 定位 定位案例 网页布局总结 元素的显示和隐藏_display种类
- 8AI作图在线软件怎么快速生成图片?只需要这3步!_ai生成图片
- 9myCobot pro 机械臂(6)逆向运动学_机械臂逆运动学
- 10Labelme格式转Coco格式_labelme 转coco
RabbitMQ 交换机类型
赞
踩
常用交换机
发布订阅(Publish/Subscribe)交换机
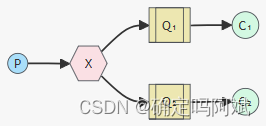
一个生产者给多个队列发送消息,X 代表交换机。
交换机的作用:类似网络路由器,主要提供转发功能,解决怎么把消息转发到不同的队列中,让消费者从不同队列取然后消费。
绑定:交换机和队列关联起来
发布订阅交换机,队列进行持久化,生产者发布消息,所有消费者都能接收到消息。
生产者代码
- public class FanoutProducer{
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "fanout_exchange";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- try (Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
- //创建交换机,参数:交换机名称,交换机类型
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- while(scanner.hasNext()){
- String message = scanner.nextLine();
- //第二个参数是路由规则
- channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "", null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + message + "'");
- }
-
- }
- }
- }

消费者代码
- public class FanoutConsumer {
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "fanout_exchange";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
- //绑定交换机,以及设置绑定规则
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");
- String queueName1 = "xiaowang";
- String queueName2 = "xiaoli";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName1, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName2, true, false, false, null);
- //创建队列,不指定队列,随机分配
- //String queueName = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
- channel.queueBind(queueName1, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");
- System.out.println(" [xiaowang] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
- //交换机绑定队列
- channel.queueBind(queueName2, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");
- System.out.println(" [xiaoli] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback1 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println( " [xiaowang] Received '" + message + "'");
- };
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback2 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println( " [xiaoli] Received '" + message + "'");
- };
- channel.basicConsume(queueName1, true, deliverCallback1, consumerTag -> {
- });
- channel.basicConsume(queueName2, true, deliverCallback2, consumerTag -> {
- });
- }
- }

channel 频道:理解为操作消息队列的 Client,通过 channel 收发消息,提供了和消息对了 server 建立通信的传输方法
channel.queueDeclare 方法参数:
queue:这是一个字符串参数,代表要声明的队列的名称。如果队列不存在,则会自动创建一个新的队列。
durable:这是一个布尔值参数,表示队列是否持久化。如果设置为true,则队列会在服务器重启后仍然存在;如果设置为false,则队列在服务器重启后会被删除。默认值为false。
exclusive:这也是一个布尔值参数,表示队列是否为独占模式。如果设置为true,则只有当前连接可以访问该队列;如果设置为false,则其他连接也可以访问该队列。默认值为false。
autoDelete:这是另一个布尔值参数,表示队列是否自动删除。如果设置为true,则当最后一个消费者取消订阅时,队列将被删除;如果设置为false,则队列将一直存在,直到手动删除或服务器重启。默认值为false。
arguments:这是一个可选参数,用于设置队列的其他属性,比如消息的最大长度、最大优先级等。
channel.basicPublish 参数:
exchange:这是一个字符串参数,代表交换机的名称。如果不需要使用特定的交换机,可以传递一个空字符串("")。交换机是RabbitMQ中用于接收生产者发送的消息并根据绑定规则路由到队列的组件。
routingKey:这也是一个字符串参数,它指定了发布消息的队列。无论通道绑定到哪个队列,最终发布的消息都会包含这个指定的路由键。路由键是用来确定消息应该发送到哪个队列的重要信息。
message:这是要发布的消息本身,通常是字节数组的形式。
properties:这是一个可选参数,用于设置消息的属性,比如消息的优先级、过期时间等。
在使用channel.basicPublish时,需要注意以下几点:
exchange和routingKey不能为空:在AMQImpl类中的实现要求这两个参数都不能为null,否则会抛出异常。
交换机类型:根据不同的需求,可以选择不同类型的交换机,如fanout、direct或topic。每种类型的交换机都有其特定的路由规则。
非命名队列:在某些情况下,比如日志系统,可以使用非命名队列,这样消费者可以接收到所有相关的日志消息,而不是特定的部分。
channel.basicConsume 参数:
queue:这是一个字符串参数,代表要消费的队列的名称。如果队列不存在,则会抛出异常。
onMessage:这是一个回调函数,当有新的消息到达时会被调用。该函数需要接收两个参数:一个表示消息内容的Delivery对象和一个表示通道的Channel对象。
consumerTag:这是一个可选参数,用于标识消费者。如果没有指定,则会自动生成一个唯一的标识符。
autoAck:这是一个布尔值参数,表示是否自动确认消息。如果设置为true,则在消息被处理后会自动发送确认信息;如果设置为false,则需要手动发送确认信息。默认值为false。
arguments:这是一个可选参数,用于设置消费者的其他属性,比如消息的最大长度、最大优先级等。
在使用channel.basicConsume时,需要注意以下几点:
队列名称:队列名称应该是唯一的,否则会抛出异常。
消息处理:在onMessage回调函数中,需要对消息进行处理,并根据需要发送确认信息。
消费者标识符:可以通过设置consumerTag来标识消费者,以便在后续操作中进行识别和管理。
消费者属性:可以通过设置消费者的其他属性来控制消费者的行为,比如设置消息的最大长度、最大优先级等。
路由交换机 (Direct exchange)
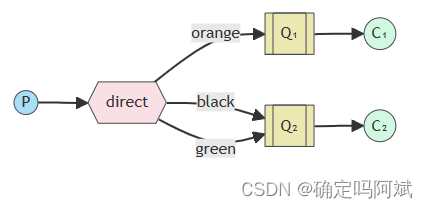
和订阅发布的区别是在交换机和队列之间有一个路由键,用来控制消息发送到哪个队列中供消费者消费。生产者给交换机一个标识,让交换机给指定的队列转发消息。
生产者代码
- public class DirectProducer {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_exchange";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- try (Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
- //创建交换机,交换机类型是 direct
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- while (scanner.hasNext()){
- String userInput = scanner.nextLine();
- //输入的时候带着标识,标识就是路由键
- String[] strs = userInput.split(" ");
- if(strs.length<1){
- continue;
- }
- //消息
- String message = strs[0];
- //路由键
- String severity = strs[1];
- //发送消息时带着路由键
- channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, severity, null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + severity + "':'" + message + "'");
- }
- }
- }
- }

