- 1鸿蒙开发笔记(二十): 常用组件 TextInput/TextArea, 弹窗,视频播放Video_鸿蒙 textinput
- 2C++图论 最短路问题总结_c++图最短距离问题
- 3Mac完全卸载idea的方法(可重新安装破解)_mac卸载idea重新安装
- 4【鸿蒙4.0】harmonyos Day 01_ohpm error: notfound package "hypium" not found fr
- 5c++数据结构之vector_c++ vector 结构体
- 6hbuilder 开发5+ APP采坑记录_5+app项目自启动
- 7AAU-net: 用于超声图像中乳腺病变分割的自适应注意力U-Net
- 82021年11月-火狐浏览器添加自定义搜索引擎之办法_手机自定义添加搜索引擎搜狗
- 9基于微信小程序的校园订餐系统(源码+文档+部署+讲解)_基于微信的校园订餐系统
- 10本科论文查重会检测AI辅写疑似度吗?7点解答你的疑惑!_学校盲审会使用aigc查重吗是真的吗
双目视觉(五)立体匹配算法之动态规划全局匹配_全局匹配算法
赞
踩
系列文章:
- 双目视觉(一)双目视觉系统
- 双目视觉(二)双目匹配的困难和评判标准
- 双目视觉(三)立体匹配算法
- 双目视觉(四)匹配代价
- 双目视觉(五)立体匹配算法之动态规划全局匹配
- 双目视觉(六)U-V视差
- 【项目实战】利用U-V视差进行地面检测
- 【项目实践】U-V视差路面检测之动态规划
代码:GitHub stereo matchhttps://github.com/Xke1718He/stereo-match https://github.com/Xke1718He/stereo-match
https://github.com/Xke1718He/stereo-match
注:分享的代码中,双目匹配的代价只有一种,如果觉得不错,可以给予支持,谢谢^0^
全局匹配算法:
全局匹配主要是利用图像的全局约束信息,通过构建全局能量函数,然后通过优化方法最小化全局能量函数以求得致密视差图。目前优化方法主要有:动态规划(DP)、置信传播(BP)、模拟退火、图割法(GC)等。
动态规划:
动态规划的思想就是把求解整个过程分解为若干子过程,逐个求解子过程。例如斐波那契数列,fib(6)分解为fib(5)和fib(4),而fib(5)分解为fib(4)和fib(3),fib(4)为一个重复子问题,而动态规划就是解决这类问题的方式之一。
这是我学习动态规划相关知识的链接:
【动态规划专题班】ACM总冠军、清华+斯坦福大神带你入门动态规划算法_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
在双目匹配中,动态规划立体匹配是基于极线约束,通过依次寻找每条极线上匹配点对的最小代价路径的动态寻优方法求解全局能量最小化,得到匹配视差图。
步骤大致如下:
- step1.构建全局能量函数
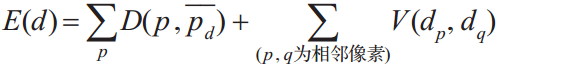
其中,![]() 为数据项,一般表示为代价函数;
为数据项,一般表示为代价函数;![]() 为视差平滑约束项。
为视差平滑约束项。
- step2. 代价函数构建
代价函数构建这里采用的是块匹配,也就是以第一图像待匹配点为中心像素创建一个n*n的窗口,在第二幅图像中,沿着极线取出与基准点领域同样大小为n*n的领域,进行领域内的相似度函数的计算。
说明:代价函数采用的是C++中的继承构建
- imageType:判断左右图像的信息相似性。比如大小是否一样大呀。
- aggregate:这也就是所谓的代价聚合函数,计算左右图像领域内的相似性度量的。
- class CostFunction {
- public:
- float lambda;
-
- cv::Mat left;//左图像
- cv::Mat right;//右图像
-
- int blocksize;//block大小
- int margin;//块的边界
-
- float normCost;
- float normWin;
- //构造函数
- CostFunction( cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, float lambda)
- {
- lambda = 1.0;
- this->left = left;
- this->right = right;
- imageType(left, right);
- this->lambda = lambda;
- }
- //虚构函数
- virtual bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.size() == right.size());
-
- return true;
- }
- //代价聚合
- virtual float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) = 0;
-
- float p(float cost) {
- return 1 - exp(-cost / lambda);
- }
-
- ~CostFunction() {}
- };
-
- class RGBCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- RGBCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {}
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_8UC3 && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- // aggregate over a ROI of input images
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for (int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- cv::Vec3b* lptr = left.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);
- cv::Vec3b* rptr = right.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);
-
- for ( int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j) {
- sum += eukl(lptr[x1 + j], rptr[x2 + j]); // cost function
- }
- }
-
- return sum / sqrt(255*255 + 255*255+255*255); // normalize to winsize*1.0
- }
-
- float eukl(cv::Vec3b l, cv::Vec3b r) {
- float a = l[0] - r[0];
- float b = l[1] - r[1];
- float c = l[2] - r[2];
- return std::sqrt(a*a + b*b + c*c);
- }
-
- ~RGBCost() {}
- };
-
- class FloatCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- FloatCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {}
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_32F && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- // aggregate over a ROI of input images
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for (int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- float* lptr = left.ptr<float>(i);
