- 1关于YOLOv5提示ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘ultralytics.yolo‘的解决办法_no module named 'ultralytics.yolo
- 2ZooKeeper的基本概念
- 3【堆/排序】堆排序的两种建堆方法_堆排序中两种建堆方法
- 4ambari 离线安装_ambari离线安装
- 5[Tb/and FPGA实现与门激励的设计]——用Tb/and FPGA打造高效与门激励_写一个与门的激励模块
- 6STM32高频注入,FOC矢量控制驱动方案及移植量产实践_dengfoc stm32移植
- 7pdps安装oracle12安装,PDPS安装使用过程问题点处理
- 8如何查看docker中有哪些容器_docker desktop里面的容器怎么看
- 9动手学深度学习(Pytorch版)代码实践 -深度学习基础-12Kaggle竞赛:预测房价
- 10AI实践与学习4_大模型之检索增强生成RAG实践_大模型 qwen 增强索引rag 离线
Deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting去模糊3D高斯溅射_deflur-gs
赞
踩
Abstract 摘要
Recent studies in Radiance Fields have paved the robust way for novel view synthesis with their photorealistic rendering quality. Nevertheless, they usually employ neural networks and volumetric rendering, which are costly to train and impede their broad use in various real-time applications due to the lengthy rendering time. Lately 3D Gaussians splatting-based approach has been proposed to model the 3D scene, and it achieves remarkable visual quality while rendering the images in real-time. However, it suffers from severe degradation in the rendering quality if the training images are blurry. Blurriness commonly occurs due to the lens defocusing, object motion, and camera shake, and it inevitably intervenes in clean image acquisition. Several previous studies have attempted to render clean and sharp images from blurry input images using neural fields. The majority of those works, however, are designed only for volumetric rendering-based neural radiance fields and are not straightforwardly applicable to rasterization-based 3D Gaussian splatting methods. Thus, we propose a novel real-time deblurring framework, deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting, using a small Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) that manipulates the covariance of each 3D Gaussian to model the scene blurriness. While deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting can still enjoy real-time rendering, it can reconstruct fine and sharp details from blurry images. A variety of experiments have been conducted on the benchmark, and the results have revealed the effectiveness of our approach for deblurring. Qualitative results are available at Deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting
最近的研究在辐射领域铺平了道路,为新的视图合成与他们的真实感渲染质量。然而,它们通常采用神经网络和体积渲染,这是昂贵的训练和阻碍其广泛使用的各种实时应用程序由于漫长的渲染时间。近年来提出了一种基于三维高斯分裂的三维场景建模方法,并在实时绘制图像的同时获得了良好的视觉效果。然而,如果训练图像是模糊的,它遭受严重的渲染质量下降。模糊通常是由于透镜散焦、物体运动和相机抖动而发生的,并且它不可避免地干扰了清晰图像的获取。之前的几项研究试图使用神经场从模糊的输入图像中渲染干净清晰的图像。 然而,这些作品中的大多数仅针对基于体积渲染的神经辐射场而设计,并且不直接适用于基于光栅化的3D高斯溅射方法。因此,我们提出了一种新的实时去模糊框架,去模糊3D高斯飞溅,使用一个小的多层感知器(MLP),操纵每个3D高斯的协方差模型的场景模糊。虽然去模糊3D高斯溅射仍然可以享受实时渲染,但它可以从模糊图像中重建精细和清晰的细节。在基准上进行了各种实验,结果表明了该方法的有效性。定性结果见https://benhenryl.github。io/去模糊-3D-Gaussian-Splatting/ Deblurring 3D Gaussian Splatting
1Introduction 1介绍
With the emergence of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) [23], Novel view synthesis (NVS) has accounted for more roles in computer vision and graphics with its photorealistic scene reconstruction and applicability to diverse domains such as augmented/virtual reality(AR/VR) and robotics. Various NVS methods typically involve modeling 3D scenes from multiple 2D images from arbitrary viewpoints, and these images are often taken under diverse conditions. One of the significant challenges, particularly in practical scenarios, is the common occurrence of blurring effects. It has been a major bottleneck in rendering clean and high-fidelity novel view images, as it requires accurately reconstructing the 3D scene from the blurred input images.
