- 1我的书签菜单_聚bt网址
- 2SLA(服务等级协议)_服务可用性sla
- 3Baidu Comate——基于AI的智能代码生成让你的编码更快、更好、更简单!_指新用户在ide中安装comate插件,并在问答区有技术类的提问,或者在编码区有采纳行
- 4Java|IDEA 运行和打包报错解决_java: java.lang.nosuchfielderror: class com.sun.to
- 5Github 2024-05-21 开源项目日报 Top10
- 6Android Studio Gradle
- 7Openlayers的交互功能(六)——编辑图斑_openlayer modify
- 8CSDN上传付费资源需要创作者等级Lv3,我的升级之路_csdn 的 综合贡献分
- 9Endnote 保姆级攻略:参考文献插入与删除、Style修改、文档格式转化(转载)_endnote插入引文 参考文献格式
- 10人工智能 ai java_人工智能需要java吗
RabbitMQ:第一章:6 种工作模式以及消息确认机制(理论与代码相结合)
赞
踩
private static ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
static {
connectionFactory.setHost(“你的rabbitmq的ip地址”);
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);//RabbitMQ的默认端口号,根据实际情况修改
connectionFactory.setUsername(“你的rabbitmq的用户名称”);
connectionFactory.setPassword(“你的rabbitmq的用户密码”);
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(“你的rabbitmq的虚拟机”);
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = connectionFactory.newConnection();
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
简单模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
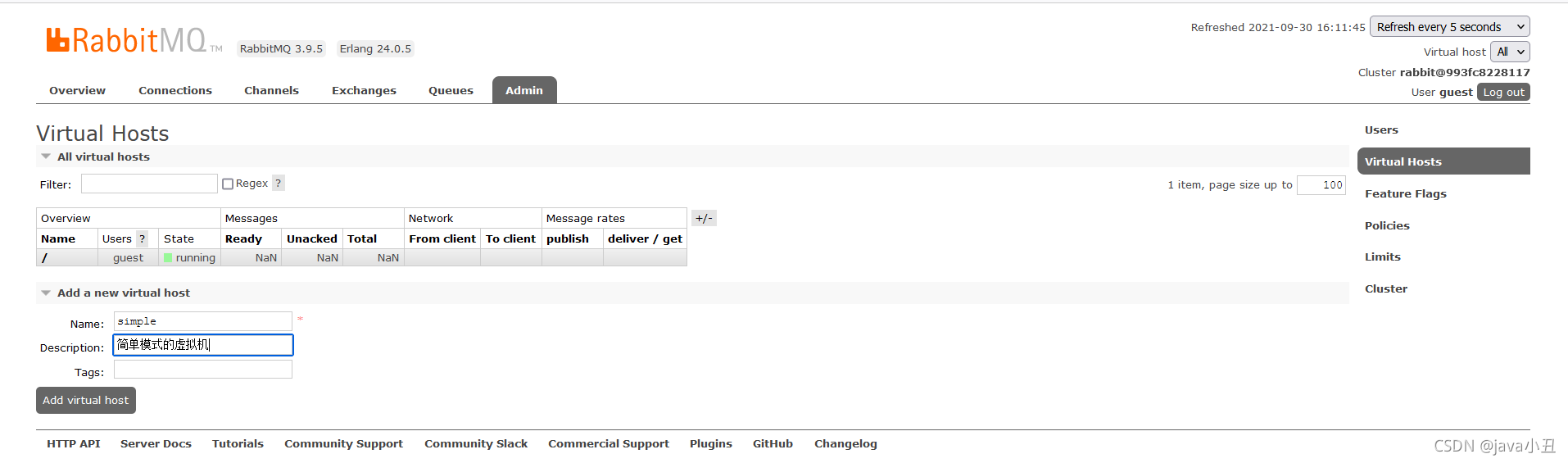
修改工具类的虚拟机:

生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection conn = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//创建通信“通道”,相当于TCP中的虚拟连接
Channel channel = conn.createChannel();
