- 1使用YOLO v8训练自己的数据集(苹果新鲜度识别)_yolov8训练需要多少张图片
- 2【模板:排序不等式】AcWing913.《排队打水》(C++)
- 3开发小记-Content Provider获取调用者包名_contentprovider 获取调用者
- 4清华ChatGLM-6B本地GPU推理部署_chatglm-6b 4bit
- 5阿里云服务器安装JDK指南
- 6【5G核心网】 3GPP TS 系列解读_3gpp ts 29.172
- 7jieba tfidf_【NLP】【三】jieba源码分析之关键字提取(TF-IDF/TextRank)
- 8如何在Linux上安装VMware Tools Debian,Ubuntu,Kali,Mint,Fedora,CentOS,RHEL发行版
- 9华为中级机试题--二分查找树的应用_二分查找树 应用
- 10全国大学生信息安全竞赛知识问答-CISCN题库_下列不属于linux设备类型的是流设备
【大数据Hive】hive 多字段分隔符使用详解_hive数据库字段分隔符
赞
踩
目录
一、前言
分隔符是hive在建表的时候要考虑的一个重要因素,根据要加载的原始数据的格式不同,通常数据文件中的分隔符也有差异,因此可以在建表的时候指定分隔符,从而映射到hive的数据表。
二、hive默认分隔符规则以及限制
Hive默认序列化类是LazySimpleSerDe,其只支持使用单字节分隔符(char)来加载文本数据,例如逗号、制表符、空格等等,默认的分隔符为”\001”。
根据不同文件的不同分隔符,我们可以通过在创建表时使用 row format delimited 来指定文件中的分割符,确保正确将表中的每一列与文件中的每一列实现一一对应的关系。
如下是hive建表语法树中的一部分

在这个语法树中,大家熟知的分隔符即 DELIMITED 关键字,从语法中看出来默认情况下,其分割的都是单字节的数据,可现实情况下,实际要处理的文本数据内容可能要复杂很多,比如下面这些情况:
2.1 正常示例:单字节分隔符数据加载示例
下面这种文本格式的原始数据,可以直接使用没问题;


2.2 特殊格式的文本数据,分隔符为特殊字符
每一行数据的分隔符是多字节分隔符,例如:”||”、“--”等,如下面这样的数据;

2.2.1 文本数据的字段中包含了分隔符
每列的分隔符为空格,但是数据中包含了分割符,时间字段中也有空格;
三、突破默认限制规则约束
3.1 数据加载不匹配情况 1
文本内容数据格式如下