随着神经辐射场(NeRF)[ 23]的出现,新视图合成(NVS)在计算机视觉和图形学中占据了更多的角色,其逼真的场景重建和适用于增强/虚拟现实(AR/VR)和机器人等不同领域。各种NVS方法通常涉及从任意视点从多个2D图像建模3D场景,并且这些图像通常在不同条件下拍摄。其中一个重大挑战,特别是在实际场景中,是模糊效果的常见发生。它一直是绘制干净和高保真的新视图图像的主要瓶颈,因为它需要从模糊的输入图像精确地重建3D场景。
NeRF [23] has shown outstanding performance in synthesizing photo-realistic images for novel viewpoints by representing 3D scenes with implicit functions. The volume rendering [7] technique has been a critical component of the massive success of NeRF. This can be attributed to its continuous nature and differentiability, making it well-suited to today’s prevalent automatic differentiation software ecosystems. However, significant rendering and training costs are associated with the volumetric rendering approach due to its reliance on dense sampling along the ray to generate a pixel, which requires substantial computational resources. Despite the recent advancements [10, 38, 24, 8, 9] that significantly reduce training time from days to minutes, improving the rendering time still remains a vital challenge.
NeRF [ 23]通过用隐式函数表示3D场景,在合成新颖视点的照片级逼真图像方面表现出出色的性能。体绘制[ 7]技术是NeRF取得巨大成功的关键组成部分。这可以归因于其连续性和差异性,使其非常适合当今流行的自动差异化软件生态系统。然而,显著的渲染和训练成本与体积渲染方法相关联,这是由于其依赖于沿射线沿着密集采样以生成像素,这需要大量的计算资源。尽管最近的进步[ 10,38,24,8,9]显着减少训练时间从几天到几分钟,提高渲染时间仍然是一个至关重要的挑战。
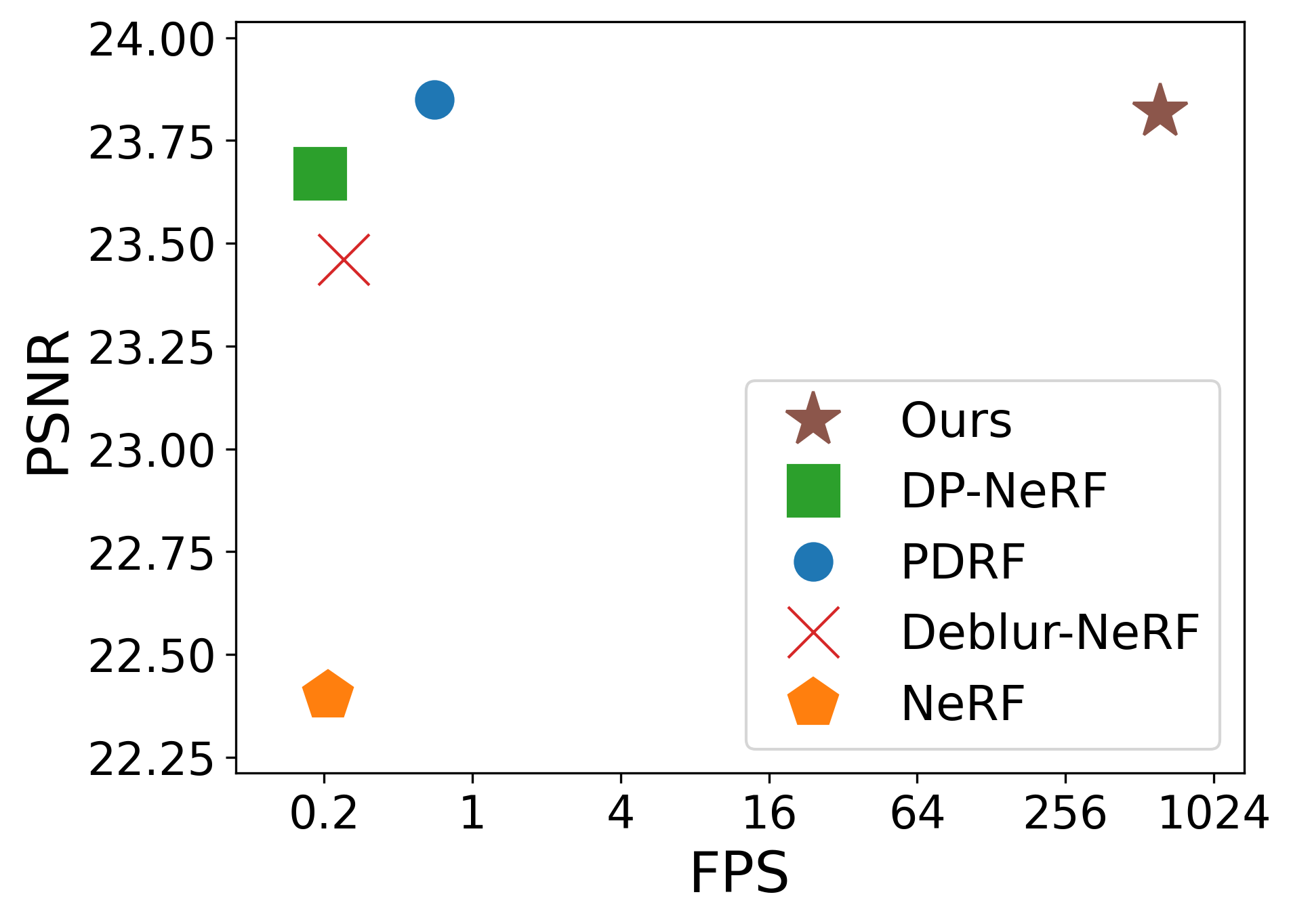
Figure 1:Performance comparison to state-of-the-art deblurring NeRFs. Ours achieved a fast rendering speed (200 fps vs. 1 fps) while maintaining competitive rendered image quality (x-axis is represented in log scale).
图1:与最先进的去模糊NeRF的性能比较。我们的实现了快速渲染速度(200 fps vs. 1 fps),同时保持了具有竞争力的渲染图像质量(x轴以对数标度表示)。
