- 1SPI_FLASH时序描述及驱动编程_在线读写25q80
- 2工作7年开发小哥转行测试:只有努力向前奔跑,才能得到你要的~
- 3RabbitMQ发布确认和消息回退(6)_rabbitmq取消消息确认
- 4“全国版双录”新政来了,容联云助力泛金融打造合规的远程双录平台_互联网销售必须录音吗
- 5Linux命令---安装unzip命令_linux安装unzip命令
- 6(三)丶RabbitMQ的四种类型交换机_rabbitmq交换机种类
- 7Windows 系统下:SSH 远程连接 Linux 服务器的完整指南_windowsssh连接linux_window 如何连接ssh
- 8Android-接入谷歌登录_id token has invalid 'aud' (audience) claim; expec
- 9Google BERT理解_decorder和encorder的模型
- 10AndroidStudio 由dolphin升级到giraffe,出现“gradle project sync failed“_as升级到鬣蜥版本程序报错
【云原生| K8S系列】Kubernetes Daemonset,全面指南
赞
踩
Kubernetes中的DaemonSet是什么?
Kubernetes是一个分布式系统,Kubernetes平台管理员应该有一些功能可以在所有节点上运行特定于平台的应用程序。例如,在所有Kubernetes节点上运行日志代理。
这就是Daemonset发挥作用的地方。
Daemonset是一个原生的Kubernetes对象。顾名思义,它旨在运行系统守护进程。
DaemonSet对象旨在确保每个工作节点上都运行一个pod。这意味着您不能在节点中扩展daemonset pods。由于某种原因,如果从节点删除daemonset pod,则daemonset控制器将再次创建它。
让我们看一个例子。如果有500个工作节点,并且您部署了一个daemonset,则默认情况下daemonset控制器将为每个工作节点运行一个pod。总共是500个Pod。但是,使用nodeSelector、nodeAffinity、Taints和Tolerations,可以限制daemonset在特定节点上运行。
例如,在有100个工作节点的集群中,一个可能有20个标记为GPU的工作节点来运行批处理工作负载。你应该在这20个工作节点上运行pod。在这种情况下,可以使用节点选择器将pod部署为守护进程。我们将在本指南的后面讨论它。
另一个例子是,您有特定数量的工作节点专用于平台工具(入口、监控、日志等),并且希望仅在标记为平台工具的节点上运行与平台工具相关的Daemonset。在这种情况下,您可以使用nodeSelector仅在平台工具专用的工作节点上运行daemonset pods。
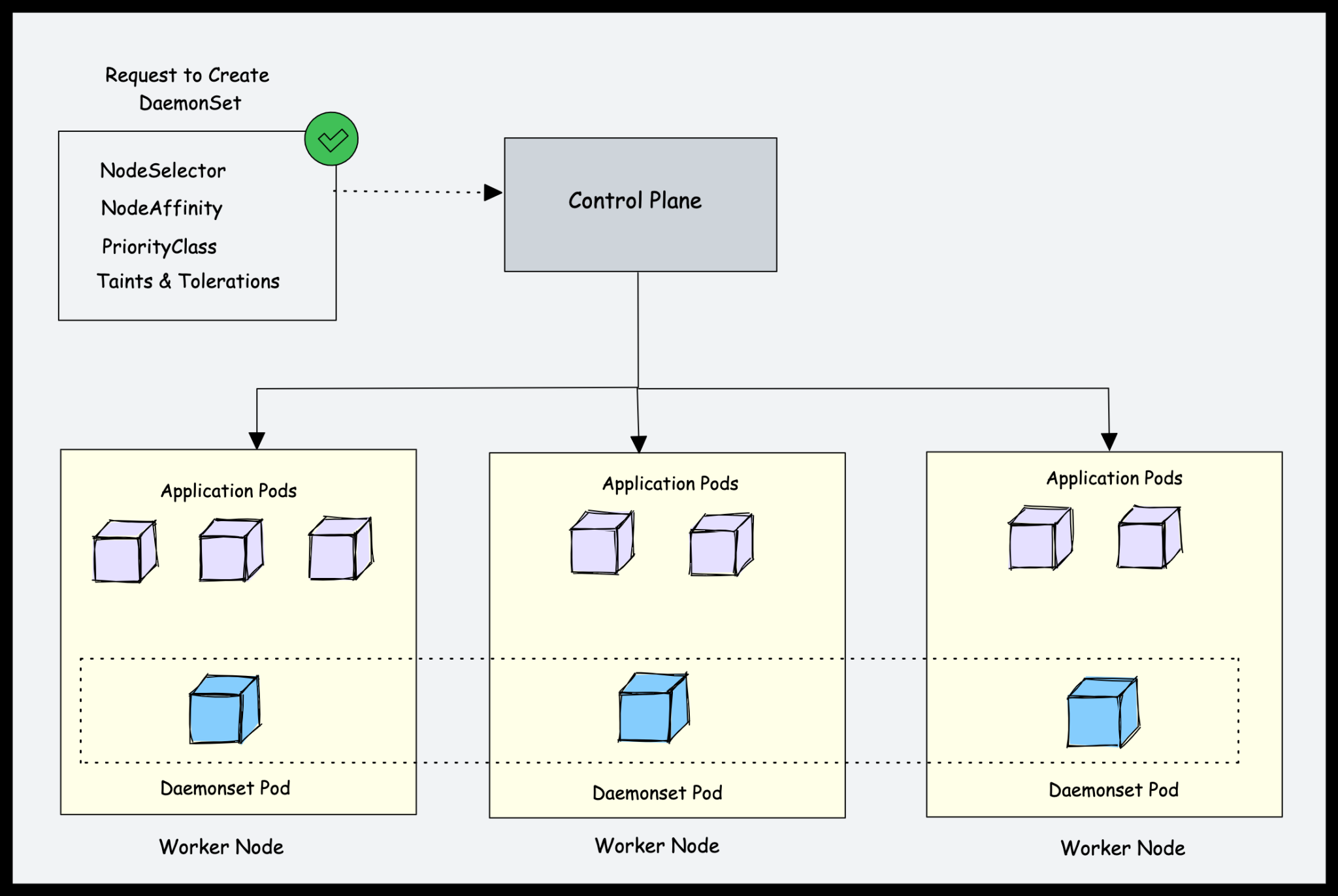
Kubernetes后台进程的用例
DaemonSet的基本用例是在集群本身中。如果你看一下Kubernetes架构,kube-proxy组件会运行一个daemonset。