建表sql,这里字段分隔符采用 || 与文本对应;
- drop table singer;
- create table singer(
- id string,
- name string,
- country string,
- province string,
- gender string,
- works string)
- row format delimited fields terminated by '||';
-
- load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/selectdata/test01.txt' into table singer;
执行建表并加载数据
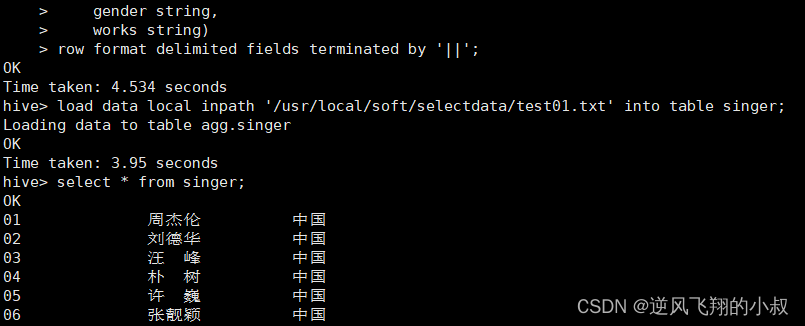
从数据来看,字段并没有解析完全,并且某些字段解析失败,和预期的不太一样,这是怎么回事呢?
3.2 数据加载不匹配情况 2
原始文本数据内容格式如下
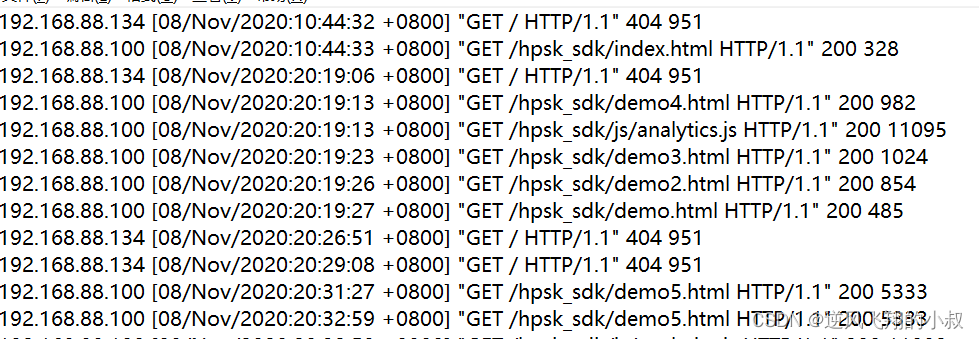
建表并加载数据,这里采用空格作为分隔符;
- drop table apachelog;
- create table apachelog( ip string,stime string,mothed string,url string,policy string,stat string,body string)
- row format delimited fields terminated by ' ';
-
- load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/selectdata/apache_web_access.log' into table apachelog;
执行完成后检查数据
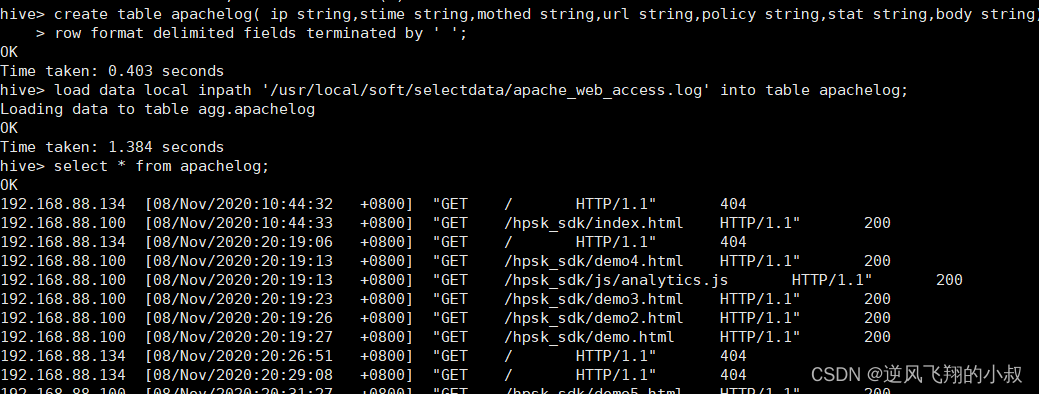
从数据来看,某些字段的解析不仅错误,而且字段也出现了错位;
从上面两个简单的示例来看,如果要解析的原始文本数据中的某些字段自身包含了分隔符,这时候再使用默认的LazySimpleSerDe序列化加载数据时,将得不到预期的结果,出现数据解析错误的情况。
关于上述问题,下面提几种常用的解决办法。
3.3 解决方案一:替换分隔符
在第一个示例中的数据,要想使用默认分隔符,可以考虑对原始数据进行预处理,将双|转换为单个|后再导入;

