- 1Java单机版五子棋的设计与实现(团队)_五子连珠游戏设计与实现
- 2DVWA的Xss跨站脚本攻击(反射型)_反射型xss攻击实例
- 3MySQL的数据类型都有哪些?它们分别用在什么的场景?_说明下列数据类型的不同应用场合。 year/int,float/decimal,varchar/bi
- 4vue项目转桌面应用程序_如何将一个springboot+vue项目打包成桌面应用
- 5PyTorch搭建卷积神经网络(CNN)实现手写数字识别_基于pytorch搭建cnn实现手写数字识别
- 6【完全开源】小安派-Eyes-R1/R2——4寸RGB屏幕驱动板_rgb屏幕电路
- 7Spring Boot 配置Druid监控以及基本特征监测使用_druid.filter.stat.db-type
- 8CSS(五)
- 9安卓studio连接手机之后,一两秒之后就自动断开了。问题解决。
- 10Kubernetes PodSecurityPolicy_kuboard 创建cephfs 检查podsecuritypolicy: cephfs-csi-n
剑指Offer 链表题目集合
赞
踩
从尾到头打印链表
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d0267f7f55b3412ba93bd35cfa8e8035
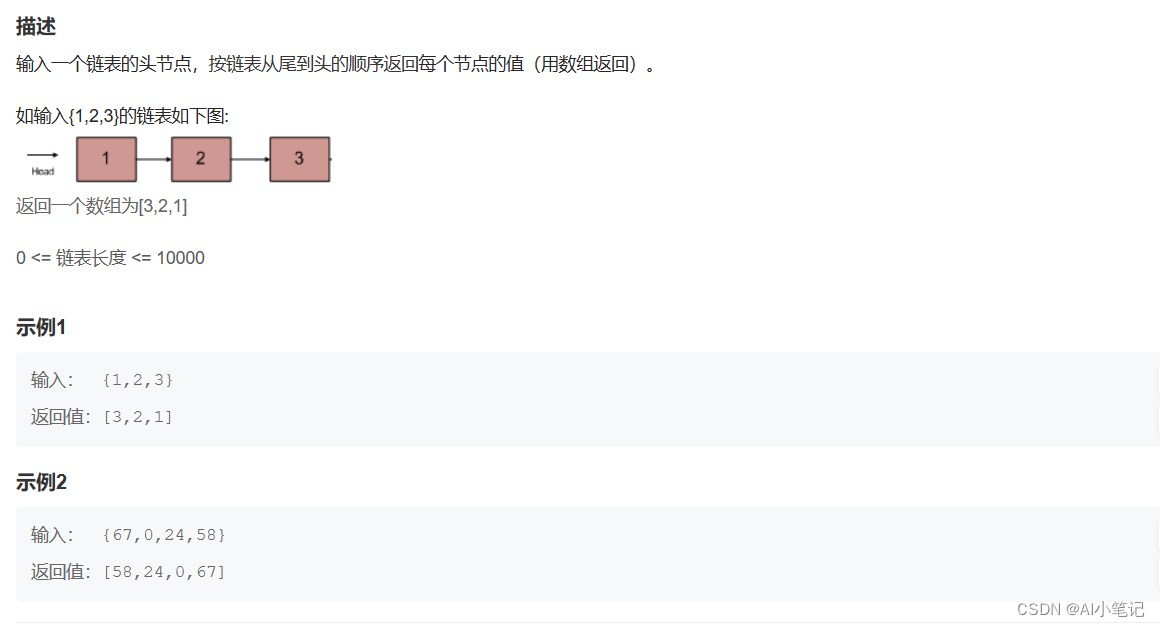
题目描述
思路一:
我的第一想法是可以遍历链表,将每个节点的值存入数组中,然后将数组进行反转。

复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。正向遍历一遍链表。
空间复杂度:O(n)。额外使用一个数组存储链表中的每个节点。
python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None # # 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 # # # @param listNode ListNode类 # @return int整型一维数组 # class Solution: def printListFromTailToHead(self , listNode: ListNode) -> List[int]: res = [] while listNode: res.append(listNode.val) listNode = listNode.next return res[::-1]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
C++
/** * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : * val(x), next(NULL) { * } * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) { vector<int> result; ListNode* current = head; while (current != nullptr) { result.push_back(current->val); current = current->next; } reverse(result.begin(), result.end()); return result; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
反转链表
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/75e878df47f24fdc9dc3e400ec6058ca
题目描述

思路一:
采用双指针迭代,在遍历链表时,将当前节点的next 指针改为指向前一个节点。由于节点没有引用其前一个节点,因此必须事先存储其前一个节点。在更改引用之前,还需要存储后一个节点。最后返回新的头引用。

复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),正向遍历一遍链表。
空间复杂度:O(1),常数空间复杂度。
python3
# class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None # # 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 # # # @param head ListNode类 # @return ListNode类 # class Solution: def ReverseList(self , head: ListNode) -> ListNode: # write code here pre , cur = None ,head while cur: # 暂存后继节点 cur.next tmp = cur.next # 修改 next 引用指向 cur.next = pre # pre 暂存 cur pre = cur # cur 访问下一节点 cur = tmp return pre
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
C++
/** * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * * * @param head ListNode类 * @return ListNode类 */ ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* head) { ListNode *cur = head,*pre=nullptr; while(cur != nullptr){ // 暂存后继节点 cur.next ListNode *tmp = cur->next; // 修改 next 引用指向 cur->next = pre; // pre 暂存 cur pre = cur; // cur 访问下一节点 cur = tmp; } return pre; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
合并两个排序的链表
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d8b6b4358f774294a89de2a6ac4d9337
题目描述