//创建队列,声明并创建一个队列,如果队列已存在,则使用这个队列
//channel.queueDeclare的五个参数
//第一个参数:队列名称ID
//第二个参数:是否持久化,false对应不持久化数据,MQ停掉数据就会丢失
//第三个参数:是否队列私有化,false则代表所有消费者都可以访问,true代表只有第一次拥有它的消费者才能一直使用,其他消费者不让访问
//第四个:是否自动删除,false代表连接停掉后不自动删除掉这个队列
//其他额外的参数, null
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST,false, false, false, null);
String message = “要发送的message”;
//channel.basicPublish的四个参数
//exchange 交换机,暂时用不到,在后面进行发布订阅时才会用到
//队列名称
//额外的设置属性
//最后一个参数是要传递的消息字节数组
channel.basicPublish(“”, RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST, null,message.getBytes());
channel.close();
conn.close();
System.out.println(“=发送成功=”);
}
}
消费者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//获取TCP长连接
Connection conn = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//创建通信“通道”,相当于TCP中的虚拟连接
Channel channel = conn.createChannel();
//创建队列,声明并创建一个队列,如果队列已存在,则使用这个队列
//第一个参数:队列名称ID
//第二个参数:是否持久化,false对应不持久化数据,MQ停掉数据就会丢失
//第三个参数:是否队列私有化,false则代表所有消费者都可以访问,true代表只有第一次拥有它的消费者才能一直使用,其他消费者不让访问
//第四个:是否自动删除,false代表连接停掉后不自动删除掉这个队列
//其他额外的参数, null
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST,false, false, false, null);
//从MQ服务器中获取数据
//创建一个消息消费者
//第一个参数:队列名
//第二个参数代表是否自动确认收到消息,false代表手动编程来确认消息,这是MQ的推荐做法
//第三个参数要传入DefaultConsumer的实现类
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TEST, false, new Reciver(channel));