至于转换的过程,可以人工处理,也可以使用MR程序处理,使用MR程序处理的话可以参考下面的伪代码,
- package bigdata.itcast.cn.hbase.mr;
-
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
- import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
- import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
-
- import java.io.IOException;
-
- /**
- * @ClassName ChangeSplitCharMR
- * @Description TODO MapReduce实现将多字节分隔符转换为单字节符
- * @Create By itcast
- */
- public class ChangeSplitCharMR extends Configured implements Tool {
- public int run(String[] arg) throws Exception {
- /**
- * 构建Job
- */
- Job job = Job.getInstance(this.getConf(),"changeSplit");
- job.setJarByClass(ChangeSplitCharMR.class);
-
- /**
- * 配置Job
- */
- //input:读取需要转换的文件
- job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
- Path inputPath = new Path("datas/split/test01.txt");
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,inputPath);
-
- //map:调用Mapper
- job.setMapperClass(ChangeSplitMapper.class);
- job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
-
- //reduce:不需要Reduce过程
- job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
-
- //output
- job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
- Path outputPath = new Path("datas/output/changeSplit");
- TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath);
-
- /**
- * 提交Job
- */
- return job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : -1;
- }
-
- //程序入口
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- //调用run
- Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- int status = ToolRunner.run(conf, new ChangeSplitCharMR(), args);
- System.exit(status);
- }
-
-
- public static class ChangeSplitMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,NullWritable>{
- //定义输出的Key
- private Text outputKey = new Text();
- //定义输出的Value
- private NullWritable outputValue = NullWritable.get();
-
- @Override
- protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- //获取每条数据
- String line = value.toString();
- //将里面的||转换为|
- String newLine = line.replaceAll("\\|\\|", "|");
- //替换后的内容作为Key
- this.outputKey.set(newLine);
- //输出结果
- context.write(this.outputKey,this.outputValue);
- }
- }
- }

3.4 解决方案二:RegexSerDe正则加载
顾名思义就是使用hive提供的相关正则的语法来处理这个问题,为什么呢?因为hive内置了很多SerDe类;
Hive内置的SerDe
- 除了使用最多的LazySimpleSerDe,Hive该内置了很多SerDe类;
- 官网地址:https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/SerDe;
- 多种SerDe用于解析和加载不同类型的数据文件,常用的有ORCSerDe 、RegexSerDe、JsonSerDe等;
1、RegexSerDe用来加载特殊数据的问题,使用正则匹配来加载数据;
2、根据正则表达式匹配每一列数据;

针对上面演示时的问题,来看看如何使用这种方式来解决,比如第一份数据,针对这份数据,只需要写一个正则,能够识别到其中的分隔符双 || ,将建表时的字段分割符使用这个正则,然后加载数据的时候就可以把hive解析出预期的数据格式了;

使用正则Regex处理这两个问题,下面看具体的操作演示
问题一处理过程:
建表并加载数据
- --如果表已存在就删除表
- drop table if exists singer;
- --创建表
- create table singer(id string,--歌手id
- name string,--歌手名称
- country string,--国家
- province string,--省份
- gender string,--性别
- works string)--作品
- --指定使用RegexSerde加载数据
- ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe'
- WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("input.regex" = "([0-9]*)\\|\\|(.*)\\|\\|(.*)\\|\\|(.*)\\|\\|(.*)\\|\\|(.*)");
-
- --加载数据
- load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/selectdata/test01.txt' into table singer;
执行过程

检查数据发现,通过这种方式数据就能正确的加载了;

问题二处理过程:
创建表并加载数据,使用正则处理
- --如果表存在,就删除表
- drop table if exists apachelog;
- --创建表
- create table apachelog(
- ip string, --IP地址
- stime string, --时间
- mothed string, --请求方式
- url string, --请求地址
- policy string, --请求协议
- stat string, --请求状态
- body string --字节大小
- )
- --指定使用RegexSerde加载数据
- ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe'
- --指定正则表达式
- WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (
- "input.regex" = "([^ ]*) ([^}]*) ([^ ]*) ([^ ]*) ([^ ]*) ([0-9]*) ([^ ]*)"
- ) stored as textfile ;
-
-
- load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/selectdata/apache_web_access.log' into table apachelog;

