热门标签
热门文章
- 1STM32 自定义频率与占空比PWM输出的方法_固定占空比输出逻辑芯片
- 2Prompt Learning:【文心一言】提示词功能系统学习,_文心一言 prompt
- 3Gradle整合Mybatis Generater自动生成_gradle mybaties 生成实体类工具
- 4鸿蒙OS 2.0 开源网址 源码仓库_鸿蒙os开原地址
- 5type trait_type traits class
- 62021-04-15_jsmh.run
- 7【Java基础】对比Vector、ArrayList、LinkedList有何区别?_java vector与数组的区别
- 8H5软键盘兼容方案_h5模拟器安卓软键盘吗
- 9没有禁用硬件图形加速的情况下解决visio卡死的问题_visio一打开就卡死的原因
- 10神经网络、前向传播、BP神经网络(反向传播算法)_反向传播神经网络和人工神经网络
当前位置: article > 正文
新手入门python实现神经网络,超级简单!_py 神经网络
作者:盐析白兔 | 2024-03-28 01:37:40
赞
踩
py 神经网络
前言:
这篇文章完全是为新手准备的。我们会通过用Python从头实现一个神经网络来理解神经网络的原理。
神经元
首先让我们看看神经网络的基本单位,神经元。神经元接受输入,对其做一些数据操作,然后产生输出。例如,这是一个2-输入神经元:
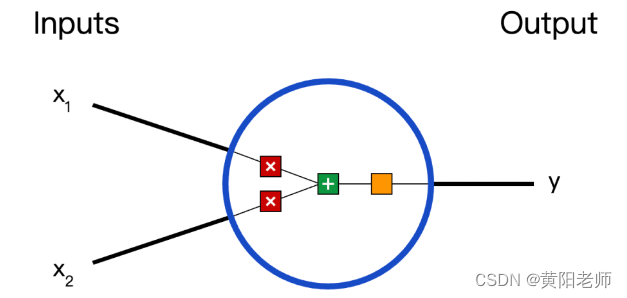
这里发生了三个事情。首先,每个输入都跟一个权重相乘(红色):
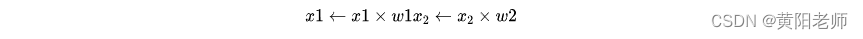 然后,加权后的输入求和,加上一个偏差b(绿色):
然后,加权后的输入求和,加上一个偏差b(绿色):
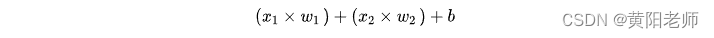
最后,这个结果传递给一个激活函数f:
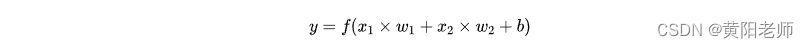
激活函数的用途是将一个无边界的输入,转变成一个可预测的形式。常用的激活函数就是S型函数:
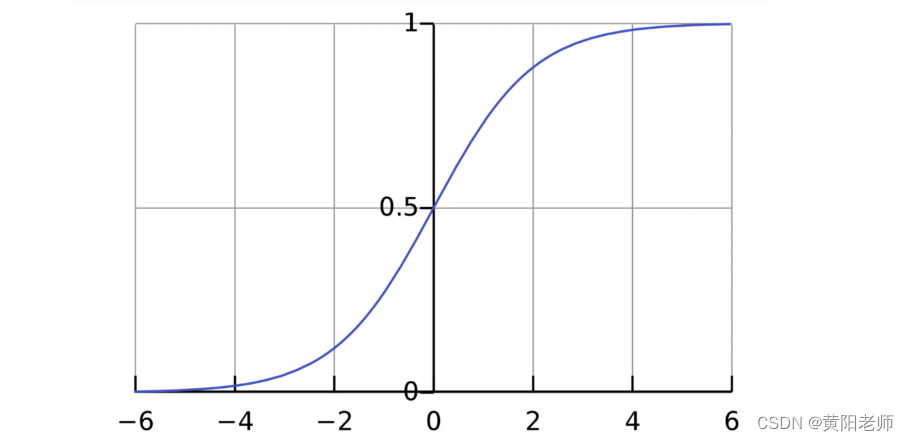
S型函数的值域是(0, 1)。简单来说,就是把(−∞, +∞)压缩到(0, 1) ,很大的负数约等于0,很大的正数约等于1。
1、一个简单的例子

2、编码一个神经元
让我们来实现一个神经元!用Python的NumPy库来完成其中的数学计算:
import numpy as np def sigmoid(x): # 我们的激活函数: f(x) = 1 / (1 + e^(-x)) return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) class Neuron: def __init__(self, weights, bias): self.weights = weights self.bias = bias def feedforward(self, inputs): # 加权输入,加入偏置,然后使用激活函数 total = np.dot(self.weights, inputs) + self.bias return sigmoid(total) weights = np.array([0, 1]) # w1 = 0, w2 = 1 bias = 4 # b = 4 n = Neuron(weights, bias) x = np.array([2, 3]) # x1 = 2, x2 = 3 print(n.feedforward(x)) # 0.9990889488055994