}
}
class Reciver extends DefaultConsumer {
private Channel channel;
//重写构造函数,Channel通道对象需要从外层传入,在handleDelivery中要用到
public Reciver(Channel channel) {
super(channel);
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(“消费者接收到的消息:”+message);
System.out.println(“消息的TagId:”+envelope.getDeliveryTag());
//false只确认签收当前的消息,设置为true的时候则代表签收该消费者所有未签收的消息
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
我先启动消费者后启动生产者,这样只要生产者一生产消息,消费者就可以立马消费。
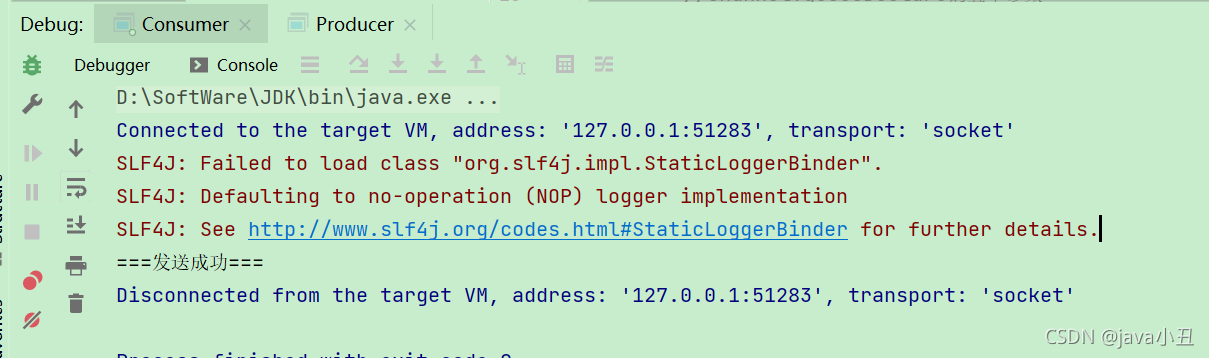

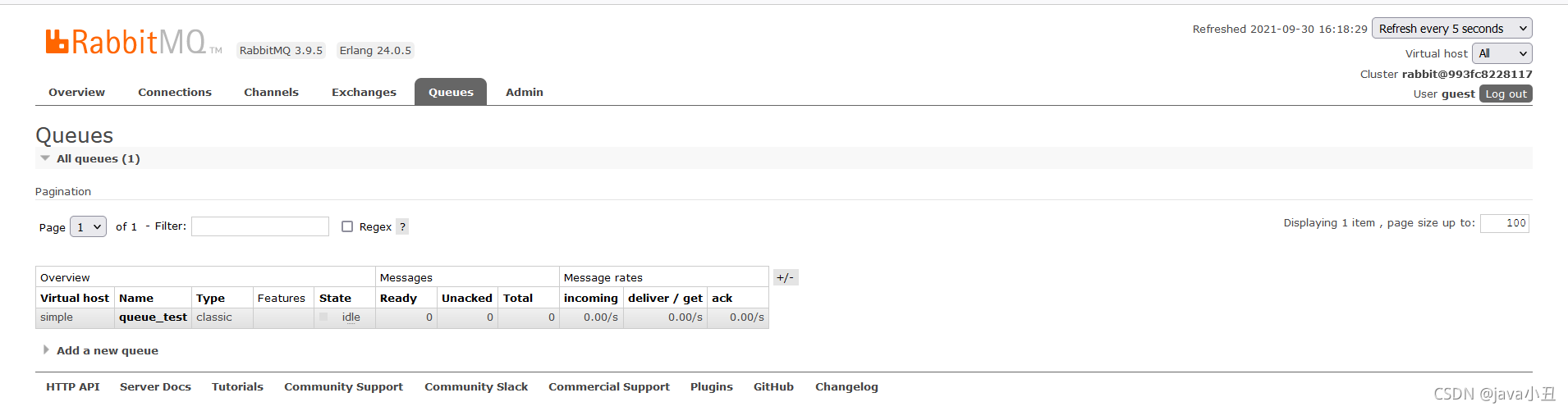
Work queues 工作队列模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
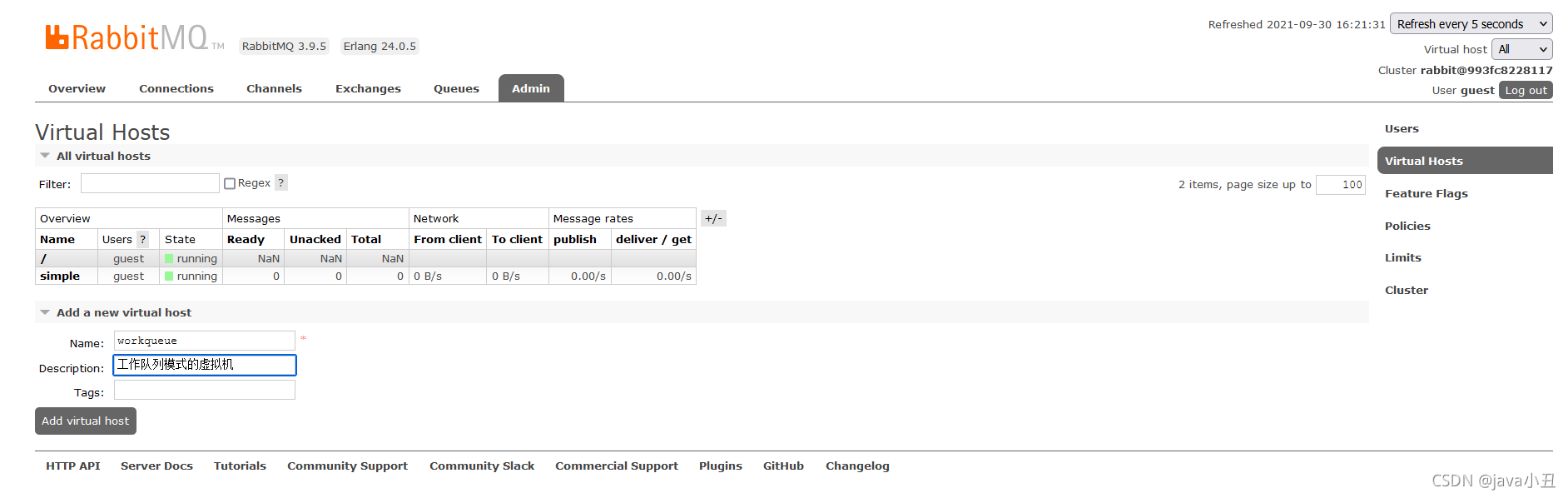 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

为了模拟某些业务,这里使用自定义实体类发送消息,所以我新建了一个自定义实体类
/**
- 自定义的实体类:发送内容
*/
public class SenderContent {
private String name;
private String content;
public SenderContent(String name, String content) {
this.name = name;
this.content = content;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
/**
- 生成者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++) {
SenderContent senderContent = new SenderContent(“姓名:” + i, “内容:” + i);
String jsonSMS = new Gson().toJson(senderContent);
channel.basicPublish(“” , RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , null , jsonSMS.getBytes());
}
System.out.println(“发送数据成功”);