下面是Daemonset的实际用例。
- 集群日志收集:在每个节点上运行日志采集器,以集中Kubernetes日志数据。例如:fluentd, logstash, fluentbit
- 集群监控:在集群中的每个节点上部署监控代理,例如Prometheus节点导出器,以收集和公开节点级度量。通过这种方式,prometheus可以获取所有工作节点的监控指标。
- 安全性和合规性:使用kube-bench等工具在每个节点上运行CIS基准测试。还要在需要额外安全措施的特定节点上部署安全代理,如入侵检测系统或漏洞扫描器。例如,处理PCI和pii兼容数据的节点。
- 存储配置:在每个节点上运行存储插件,为整个集群提供共享存储系统。
- 网络管理:在每个节点上运行网络插件或防火墙,以确保网络策略的一致执行。例如,Calico CNI插件在所有节点上以Daemonset的形式运行。
根据需求,我们可以为一种守护进程部署多个DaemonSet,对各种硬件类型使用各种标志或内存和CPU请求。
DaemonSet例子
像其他Kubernetes对象一样,DaemonSet也通过使用YAML文件来配置。我们需要创建一个清单文件,其中将包含守护进程所需的所有配置信息。
假设我们想在集群的所有工作节点上部署一个fluentd日志代理作为Deamonset。
下面是daemonset的示例。部署在logging命名空间中的Yaml文件。
您还可以从Github Repo的Kubernetes课程中获得daemonset YAML示例。
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: fluentd namespace: logging labels: app: fluentd-logging spec: selector: matchLabels: name: fluentd template: metadata: labels: name: fluentd spec: containers: - name: fluentd-elasticsearch image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2 resources: limits: memory: 200Mi requests: cpu: 100m memory: 200Mi volumeMounts: - name: varlog mountPath: /var/log terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 volumes: - name: varlog hostPath: path: /var/log
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
让我们来了解一下清单文件。
