- 1我的春招实习+秋招总结【前端开发】_前端找不到实习秋招是不是完了
- 2解决:fatal:unable to access‘https://github.com/xx/xx.git/‘:OpenSSL SSL_read:Connection was reset errno_fatal: unable to access
- 3数据中心GPU集群高性能组网技术分析
- 4LIama3 五一超级课堂 前置知识VScode 远程连接开发机_liama3 使用指南
- 5备忘: 使用langchain结合千问大模型,用本地知识库辅助AI生成代码_langchain和本地大语言模型 摘要提取
- 6PTA 7-9 树层次遍历_我们已知二叉树与其自然对应的树相比,二叉树中结点的左孩子对应树中结点的左孩子,
- 7MySQL数据库之索引_mysql 索引文件
- 8AI探索测试未来:人工智能与自动化测试的结合实战,文末实用干货自行领取!_面向未来的ai自动化测试工具
- 94.0 树莓派做下位机播放视频、控制电机舵机、超声波检测、paj7620手势传感器控制,树莓派串口通信等程序分析_树莓派 播放视频
- 10AITM2-0007 比光密度测定_aitm 2.0007下载
使用MMDetection训练自己的数据集
赞
踩
MMDetection推荐大家最好还是在linux系统下使用,windows系统上使用起来属实bug太多
下面的教程将会教会大家如何使用MMDetection来训练一个自己的目标检测模型,MMDetection设计的非常nice,准备好数据之后,只需要稍微修改一下配置文件就能完成训练,大多数模型的配置文件在MMDetection都进行了提供,只需要继承这些配置文件并重写其中的一些参数即可。
安装MMDetection
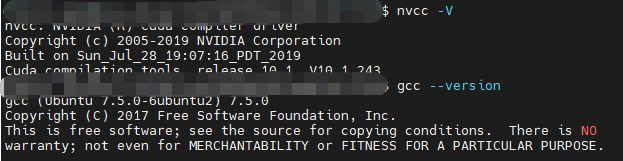
首先,通过下面的命令检查你的nvcc和gcc的版本,其中nvcc是调用gpu的关键,gcc是编译代码的关键。
# Check nvcc version
!nvcc -V
# Check GCC version
!gcc --version
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
你的电脑将会输出下列信息:
然后大家需要安装mmdetection,mmdetection是openmmlab提供的一个计算机视觉的目标检测组件,他还提供了语义分割,分类等多种计算机视觉组件库,这些组件库基本都依赖与mmcv,安装的时候一定要注意保持mmcv和组件库的版本匹配,比如下图是mmcv和mmdetection的匹配关系。
| MMDetection version | MMCV version |
|---|---|
| master | mmcv-full>=1.3.8, <1.4.0 |
| 2.15.1 | mmcv-full>=1.3.8, <1.4.0 |
| 2.15.0 | mmcv-full>=1.3.8, <1.4.0 |
| 2.14.0 | mmcv-full>=1.3.8, <1.4.0 |
| 2.13.0 | mmcv-full>=1.3.3, <1.4.0 |
| 2.12.0 | mmcv-full>=1.3.3, <1.4.0 |
| 2.11.0 | mmcv-full>=1.2.4, <1.4.0 |
| 2.10.0 | mmcv-full>=1.2.4, <1.4.0 |
| 2.9.0 | mmcv-full>=1.2.4, <1.4.0 |
| 2.8.0 | mmcv-full>=1.2.4, <1.4.0 |
| 2.7.0 | mmcv-full>=1.1.5, <1.4.0 |
| 2.6.0 | mmcv-full>=1.1.5, <1.4.0 |
| 2.5.0 | mmcv-full>=1.1.5, <1.4.0 |
| 2.4.0 | mmcv-full>=1.1.1, <1.4.0 |
| 2.3.0 | mmcv-full==1.0.5 |
| 2.3.0rc0 | mmcv-full>=1.0.2 |
| 2.2.1 | mmcv==0.6.2 |
| 2.2.0 | mmcv==0.6.2 |
| 2.1.0 | mmcv>=0.5.9, <=0.6.1 |
| 2.0.0 | mmcv>=0.5.1, <=0.5.8 |
如果你是jupyter的环境,你可以执行下面的命令完成安装。
# install dependencies: (use cu101 because colab has CUDA 10.1)
!pip install -U torch==1.5.1+cu101 torchvision==0.6.1+cu101 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
# install mmcv-full thus we could use CUDA operators
!pip install mmcv-full
# Install mmdetection
!rm -rf mmdetection
!git clone https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection.git
%cd mmdetection
!pip install -e .
