- 1使用idea 把一个git分支的部分提交记录合并到另一个git分支上_idea 将一部分提交同步到其他项目
- 2【OpenCV】给图像添加噪声_翻转,切割,增加噪声
- 3python批量命名教程_《自拍教程69》Python 批量重命名音频文件,AV专家必备!
- 4四年背的单词 笔记目录_119.23.244.79:8081/topic/frame/race/login.html
- 5pip安装pandas
- 6Kafka:什么是kafka? ①_kafka kafka
- 7Linux如何创建文件在指定的目录?_在指定目录下创建文件
- 8Unity_VRTK 3.2.1_UI手柄射线检测点击事件的问题_unity htc vrtk 射线 点击ui
- 9YOLOV5源码的详细解读_yolov5代码详解
- 10资深SRE带你看阿里云香港故障_sre故障复盘需要关注的问题
pyecharts+Django 使用指南====>Anaconda实现运行_from pyecharts.constants import default_host
赞
踩
1、参考自:http://blog.csdn.net/u013421629/article/details/78192402
别人的 :
本指南按照 Django 官方教程,通过完成一个 Django 小项目来说明如何在 Django 中使用 pyecharts。如果对 Django 还不太熟悉的开发者,可仔细阅读官方提供的最新文档。
Step 0: 使用新的 virtualenv 环境
建议开发者使用 1.11.4 版本的 Django
- $ virtualenv --no-site-packages pyecharts-env
- $ source pyecharts-env/bin/activate
- $ pip install django==1.11.4
- $ pip install pyecharts
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Step 1: 新建一个 django 项目
$ django-admin startproject myechartsite
- 1
创建一个应用程序
- $ python manage.py startapp myfirstvis
- $ ls
- db.sqlite3 manage.py myechartsite myfirstvis
- 1
- 2
- 3
在 myechartsite/settings.py 中注册应用程序
- # myechartsite/settings.py
- ...
- INSTALLED_APPS = [
- 'django.contrib.admin',
- 'django.contrib.auth',
- 'django.contrib.contenttypes',
- 'django.contrib.sessions',
- 'django.contrib.messages',
- 'django.contrib.staticfiles',
- 'myfirstvis' # <---
- ]
- ...
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
我们先编辑 urls.py.这文件在 Django 里的功能是把前段的 HTTP 需求和后台服务函数挂钩。在 Step3,我们再引入后端服务函数
- # myfirstvis/urls.py
- from django.conf.urls import url
-
- from . import views
-
- urlpatterns = [
- url(r'^$', views.index, name='index'),
- ]
- 在 myechartsite/urls.py 中新增 'myfirstvis.urls'
-
- myechartsite/urls.py
- from django.conf.urls import include, url
- from django.contrib import admin
-
- urlpatterns = [
- url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
- url(r'myfirstvis/', include('myfirstvis.urls')) # <---
- ]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

Step 2: 处理视图功能部分
将下列代码保存到 myfirstvis/views.py 中。
- from __future__ import unicode_literals
- import math
-
- from django.http import HttpResponse
- from django.template import loader
- from pyecharts import Line3D
-
- from pyecharts.constants import DEFAULT_HOST
-
-
- def index(request):