- float* rptr = right.ptr<float>(i);
-
- for ( int j = -margin ; j <= margin; ++j) {
- sum += abs(lptr[x1 + j] - rptr[x2 + j]); // cost function
- }
- }
-
- return sum / (blocksize*blocksize*lambda);
- }
- };
-
- class CondHistCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- cv::Mat nuLeft, nuRight;
- CondHistCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {
- cv::Mat histl = condHist(left, 3);
- nuLeft = switchColors(left, histl);
- cv::Mat histr = condHist(right, 3);
- nuRight = switchColors(right, histr);
- }
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_32F && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- // aggregate over a ROI of input images
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for (int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- float* lptr = nuLeft.ptr<float>(i);
- float* rptr = nuRight.ptr<float>(i);
-
- for ( int j = -margin ; j <= margin; ++j) {
- sum += abs(lptr[x1 + j] - rptr[x2 + j]); // cost function
- }
- }
-
- return sum / (blocksize*blocksize*lambda);
- }
- };
-
-
- class GrayCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- GrayCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {}
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_8UC1 && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- // aggregate over a ROI of input images
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for (int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- uchar* lptr = left.ptr<uchar>(i);
- uchar* rptr = right.ptr<uchar>(i);
-
- for ( int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j) {
- sum += abs(lptr[x1 + j] - rptr[x2 + j]); // cost function
- }
- }
-
- return sum / (blocksize*blocksize*255.0);
- }
- };
-
- class GradientCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- cv::Mat l_grad; // 3 channel float
- cv::Mat r_grad; // 3 channel float
-
- GradientCost(const cv::Mat left, const cv::Mat right, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {
- l_grad = getRGBGradientAngle(left);
- r_grad = getRGBGradientAngle(right);
-
- //displayGradientPic(l_grad);
- //displayGradientPic(r_grad);
- }
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_8UC3 && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- // aggregate over a ROI of input images
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for (int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- cv::Vec3f* lptr = l_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(i);
- cv::Vec3f* rptr = r_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(i);
-
- for ( int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j) {
- sum += eukl(lptr[x1 + j], rptr[x2 + j]); // cost function
- }
- }
-
- return sum / sqrt(255*255 + 255*255 + 255*255); // normalize to winSize * 1.0
- }
-
- float eukl(cv::Vec3f l, cv::Vec3f r) {
- float a = l[0] - r[0];
- float b = l[1] - r[1];
- float c = l[2] - r[2];
- return std::sqrt(a*a + b*b + c*c);
- }
-
- ~GradientCost() {
- l_grad.release();
- r_grad.release();
- }
- };
-
- class CensusCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- int censusWindow;
- int censusMargin;
- CensusCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, int censusWindow, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {
- // census.... nimmt einen Block
- this->censusWindow = censusWindow;
- this->censusMargin = censusWindow / 2;
-
- this->normWin = censusWindow * censusWindow;
- // nimmt einen Block
- }
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_8UC1 && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- unsigned int census(int x1, int x2, int y, uchar c1, uchar c2) {
- unsigned int diff = 0;
-
