- 1C#中Winform使用OpenFileDialog选择文件打开并获取文件路径_通过openfiledialog选择文件路径
- 2react项目内存溢出,加大内存的方式之一 Ineffective mark-compacts near heap limit Allocation failed - JavaScript heap_vscode的react项目内存溢出
- 3Redis实现分布式锁的原理:常见问题解析及解决方案、源码解析Redisson的使用_分布式事务redis解决方案
- 42024永久免费版CrossOver软件下载及使用方法详细的步骤_crossover安装包
- 5guitar pro 8许可证忘记了怎么办 guitar pro8谱数字可以改吗
- 6基于微信学生新生报到小程序系统设计与实现
- 7ROS Motion Planning运动规划库安装方法及进阶使用方法详细介绍
- 8pom可视化idea_GitHub - haizlin-idea/rsbi-pom: 睿思BI-数据仪表盘,开源商业智能,数据可视化系统...
- 9在CDH集群安装Flink
- 10单片机学习笔记---独立按键控制LED亮灭_单片机按键控制led灯亮灭
yolov3-tensorflow版的实现与详解(一)网络结构分析_yolo tensorflow
赞
踩
最近在学习yolo检测算法,并细读了tensorflow版的代码,现总结一下,分享给各位童鞋们。首先讲解一下yolov3的网络结构,阅读过yolov3论文的童鞋们应该有所体会,读完感觉内容并不多,讲解不是很细致,所以本人根据阅读的代码进一步分析网络,并附上相应的代码。
1.Darknet-53 network
在论文中虽然有给网络的图,但我还是简单说一下。这个网络主要是由一系列的1x1和3x3的卷积层组成(每个卷积层后都会跟一个BN层和一个LeakyReLU)层,作者说因为网络中有53个convolutional layers,所以叫做Darknet-53(我数了下,作者说的53包括了全连接层但不包括Residual层)。下图就是Darknet-53的结构图,在右侧标注了一些信息方便理解。(卷积的strides默认为(1,1),padding默认为same,当strides为(2,2)时padding为valid)
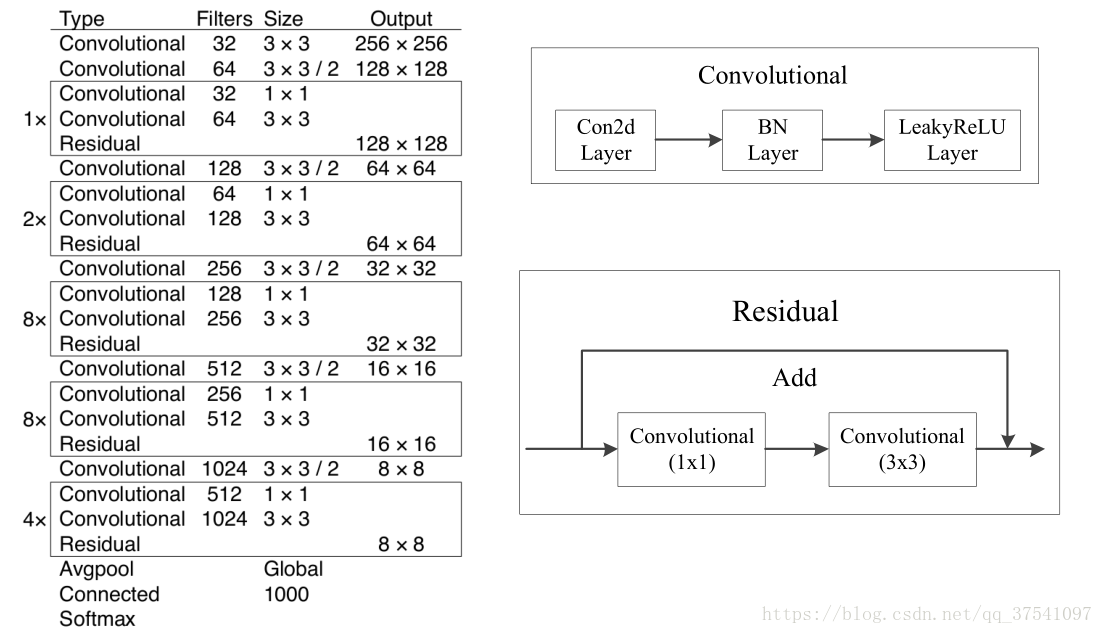
看完上图应该就能自己搭建出Darknet-53的网络结构了,上图是以输入图像256 x 256进行预训练来进行介绍的,常用的尺寸是416 x 416,都是32的倍数。首先在common.py中定义卷积操作,根据srides的不同,决定是否需要padding。
import tensorflow as tf # 构建模型的基本组件 slim = tf.contrib.slim def _conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=1): if strides > 1: inputs = _fixed_padding(inputs, kernel_size) inputs = slim.conv2d(inputs, filters, kernel_size, stride=strides, padding=('SAME' if strides == 1 else 'VALID')) return inputs @tf.contrib.framework.add_arg_scope def _fixed_padding(inputs, kernel_size, *args, mode='CONSTANT', **kwargs): """ 与输入大小无关, 只有与所使用的卷积核有关,左右两边进行填充 Args: inputs: A tensor of size [batch, channels, height_in, width_in] or [batch, height_in, width_in, channels] depending on data_format. kernel_size: The kernel to be used in the conv2d or max_pool2d operation. Should be a positive integer. mode: The mode for tf.pad. Returns: A tensor with the same format as the input with the data either intact (if kernel_size == 1) or padded (if kernel_size > 1). """ # 使得kernel完整走过边缘 pad_total = kernel_size - 1 pad_beg = pad_total // 2 pad_end = pad_total - pad_beg padded_inputs = tf.pad(inputs, [[0, 0], [pad_beg, pad_end], [pad_beg, pad_end], [0, 0]], mode=mode) return padded_inputs
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
在yolov3.py中定义了yolov3的网络结构,首先是Darknet-53网络部分的实现:
import tensorflow as tf from core import common slim = tf.contrib.slim class darknet53(object): #用于执行特征提取的网络 def __init__(self, inputs): self.outputs = self.forward(inputs) def _darknet53_block(self, inputs, filters): """ implement residuals block in darknet53 """ shortcut = inputs inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 1, 1) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 2, 3) inputs = inputs + shortcut return inputs def forward(self, inputs): inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, 