- template = loader.get_template('myfirstvis/pyecharts.html')
- l3d = line3d()
- context = dict(
- myechart=l3d.render_embed(),
- host=DEFAULT_HOST,
- script_list=l3d.get_js_dependencies()
- )
- return HttpResponse(template.render(context, request))
-
-
- def line3d():
- _data = []
- for t in range(0, 25000):
- _t = t / 1000
- x = (1 + 0.25 * math.cos(75 * _t)) * math.cos(_t)
- y = (1 + 0.25 * math.cos(75 * _t)) * math.sin(_t)
- z = _t + 2.0 * math.sin(75 * _t)
- _data.append([x, y, z])
- range_color = [
- '#313695', '#4575b4', '#74add1', '#abd9e9', '#e0f3f8', '#ffffbf',
- '#fee090', '#fdae61', '#f46d43', '#d73027', '#a50026']
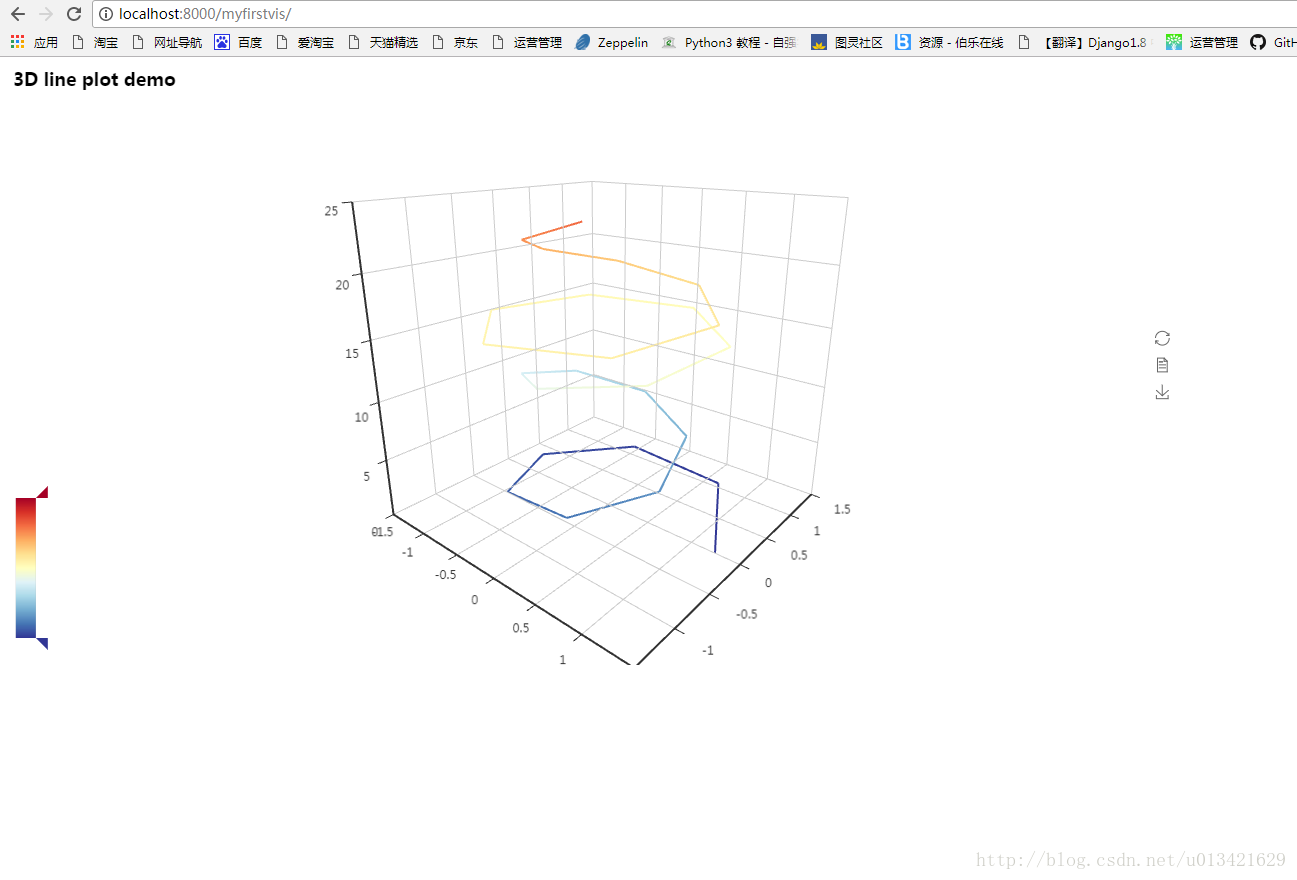
- line3d = Line3D("3D line plot demo", width=1200, height=600)
- line3d.add("", _data, is_visualmap=True,
- visual_range_color=range_color, visual_range=[0, 30],
- is_grid3D_rotate=True, grid3D_rotate_speed=180)
- return line3d
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37

script_list 是 Page() 类渲染网页所需要依赖的 echarts js 库,依赖的库的数量取决于所要渲染的图形种类。
host 是 echarts js 库的地址,默认的地址为 http://chfw.github.io/jupyter-echarts/echarts 当然,如果你愿意你也可以改变这个地址,先克隆 https://github.com/chfw/jupyter-echarts 然后将 echarts 文件夹挂载在你自己的服务器上即可。
Step 3: 为项目提供自己的模板
前面的步骤是按照 tutorial part 1,接下来我们跳到 tutorial part 3
Linux/macos 系统
$ mkdir templates/myfirstvis -p
- 1
Windows 系统
在 myfirstvis 目录下,新建 templates/myfirstvis 子目录
myfirstvis 目录
─ myfirstvis
├── admin.py
├── apps.py
├── init.py
├── migrations
│ ├── init.py
├── models.py
├── templates
│ └── myfirstvis
│ └── pyecharts.html
├── tests.py
├── urls.py
└── views.py
将下面 html 模板代码保存为 pyecharts.html,请确保 pyecharts.html 文件的绝对路径为 /myfirstvis/templates/myfirstvis
- <!-- myfirstvis/templates/pyecharts.html -->
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
-
- <head>
- <meta charset="utf-8">
- <title>Proudly presented by PycCharts</title>
- {% for jsfile_name in script_list %}
- <script src="{{host}}/{{jsfile_name}}.js"></script>
- {% endfor %}
- </head>
-
- <body>
- {{myechart|safe}}
- </body>
-
- </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17

Step 4: 运行项目
- $ cd myechartsite
- $ python manage.py runserver
- 1
- 2
- You have 13 unapplied migration(s). Your project may not work properly until you apply the migrations for app(s): admin, auth, contenttypes, sessions.