- for(int i = y - censusMargin; i <= y + censusMargin; ++i) {
- uchar* lptr = left.ptr<uchar>(i);
- uchar* rptr = right.ptr<uchar>(i);
-
- for(int j = -censusMargin; j <= censusMargin; ++j) {
- bool t1 = (c1 < lptr[x1 + j]);
- bool t2 = (c2 < rptr[x2 + j]);
-
- if(t1 != t2) diff++;
- }
- }
-
- return diff; /// (censusWindow*censusWindow);
- }
-
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- /*for(int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- uchar *lptr = left.ptr<uchar>(i);
- uchar *rptr = right.ptr<uchar>(i);
- for(int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j)
- sum += census(x1 + j, x2 + j, i, lptr[x1 + j], rptr[x2 + j]);
- }*/
- uchar *lptr = left.ptr<uchar>(y);
- uchar *rptr = right.ptr<uchar>(y);
- sum = census(x1, x2, y, lptr[x1], rptr[x2]);
- return sum / normWin;
- }
- };
-
- class CensusFloatCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- int censusWindow;
- int censusMargin;
-
- CensusFloatCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, int censusWindow, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {
- // census.... nimmt einen Block
- this->censusWindow = censusWindow;
- this->censusMargin = censusWindow / 2;
- }
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_32F && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- unsigned int census(int x1, int x2, int y, float c1, float c2) {
- unsigned int diff = 0;
-
- for(int i = y - censusMargin; i <= y + censusMargin; ++i) {
- float* lptr = left.ptr<float>(i);
- float* rptr = right.ptr<float>(i);
-
- for(int j = -censusMargin; j <= censusMargin; ++j) {
- bool t1 = (c1 < lptr[x1 + j]);
- bool t2 = (c2 < rptr[x2 + j]);
-
- if(t1 != t2) diff++;
- }
- }
-
- return diff;
- }
-
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for(int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- float *lptr = left.ptr<float>(i);
- float *rptr = right.ptr<float>(i);
-
- for(int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j)
- sum += census(x1 + j, x2 + j, i, lptr[x1 + j], rptr[x2 + j]);
- }
- float *lptr = left.ptr<float>(y);
- float *rptr = right.ptr<float>(y);
- //sum = census(x1, x2, y, lptr[x1], rptr[x2]);
- return sum / (censusWindow*censusWindow*lambda);
- }
- };
-
- class RGBCensusCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- int censusWindow;
- int censusMargin;
-
- RGBCensusCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, int censusWindow, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {
- // census.... nimmt einen Block
- this->censusWindow = censusWindow;
- this->censusMargin = censusWindow / 2;
- normCost = censusWindow*censusWindow*3;
- // nimmt einen Block
- }
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_8UC3 && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- unsigned int census(int x1, int x2, int y, cv::Vec3b c1, cv::Vec3b c2) {
- unsigned int diff = 0;
-
- for(int i = y - censusMargin; i <= y + censusMargin; ++i) {
- cv::Vec3b* lptr = left.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);
- cv::Vec3b* rptr = right.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);
-
- for(int j = -censusMargin; j <= censusMargin; ++j) {
- cv::Vec3b cl = lptr[x1 + j];
- cv::Vec3b cr = rptr[x2 + j];
-
- for(int ch = 0; ch < 3; ++ch) {
- bool t1 = (c1[ch] < cl[ch]);
- bool t2 = (c2[ch] < cr[ch]);
-
- if(t1 != t2) diff++;
- }
- }
- }
-
- return diff;
- }
-
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- for(int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- cv::Vec3b *lptr = left.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);
- cv::Vec3b *rptr = right.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(i);
-
- for(int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j)