32, 3, strides=1) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, 64, 3, strides=2) # 208 inputs = self._darknet53_block(inputs, 32) # inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, 128, 3, strides=2) # 104 for i in range(2): inputs = self._darknet53_block(inputs, 64) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, 256, 3, strides=2) # 52 for i in range(8): inputs = self._darknet53_block(inputs, 128) route_1 = inputs inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, 512, 3, strides=2) # 26 for i in range(8): inputs = self._darknet53_block(inputs, 256) route_2 = inputs inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, 1024, 3, strides=2) # 13 for i in range(4): inputs = self._darknet53_block(inputs, 512) return route_1, route_2, inputs
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
2.Feature Extractor
作者在论文中提到利用三个特征层进行边框的预测,具体在哪三层我感觉作者在论文中表述的并不清楚(例如文中有“添加几个卷积层”这样的表述),同样根据代码我将这部分更加详细的分析展示在下图中。注意:原Darknet53中的尺寸是在图片分类训练集上训练的,所以输入的图像尺寸是256x256,下图是以YOLO v3 416模型进行绘制的,所以输入的尺寸是416x416,预测的三个特征层大小分别是52,26,13。
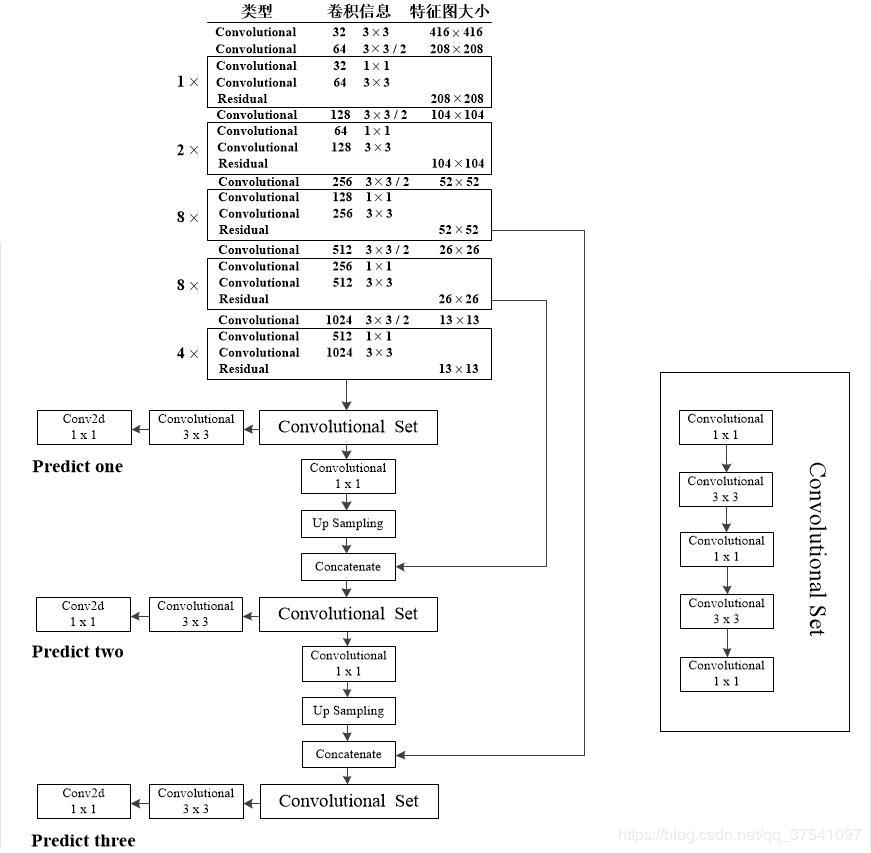
在上图中我们能够很清晰的看到三个预测层分别来自的什么地方,以及Concatenate层与哪个层进行拼接。注意Convolutional是指Conv2d+BN+LeakyReLU,和Darknet53图中的一样,而生成预测结果的最后三层都只是Conv2d。通过上图小伙伴们就能更加容易地搭建出YOLOv3的网络框架了。
那么下面我们看一下源码,经过darknet53之后,会得到route_1, route_2, inputs,inputs会进入Convoltional Set,源码中在 def _yolo_block(self, inputs, filters)中定义(Convolutional3*3也在里面),然后经过Conv2d得到相应的featuremap。route_1, route_2会与经过上采样得到的结果concat再经过卷积获得相应的featuremap,涉及到的代码如下:
class yolov3(object): def __init__(self, num_classes, anchors, batch_norm_decay=0.9, leaky_relu=0.1): ''' :param num_classes: class :param anchors: number of anchors 列表 :param batch_norm_decay: :param leaky_relu: ''' # self._ANCHORS = # [[10 ,13], [16 , 30], [33 , 23], # [30 ,61], [62 , 45], [59 ,119], # [116,90], [156,198], [373,326]] self._ANCHORS = anchors self._BATCH_NORM_DECAY = batch_norm_decay self._LEAKY_RELU = leaky_relu self._NUM_CLASSES = num_classes self.feature_maps = [] # [[None, 13, 13, 255], [None, 26, 26, 255], [None, 52, 52, 255]] def _yolo_block(self, inputs, filters): # if stride > 1 , padding inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 1, 1) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 2, 3) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 1, 1) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 2, 3) inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 1, 1) route = inputs inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(inputs, filters * 2, 3) return route, inputs # 目标识别的层, 转换到合适的深度,以满足不同class_num数据的分类 def _detection_layer(self, inputs, anchors): num_anchors = len(anchors) feature_map = slim.conv2d(inputs, num_anchors * (5 + self._NUM_CLASSES), 1, stride=1, normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=None, biases_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()) return