# install Pillow 7.0.0 back in order to avoid bug in colab
!pip install Pillow==7.0.0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
并执行下面的python代码来检查是否安装成功。
# Check Pytorch installation
import torch, torchvision
print(torch.__version__, torch.cuda.is_available())
# Check MMDetection installation
import mmdet
print(mmdet.__version__)
# Check mmcv installation
from mmcv.ops import get_compiling_cuda_version, get_compiler_version
print(get_compiling_cuda_version())
print(get_compiler_version())
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
如果安装成功之后,将会在你的命令行中输出下列的信息。

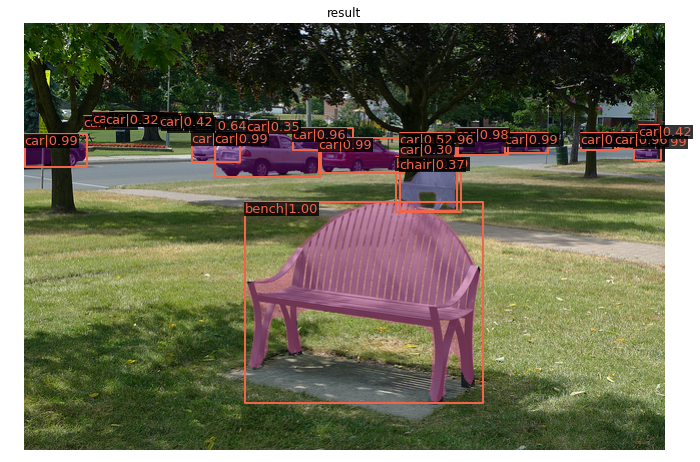
或者你可以通过下面的代码来使用他官方提供的maskrnn的模型。
!mkdir checkpoints !wget -c https://download.openmmlab.com/mmdetection/v2.0/mask_rcnn/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco_bbox_mAP-0.408__segm_mAP-0.37_20200504_163245-42aa3d00.pth \ -O checkpoints/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco_bbox_mAP-0.408__segm_mAP-0.37_20200504_163245-42aa3d00.pth from mmdet.apis import inference_detector, init_detector, show_result_pyplot # Choose to use a config and initialize the detector config = 'configs/mask_rcnn/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco.py' # Setup a checkpoint file to load checkpoint = 'checkpoints/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco_bbox_mAP-0.408__segm_mAP-0.37_20200504_163245-42aa3d00.pth' # initialize the detector model = init_detector(config, checkpoint, device='cuda:0') # Use the detector to do inference img = 'demo/demo.jpg' result = inference_detector(model, img) # Let's plot the result show_result_pyplot(model, img, result, score_thr=0.3)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
效果如下:
准备数据
官方文档:Tutorial 2: Customize Datasets — MMDetection 2.15.1 documentation
目标检测的数据大多数需要处理成voc或者coco的格式,其中voc的格式是xml文件,bbox是左上角和右下角的坐标,coco是一个json文件,bbox是左上角的坐标和宽高。下面我们将会使用一个小规模的kitti数据集来作为我们使用的数据集,下载地址如下:
# download, decompress the data
!wget https://download.openmmlab.com/mmdetection/data/kitti_tiny.zip
!unzip kitti_tiny.zip > /dev/null
- 1
- 2
- 3
数据集的格式如下:
# Check the directory structure of the tiny data # Install tree first !apt-get -q install tree !tree kitti_tiny # 数据集格式 images目录是是图片,labels目录下是标签,train和val分别记录了训练和验证使用到的数据 kitti_tiny ├── training │ ├── image_2 │ │ ├── 000000.jpeg │ │ ├── 000001.jpeg │ │ ├── 000002.jpeg │ │ ├── 000003.jpeg │ └── label_2 │ ├── 000000.txt │ ├── 000001.txt │ ├── 000002.txt │ ├── 000003.txt ├── train.txt └── val.txt
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
可以通过下面的代码来查看一下图片大致是什么样子的
# Let's take a look at the dataset image
import mmcv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = mmcv.imread('kitti_tiny/training/image_2/000073.jpeg')
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
plt.imshow(mmcv.bgr2rgb(img))
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8

训练模型
准备好数据之后,我们只需要修改我们的配置文件即可完成训练:
首先需要加载基本的配置文件,在configs目录下你可以找到这些配置文件,比如这里我们加载的是faster_rcnn的配置文件。
from mmcv import Config
cfg = Config.fromfile('./configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain_1x_coco.py')
- 1
- 2
修改并将修改之后的配置文件保存,在后面推理的时候我们可以直接加载我们的配置文件。