执行过程
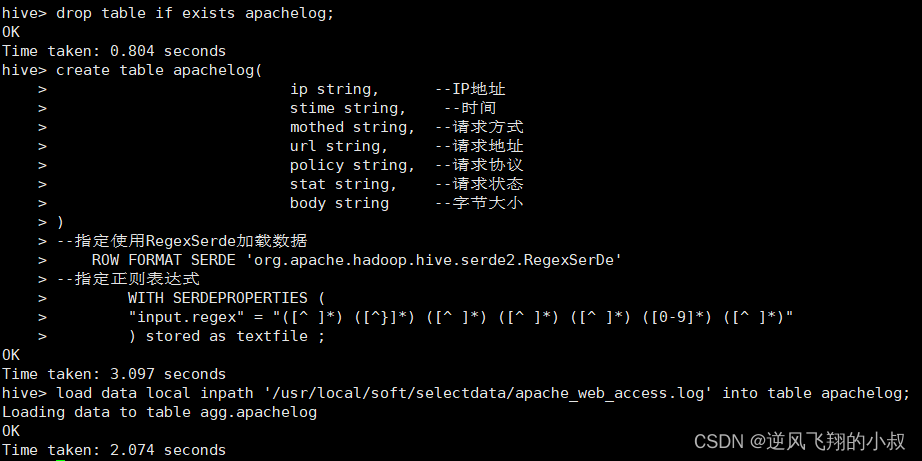
检查数据发现,通过这种方式数据就能正确的加载了;

3.5 解决方案三:自定义InputFormat
Hive中也允许使用自定义InputFormat来解决以上问题,通过在自定义InputFormat,来自定义解析逻辑实现读取每一行的数据。
下面是官方文档关于该方案的说明;
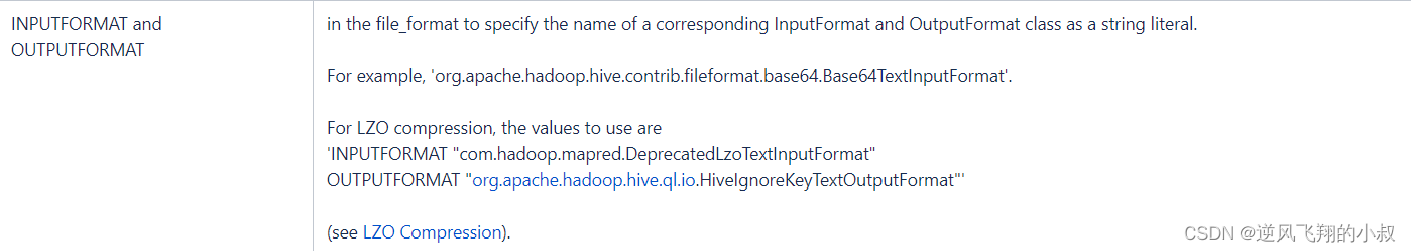
3.5.1 操作流程
自定义InputFormat,与MapReudce中自定义InputFormat一致,继承TextInputFormat,下面是完整的代码;
自定义UserInputFormat
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.*;
-
- import java.io.IOException;
-
- /**
- * @ClassName UserInputFormat
- * @Description TODO 用于实现自定义InputFormat,读取每行数据
- */
-
- public class UserInputFormat extends TextInputFormat {
- @Override
- public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> getRecordReader(InputSplit genericSplit, JobConf job,
- Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
- reporter.setStatus(genericSplit.toString());
- UserRecordReader reader = new UserRecordReader(job,(FileSplit)genericSplit);
- return reader;
- }
- }