- Run 'python manage.py migrate' to apply them.
-
- August 08, 2017 - 05:48:38
- Django version 1.11.4, using settings 'myechartsite.settings'
- Starting development server at http://127.0.0.1:8000/
- Quit the server with CONTROL-C.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
访问 http://localhost:8000/myfirstvis/,你就可以看到酷炫的 3D 图了
自己的:
在自己电脑上安装了Anaconda,并且用conda install pyecharts,Django,安装了pyecharts,Django。
此时默认是py2
然后就可以在
命令行下,创建Django项目,该项目可以放到任意自己想放的文件夹下。最后Django项目写好后,直接python manage.py runserver即可。
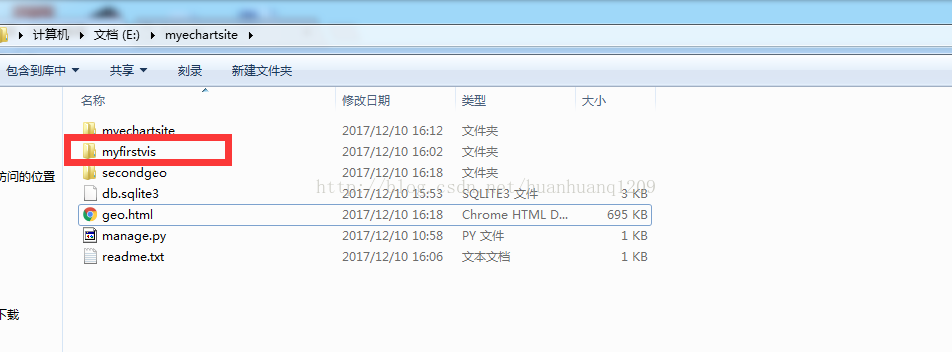
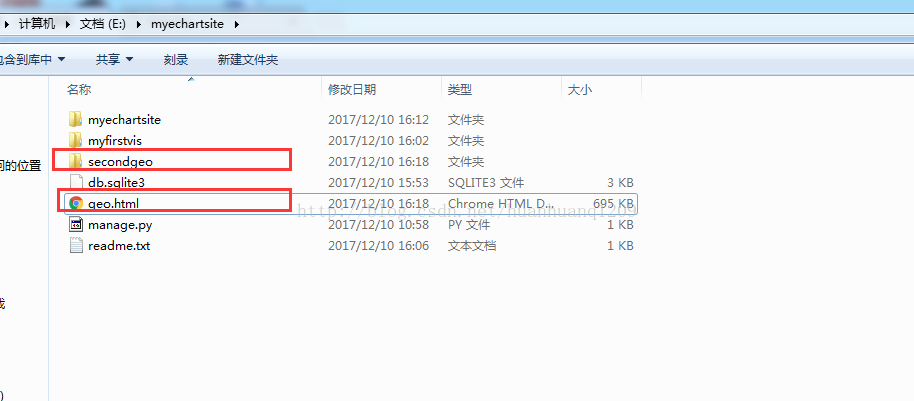
项目目录结构:
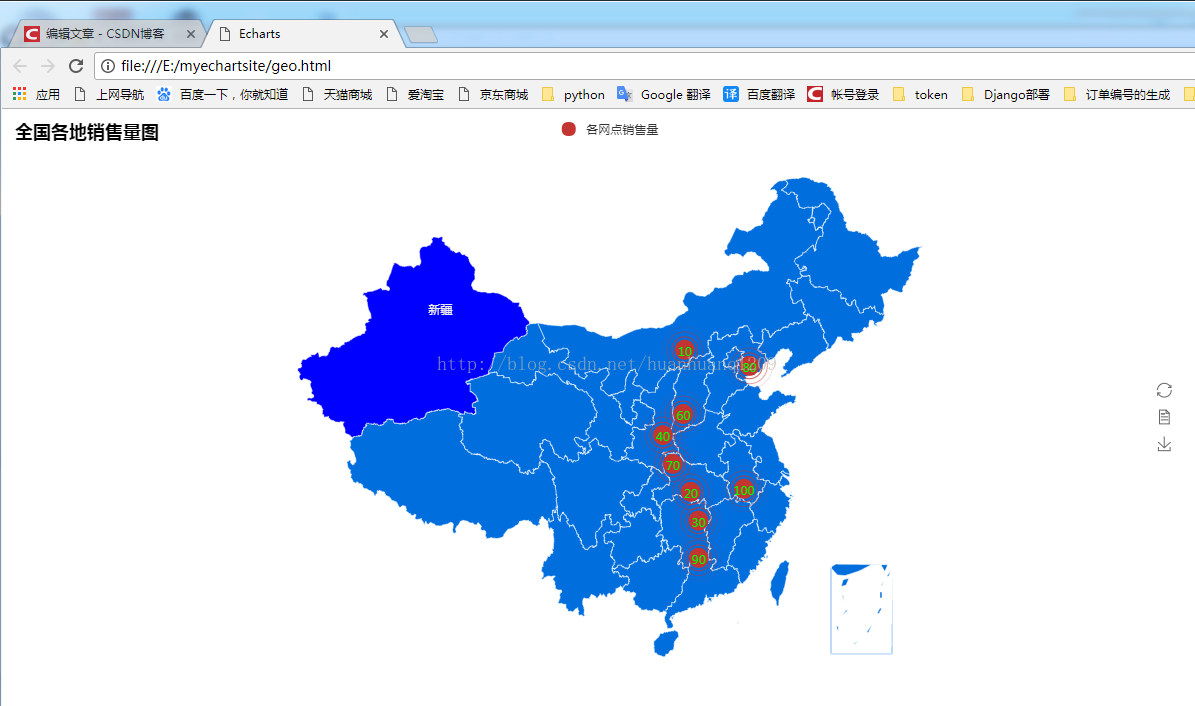
二、地图:首先呈现以下效果图:
该图是自己在借用别人代码(http://blog.csdn.net/lxb1022/article/details/77119553)的基础上实现的:
其中geo.html是项目运行secondgeo App后生成的。然后打开geo.html即可。代码如下,secondgeo中的views.py:
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- from __future__ import unicode_literals
- from django.http import HttpResponse
- #from django.shortcuts import render
-
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- from pyecharts import Geo
- def index(request):