from mmdet.apis import set_random_seed # Modify dataset type and path cfg.dataset_type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.test.type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data.test.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.test.ann_file = 'train.txt' cfg.data.test.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' cfg.data.train.type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data.train.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.train.ann_file = 'train.txt' cfg.data.train.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' cfg.data.val.type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data.val.data_root = 'kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.val.ann_file = 'val.txt' cfg.data.val.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' # modify num classes of the model in box head cfg.model.roi_head.bbox_head.num_classes = 3 # We can still use the pre-trained Mask RCNN model though we do not need to # use the mask branch cfg.load_from = 'checkpoints/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco_bbox_mAP-0.408__segm_mAP-0.37_20200504_163245-42aa3d00.pth' # Set up working dir to save files and logs. cfg.work_dir = './tutorial_exps' # The original learning rate (LR) is set for 8-GPU training. # We divide it by 8 since we only use one GPU. cfg.optimizer.lr = 0.02 / 8 cfg.lr_config.warmup = None cfg.log_config.interval = 10 # Change the evaluation metric since we use customized dataset. cfg.evaluation.metric = 'mAP' # We can set the evaluation interval to reduce the evaluation times cfg.evaluation.interval = 12 # We can set the checkpoint saving interval to reduce the storage cost cfg.checkpoint_config.interval = 12 # Set seed thus the results are more reproducible cfg.seed = 0 set_random_seed(0, deterministic=False) cfg.gpu_ids = range(1) # We can initialize the logger for training and have a look # at the final config used for training print(f'Config:\n{cfg.pretty_text}') # 保存模型的各种参数(一定要记得嗷) cfg.dump(F'{cfg.work_dir}/customformat_kitti.py')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
然后训练就可以了
from mmdet.datasets import build_dataset from mmdet.models import build_detector from mmdet.apis import train_detector # Build dataset datasets = [build_dataset(cfg.data.train)] # Build the detector model = build_detector( cfg.model, train_cfg=cfg.get('train_cfg'), test_cfg=cfg.get('test_cfg')) # Add an attribute for visualization convenience model.CLASSES = datasets[0].CLASSES # Create work_dir mmcv.mkdir_or_exist(osp.abspath(cfg.work_dir)) train_detector(model, datasets, cfg, distributed=False, validate=True)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
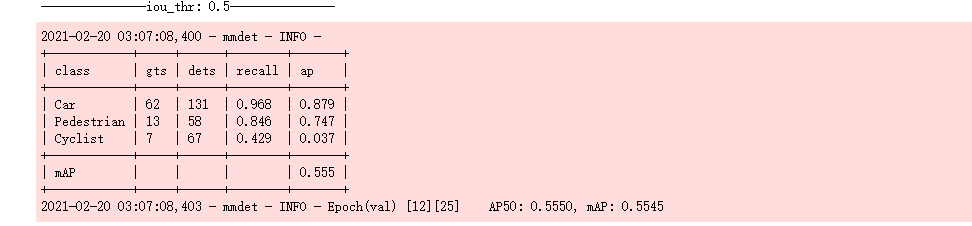
经过漫长的训练,你将会得到下面的训练记录,并生成日志文件
?如何从训练日志中获取信息
从日志中,我们可以对训练过程有一个基本的了解,知道检测器的训练效果如何。
首先,加载在 ImageNet 上预训练的 ResNet-50 主干,这是一种常见做法,因为从头开始训练成本更高。日志显示除了 conv1.bias 之外,ResNet-50 主干的所有权重都被加载,它已合并到 conv.weights 中。
其次,由于我们使用的数据集很小,我们加载了一个 Mask R-CNN 模型并对其进行了微调以进行检测。因为我们实际使用的检测器是 Faster R-CNN,所以掩码分支中的权重,例如roi_head.mask_head,是源 state_dict 中的意外键,未加载。原始的 Mask R-CNN 在包含 80 个类的 COCO 数据集上进行训练,但 KITTI Tiny 数据集只有 3 个类。因此,用于分类的预训练Mask R-CNN的最后一个FC层具有不同的权重形状,未使用。
第三,训练后,检测器通过默认的 VOC 式评估进行评估。结果表明,检测器在 val 数据集上达到了 54.1 mAP,不错!