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) [15] has gained significant attention, demonstrating a capability to produce high-quality images at a remarkably fast rendering speed. It combines a large number of colored 3D Gaussians to represent 3D scenes with a differentiable splatting-based rasterization, substituting NeRF’s time-demanding volumetric rendering. The rendering process projects 3D Gaussian points onto the 2D image planes, and the positions, sizes, rotations, colors, and opacities of these Gaussians are adjusted via gradient-based optimization to better capture the 3D scenes. 3D-GS leverages rasterization, which can be significantly more efficient than volume rendering techniques on modern graphics hardware, thereby enabling rapid real-time rendering.
最近,3D高斯溅射(3D-GS)[ 15]获得了极大的关注,证明了以非常快的渲染速度生成高质量图像的能力。它结合了大量的彩色3D高斯来表示3D场景,并使用可区分的基于splatting的光栅化,取代了NeRF的时间要求很高的体积渲染。渲染过程将3D高斯点投影到2D图像平面上,并且通过基于梯度的优化来调整这些高斯点的位置、大小、旋转、颜色和不透明度,以更好地捕获3D场景。3D-GS利用光栅化,这可以比现代图形硬件上的体渲染技术更有效,从而实现快速实时渲染。
Expanding on the impressive capabilities of 3D-GS, we aim to further improve its robustness and versatility for more realistic settings, especially those involving blurring effects. Several approaches have attempted to handle the blurring issues in the recent NeRF literature [22, 20, 6, 41, 43]. The pioneering work is Deblur-NeRF [22], which renders sharp images from the neural radiance fields and uses an extra multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to produce the blur kernels. DP-NeRF [20] constrains neural radiance fields with two physical priors derived from the actual blurring process to reconstruct clean images. PDRF [28] uses a two-stage deblurring scheme and a voxel representation to further improve deblurring and training time. All works mentioned above have been developed under the assumption of volumetric rendering, which is not straightforwardly applicable to rasterization-based 3D-GS. Another line of works [41, 6], though not dependent on volume rendering, only address a specific type of blur, i.e., camera motion blur, and are not valid for mitigating the defocus blur.