消费者代码
- public class DirectConsumer {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct_exchange";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
- String queueName1 = "xiaohong";
- String queueName2 = "xiaobai";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName1, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName2, true, false, false, null);
- //交换机使用路由键绑定队列
- channel.queueBind(queueName1, EXCHANGE_NAME, "xiaohong");
- channel.queueBind(queueName2, EXCHANGE_NAME, "xiaobai");
- System.out.println(" [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
-
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback1 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [xiaohong] Received '" +
- delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback2 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [xiaobai] Received '" +
- delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- channel.basicConsume(queueName1, true, deliverCallback1, consumerTag -> {
- });
- channel.basicConsume(queueName2, true, deliverCallback2, consumerTag -> {
- });
- }
- }

主题交换机 (Topic exchange)
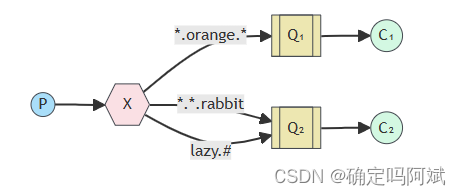
在路由交换机的基础上,消息会具有一个模糊的路由键转发给指定的对俄(一系列的路由键、一类的路由键)
1. (*)标识匹配一个单词,比如 *.orange 表示 a.orange b.orange 都能匹配
2. (#)表示 0 个或多个单词,比如 a,#, a.a, a.b 都可以
生产者代码
- public class TopicProduce {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_exchange1";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- try (Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
-
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- while (scanner.hasNext()) {
- String userInput = scanner.nextLine();
- String[] strs = userInput.split(" ");
- if (strs.length < 1) {
- continue;
- }
- //消息
- String message = strs[0];
- //路由键
- String severity = strs[1];
-
- channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, severity, null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + severity + "':'" + message + "'");
- }
- }
- }
- }