UserRecordReader
用于自定义读取器,在自定义InputFormat中使用,将读取到的每行数据中的||替换为|
代码如下
- import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
- import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
- import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Seekable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.*;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileSplit;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.LineRecordReader;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.RecordReader;
-
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.InputStream;
-
- /**
- * @ClassName UserRecordReader
- * @Description TODO 用于自定义读取器,在自定义InputFormat中使用,将读取到的每行数据中的||替换为|
- */
-
-
- public class UserRecordReader implements RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> {
- private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(LineRecordReader.class.getName());
- int maxLineLength;
- private CompressionCodecFactory compressionCodecs = null;
- private long start;
- private long pos;
- private long end;
- private LineReader in;
- private Seekable filePosition;
- private CompressionCodec codec;
- private Decompressor decompressor;
-
- public UserRecordReader(Configuration job, FileSplit split) throws IOException {
- this.maxLineLength = job.getInt("mapred.linerecordreader.maxlength", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- start = split.getStart();
- end = start + split.getLength();
- final Path file = split.getPath();
- compressionCodecs = new CompressionCodecFactory(job);
- codec = compressionCodecs.getCodec(file);
- FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
- FSDataInputStream fileIn = fs.open(split.getPath());
- if (isCompressedInput()) {
- decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
- if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
- final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn = ((SplittableCompressionCodec) codec)
- .createInputStream(fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
- SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
- in = new LineReader(cIn, job);
- start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
- end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
- filePosition = cIn; // take pos from compressed stream
- } else {
- in = new LineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn, decompressor), job);
- filePosition = fileIn;
- }
- } else {
- fileIn.seek(start);
- in = new LineReader(fileIn, job);
- filePosition = fileIn;
- }
- if (start != 0) {
- start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
- }
- this.pos = start;
- }
-
- private boolean isCompressedInput() {
- return (codec != null);
- }
-
- private int maxBytesToConsume(long pos) {
- return isCompressedInput() ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : (int) Math.min(Integer.MAX_VALUE, end - pos);
- }
-
- private long getFilePosition() throws IOException {
- long retVal;
- if (isCompressedInput() && null != filePosition) {
- retVal = filePosition.getPos();
- } else {
- retVal = pos;
- }
- return retVal;
- }
-
- public LongWritable createKey() {
- return new LongWritable();
- }
-
- public Text createValue() {
- return new Text();
- }
-
- /**
- * Read a line.
- */
- public synchronized boolean next(LongWritable key, Text value) throws IOException {
- while (getFilePosition() <= end) {
- key.set(pos);
- int newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, Math.max(maxBytesToConsume(pos), maxLineLength));
- String str = value.toString().replaceAll("\\|\\|", "\\|");
- value.set(str);
- pos += newSize;
- if (newSize == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- if (newSize < maxLineLength) {
- return true;
- }
- LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " + (pos - newSize));
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public float getProgress() throws IOException {
- if (start == end) {
- return 0.0f;
- } else {
- return Math.min(1.0f, (getFilePosition() - start) / (float) (end - start));
- }
- }
-
- public synchronized long getPos() throws IOException {
- return pos;
- }
-
- public synchronized void close() throws IOException {
- try {
- if (in != null) {
- in.close();
- }
- } finally {
- if (decompressor != null) {
- CodecPool.returnDecompressor(decompressor);
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static class LineReader extends org.apache.hadoop.util.LineReader {
- LineReader(InputStream in) {
- super(in);
- }
-
- LineReader(InputStream in, int bufferSize) {
- super(in, bufferSize);
- }
-
- public LineReader(InputStream in, Configuration conf) throws IOException {
- super(in, conf);
- }
- }
- }

本地打成jar包并上传到服务器
使用命令上传jar到hive的依赖包目录
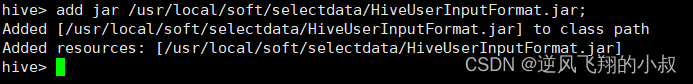
重新创建表,加载数据,同时指定InputFormat为自定义的InputFormat
- --如果表已存在就删除表
- drop table if exists singer;
-
- --创建表
- create table singer(
- id string,--歌手id
- name string,--歌手名称
- country string,--国家
- province string,--省份
- gender string,--性别
- works string)
- --指定使用分隔符为|
- row format delimited fields terminated by '|'
- --指定使用自定义的类实现解析
- stored as
- inputformat 'bigdata.com.congge.hive.mr.UserInputFormat'
- outputformat 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat';
-
- --加载数据
- load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/selectdata/test01.txt' into table singer;

执行过程

检查数据,可以发现通过这种方式也可以成功的将数据加载到表中;