扩展3D-GS令人印象深刻的功能,我们的目标是进一步提高其鲁棒性和多功能性,以实现更逼真的设置,特别是那些涉及模糊效果的设置。在最近的NeRF文献中,有几种方法试图处理模糊问题[ 22,20,6,41,43]。开创性的工作是Deflur-NeRF [ 22],它从神经辐射场呈现清晰的图像,并使用额外的多层感知器(MLP)来产生模糊内核。DP-NeRF [ 20]使用从实际模糊过程中导出的两个物理先验来约束神经辐射场,以重建干净的图像。PDRF [ 28]使用两阶段去模糊方案和体素表示来进一步改善去模糊和训练时间。上述所有工作都是在体绘制的假设下开发的,这并不直接适用于基于光栅化的3D-GS。 另一行作品[ 41,6]虽然不依赖于体绘制,但仅解决了特定类型的模糊,即,相机运动模糊,并且对于减轻散焦模糊无效。
In this work, we propose Deblurring 3D-GS, the first defocus deblurring algorithm for 3D-GS, which is well aligned with rasterization and thus enables real-time rendering. To do so, we modify the covariance matrices of 3D Gaussians to model the blurriness. Specifically, we employ a small MLP, which manipulates the covariance of each 3D Gaussian to model the scene blurriness. As blurriness is a phenomenon that is based on the intermingling of the neighboring pixels, our Deblurring 3D-GS simulates such an intermixing during the training time. To this end, we designed a framework that utilizes an MLP to learn the variations in different attributes of 3D Gaussians. These small variations are multiplied to the original values of the attributes, which in turn determine the updated shape of the resulting Gaussians. During the inference time, we render the scene using only the original components of 3D-GS without any additional offsets from MLP; thereby, 3D-GS can render sharp images because each pixel is free from the intermingling of nearby pixels. Further, since the MLP is not activated during the inference time, it can still enjoy real-time rendering similar to the 3D-GS while it can reconstruct fine and sharp details from the blurry images.
在这项工作中,我们提出了去模糊3D-GS,第一个散焦去模糊算法的3D-GS,这是很好地对准光栅化,从而使实时渲染。为此,我们修改3D高斯的协方差矩阵来对模糊度进行建模。具体来说,我们采用了一个小的MLP,它操纵每个3D高斯的协方差模型的场景模糊。由于模糊是一种基于相邻像素混合的现象,因此我们的Deflurring 3D-GS在训练时间内模拟了这种混合。为此,我们设计了一个框架,利用MLP来学习3D高斯的不同属性的变化。这些小的变化被乘以属性的原始值,这反过来又决定了结果高斯的更新形状。 在推理期间,我们仅使用3D-GS的原始组件渲染场景,而不使用来自MLP的任何额外偏移;因此,3D-GS可以渲染清晰的图像,因为每个像素都没有与附近像素的混合。此外,由于MLP在推理时间期间不被激活,因此它仍然可以享受类似于3D-GS的实时渲染,同时它可以从模糊图像重建精细和清晰的细节。

Figure 2:Our method’s overall workflow. �(⋅) denotes positional encoding, ⊙ denotes hadamard product, and �, �, � stand for position, quaternion, and scaling of 3D Gaussian respectively. Given a set of 3D Gaussians �, we extract �, �, � from each 3D Gaussian. Viewing direction � from the dataset and � are positionally encoded and then fed to ��, a small MLP parameterized with �, which yields offsets �� and �� for each Gaussian. These �� and �� are element-wisely multiplied to their respective Gaussians’s � and � respectively, and these computed attributes are used to construct transformed 3D Gaussians �′(�,�⋅��,�⋅��). These transformed Gaussians �′ are differentiably rasterized to render blurred image during training time. However, for inference stage, � is directly fed to differentiable rasterizer, without involving any MLP, to render sharp image.