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
//如果不写basicQos(1),则自动MQ会将所有请求平均发送给所有消费者
//basicQos,MQ不再对消费者一次发送多个请求,而是消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String jsonSMS = new String(body);
System.out.println(“ConsumerOne-发送成功:” + jsonSMS);
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//确认签收
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
//如果不写basicQos(1),则自动MQ会将所有请求平均发送给所有消费者
//basicQos,MQ不再对消费者一次发送多个请求,而是消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String jsonSMS = new String(body);
System.out.println(“ConsumerTwo-发送成功:” + jsonSMS);
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//确认签收
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者三:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者3
*/
public class ConsumerThree {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT, false, false, false, null);
//如果不写basicQos(1),则自动MQ会将所有请求平均发送给所有消费者
//basicQos,MQ不再对消费者一次发送多个请求,而是消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_SENDER_CONTENT , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String jsonSMS = new String(body);
System.out.println(“ConsumerThree-发送成功:” + jsonSMS);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//确认签收
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
这里对每个消费者设置不同的休眠时间演示每个消费者处理业务的时间不同,查看消息消费的情况
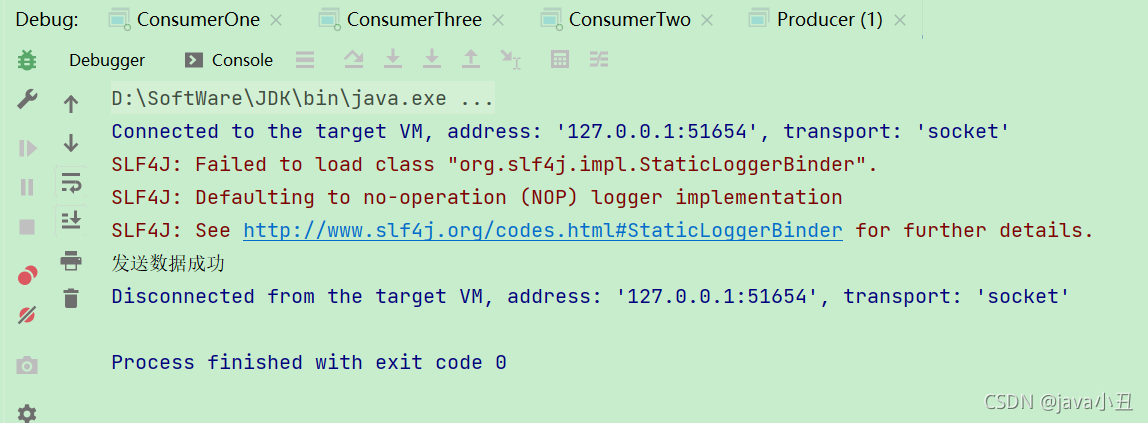
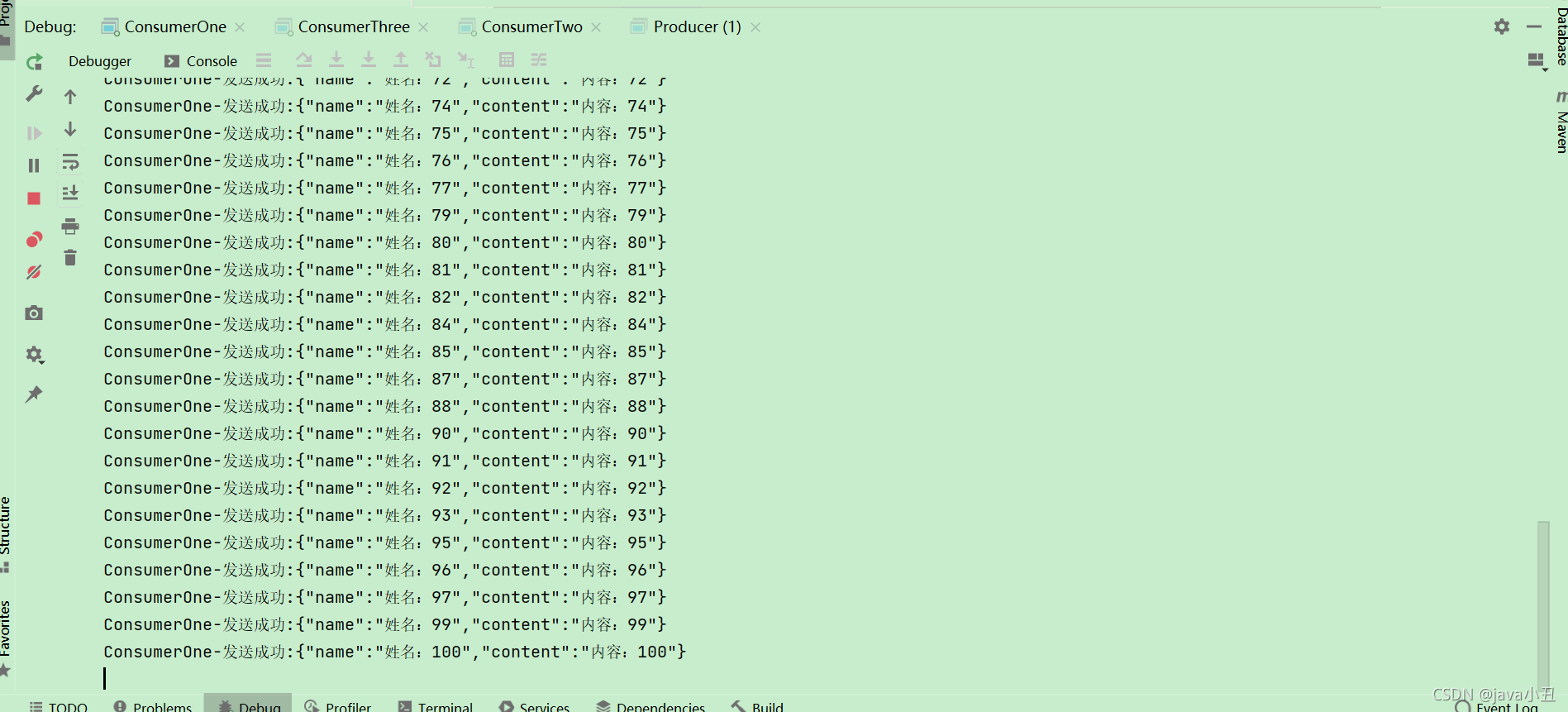
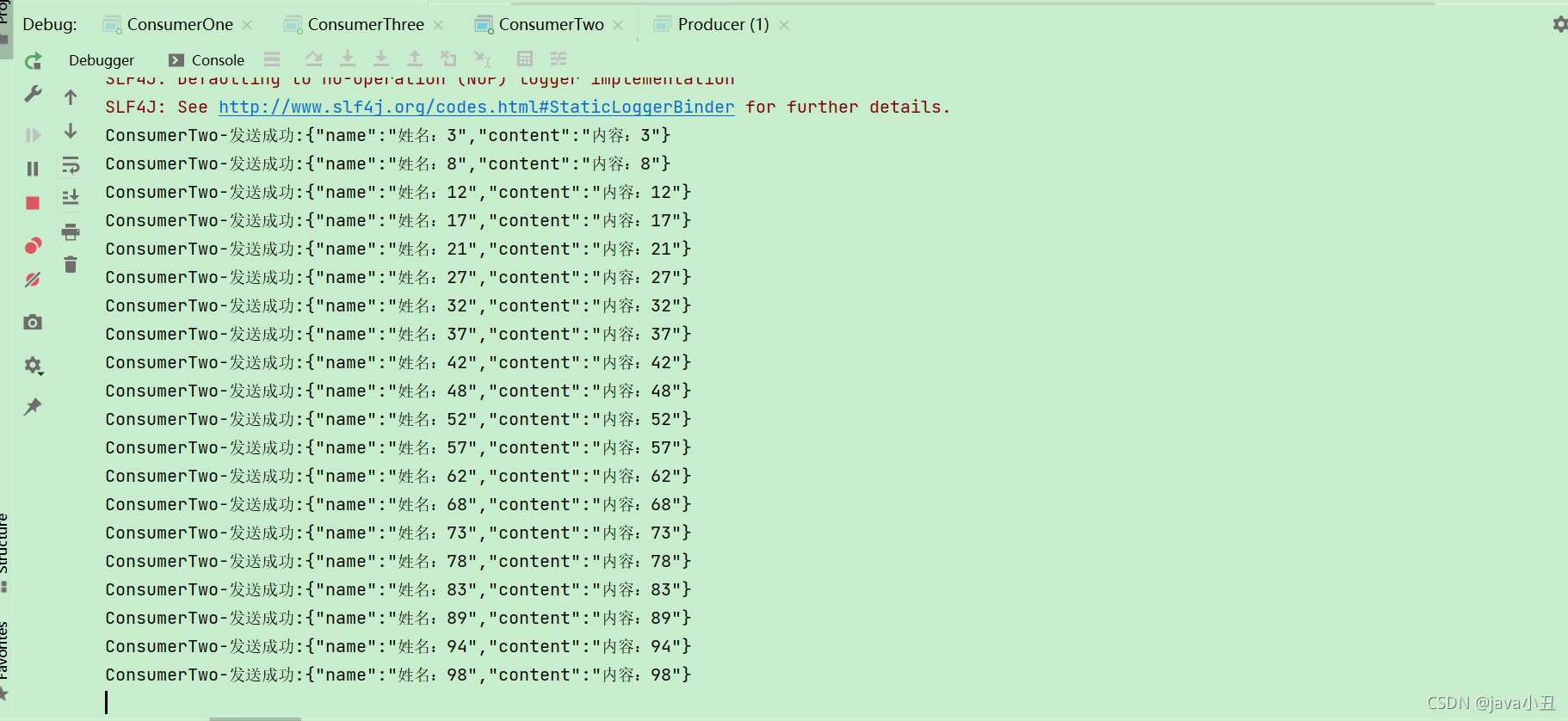
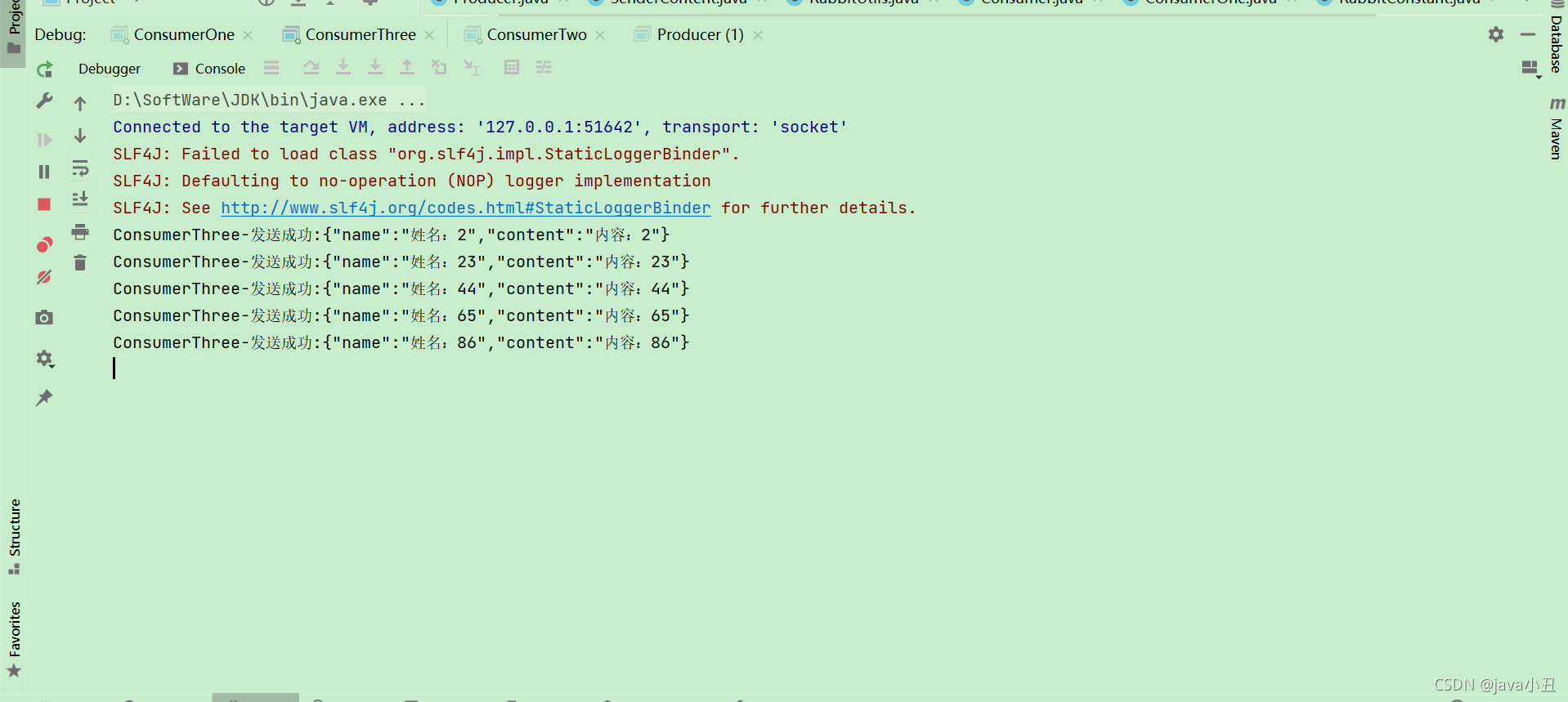
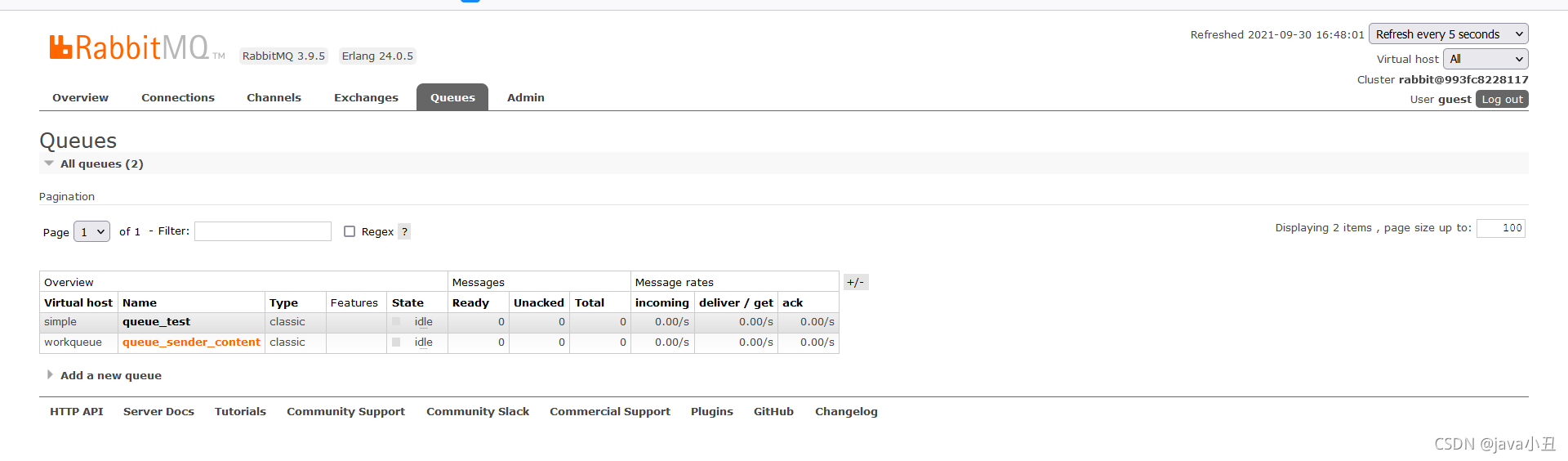
可以看出消费者一消费的最多,消费者三消费的最少,因为代码中设置了这个
channel.basicQos(1);//处理完一个取一个
消费者处理完一个消息后(确认后),在从队列中获取一个新的。
Pub/Sub 订阅模式 :
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
 创建一个交换机:这里用广播模式作为交换机的类型用来演示
创建一个交换机:这里用广播模式作为交换机的类型用来演示
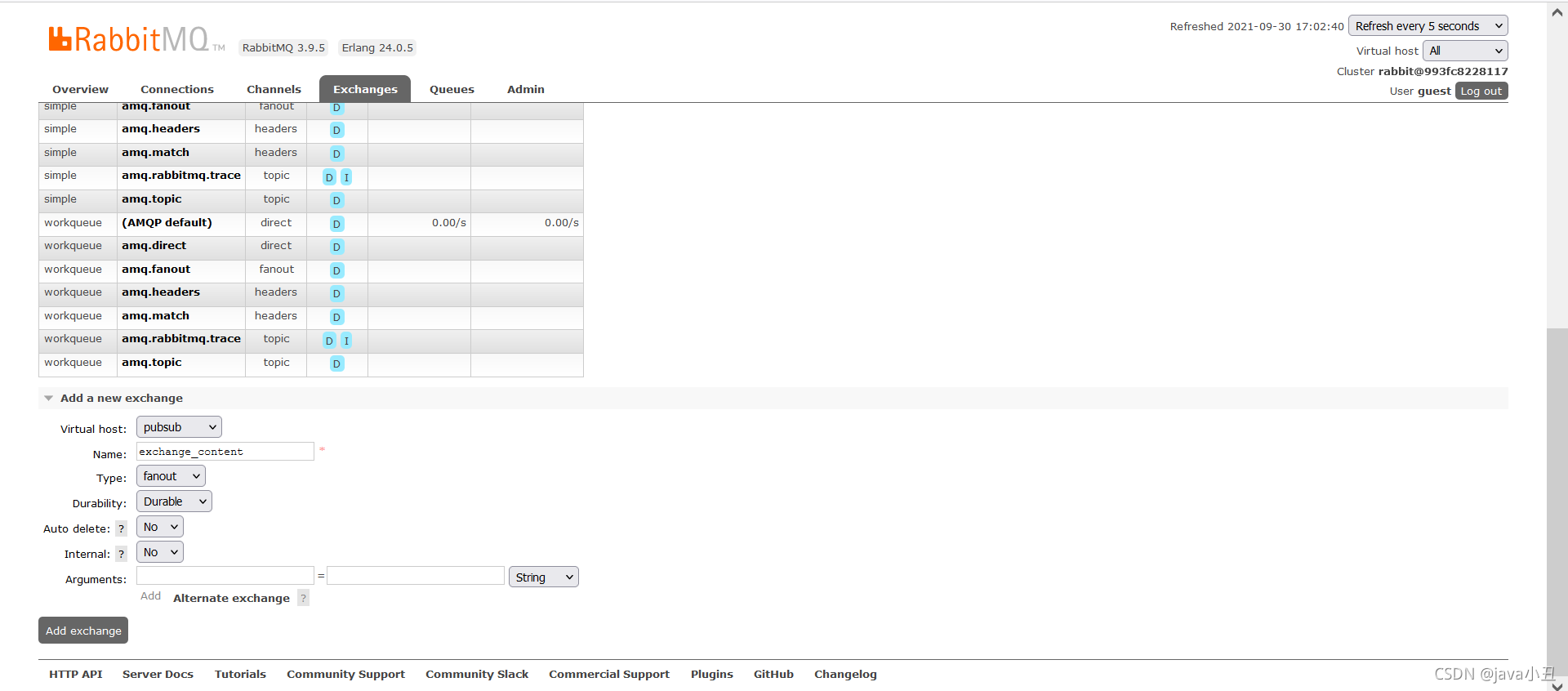
修改工具类的虚拟机

生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
- 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//键盘输入
String input = new Scanner(System.in).next();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//第一个参数交换机名字 其他参数和之前的一样
channel.basicPublish(RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT,“” , null , input.getBytes());
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//获取虚拟连接
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列信息
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key(暂时用不到)
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT, “”);
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(“消费者一收到信息:” + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取TCP长连接
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
//获取虚拟连接
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列信息