消费者代码
- public class TopicConsumer {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "topic_exchange1";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
-
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
- String queueName1 = "xiaohei";
- String queueName2 = "xiaolv";
- String queueName3 = "xiaohuang";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName1, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName2, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName3, true, false, false, null);
- //交换机使用路由键绑定队列,路由键绑定在第三个参数
- channel.queueBind(queueName1, EXCHANGE_NAME, "#.前端.#");
- channel.queueBind(queueName2, EXCHANGE_NAME, "#.后端.#");
- channel.queueBind(queueName2, EXCHANGE_NAME, "#.产品.#");
- System.out.println(" [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
- //收到消息后如何处理
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback1 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [xiaohei] Received '" + delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback2 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [xiaolv] Received '" + delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback3 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [xiaohuang] Received '" + delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- channel.basicConsume(queueName1, true, deliverCallback1, consumerTag -> {
- });
- channel.basicConsume(queueName2, true, deliverCallback2, consumerTag -> {
- });
- channel.basicConsume(queueName3, true, deliverCallback3, consumerTag -> {
- });
-
-
- }
- }

核心机制
消息过期机制
官方文档:Preventing Unbounded Buffers with RabbitMQ | RabbitMQ
每个消息指定一个有效期,一段时间内没有被消费者处理,就过期了。
比如消费者挂了,消息一直不被处理,订单就会失效。
可以清理过期的数据,模拟延迟队列的实现。
给每条消息都设置过期时间:
- Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<String, Object>();
- args.put("x-message-ttl", 60000);
- channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, args);
给队列设置过期时间,设置在生产者中
- AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties.Builder()
- .expiration("1000")
- .build();
生产者代码
- public class TtlProducer {
-
- private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "Tll_queue";
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- //创建连接
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- //设置了本地连接,如果修改了用户名和密码,需要设置
- /*factory.setPassword();
- factory.setUsername();*/
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- //建立连接、创建频道
- //频道,类似客户端,用于调用server
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
- String message = "Hello World!";
- //发消息设置过期时间
- AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties.Builder()
- .expiration("1000")
- .build();
- //发送消息
- channel.basicPublish("",QUEUE_NAME,properties,message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
- System.out.println(" [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
-
- }
- }

消费者代码
- public class TtlConsumer {
-
- private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "Tll_queue";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
- //声明队列,同一个消息队列参数必须一致
- Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<String, Object>();
- args.put("x-message-ttl", 60000);
- channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, args);
- //定义了如何处理消息
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
- };
- //接收、消费消息 第二个参数 autoAck
- channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, deliverCallback, consumerTag -> { });
- System.out.println(" [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
-
- }
- }

死信队列
官方文档:Dead Letter Exchanges | RabbitMQ
为了保证消息的可靠性,比如每条消息都成功消费,需要提供一个容错机制,即:失效的消息怎么办?
死信:过期的消息、拒收的消息、消息队列满了、处理失败的消息的统称。
死信队列:处理死信的队列。
死信交换机:专门给死信队列转发消息的,存在路由绑定关系
实际就是设置一个普通的队列,专门将死信发送到这个队列中处理。
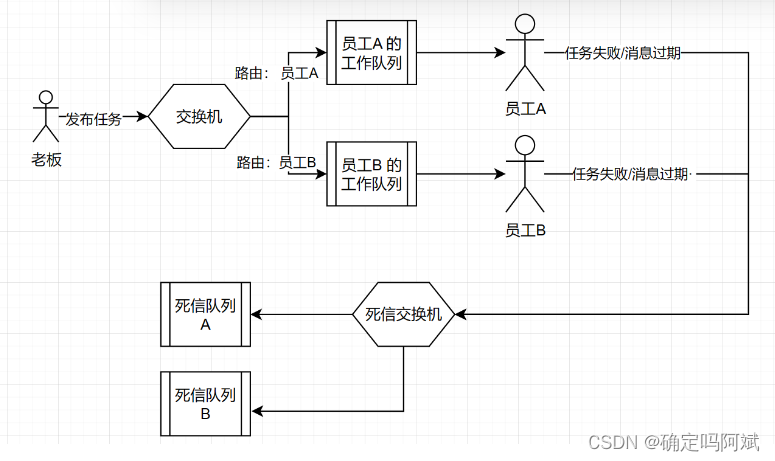
1. 创建死信交换机和死信队列
- //声明死信交换机
- String queueName = "laoban_dlx_queue";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueBind(queueName, EXCHANGE_NAME, "laoban");
2. 给失败之后需要容错处理的队列绑定死信交换机
args2.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME);3. 绑定交换机到死信队列
args2.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "waibao");生产者代码
- public class DLXDirectProducer {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct2_exchange";
- private static final String DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME = "dlx_direct2_exchange";
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- try (Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {
- //声明死信交换机
- channel.exchangeDeclare(DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
- String queueName = "laoban_dlx_queue";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueBind(queueName, DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME, "laoban");
-
- String queueName2 = "waibao_dlx_queue";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName2, true, false, false, null);
- channel.queueBind(queueName2, DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME, "waibao");
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback1 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [laoban] Received '" +
- delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback2 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [waibao] Received '" +
- delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- channel.basicConsume(queueName, false, deliverCallback1, consumerTag -> {
- });
- channel.basicConsume(queueName2, false, deliverCallback2, consumerTag -> {
- });
- Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
- while (scanner.hasNext()){
- String userInput = scanner.nextLine();
- String[] strs = userInput.split(" ");
- if(strs.length<1){
- continue;
- }
- //消息
- String message = strs[0];
- //路由键
- String severity = strs[1];
-
- channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, severity, null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
- System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + severity + "':'" + message + "'");
- }
-
- }
- }
- }