小结
当数据文件中出现多字节分隔符或者数据中包含了分隔符时,会导致数据加载与实际表的字段不匹配的问题,基于这个问题我们提供了三种方案:
- 替换分隔符;
- 正则加载RegexSerde;
- 自定义InputFormat;
其中替换分隔符无法解决数据字段中依然存在分隔符的问题,自定义InputFormat的开发成本较高,所以整体推荐使用正则加载的方式来实现对于特殊数据的处理。
四、URL解析函数
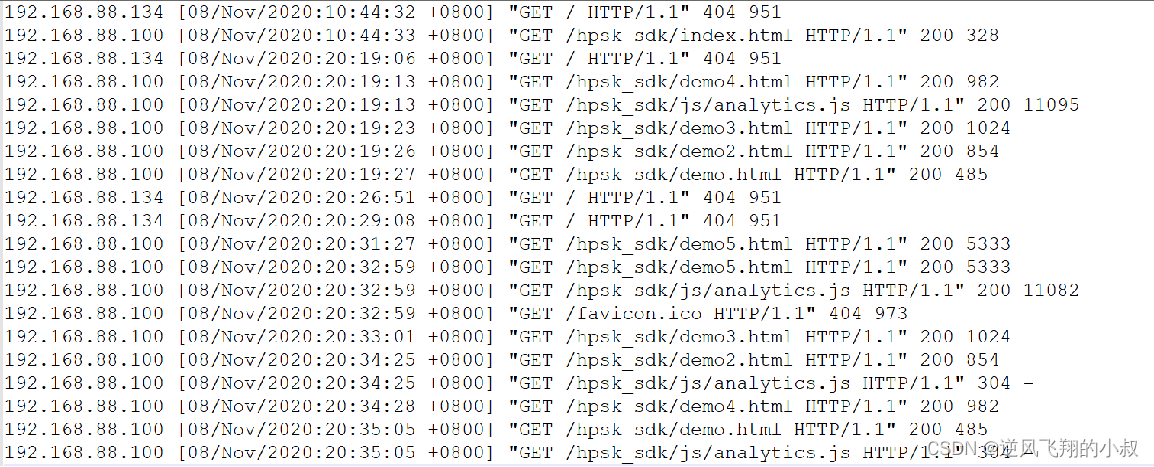
业务需求中,经常需要对用户的访问、用户的来源进行分析,用于支持运营和决策。例如对用户访问的页面进行统计分析,分析热门受访页面的Top10,观察大部分用户最喜欢的访问最多的页面等。如下截取的是统计到的一个关于网站访问地址稍微汇总数据。
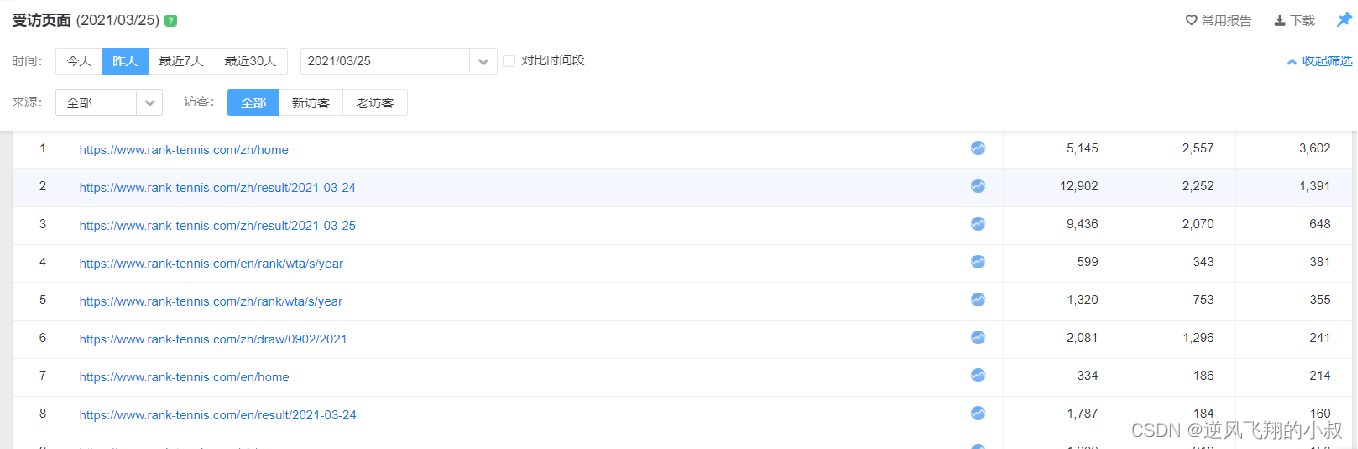
业务上,需要对用户访问的页面进行统计分析,比如说:分析热门受访页面的Top10,观察大部分用户最喜欢的访问最多的页面等,然后通过图表的方式展示出来,以支撑运营和商业决策等;
4.1 URL基本组成
要想实现上面的受访分析、来源分析等业务,必须在实际处理数据的过程中,对用户访问的URL和用户的来源URL进行解析处理,获取用户的访问域名、访问页面、用户数据参数、来源域名、来源路径等信息。
在对URL进行解析时,我们要先了解URL的基本组成部分,再根据实际的需求从URL中获取对应的部分,例如一条URL由以下几个部分组成:
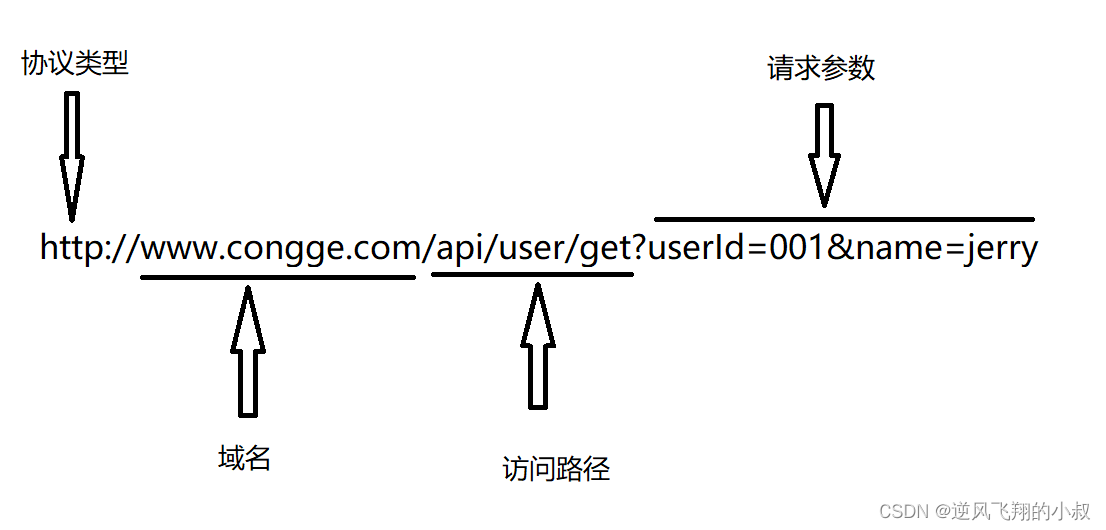
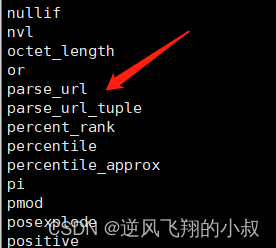
试想如果要将上面这个完整的URL的各个部分解析出来,你会怎么做呢?可以通过正则,或者字段分割,或者截取等方式达到目的,但这些都不是最好的方式,Hive中为了实现对URL的解析,专门提供了解析URL的函数parse_url和parse_url_tuple,在show functions中可以看到对应函数;