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
还记得这个数字吗?就是我们前面算出来的例子中的0.999。
把神经元组装成网络
所谓的神经网络就是一堆神经元。这就是一个简单的神经网络:
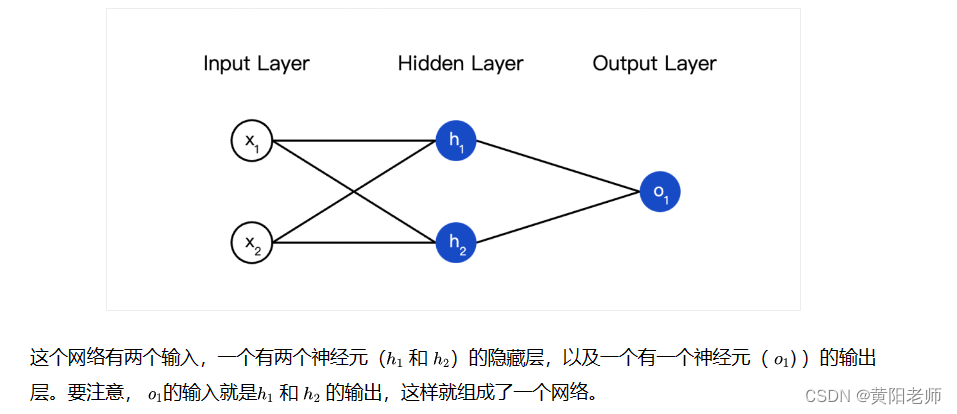
隐藏层就是输入层和输出层之间的层,隐藏层可以是多层的。
1、例子:前馈

2、编码神经网络:前馈
接下来我们实现这个神经网络的前馈机制,还是这个图:
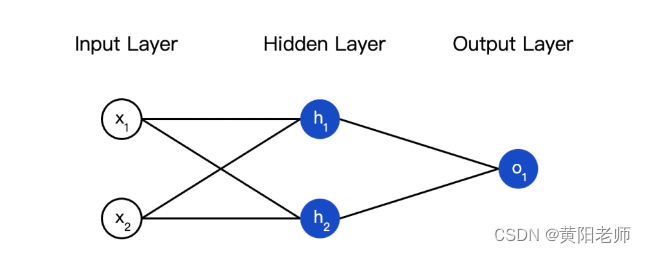
import numpy as np def sigmoid(x): # 我们的激活函数:f(x)=1/(1+e^(-x)) return 1/(1+np.exp(-x)) # 单个神经元 class Neuron: def __init__(self,weights,bias): self.weights=weights self.bias=bias def feedforward(self,inputs): total=np.dot(self.weights,inputs)+self.bias return sigmoid(total) class OurNeuralNetwork: ''' A neural network with: - 2 inputs - a hidden layer with 2 neurons (h1, h2) - an output layer with 1 neuron (o1) Each neuron has the same weights and bias: - w = [0, 1] - b = 0 ''' def __init__(self): weights = np.array([0, 1]) bias = 0 # 这里是来自前一节的神经元类 self.h1 = Neuron(weights, bias) self.h2 = Neuron(weights, bias) self.o1 = Neuron(weights, bias) def feedforward(self, x): out_h1 = self.h1.feedforward(x) out_h2 = self.h2.feedforward(x) # o1的输入是h1和h2的输出 out_o1 = self.o1.feedforward(np.array([out_h1, out_h2])) return out_o1 network = OurNeuralNetwork() x = np.array([2, 3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/盐析白兔/article/detail/328005
推荐阅读
相关标签





