热门标签
热门文章
- 1LeetCode刷题笔记第1859题:将句子排序
- 2一段c语言的代码,一段C语言代码 据说是最烂的代码
- 3java json 嵌套list_java-嵌套JSON的POJO格式?
- 4验证二叉搜索树
- 5用 | 操作符进行取整操作-Ts_ts 取整
- 6Xilinx DDR3 IP核使用问题汇总(持续更新)和感悟
- 7任意命令执行漏洞
- 8Linux 的 MySQL 5.x - 关于 Windows 10 的 Navicat Premium 导入 Excel (.xlsx)文件,报错问题集锦_navicat导入excel数据报错
- 9linux secure boot(安全启动)下为内核模块签名
- 10紫光 DDR3 IP核调试_紫光ddr调试
当前位置: article > 正文
【C++】:const成员,取地址及const取地址操作符重载
作者:笔触狂放9 | 2024-05-22 12:00:41
赞
踩
【C++】:const成员,取地址及const取地址操作符重载
一,const成员
将const修饰的“成员函数”称之为const成员函数,const修饰类成员函数,实际修饰该成员函数隐含的this指针,表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改。
使用方式:规定在函数后面加 const。
看看下面的几段代码:
代码1:对象d1是const类型,Print函数后面没有const,运行结果报错。
class Date { public: Date(int year, int month, int day) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } //d1.Print(&d1); d1对象类型是 const Date* 只读 void Print() //Date* const this 可读可写 权限放大了 { cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main() { //d1是const对象,d1对象类型是const Date* const Date d1(2024, 4, 14); d1.Print(); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
代码2:对象d1是const类型,在 Print 函数后加了const,正常运行。
class Date { public: Date(int year, int month, int day) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } //d1.Print(&d1); d1对象类型是 const Date* 只读 //const Date* const this,const修饰*this,本质改变this的类型 void Print() const { cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main() { const Date d1(2024, 4, 25); //d1是const对象,d1对象类型是 const Date* d1.Print(); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
代码3:对象d2不是const类型,在 Print 函数后加了const,正常运行。
class Date { public: Date(int year, int month, int day) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } //d2.Print(&d2); d2对象类型是Date* const,可读可写 void Print() const { cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl; } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; int main() { Date d2(2024, 4, 25);//d2是非const对象 d2.Print();//调用Print就是权限的缩小 return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
上述三段代码的原理图解如下:
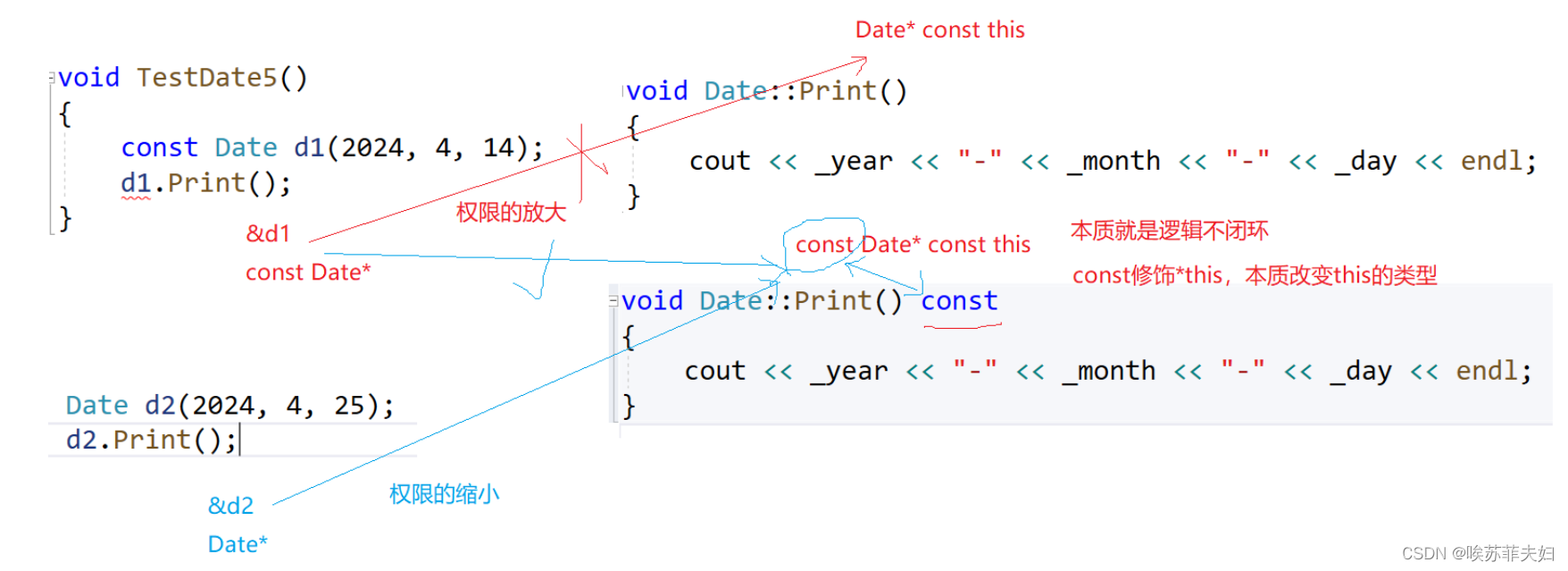
总结:const成员函数是具有优势的,因为不管是传递含const对象,还是传递不含const对象,成员函数都可以调用。所以当我们要使用的对象不发生改变时,即隐含的this的内容不改变,一般都用const成员函数。
二,取地址及const取地址操作符重载
取地址操作函数和加了const的取地址操作函数构成重载。正常情况取出的是this指针的地址。
这两个默认成员函数一般不用我们自己定义 ,编译器默认会生成。
使用如下:
class A { public: A* operator&() { cout << "A* operator&()" << endl; return this; } const A* operator&() const { cout << "const A* operator&() const" << endl; return this; } private: int _a = 1; int _b = 2; int _c = 3; }; int main() { A aa1; const A aa2; cout << &aa1 << endl; cout << &aa2 << endl; return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31

除非不想让该类型的对象被取地址,就可以自己定义,返回指定地址(如空地址或是假地址) 。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/笔触狂放9/article/detail/608152
推荐阅读
相关标签