图2:我们的方法的总体工作流程。 �(⋅) 表示位置编码, ⊙ 表示hadamard积, � 、 � 、 � 分别代表3D高斯的位置、四元数和缩放。给定一组3D高斯 � ,我们从每个3D高斯中提取 � , � , � 。对来自数据集的观看方向 � 和 � 进行位置编码,然后将其馈送到 �� ,即用 � 参数化的小MLP,这为每个高斯产生偏移 �� 和 �� 。将这些 �� 和 �� 分别逐元素地乘以它们各自的高斯 � 和 � ,并且这些计算的属性用于构造变换的3D高斯 �′(�,�⋅��,�⋅��) 。这些变换后的高斯 �′ 在训练时间期间被可微分地光栅化以渲染模糊图像。然而,对于推理阶段, � 被直接馈送到可微分光栅化器,而不涉及任何MLP,以呈现清晰的图像。
3D-GS [15] models a 3D scene from a sparse point cloud, which is usually obtained from the structure-from-motion (SfM) [35]. SfM extracts features from multi-view images and relates them via 3D points in the scene. If the given images are blurry, SfM fails heavily in identifying the valid features, and ends up extracting a very small number of points. Even worse, if the scene has a larger depth of field, SfM hardly extracts any points which lie on the far end of the scene. Due to this excessive sparsity in the point cloud constructed from set of blurry images, existing methods, including 3D-GS [15], that rely on point clouds fail to reconstruct the scene with fine details. To compensate for this excessive sparsity, we propose to add extra points with valid color features to the point cloud using N-nearest-neighbor interpolation [29]. In addition, we prune Gaussians based on their position to keep more Gaussians on the far plane.
3D-GS [ 15]从稀疏点云建模3D场景,稀疏点云通常从运动恢复结构(SfM)[ 35]获得。SfM从多视图图像中提取特征,并通过场景中的3D点将它们关联起来。如果给定的图像是模糊的,SfM在识别有效特征时会严重失败,最终提取的点数量非常少。更糟糕的是,如果场景具有较大的景深,则SfM几乎无法提取位于场景远端的任何点。由于从一组模糊图像构建的点云中的这种过度稀疏性,依赖于点云的现有方法(包括3D-GS [ 15])无法重建具有精细细节的场景。为了补偿这种过度的稀疏性,我们建议使用N-最近邻插值向点云添加具有有效颜色特征的额外点[ 29]。此外,我们根据高斯分布的位置对它们进行修剪,以使更多的高斯分布保持在远平面上。
A variety of experiments have been conducted on the benchmark, and the results have revealed the effectiveness of our approach for deblurring. Tested under different evaluation matrices, our method achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality or performs on par with the currently leading models while achieving significantly faster rendering speed (> 200 FPS)
在基准上进行了各种实验,结果表明了该方法的有效性。在不同的评估矩阵下进行测试,我们的方法达到了最先进的渲染质量或与当前领先的模型相当,同时实现了更快的渲染速度( > 200 FPS)
To sum up, our contributions are the following:
总而言之,我们的贡献如下:
- •
We propose the first real-time rendering-enabled defocus deblurring framework using 3D-GS.
·我们提出了第一个使用3D-GS的实时渲染支持的散焦去模糊框架。 - •
We propose a novel technique that manipulates the covariance matrix of each 3D Gaussian differently to model spatially changing blur using a small MLP.
·我们提出了一种新的技术,该技术不同地操纵每个3D高斯的协方差矩阵,以使用小的MLP来对空间变化的模糊进行建模。 - •
To compensate for sparse point clouds due to the blurry images, we propose a training technique that prunes and adds extra points with valid color features so that we can put more points on the far plane of the scene and harshly blurry regions.
·为了补偿由于模糊图像而导致的稀疏点云,我们提出了一种训练技术,该技术可以修剪并添加具有有效颜色特征的额外点,以便我们可以将更多点放在场景的远平面和严重模糊的区域上。 - •
We achieve FPS > 200 while accomplishing superior rendering quality or performing on par with the existing cutting-edge models under different metrics.
