热门标签
热门文章
- 1微调预训练模型Bert实现中文文本分类(bert_base_chinese) 1_bert网盘下载
- 2Git第六阶段:Rebase -> 合并多个commit为一个,使提交更为简洁。_rebase onto remote和drop local
- 3ComfyUI 秋叶整合包:工作流界面,解压即用,快速入门AI绘画_comfyui秋叶
- 4李宏毅机器学习笔记一_李宏毅机器学习笔记csdn
- 5huggingface实战bert-base-chinese模型(训练+预测)
- 6IOS 创建CocoaPods远程私有代码库和公开库
- 7No module named ‘cv2‘问题解决方法——亲试好用_no module named 'cv2
- 8Java基于web的问卷调查系统(开题+源码)_基于javaweb的问卷调查系统
- 9机器学习相关的 项目 数据集 源代码_机器学习源码
- 10AI 人工智能基础及应用_医学领域常见的人工智能算法有哪些
当前位置: article > 正文
dfs与bfs_dfs bfs
作者:知新_RL | 2024-05-12 18:00:56
赞
踩
dfs bfs
深度优先搜素(dfs)
对二叉树尽可能地往节点的终点搜索,只有走到终点才会返回到分叉路口
特点:执着,不撞南墙不回头
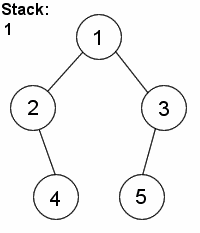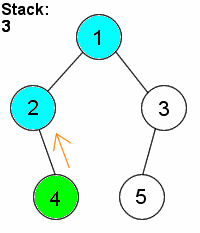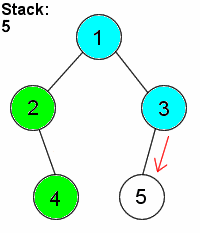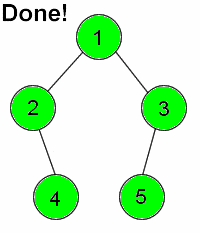
宽度优先搜素(bfs)
对二叉树一层层搜索,只有该层完全搜索完成后才会进行到下一层
特点:稳重,喜欢薅羊毛
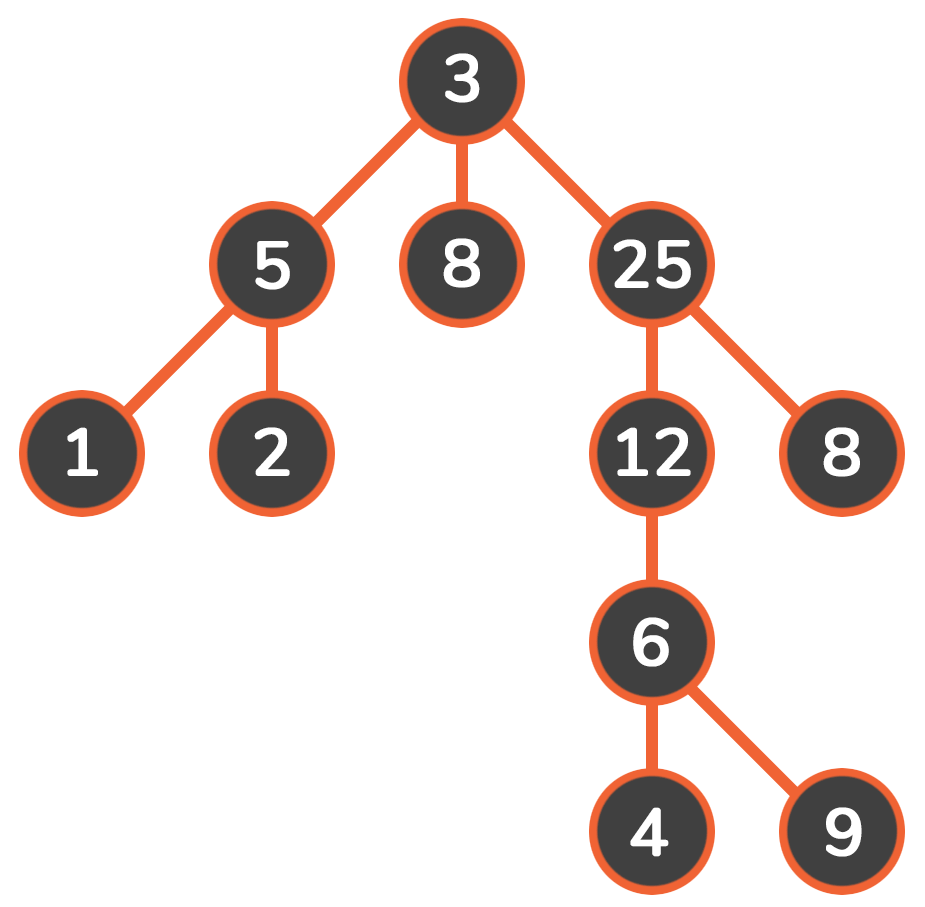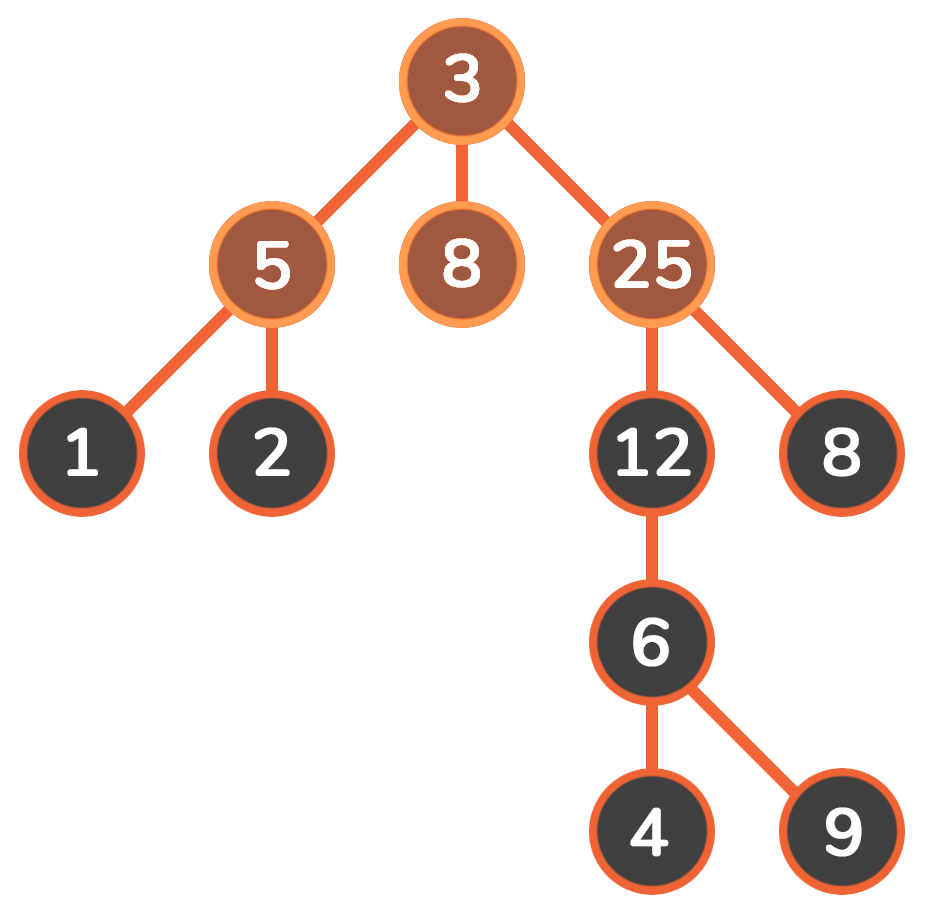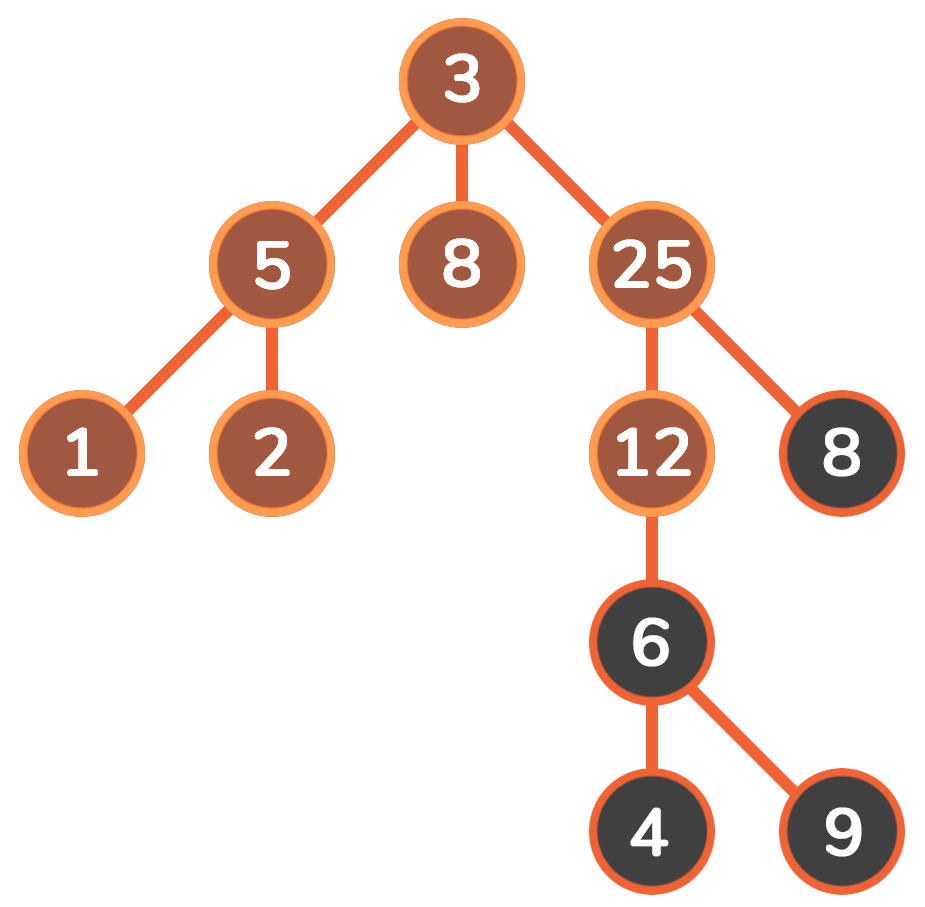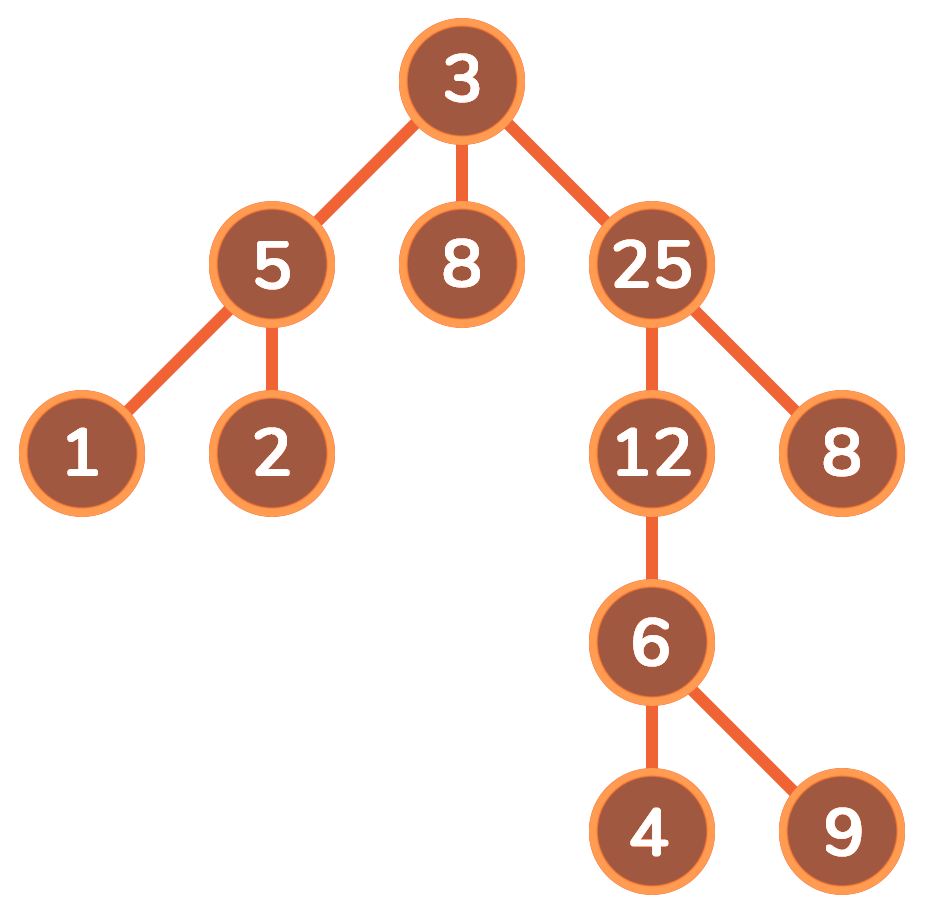
对比
从使用的数据结构来看,dfs使用的是栈,bfs使用的是队列
从使用空间看,dfs只需记录这条路径的所有点,空间复杂度为O(h),bfs记录每层的节点,空间复杂度为O(z ^ h),该特点使bfs有了一个最短路的概念
例题
全排列问题(dfs)