apiVersion:apps/v1用于DaemonSetkind:后台进程,如Pod、部署和服务metadata:放置DaemonSet的名称、提及命名空间、注释和标签。在我们的例子中,DaemonSet的名称是fluentd。spec.selector: pods的选择器由DaemonSet管理。这个值必须是在pod模板中指定的标签。这个值是不可变的。spec.template:这是一个必填字段,指定守护进程要使用的pod模板。以及容器的所有必填字段。除了apiVersion和kind之外,它具有pod schema的所有内容。
template.metadata包含pod和模板的详细信息。Spec将具有pod的模式。
在pod模板中,我们使用quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2镜像,它将在Kubernetes集群的每个节点上运行。每个pod将收集日志并将数据发送到ElasticSearch。增加了对pod的资源限制和请求,以及相应的volume和volumeMount。
我们不提供任何副本计数,这是因为DaemonSet的副本计数本质上是动态的,因为它依赖于集群的节点计数。
让我们使用以下命令来部署此清单文件。首先,我们必须创建一个命名空间,并在该命名空间中部署daemonset。
kubectl create ns logging
kubectl apply -f daemonset.yaml
- 1
- 2
检查DaemonSet状态和pods状态。
kubectl get daemonset -n logging
kubectl get pods -n logging -o wide
- 1
- 2
- 3

你可以看到fluentd pods运行在两个可用的工作节点上。
下面是一些其他有用的命令来描述、编辑和获取DaemonSet。
kubectl describe daemonset -n logging
kubectl edit daemonset -n logging
kubectl get ds
- 1
- 2
- 3
应用污点和对Daemonset的耐受
Taints和tolerance是Kubernetes的功能,它允许你确保pods不会被放置在不合适的节点上。我们污染节点并在pod模式中添加公差。
kubectl taint 节点 node1 key1=value1:<效果>
- 1
有3种效果:
NoSchedule:Kubernetes调度器只允许调度对受污染节点具有容错能力的pods。PreferNoSchedule: Kubernetes调度器将尝试避免调度对受污染节点不具有容错能力的pods。NoExecute:如果pods对受污染的节点不具有容错能力,Kubernetes将从节点中移除正在运行的pods。
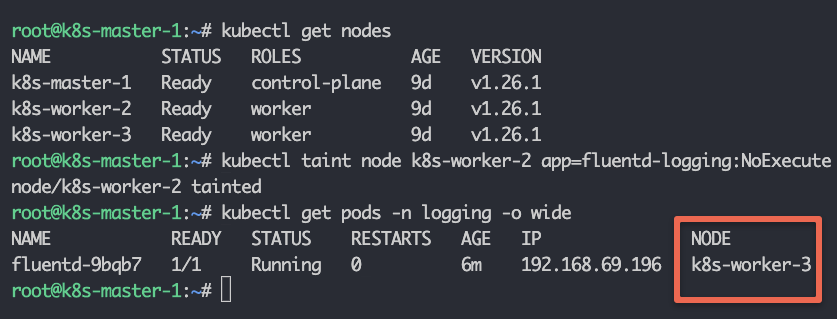
下面,我用关键应用程序和价值监控污染了其中一个节点,效果是NoExecute。我们不希望DaemonSet在这个特定节点上运行pod。
kubectl taint node k8s-worker-2 app=fluentd-logging:NoExecute
- 1
现在在daemonset.yaml中添加类似这样的容错功能.