feature_map def _upsample(inputs, out_shape): # 上采样, 放大图片 new_height, new_width = out_shape[1], out_shape[2] inputs = tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(inputs, (new_height, new_width)) # 使用最近邻改变图像大小 inputs = tf.identity(inputs, name='upsampled') return inputs # 前向传播,得到3个feature_map def forward(self, inputs, is_training=False, reuse=False): """ Creates YOLO v3 model. :param inputs: a 4-D tensor of size [batch_size, height, width, channels]. Dimension batch_size may be undefined. The channel order is RGB. :param is_training: whether is training or not. :param reuse: whether or not the network and its variables should be reused. :return: """ # it will be needed later on 他在稍后将被需要 self.img_size = tf.shape(inputs)[1:3] # set batch norm params batch_norm_params = { 'decay': self._BATCH_NORM_DECAY, 'epsilon': 1e-05, 'scale': True, 'is_training': is_training, 'fused': None, # Use fused batch norm if possible. } # Set activation_fn and parameters for conv2d, batch_norm. with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.batch_norm, common._fixed_padding], reuse=reuse): with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm, # 给定list(slim.conv2d)中的值设置默认值(normlizer,biase.....) normalizer_params=batch_norm_params, biases_initializer=None, activation_fn=lambda x: tf.nn.leaky_relu(x, alpha=self._LEAKY_RELU)): with tf.variable_scope('darknet-53'): route_1, route_2, inputs = darknet53(inputs).outputs # 得到图片张量 # route_1 : 52x52x256 # route_2 : 26x26x512 # inputs : 13x13x1024 with tf.variable_scope('yolo-v3'): # feature_map1 13x13x1024 --> 13x13x[3x(5+class_num)] route, inputs = self._yolo_block(inputs, 512) feature_map_1 = self._detection_layer(inputs, self._ANCHORS[6:9]) feature_map_1 = tf.identity(feature_map_1, name='feature_map_1') # feature_map2 26x26x512 --> 26x26x[3x(5+class_num)] inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(route, 256, 1) upsample_size = route_2.get_shape().as_list() # 52x52 --> 26x26 inputs = self._upsample(inputs, upsample_size) # 通过直接放大进行上采样 inputs = tf.concat([inputs, route_2], axis=3) # 在axis=3 进行连接, route, inputs = self._yolo_block(inputs, 256) feature_map_2 = self._detection_layer(inputs, self._ANCHORS[3:6]) feature_map_2 = tf.identity(feature_map_2, name='feature_map_2') # feature_map3 52x52x256 --> 52x52x[3x(5+class_num)] inputs = common._conv2d_fixed_padding(route, 128, 1) upsample_size = route_1.get_shape().as_list() # 26x26 --> 52x52 inputs = self._upsample(inputs, upsample_size) inputs = tf.concat([inputs, route_1], axis=3) route, inputs = self._yolo_block(inputs, 128) feature_map_3 = self._detection_layer(inputs, self._ANCHORS[0:3]) feature_map_3 = tf.identity(feature_map_3, name='feature_map_3') return feature_map_1, feature_map_2, feature_map_3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107