dfs俗称暴搜,他的关键是顺序
题目描述
按照字典序输出自然数 1 到 n 所有不重复的排列,即 n 的全排列,要求所产生的任一数字序列中不允许出现重复的数字。
输入格式
一个整数 n。
输出格式
由 1 - n组成的所有不重复的数字序列,每行一个序列。
每个数字保留 5场宽。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3
- 1
样例输出 #1
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
提示
1≤n≤9。
实现代码
//假设排列1-3 //当你一个数填2时,后面两个的数就不能和前面一样 //如果某一子路径走完了,就需要回溯到上一节点,枚举下一节点 //回溯的同时要记得恢复现场,将改变的变回来 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 10; int n; int path[N]; bool st[N];//默认为false,如果为true表示该层的某个数被占用 void dfs(int u)//u即层数 { if (u == n)//代表path数组填满了,该条路劲走完 { for (int i = 0;i < n;++i) printf("%5d", path[i]); printf("\n"); return; } for (int i = 1;i <= n;++i)//排 1 2 3 { if (!st[i])//判断哪个数被占用 { path[u] = i; st[i] = true; dfs(u + 1); st[i] = false;//恢复现场 } } } int main() { cin >> n; dfs(0); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
n皇后问题
关键:剪枝,即遇到不合理的情况立刻回溯

输入格式
共一行,包含整数 n。
输出格式
每个解决方案占 n 行,每行输出一个长度为 n 的字符串,用来表示完整的棋盘状态。
其中 . 表示某一个位置的方格状态为空,Q 表示某一个位置的方格上摆着皇后。
每个方案输出完成后,输出一个空行。
注意:行末不能有多余空格。
输出方案的顺序任意,只要不重复且没有遗漏即可。
数据范围
1≤n≤9
输入样例:
4
- 1
输出样例:
.Q…
…Q
Q…
…Q.
…Q.
Q…
…Q
.Q…