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key(暂时用不到)
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT, “”);
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(“消费者二收到信息:” + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
演示效果:
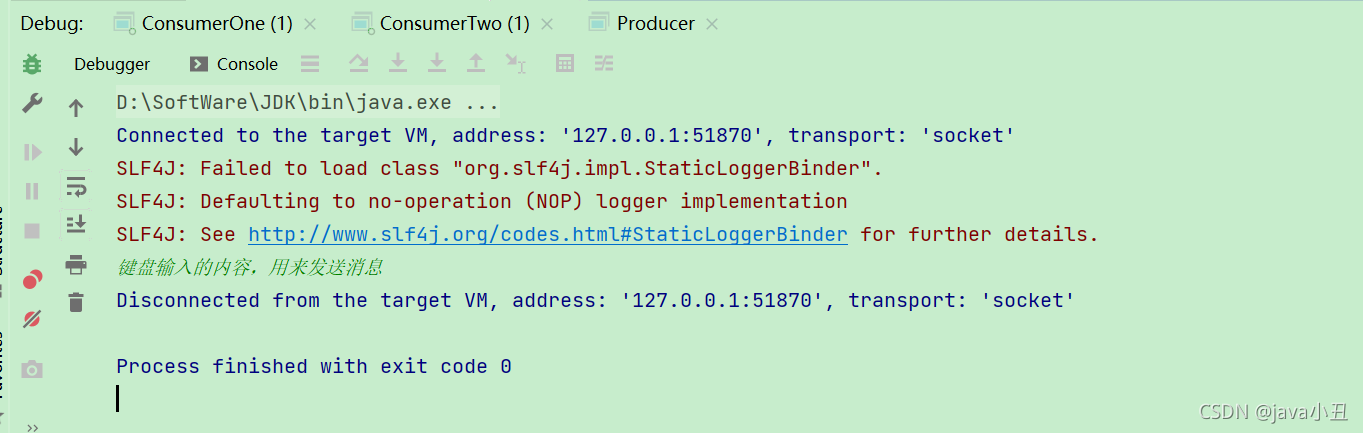

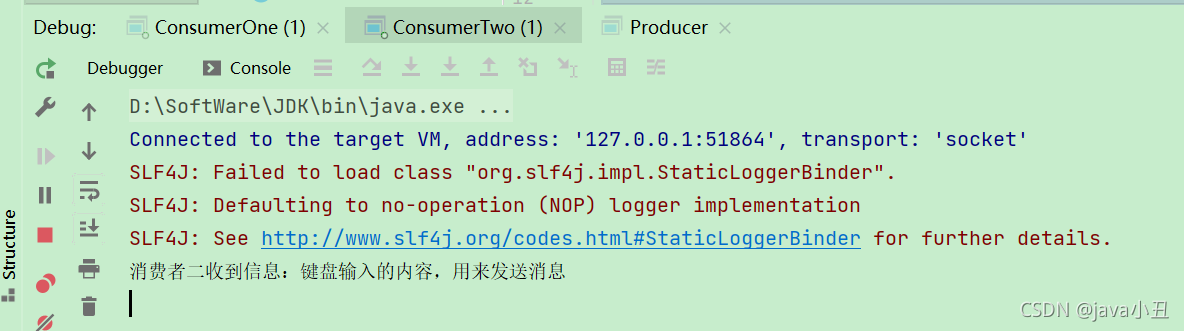
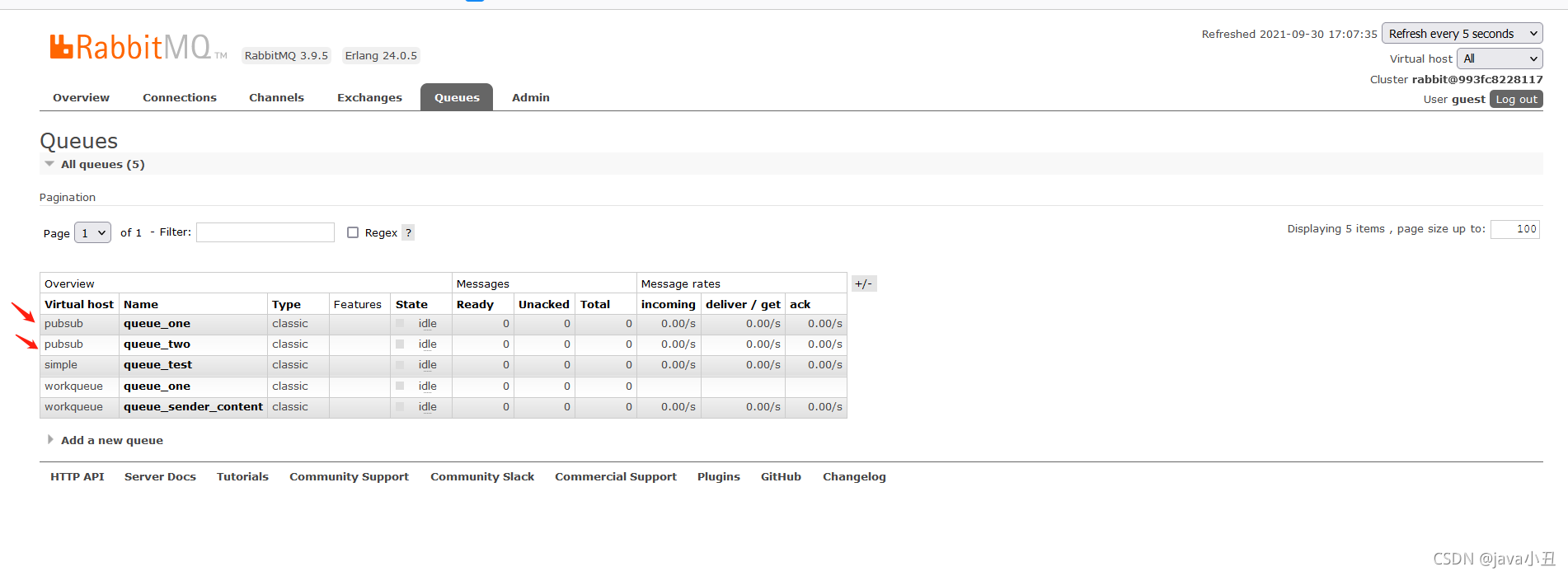
Routing 路由模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
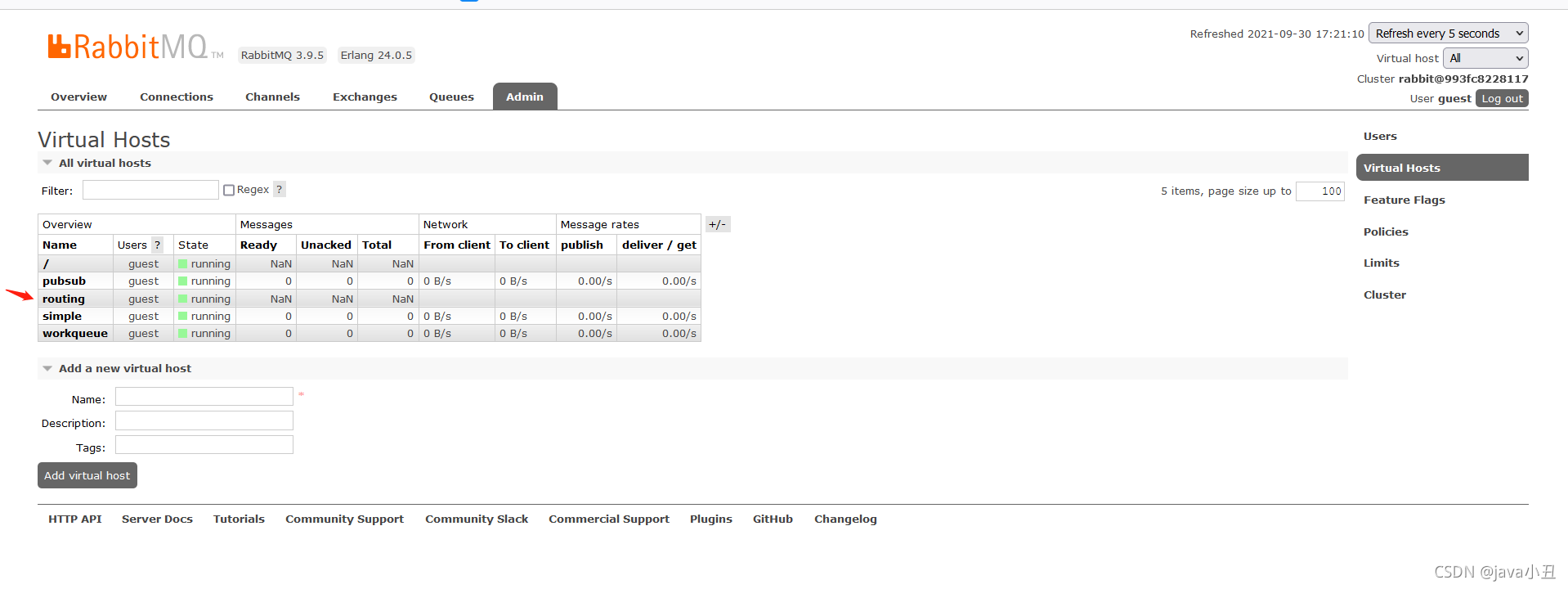 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

创建交换机:这里的交换机type类型一定要改成routing模式,如果还是广播模式的fanout的话,跟上面发布和订阅模式出现的效果会是一样的。
错误实例:
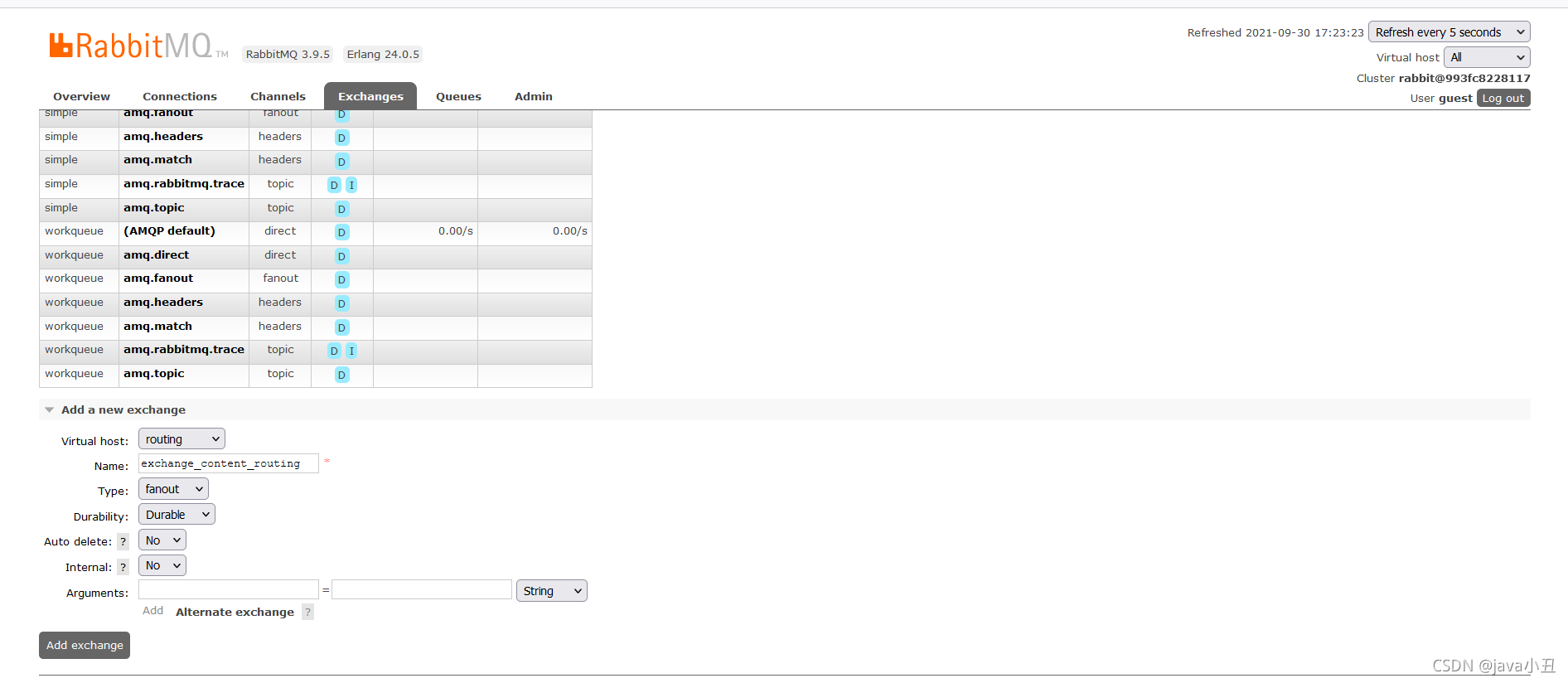 正确的实例:
正确的实例:
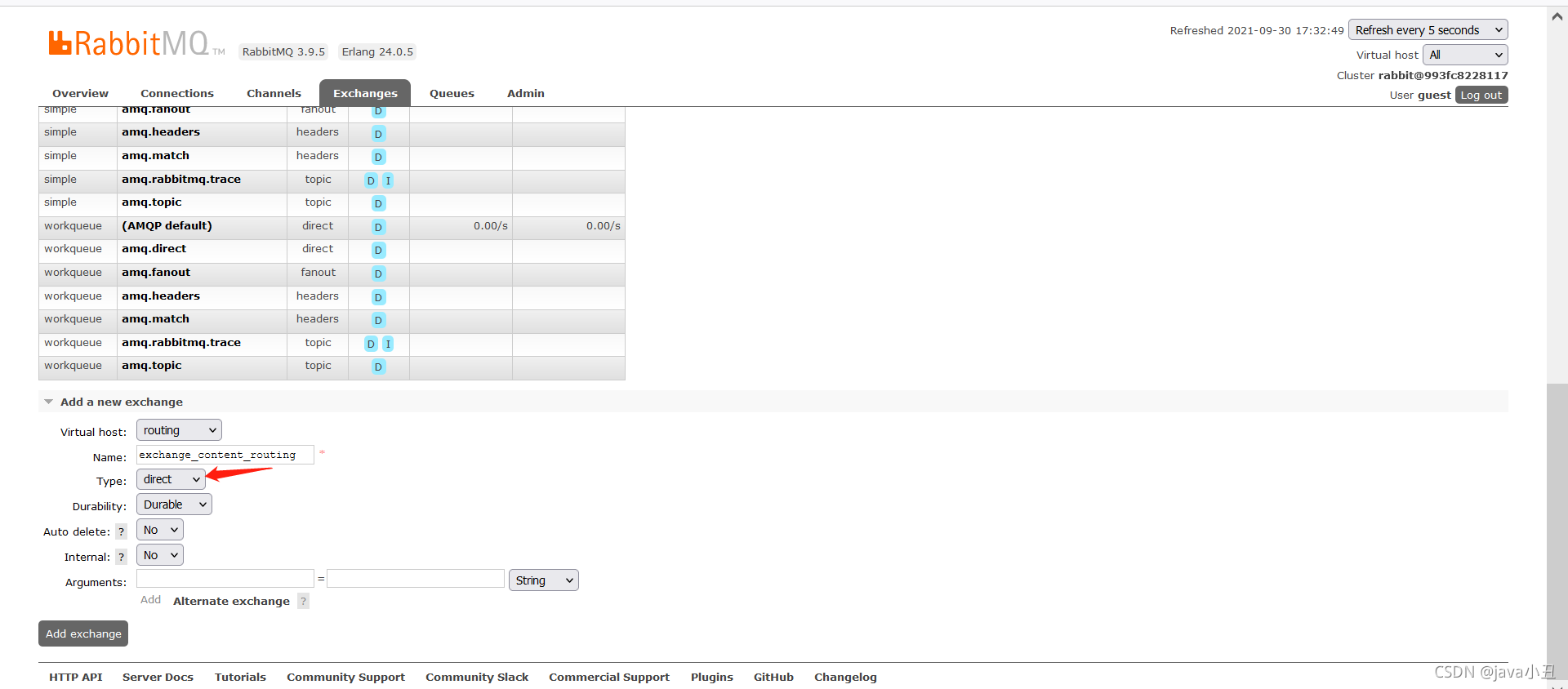 生产者:
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
- 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map area = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
area.put(“routing.one.a.20201127”, “中国湖南长沙20201127私密数据”);
area.put(“routing.one.d.20201128”, “中国河北石家庄20201128私密数据”);
area.put(“routing.two.b.20201127”, “中国湖北武汉20201127私密数据”);
area.put(“routing.two.e.20201128”, “中国湖北武汉20201128私密数据”);
area.put(“routing.three.c.20201127”, “中国湖南株洲20201128私密数据”);
area.put(“routing.three.f.20201128”, “中国河南郑州20201128私密数据”);
area.put(“us.one.a.20201127”, “美国加州洛杉矶20201127私密数据”);