思路一:
由于两个链表是递增的,可以使用双指针遍历两个链表,通过pHead1.val与pHead2.val的大小关系确定节点添加顺序,两节点指针交替前进,直至遍历完毕。

复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m+n),m,n 分别为两个链表的长度。
空间复杂度:O(1),常数空间复杂度。
python3
# class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None # # 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 # # # @param pHead1 ListNode类 # @param pHead2 ListNode类 # @return ListNode类 # class Solution: def Merge(self , pHead1: ListNode, pHead2: ListNode) -> ListNode: cur = head = ListNode(0) while pHead1 and pHead2: if pHead1.val <= pHead2.val: cur.next, pHead1 = pHead1, pHead1.next else: cur.next, pHead2 = pHead2, pHead2.next cur = cur.next cur.next = pHead1 if pHead1 else pHead2 return head.next
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
C++
/** * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * * * @param pHead1 ListNode类 * @param pHead2 ListNode类 * @return ListNode类 */ ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { ListNode *cur = new ListNode(0); ListNode *head = cur; while(pHead1 != nullptr && pHead2 != nullptr){ if(pHead1->val <= pHead2->val){ cur->next = pHead1; pHead1 = pHead1->next; } else{ cur->next = pHead2; pHead2 = pHead2->next; } cur = cur->next; } cur->next = pHead1 ? pHead1 : pHead2; return head->next; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
两个链表的第一个公共结点
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6ab1d9a29e88450685099d45c9e31e46
题目描述

思路一:
两个链表长度不一定相等,但两个链表相加的长度是相等的,即L1+L2 = L2+L1,使用两个指针分别从两个链表头节点出发,两个指针分别走完当前链表后,再从另一个链表重新开始走,直到相遇。

复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m+n),需遍历m + n 个节点。
空间复杂度:O(1),常数空间复杂度。
python3
# class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None # # # @param pHead1 ListNode类 # @param pHead2 ListNode类 # @return ListNode类 # class Solution: def FindFirstCommonNode(self , pHead1 , pHead2 ): p1 = pHead1 p2 = pHead2 while p1 != p2: p1 = p1.next if p1 else pHead2 p2 = p2.next if p2 else pHead1 return p1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
C++
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } };*/ class Solution { public: ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { ListNode *p1 = pHead1; ListNode *p2 = pHead2; while (p1 != p2) { p1 = (p1 ? p1->next : pHead2); p2 = (p2 ? p2->next : pHead1); } return p1; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
链表中环的入口结点
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/253d2c59ec3e4bc68da16833f79a38e4
题目描述

思路一:
可以通过哈希表来实现。遍历链表,如果节点在哈希表中,则说明这个节点就是环的入口节点,否则就将该节点存入哈希表。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),需遍历链表。
空间复杂度:O(n),至多存整个链表的所有的结点。
python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
nodes = {}
while pHead:
if pHead in nodes:
return pHead
else:
nodes[pHead] = 1
pHead = pHead.next
return None
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
C++
/* struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next; ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) { } }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) { std::unordered_map<ListNode*, int> nodes; while (pHead) { if (nodes.find(pHead) != nodes.end()) { return pHead; } else { nodes[pHead] = 1; pHead = pHead->next; } } return nullptr; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
链表中倒数最后k个结点
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/886370fe658f41b498d40fb34ae76ff9
题目描述

思路一:
快慢针间隔k步,然后遍历链表,快慢指针同步移动,当快指针到达链表尾部的时候,慢指针正好到了倒数k个元素的位置。

复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),需遍历链表。
空间复杂度:O(1),常数级指针变量,无额外辅助空间使用。
python3
# class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None # # 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 # # # @param pHead ListNode类 # @param k int整型 # @return ListNode类 # class Solution: def FindKthToTail(self , pHead: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode: p1 = p2 = pHead for i in range(k): if p2 != None: p2 = p2.next #达不到k步说明链表过短,没有倒数k else: return None while p2: p2 = p2.next p1 = p1.next return p1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
C++
/** * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * * * @param pHead ListNode类 * @param k int整型 * @return ListNode类 */ ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) { ListNode* p1 = pHead; ListNode* p2 = pHead; for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) { if (p2 != nullptr) { p2 = p2->next; } else { return nullptr; // 链表过短,没有倒数第 k 个节点 } } while (p2 != nullptr) { p2 = p2->next; p1 = p1->next; } return p1; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
删除链表的节点
刷题链接:
https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/f9f78ca89ad643c99701a7142bd59f5d
题目描述

思路一:
双指针遍历链表,找到目标节点,则将pre.next指向cur.next。

复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),需遍历链表。
空间复杂度:O(1),常数级指针变量,无额外辅助空间使用。
python3
# class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None # # 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 # # # @param head ListNode类 # @param val int整型 # @return ListNode类 # class Solution: def deleteNode(self , head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode: if(head.val == val):return head.next pre = head cur = head.next while cur != None and cur.val != val: pre =cur cur = cur.next pre.next = cur.next return head
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
C++
/** * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * * * @param head ListNode类 * @param val int整型 * @return ListNode类 */ ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) { if (head == nullptr) { return nullptr; } if (head->val == val) { return head->next; } ListNode* pre = head; ListNode* cur = head->next; while (cur != nullptr && cur->val != val) { pre = pre->next; cur = cur->next; } pre->next = cur->next; return head; } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38