4.1.1 parse_url
语法格式
parse_url(url, partToExtract[, key]) - extracts a part from a URL
Parts: HOST, PATH, QUERY, REF, PROTOCOL, AUTHORITY, FILE, USERINFO key
比如尝试使用该函数解析上面图中的URL,可以看到HOST部分就被解析出来了;
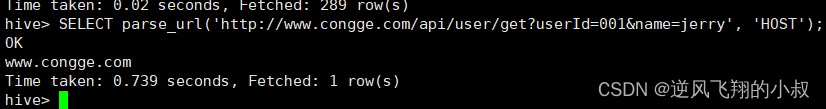
或者解析参数信息
- SELECT parse_url('http://www.congge.com/api/user/get?userId=001&name=jerry', 'QUERY');
-
- SELECT parse_url('http://www.congge.com/api/user/get?userId=001&name=jerry', 'QUERY', 'name');
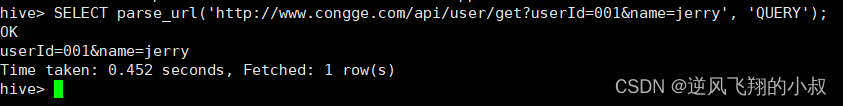
4.1.2 问题分析
上面这种解析方式,每次解析时只能解析出其中一个参数,也就是说,该函数为普通的一对一函数类型。如果想一次解析多个参数,需要使用多次函数,这就带来了很大的不便,这时候,parse_url_tuple函数就派上用场了。
4.1.3 parse_url_tuple
parse_url_tuple函数是Hive中提供的基于parse_url的url解析函数,可以通过一次指定多个参数,从URL解析出多个参数的值进行返回多列,函数为特殊的一对多函数类型,即通常所说的UDTF函数类型。
语法格式
parse_url_tuple(url, partname1, partname2, ..., partnameN) - extracts N (N>=1) parts from a URL;