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
实现代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int n; const int N = 10; char g[N][N]; bool col[N], dg[N],udg[N];//列,对角线,反对角线 void dfs(int u) { if (u == n) { for (int i = 0;i < n;++i) printf("%s\n", g[i]); return; } for (int i = 0;i < n;++i) { if (!col[i] && dg[u + i] && udg[n - u + i]) { g[u][i] = 'Q'; col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = true; dfs(u + 1); col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = false; } } } int main() { cin >> n; for (int i = 0; i < n;++i) { for (int j = 0;j < n;++j) g[i][j] = '.'; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
真全排列
//1-9 9个数凑一个等式,其中每个数由3个数字组成 //比如 124 + 659 = 783 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; int a[10]; bool st[10]; void dfs(int u) { if (u == 10) { if (a[1] * 100 + a[2] * 10 + a[3] + a[4] * 100 + a[5] * 10 + a[6] == a[7] * 100 + a[8] * 10 + a[9])//判断是否符合9个数刚好能得到正确结果 printf("%d%d%d + %d%d%d = %d%d%d\n", a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5], a[6], a[7], a[8],a[9]); return; } for (int i = 1;i <= 9;++i) { if (!st[i]) { a[u] = i; st[i] = true; dfs(u + 1); st[i] = false;//恢复现场 } } } int main() { dfs(1);//从1开始遍历 return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
走迷宫(bfs)
#include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstring> using namespace std; typedef pair<int, int> PII; int n, m; const int N = 101; int g[N][N];//记录图形 int d[N][N];//记录路径数 queue<PII> q;//起始位置 int bfs() { memset(d, -1, sizeof(d)); d[0][0] = 0; q.push({ 0,0 }); int dx[4] = { 1,0,-1,0 }, dy[4] = { 0,1,0,-1 }; while (!q.empty()) { PII t = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4;++i) { int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i]; if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1) { d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;//路径数 + 1 q.push({x,y});//下一次起始位置 } } } return d[n - 1][m - 1]; } int main() { cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0;i < n;++i) { for (int j = 0;j < m;++j) cin >> g[i][j]; } cout << bfs() << endl; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/知新_RL/article/detail/560091
推荐阅读
相关标签