- value = [20,30,40,60,70,80,90,100,10]
- attr = ['荆州','长沙','渭南','临汾','十堰','唐山','郴州','铜陵','呼和浩特']
- geo = Geo("全国各地销售量图",width=1200,height=600)
- geo.add("各网点销售量",attr,value,type="effectScatter",border_color="#ffffff",symbol_size=20,
- is_label_show=True,label_text_color="#00FF00",label_pos="inside",symbol="circle",
- symbol_color="FF0000",geo_normal_color="#006edd",geo_emphasis_color="#0000ff")
- geo.show_config()
- geo.render("geo.html")
- return HttpResponse( )

分析:
分三步,参数解释:
geo=Geo()
正标题,副标题,地图大小。
title_pos="center":标题位置
title_color="#fff":标题颜色
background_color='#404a59':背景颜色
geo.add()
type="effectScatter":是否有涟漪动画效果。
effect_scale=5:涟漪的多少。
symbol="circle":标记的形状(circle,pin,rect,diamon,roundRect,arrow,triangle)
symbol_size=20:标记大小
symbol_color="FF0000":标记颜色
geo_normal_color="#006edd":地图颜色
border_color="#ffffff":地图线条颜色
geo_emphasis_color="#0000ff":鼠标放在地图上的颜色
is_label_show=True:显示标签
label_text_color="#00FF00":标签颜色,本例是绿色
label_pos="inside":标签位置(inside,top,bottom,left,right)
is_visualmap=True:显示图例条
visual_range=[0, 300]:图例条范围
visual_text_color='#fff':图例条颜色
geo.render()
参数为保存的路径和名称。默认在当前目录下,,geo.html