·我们实现了FPS > 200,同时实现了上级渲染质量或在不同指标下与现有尖端模型的性能相当。
2Related Works 2相关作品
2.1Image Deblurring 2.1图像去模糊
It is common to observe that when we casually take pictures with optical imaging systems, some parts of scene appear blurred in the images. This blurriness is caused by a variety of factors, including object motion, camera shake, and lens defocusing [1, 34]. When the image plane is separated from the ideal reference plane during the imaging process, out-of-focus or defocus blur happens. The degradation induced by defocus blur of an image is generally expressed as follows:
当我们用光学成像系统随意拍照时,我们经常会观察到场景的某些部分在图像中出现模糊。这种模糊是由多种因素引起的,包括物体运动、相机抖动和透镜散焦[ 1,34]。在成像过程中,当像面与理想参考面分离时,会产生离焦或散焦模糊。由图像的散焦模糊引起的劣化通常表示如下:
| �(�)=∑�∈�ℎℎ(�,�)�(�)+�(�),�∈��, | (1) |
where �(�) represents an observed blurry image, ℎ(�,�) is a blur kernel or Point Spread Function (PSF), �(�) is a latent sharp image, and �(�) denotes an additive white Gaussian noise that frequently occurs in nature images. ��⊂ℝ2 is a support set of an image and �ℎ⊂ℝ2 is a support set of a blur kernel or PSF [18].
其中 �(�) 表示观察到的模糊图像, ℎ(�,�) 是模糊核或点扩散函数(PSF), �(�) 是潜在清晰图像,而 �(�) 表示在自然图像中频繁出现的加性白色高斯噪声。 ��⊂ℝ2 是图像的支持集, �ℎ⊂ℝ2 是模糊内核或PSF的支持集[ 18]。
The first canonical approach to deconvolve an image is [33]. It applies iterative minimization to an energy function to obtain a maximum likelihood approximation of the original image, using a known PSF (the blur kernel). Typically, the blurring kernel � and the sharp image � are unknown. The technique termed as image blind deblurring [42] involves recovering the latent sharp image given just one blurry image �. In this procedure, the deblurred image is obtained by first estimating a blurring kernel. Image blind deblurring is a long-standing and ill-posed problem in the field of image and vision. Numerous approaches to address the blurring issue have been suggested in the literature. Among them, traditional methods often construct deblurring as an optimization problem and rely on natural image priors [21, 26, 44, 47]. Conversely, the majority of deep learning-based techniques use convolutional neural networks (CNN) to map the blurry image with the latent sharp image directly [25, 46, 31]. While series of studies have been actively conducted for image deblurring, they are mainly designed for deblurring 2D images and are not easily applicable to 3D scenes deblurring due to the lack of 3D view consistency.
去卷积图像的第一个规范方法是[ 33]。它使用已知的PSF(模糊核)对能量函数进行迭代最小化,以获得原始图像的最大似然近似。通常,模糊核 � 和清晰图像 � 是未知的。被称为图像盲去模糊的技术[ 42]涉及在仅给定一个模糊图像 � 的情况下恢复潜在的清晰图像。在该过程中,通过首先估计模糊核来获得去模糊图像。图像盲去模糊是图像与视觉领域中一个长期存在的病态问题。在文献中已经提出了许多解决模糊问题的方法。其中,传统方法通常将去模糊构造为优化问题,并依赖于自然图像先验[ 21,26,44,47]。 相反,大多数基于深度学习的技术使用卷积神经网络(CNN)直接将模糊图像与潜在清晰图像映射[25,46,31]。虽然已经针对图像去模糊积极地进行了一系列研究,但是它们主要是针对2D图像去模糊而设计的,并且由于缺乏3D视图一致性而不容易适用于3D场景去模糊。
2.2Neural Radiance Fields
2.2神经辐射场
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) are a potent method that has recently gained popularity for creating high-fidelity 3D scenes from 2D images. Realistic rendering from novel viewpoints is made possible by NeRF, which uses deep neural networks to encode volumetric scene features. To estimate density �∈[0,∞) and color value �∈[0,1]3 of a given point, a radiance field is a continuous function � that maps a 3D location �∈ℝ3 and a viewing direction �∈
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