使用训练好的模型
如果你是jupyter的代码,你可以继续执行下列的文件来使用训练好的模型。
img = mmcv.imread('kitti_tiny/training/image_2/000068.jpeg')
model.cfg = cfg
result = inference_detector(model, img)
show_result_pyplot(model, img, result)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
如果你是在pycharm等工具中完成的开发,可以参考这篇博客使用你的模型。
使用MMDetection进行目标检测_dejahu的博客-CSDN博客
最后附上完整的训练代码
from mmcv import Config from mmdet.datasets import build_dataset from mmdet.models import build_detector from mmdet.apis import train_detector from mmdet.apis import set_random_seed import os.path as osp import mmcv import numpy as np from mmdet.datasets.builder import DATASETS from mmdet.datasets.custom import CustomDataset import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') @DATASETS.register_module() class KittiTinyDataset(CustomDataset): CLASSES = ('Car', 'Pedestrian', 'Cyclist') def load_annotations(self, ann_file): cat2label = {k: i for i, k in enumerate(self.CLASSES)} # load image list from file image_list = mmcv.list_from_file(self.ann_file) data_infos = [] # convert annotations to middle format for image_id in image_list: filename = f'{self.img_prefix}/{image_id}.jpeg' image = mmcv.imread(filename) height, width = image.shape[:2] data_info = dict(filename=f'{image_id}.jpeg', width=width, height=height) # load annotations label_prefix = self.img_prefix.replace('image_2', 'label_2') lines = mmcv.list_from_file(osp.join(label_prefix, f'{image_id}.txt')) content = [line.strip().split(' ') for line in lines] bbox_names = [x[0] for x in content] bboxes = [[float(info) for info in x[4:8]] for x in content] gt_bboxes = [] gt_labels = [] gt_bboxes_ignore = [] gt_labels_ignore = [] # filter 'DontCare' for bbox_name, bbox in zip(bbox_names, bboxes): if bbox_name in cat2label: gt_labels.append(cat2label[bbox_name]) gt_bboxes.append(bbox) else: gt_labels_ignore.append(-1) gt_bboxes_ignore.append(bbox) data_anno = dict( bboxes=np.array(gt_bboxes, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 4), labels=np.array(gt_labels, dtype=np.long), bboxes_ignore=np.array(gt_bboxes_ignore, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 4), labels_ignore=np.array(gt_labels_ignore, dtype=np.long)) data_info.update(ann=data_anno) data_infos.append(data_info) return data_infos cfg = Config.fromfile('./configs/faster_rcnn/faster_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain_1x_coco.py') # Modify dataset type and path cfg.dataset_type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data_root = 'data/kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.test.type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data.test.data_root = 'data/kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.test.ann_file = 'train.txt' cfg.data.test.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' cfg.data.train.type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data.train.data_root = 'data/kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.train.ann_file = 'train.txt' cfg.data.train.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' cfg.data.val.type = 'KittiTinyDataset' cfg.data.val.data_root = 'data/kitti_tiny/' cfg.data.val.ann_file = 'val.txt' cfg.data.val.img_prefix = 'training/image_2' # modify num classes of the model in box head cfg.model.roi_head.bbox_head.num_classes = 3 # We can still use the pre-trained Mask RCNN model though we do not need to # use the mask branch cfg.load_from = 'checkpoints/mask_rcnn_r50_caffe_fpn_mstrain-poly_3x_coco_bbox_mAP-0.408__segm_mAP-0.37_20200504_163245-42aa3d00.pth' # Set up working dir to save files and logs. cfg.work_dir = './tutorial_exps' # The original learning rate (LR) is set for 8-GPU training. # We divide it by 8 since we only use one GPU. cfg.optimizer.lr = 0.02 / 8 cfg.lr_config.warmup = None cfg.log_config.interval = 10 # Change the evaluation metric since we use customized dataset. cfg.evaluation.metric = 'mAP' # We can set the evaluation interval to reduce the evaluation times cfg.evaluation.interval = 12 # We can set the checkpoint saving interval to reduce the storage cost cfg.checkpoint_config.interval = 12 # Set seed thus the results are more reproducible cfg.seed = 0 set_random_seed(0, deterministic=False) cfg.gpu_ids = range(1) # We can initialize the logger for training and have a look # at the final config used for training print(f'Config:\n{cfg.pretty_text}') # 保存模型的各种参数(一定要记得嗷) cfg.dump(F'{cfg.work_dir}/customformat_kitti.py') # 训练主要进程 # Build dataset datasets = [build_dataset(cfg.data.train)] # Build the detector model = build_detector( cfg.model, train_cfg=cfg.get('train_cfg'), test_cfg=cfg.get('test_cfg')) # Add an attribute for visualization convenience model.CLASSES = datasets[0].CLASSES # Create work_dir mmcv.mkdir_or_exist(osp.abspath(cfg.work_dir)) train_detector(model, datasets, cfg, distributed=False, validate=True)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121