- sum += census(x1 + j, x2 + j, i, lptr[x1 + j], rptr[x2 + j]);
- }
- //cv::Vec3b *lptr = left.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(y);
- //cv::Vec3b *rptr = right.ptr<cv::Vec3b>(y);
-
- return sum / normCost;
- }
- };
-
- class RGBGradCensusCost : public CostFunction {
- public:
- int censusWindow;
- int censusMargin;
-
- float normCost;
- float normWin;
-
- cv::Mat l_grad;
- cv::Mat r_grad;
-
- RGBGradCensusCost(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right, int censusWindow, float lambda) : CostFunction(left, right, lambda) {
- // census.... nimmt einen Block
- this->censusWindow = censusWindow;
- this->censusMargin = censusWindow / 2;
- normWin = censusWindow*censusWindow*3;
- // nimmt einen Block
- l_grad = getRGBGradientAngle(left);
- r_grad = getRGBGradientAngle(right);
- }
-
- bool imageType(cv::Mat left, cv::Mat right) {
- assert(left.type() == right.type() && "imgL imgR types not equal");
- assert(left.type() == CV_8UC3 && "img type not supported");
-
- return true;
- }
-
- unsigned int census(int x1, int x2, int y, cv::Vec3f c1, cv::Vec3f c2) {
- unsigned int diff = 0;
-
- for(int i = y - censusMargin; i <= y + censusMargin; ++i) {
- cv::Vec3f* lptr = l_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(i);
- cv::Vec3f* rptr = r_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(i);
-
- for(int j = -censusMargin; j <= censusMargin; ++j) {
- cv::Vec3f cl = lptr[x1 + j];
- cv::Vec3f cr = rptr[x2 + j];
-
- for(int ch = 0; ch < 3; ++ch) {
- bool t1 = (c1[ch] < cl[ch]);
- bool t2 = (c2[ch] < cr[ch]);
-
- if(t1 != t2) diff++;
- }
- }
- }
-
- return diff;
- }
-
- float aggregate(int x1, int x2, int y) {
- float sum = 0;
- /*for(int i = y - margin; i <= y + margin; ++i) {
- cv::Vec3f *lptr = l_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(i);
- cv::Vec3f *rptr = r_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(i);
- for(int j = -margin; j <= margin; ++j)
- sum += census(x1 + j, x2 + j, i, lptr[x1 + j], rptr[x2 + j]);
- }*/
- cv::Vec3f *lptr = l_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(y);
- cv::Vec3f *rptr = r_grad.ptr<cv::Vec3f>(y);
-
- sum = census(x1, x2, y, lptr[x1], rptr[x2]);
- return sum / normWin;
- }
- };
step3.视差空间的构建

DSI(Disparity Space Image)视差空间图像为一个三维矩阵,主要由横轴x,纵轴y,视差搜索范围d构成,传统的DP方法一般就是为了在某固定的Y(也就是某极线上)寻找一条从最左段到最右段的最小代价路径,每条路径的代价为![]()
- 视差空间的构建
输入参数:
- imageSize:图像的大小
- blocksize:块的大小
- y:某条极线
输出参数:
- map:某极线上左右图像两两领域相互的代价值
- 左范围:[margin,imageSize.width - margin]
- 右范围:[margin,imageSize.width - margin]
- cv::Mat BlockMatching::disparitySpace(Size imageSize, int blocksize, int y)
- {
- int margin = blocksize / 2;
- int start = margin;
- int stopW = imageSize.width - margin;
- int workSpace = stopW - start;
-
- // leave out the borders
- //Mat map = Mat(workSpace, workSpace, CV_32F); // not preinitialized.. // numeric_limits<float>::max());
- Mat map = Mat(workSpace, workSpace, CV_32F, numeric_limits<float>::max());
-
- //int dmax = 101;
- for(int x1 = start; x1 < stopW; x1++) {
- float* ptr = map.ptr<float>(x1 - margin); // [x1 - margin, x2 - margin]
-
- //ptr[max(x1 - 1, start) - margin] = numeric_limits<float>::max(); // fast borders
- //ptr[min(x1 + dmax, stopW - 1) - margin] = numeric_limits<float>::max();
- //for(int x2 = x1; x2 < min(x1 + dmax, stopW); x2++) {
- for(int x2 = start; x2 < stopW; x2++) {
-
- // combine costs
- float cost = 0;
- for(size_t i = 0; i < functions.size(); ++i) {
- float val = functions[i]->aggregate(x1, x2, y);
- mins[i] = min(mins[i], val); // debug
- maxs[i] = max(maxs[i], val); // debug
- cost += val;
- }
-
- // x1, x2. Das heißt x1 sind die Zeilen. Wir gehen jedes Mal die Zeilen runter.