spec:
tolerations:
- key: app
value: fluentd-logging
operator: Equal
effect: NoExecute
containers:
-----
-----
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
当您更新DaemonSet时,您将看到一个在节点k8s-worker-2上运行的pod被删除。DaemonSet现在不会在这个节点上调度任何pod。
为Daemonset Pods使用Nodeselector
我们可以使用nodeSelector在一些特定节点上运行pods。DaemonSet控制器将在与节点选择器的键和值匹配的节点上创建Pods
首先,您需要为节点添加一个标签。
kubectl label node <node-name> key=value
- 1
例如,假设您想将一个节点标记为type=platform-tools,可以使用以下命令。
kubectl label node k8s-worker-1 type=platform-tools
- 1
现在,要将nodeSelector应用到Daemonset,请在spec部分下使用键和值添加nodeSelector,如下所示。
spec:
nodeSelector:
<key>: <value>
- 1
- 2
- 3
下图显示了Daemonset YAML,其中nodeSelector spec高亮显示为黄色。
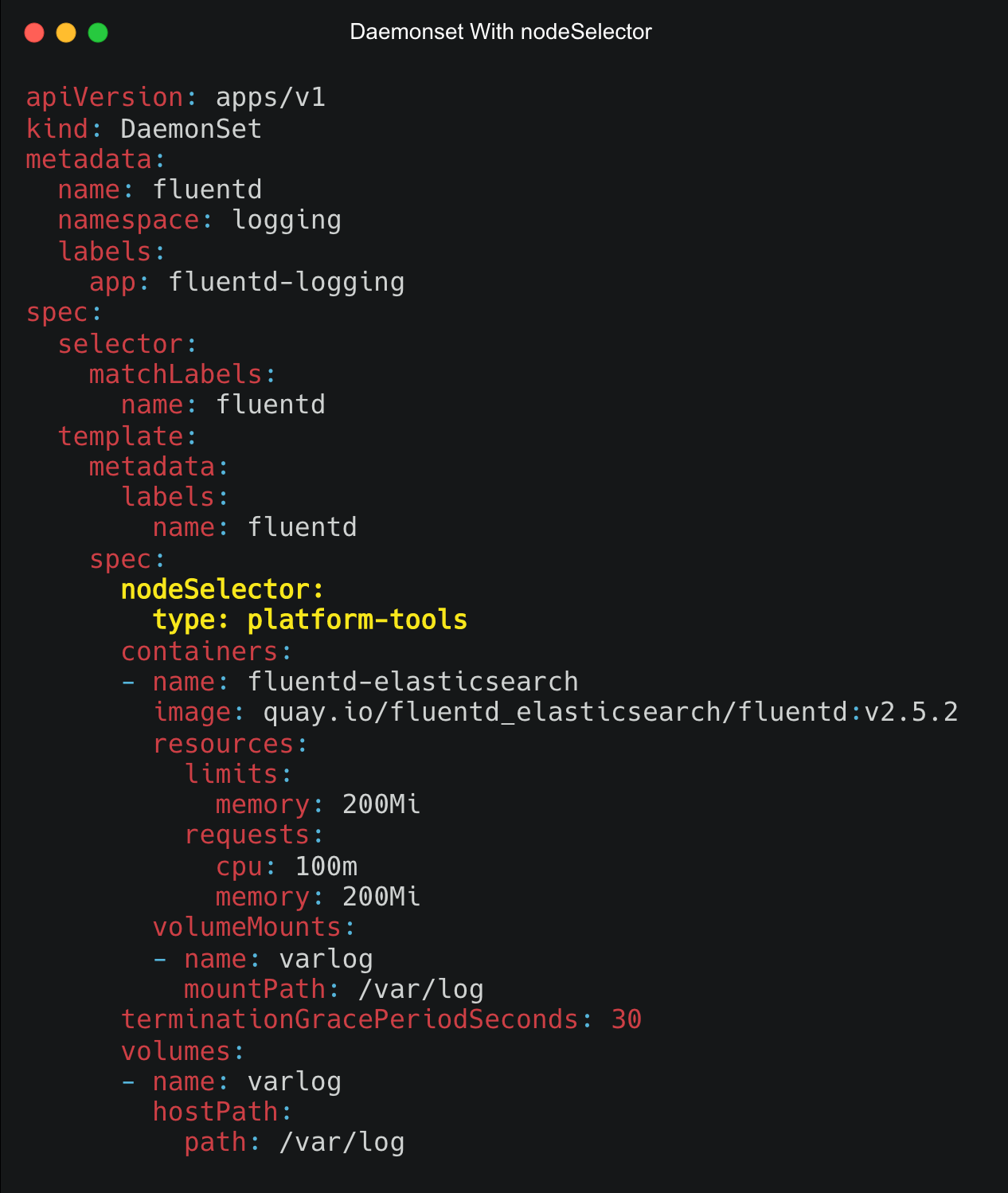
Daemonset节点亲和性
我们还可以使用节点亲和性实现对节点如何选择的更细粒度的控制。DaemonSet控制器将在与节点亲和性相匹配的节点上创建Pods。
Node affinity在概念上类似于nodeSelector,允许你根据节点标签约束pod可以调度哪些节点。节点关联有两种类型:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:除非满足规则,否则调度器无法调度Pod。它的功能类似于nodeSelector,但语法更有表现力。preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:调度器试图找到满足规则的节点。如果没有匹配的节点可用,调度器仍然调度Pod。
我们可以像这样给清单文件添加一个关联
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchFields:
- key: key-name
operator: In
values:
- value-name
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
pod只允许运行在具有matchFields节中提到的键和值的节点上。
下面的Daemonset YAML使用了以粗体突出显示的两个关联规则。节点标签所需的规则和选择实例标签实例类型t2.large的节点的首选规则。
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: fluentd namespace: logging labels: app: fluentd-logging spec: selector: matchLabels: name: fluentd template: metadata: labels: name: fluentd spec: affinity: nodeAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: type operator: In values: - platform-tools preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: - weight: 1 preference: matchExpressions: - key: instance-type operator: In values: - t2.large containers: - name: fluentd-elasticsearch image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2 resources: limits: memory: 200Mi requests: cpu: 100m memory: 200Mi volumeMounts: - name: varlog mountPath: /var/log terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 volumes: - name: varlog hostPath: path: /var/log
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
