热门标签
热门文章
- 1如何在OpenWRT部署uhttpd搭建服务器实现远程访问本地web站点
- 2MIPS指令集_mips beqz
- 3Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/spark/SparkConf
- 4where 1=1的作用
- 5{txt-to-video}——文本转视频思路_txt_to_video
- 6NLP算法-中文分词工具-Jieba_jieba分词
- 7网络工程师练习题4
- 8Uncaught TypeError: app.component is not a function_typeerror: components is not a function
- 9 oracle先排序再分页
- 10IDEA启动服务时提示端口被占用,提示:Web server failed to start. Port 8080 was already in use._ide端口被占用启动程序失败怎么办
当前位置: article > 正文
关于python中open()新建文件的用法小结_python里面open(file_path,"w")
作者:繁依Fanyi0 | 2024-03-21 04:53:12
赞
踩
python里面open(file_path,"w")
open()用于新建文件:
file = open(‘path’+filename+‘文件格式’,‘w’)
例子
import os
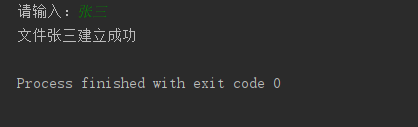
name=input('请输入:')
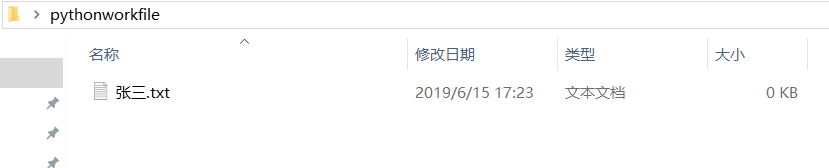
file = open('C:\\Users\\shen\\Desktop\\pythonworkfile\\' + name + '.txt', 'w')
if os.path.exists('C:\\Users\\shen\\Desktop\\pythonworkfile\\'):
print('文件'+name+'建立成功')
else:
print('建立失败')
file.close()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
在open方法的后面有一个‘w’,w决定了打开文件的模式为:写入
r:以只读方式打开文件;
r+:打开文件用于读写,指针位于文件的开头;
w+:打开文件用于读写,如果文件存在则打开文件,将原有内容删除;文件不存在则创建文件;
a:打开文件用于追加,指针放在文件末尾,新写入的内容会接在已有内容后面;
a+:打开一个文件用于读写,如果文件存在,则追加模式;文件不存在,新建文件,用于读写;
更详细了解:https://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-open.html
运行截图:
在上述例子中,还用到了另一种方法:
if os.path.exists(‘C:\Users\shen\Desktop\pythonworkfile\’):
这个方法可以判断具体的文件的存在
删除文件:
例子:
import os
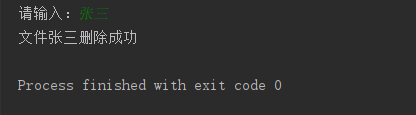
name=input('请输入:')
if os.path.exists('C:\\Users\\shen\\Desktop\\pythonworkfile\\'):
os.remove('C:\\Users\\shen\\Desktop\\pythonworkfile\\'+name+'.txt')
print('文件'+name+'删除成功')
else:
print('文件不存在')
file.close()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
运行结果:
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/繁依Fanyi0/article/detail/278595
推荐阅读
相关标签