- // geht nur von 0 - workspace, deshalb margin abziehen
- //map.at<float>(x1 - margin, x2 - margin) = greySad(leftRoi, rightRoi);
- ptr[x2 - margin] = cost;
- }
- }
- return map;
- }
step4:动态规划
主要分为四步:
- 设置初始位置的值(已知的值,这里设置的最后一行,最后一列的点为初始值)
- 计算边界上的代价(最后一行、最后一列)
- 从三个方向(向上、向左、斜向上)计算代价
- 记录每一步的方向
- 第一行的最小值即为视差点
这里不容易理解,其实它和Leetcode的最短路径的题是相似的
题目:给定一个矩阵,从左上角开始每次只能向右或者向下移动,最后到达右下角的位置,路径上的所有的数字累加起来作为这条路径的路劲和。要求返回所有路径和中的最小路径和
1 3 1 1 5 1 4 2 1 路径1,3,1,1,1,1是所有路径中路径和最小的,所以返回其和7。
- 第一步:起始点1
- 第二步:如果一直向下或者向右:
1 4 5 2 5 1 6 2 1
- 第三步:计算第二行第二列的值,比较第一行第二列和第二行第一列的数谁小就选谁,依次类推。
1 4 5 2 7 6
1 4 5 2 7 6 6 8
1 4 5 2 7 6 6 8 7
-
最小路径和的代码
- int minPathSum1(int matrix[][col], int dp[][col], int path[][col])
- {
- if(matrix == NULL)
- {
- return 0;
- }
-
- dp[0][0] = matrix[0][0];
-
- //计算第一列的值
- for(int i = 1; i < row; i ++)
- {
- dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0] + matrix[i][0];
-
- path[i][0] = 0;
- }
-
- //计算第一行的值
- for(int j = 1; j < col; j++)
- {
- dp[0][j] = dp[0][j- 1] + matrix[0][j];
-
- path[0][j] = 1;
- }
-
- //计算其它的值
- for(int i = 1; i < row; i++)
- {
- for(int j = 1; j < col; j++)
- {
- int direction = dp[i][j-1] < dp[i-1][j] ? 1 : 0;
- dp[i][j] = (direction ? dp[i][j-1] : dp[i-1][j]) + matrix[i][j];
- path[i][j] = direction;
- }
- }//for
-
-
- return dp[row - 1][col - 1];
- }
- dp视差空间代码
- // (1) set last entry sink in matrix (last value)
- // (2-3) Initializ Edges
- // (2) initialize travelpath for last col (only south direction)
- // (3) initialize travelpath for last row (only east direction)
- // (4) calculate paths till last sink (last entry) till xLast - 1, yLast - 1
- // (-) save all (chosen) directions along the way
- void DPmat::preCalc(Mat &matrix, Mat &sum, Mat &dirs) {
- float occlusion_south = 1.0f;
- float occlusion_east = 1.0f;
- sum = Mat::zeros(matrix.rows, matrix.cols, matrix.type()); // not initialized with zero, should not be a problem,
- dirs = Mat::zeros(matrix.rows, matrix.cols, CV_16U); // because traversion is pre initialized with borders
-
- // dirs = (1, south), (2, south-east), (3, east)
-
- int rowLast = matrix.rows - 1; // last index inclusive
- int colLast = matrix.cols - 1; // last index inclusive
-
- // (1) initialize sink (last Entry/ terminal point/ matrix exit value)
- sum.at<float>(rowLast, colLast) = matrix.at<float>(rowLast, colLast);
-
- // (2-3) Initialize Edges
-
- // (2) calculate all last row entries down to exit value | only downward directions (so upward pre calculation)
- for(int y = rowLast - 1; y >= 0; --y) {
- // sum[y,x] = M[y,x] * occlusion_south + sum[y+1,x]
- sum.at<float>(y, colLast) = matrix.at<float>(y, colLast) * occlusion_south + sum.at<float>(y + 1, colLast); // add current value + successor min(value)
- dirs.at<ushort>(y, colLast) = 1; // south
- }
-
- // (3) initialize last
- for(int x = colLast - 1; x >= 0; --x) {
- // sum[y,x] = M[y,x] * occlusion_east + sum[y+1,x]