It takes a URL and one or multiple partnames, and returns a tuple;
4.1.4 案例操作演示
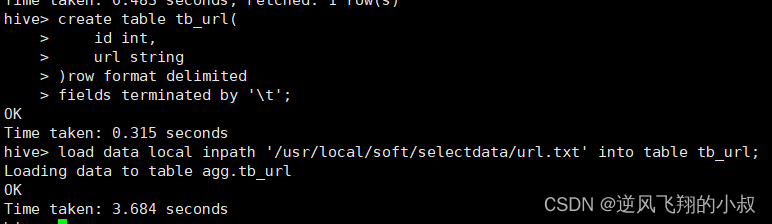
创建一张表并加载数据
- drop table if exists tb_url;
- --建表
- create table tb_url(
- id int,
- url string
- )row format delimited
- fields terminated by '\t';
-
- --加载数据
- load data local inpath '/usr/local/soft/selectdata/url.txt' into table tb_url;
执行过程
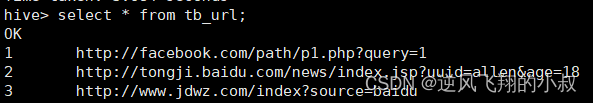
检查数据是否加载成功
接下来体验下parse_url_tuple函数的使用
解析host和path
select parse_url_tuple(url,"HOST","PATH") as (host,path) from tb_url;
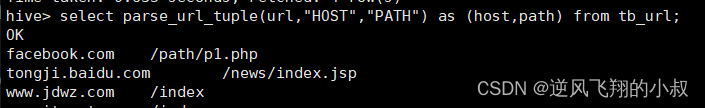
解析出 PROTOCOL,HOST和PATH
select parse_url_tuple(url,"PROTOCOL","HOST","PATH") as (protocol,host,path) from tb_url;

解析查询参数
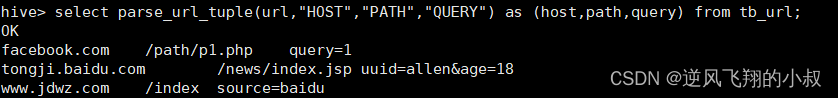
select parse_url_tuple(url,"HOST","PATH","QUERY") as (host,path,query) from tb_url;