area.put(“us.two.b.20201128”, “美国加州洛杉矶20201128私密数据”);
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> itr = area.entrySet().iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> me = itr.next();
//第一个参数交换机名字 第二个参数作为 消息的routing key
channel.basicPublish(RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING,me.getKey() , null , me.getValue().getBytes());
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者一:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者1
*/
public class ConsumerOne {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, “routing.one.a.20201127”);
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, “us.one.a.20201127”);
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_ONE , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(“消费者1收到信息:” + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
消费者二:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
- 消费者2
*/
public class ConsumerTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Connection connection = RabbitUtils.getConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, false, false, false, null);
//queueBind用于将队列与交换机绑定
//参数1:队列名 参数2:交互机名 参数三:路由key
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, “routing.one.d.20201128”);
channel.queueBind(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO, RabbitConstant.EXCHANGE_CONTENT_ROUTING, “routing.two.e.20201128”);
channel.basicQos(1);
channel.basicConsume(RabbitConstant.QUEUE_TWO , false , new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(“消费者2收到信息:” + new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag() , false);
}
});
}
}
效果:
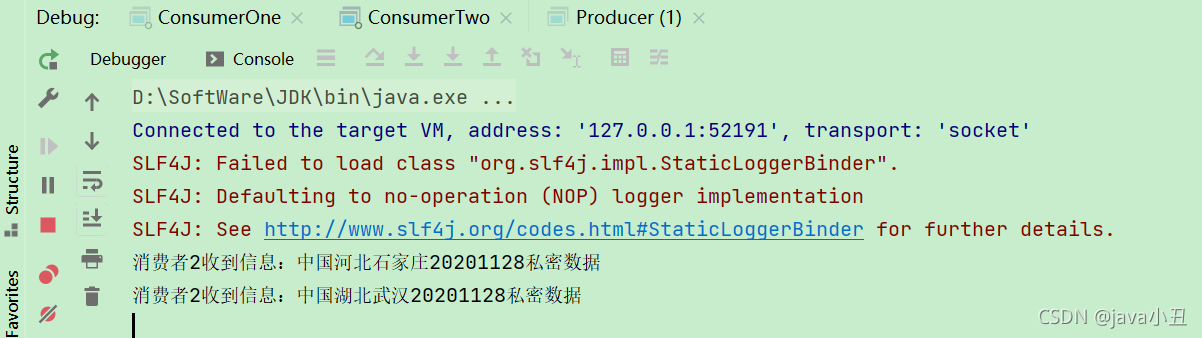
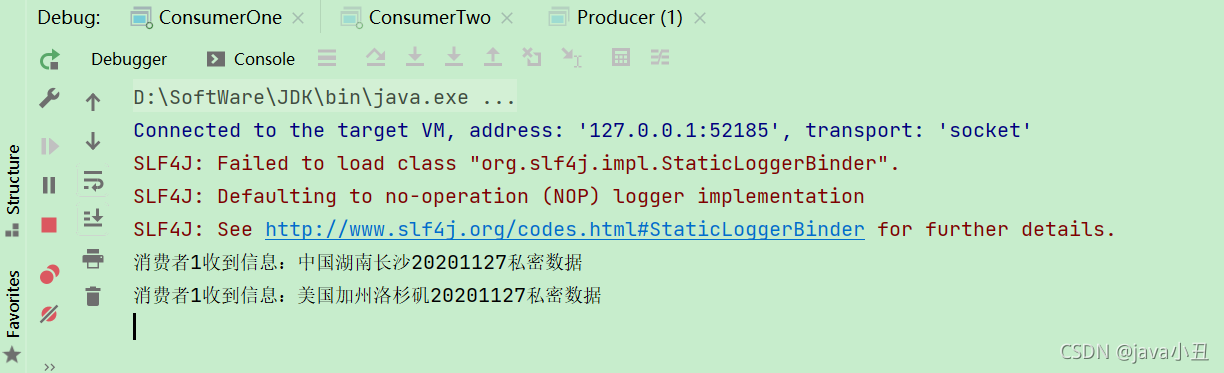
 路由模式需要消费者指定路由key
路由模式需要消费者指定路由key
Topics 通配符模式:
为了区分好理解,我每个模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
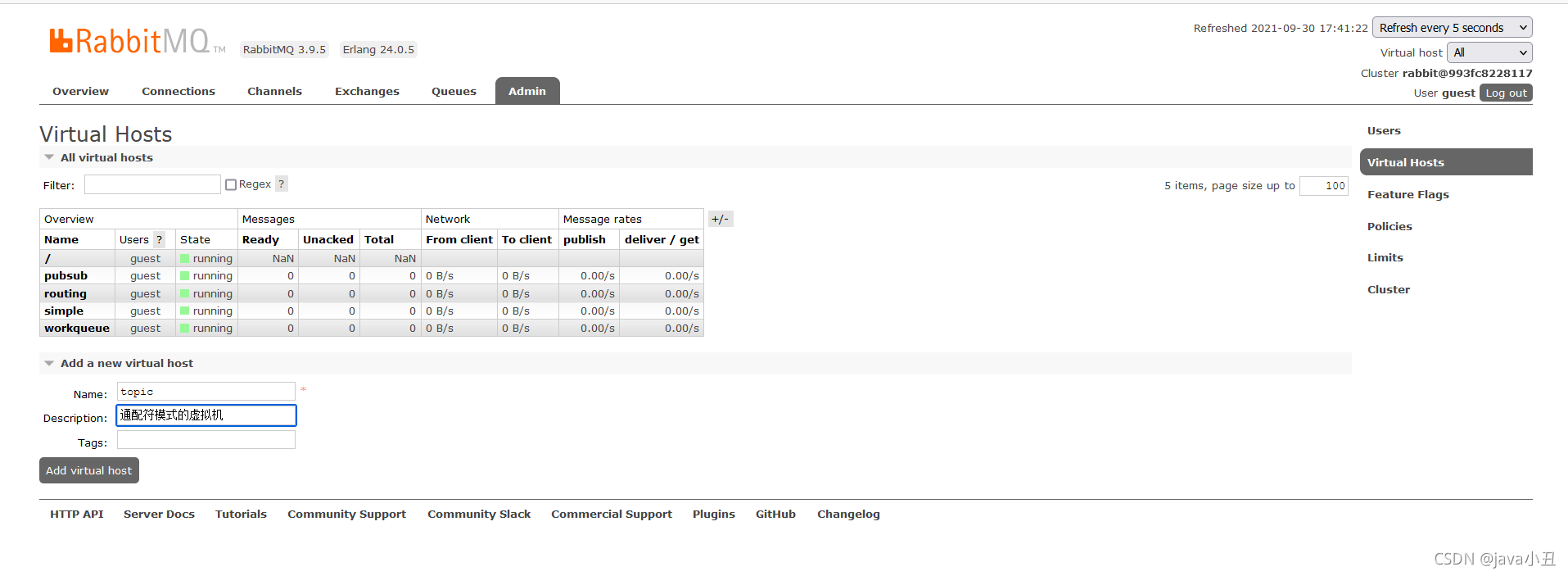 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

创建交互机,类型为topic
 生产者:
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
- 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
最后
分享一些资料给大家,我觉得这些都是很有用的东西,大家也可以跟着来学习,查漏补缺。
《Java高级面试》

《Java高级架构知识》

《算法知识》

模式都去创建一个虚拟机,这里我先去rabbitMq管控页面创建一个虚拟机
 修改工具类的虚拟机
修改工具类的虚拟机

创建交互机,类型为topic
 生产者:
生产者:
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitConstant;
import com.liao.rabbitmq.utils.RabbitUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
- 发布者
*/
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
最后
分享一些资料给大家,我觉得这些都是很有用的东西,大家也可以跟着来学习,查漏补缺。
《Java高级面试》
[外链图片转存中…(img-OIqoAHEF-1714438999323)]
《Java高级架构知识》
[外链图片转存中…(img-BKdSUFs8-1714438999324)]
《算法知识》
[外链图片转存中…(img-gPyJUKuG-1714438999324)]