- sum.at<float>(rowLast, x) = matrix.at<float>(rowLast, x) * occlusion_east + sum.at<float>(rowLast, x + 1); // add current value + successor min(value)
- dirs.at<ushort>(rowLast, x) = 3; // east
- }
-
- // (4) Main calculation (3 way [south(s), east(e), south-east(se)])
- for(int y = rowLast - 1; y >= 0; --y) {
- float* sum_ptr = sum.ptr<float>(y);
- float* sum_south_ptr = sum.ptr<float>(y+1);
- float* mat_ptr = matrix.ptr<float>(y);
- ushort* dirs_ptr = dirs.ptr<ushort>(y);
-
- for(int x = colLast - 1; x >= 0; --x) {
- // dirs
- //float s = sum.at<float>(y + 1, x);
- //float se = sum.at<float>(y + 1, x + 1);
- //float e = sum.at<float>(y, x + 1);
- float s = sum_south_ptr[x] * occlusion_south; // (y+1,x) occlusion dir
- float se = sum_south_ptr[x + 1]; // (y+1,x+1)
- float e = sum_ptr[x + 1] * occlusion_east; // (y, x+1) occlusion dir
-
- // lowest cost till current point
- float p = min(s, min(se, e));
-
- //sum.at<float>(y, x) = p + matrix.at<float>(y, x); // sum till current (cost + lowest path)
- sum_ptr[x] = p + mat_ptr[x]; // sum[y,x] = p + mat[y, x]
-
- // selection for traversion direction
- //if(p == s) dirs.at<ushort>(y, x) = 1; // occlusion
- //if(p == se) dirs.at<ushort>(y, x) = 2; // math
- //if(p == e) dirs.at<ushort>(y, x) = 3; // occlusion
-
- if(p == s) dirs_ptr[x] = 1; // occlusion
- if(p == se) dirs_ptr[x] = 2; // math
- if(p == e) dirs_ptr[x] = 3; // occlusion
- }
- }
- }
- void DPmat::disparityFromDirs(Mat &sum, Mat &dirs, Mat &disp, int line, int offset) {
- assert(dirs.type() == CV_16U);
-
- // wir bekommen jetzt einen index x, y
- int rowLast = dirs.rows - 1;
- int colLast = dirs.cols - 1;
-
- int lastval = -1;
- int x1 = 0;
- int x2 = 0;
-
- float minVal = numeric_limits<float>::max();
- int minIndex = 0;
- // seek top entry
- for(x2 = 0; x2 < sum.cols; ++x2) {
- float val = sum.at<float>(x1, x2);
- if(val > minVal) {
- minIndex = x2;
- minVal = val;
- }
- }
-
- x2 = minIndex;
-
- // safe x1, x2 as disparity match
- ushort disparity = abs(x2 - x1);
- ushort* disp_ptr = disp.ptr<ushort>(line);
-
- disp_ptr[x1 + offset] = disparity;
-
- while(x1 < rowLast && x2 < colLast) {
- ushort d = dirs.at<ushort>(x1, x2);
-
- if(d == 1) { // 1 = down, skipping left index, left got occloded (occlusion from right)
- x1++;
- if(lastval >= 0) disp_ptr[x1 + offset] = lastval; // dips[line, x1 + offset] = lastval
- //disp_ptr[x1 + offset] = 0;
- }
- if(d == 2) { // match
- // next entry will be match
- x1++;
- x2++;
- disparity = abs(x2 - x1);
-
- disp_ptr[x1 + offset] = disparity;
- lastval = disparity;
- }
- if(d == 3) { // 2 = right, skipping right index, occlusion don't care..
- x2++;
- if(lastval >= 0) disp_ptr[x1 + offset] = lastval; // dips[line, x1 + offset] = lastval
- //disp_ptr[x1 + offset]= 0;
- }
- }
- }
原图像:


视差图像:

结论:
这种只考虑了图像左右相邻像素的视差约束,而忽略了上下领域像素之间的视差约束,这种方法得到的解因此也称为扫描线最优解,不能称为严格意义上的最优解,视差图像也出现了明显的横向条纹瑕疵。而且其计算时间也比较慢
![]()
- 组件之间数据通信调用组件wxmlbind+组件内的方法名 -->
赞
踩