消费者代码
- public class DLXDirectConsumer {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "direct2_exchange";
- private static final String DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME = "dlx_direct2_exchange";
-
-
- public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
- //死信交换机绑定工作队列,当信息错误就从工作队列发送到死信交换机
- Map<String, Object> args1 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
- //指定绑定哪个交换机
- args1.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME);
- //死信要发送到哪个队列
- args1.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "laoban");
- String queueName1 = "doghuang";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName1, true, false, false, args1);
- channel.queueBind(queueName1, EXCHANGE_NAME, "doghuang");
-
- //绑定cat 队列
-
- String queueName2 = "catbai";
- Map<String, Object> args2 = new HashMap<String, Object>();
- args2.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_EXCHANGE_NAME);
- args2.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "waibao");
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName2, true, false, false, args2);
- channel.queueBind(queueName2, EXCHANGE_NAME, "catbai");
-
-
- //交换机使用路由键绑定队列
- System.out.println(" [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
-
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback1 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- channel.basicNack(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(),false,false);
- System.out.println(" [doghuang] Received '" +
- delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- DeliverCallback deliverCallback2 = (consumerTag, delivery) -> {
- String message = new String(delivery.getBody(), "UTF-8");
- System.out.println(" [catbai] Received '" +
- delivery.getEnvelope().getRoutingKey() + "':'" + message + "'");
- };
- channel.basicConsume(queueName1, false, deliverCallback1, consumerTag -> {
- });
- channel.basicConsume(queueName2, false, deliverCallback2, consumerTag -> {
- });
-
- }
- }

项目实战
项目中使用可以选择两种方法
1. 官方的客户端,兼容性好,灵活,需要自己维护管理
2. 使用封装好的客户端,比如 Spring Boot RabbitMQ Starter
优点:简单易用
缺点:不够灵活,被框架限制
小项目使用封装好的足够
1. 依赖引入
引入和自己 Spring Boot 版本相同的依赖,避免出现不能运行的错误
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-amqp -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
- <version>2.6.13</version>
- </dependency>
2. 引入配置
- rabbitmq:
- host: localhost
- port: 5672
- password: guest
- username: guset
3. 创建交换机和消息队列,这个只需要启动一次创建即可
- /**
- * 只启动一次,创建交换机和消息队列
- */
- public class MqInitMain {
-
- private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "code_exchange";
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
- factory.setHost("localhost");
- Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
- Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
- channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
-
- //绑定一个队列
- String queueName = "code_queue";
- channel.queueDeclare(queueName,true,false,false,null);
- channel.queueBind(queueName,EXCHANGE_NAME,"BI_routingKey");
- }
- }

4. 生产者
- /**
- * 生产者
- */
- @Component
- public class MyMessageProducer {
-
-
- @Resource
- private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
-
- //1.交换机名称2. 交换机路由键3.发送的消息
- public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey,String message){
- rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange,routingKey,message);
- }
-
- }

5. 消费者
- /**
- * 消费者
- */
- @Component
- @Slf4j
- public class MessageConsumer {
-
- @RabbitListener(queues = {"code_queue"},ackMode = "MANUAL")
- public void receiveMessage(String message, Channel channel,@Header(AmqpHeaders.DELIVERY_TAG) long delivery){
- log.info("receiveMessage message={}",message);
- try {
- channel.basicAck(delivery,false);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new RuntimeException(e);
- }
- }
- }

6. 测试
- @SpringBootTest
- class MyMessageProducerTest {
-
- @Resource
- private MyMessageProducer myMessageProducer;
- @Test
- void sendMessage() {
- myMessageProducer.sendMessage("code_exchange","BI_routingKey","你好吗");
- }
- }