Daemonset特权访问
在某些情况下,您需要从Deamonset pod获得访问主机的特权。例如,calico CNI daemoset需要对其网络需求进行主机级访问,因为它需要修改IPtables。
另一个例子是Kube-proxy的daemonset。它还需要特权访问。
你可以使用Pod规范中的securityContext来允许或拒绝特权访问。安全上下文定义Pod或容器的权限和访问控制设置。要为pod指定安全设置,需要在pod清单文件中包含securityContext字段。
spec:
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
containers:
- name: fluentd-elasticsearch
image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
-------
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
第一个是由对象定义的pod级安全上下文,第二个是由单个容器定义的SecurityContext。
allowPrivilegeEscalation:控制进程是否可以获得比其父进程更多的权限。privileged:以特权模式运行容器。特权容器中的进程本质上等同于主机上的root。runAsNonRoot:表示容器必须以非root用户运行。runAsUser:运行容器进程入口点的UID。runAsGroup:运行容器进程入口点的GID。
滚动更新、回滚和删除Daemonset
让我们看一下更新、删除和回滚守护进程部署的概念。
滚动更新
DaemonSet有两种更新策略类型:
OnDelete:使用OnDelete策略,只有当我们手动删除任何pod时,才会创建DaemonSet pod。RollingUpdate:这是默认的更新策略。使用RollingUpdate策略,每当更新DaemonSet模板时,旧的pod将被终止,新的pod将被自动创建。最多只有一个DaemonSet的pod在运行。
spec:
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
回滚
我们可以使用以下命令回滚DaemonSet:
kubectl rollout undo daemonset <daemonset-name>
- 1
检查DaemonSet的所有修订版本:
kubectl rollout history daemonset <daemonset-name>
- 1
如果想回滚到特定的版本,可以使用:
kubectl rollout undo daemonset <daemonset-name> --to-revision=<revision>
- 1
删除
kubectl delete daemonset <daemonset-name>
- 1
如果你想让pod在节点上运行,请使用--cascade=false。
DaemonSet Pod Priority
Kubernetes Pod优先级决定了一个Pod相对于另一个Pod的重要性。
我们可以为DaemonSet设置更高的pod PriorityClass,以防将关键系统组件作为一个DaemonSet运行。这确保了守护进程的pod不会被低优先级或不那么关键的pod抢占。
PriorityClass用于定义pod的优先级。PriorityClass对象可以是任何小于或等于10亿的32位整数值。值越高,优先级越高。
创建一个优先级类,并将其用于DaemonSet pod spec
apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1
kind: PriorityClass
metadata:
name: high-priority
value: 100000
globalDefault: false
description: "daemonset priority class"
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
运行此命令检查
kubectl get priorityClass
- 1
我们需要在daemonset.yaml中添加priorityClass
spec:
priorityClassName: high-priority
containers:
------
------
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
------
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
如果您查看Kube-Proxy & Cluser CNI (Calico)守护进程集,它的priority类设置为system-node-critical,它具有最高的优先级。它是Kubernetes中内置的priority类,应用于pod,在任何情况下都不应该被删除。



