热门标签
热门文章
- 1web,jsp,html网站中英文切换,资源国际化解决方案及代码(其中包含动态切换数据源及URL拦截器)_jsp 切换语言
- 2css3动画性能优化--针对移动端卡顿问题
- 3边界值法中的上点、内点和离点分析
- 4综述 | 多模态 LLM,大模型的未来
- 5独家 | 一文读懂自然语言处理NLP(附学习资料)
- 6NLP:NLTK、spaCy、pattern库_nltk wordnet spacy
- 7LeetCode-热题100:74. 搜索二维矩阵
- 8pyqt5安装及基础_pyuic5' 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序 或批处理文件。
- 9JavaScript高级面试题(2)_高级js 面试提
- 10CSS 媒体查询 @media【详解】_css媒体查询 @media
当前位置: article > 正文
UNet网络实现图像分割_基于unet的图像分割
作者:花生_TL007 | 2024-04-02 06:46:30
赞
踩
基于unet的图像分割
UNet网络实现图像分割
最近在b站上找到一篇UNet网络实现图像分割的教学视频,进行相关学习后决定记录相关知识和自己的理解。
标题首先,分享下教学视频:图像分割UNet硬核讲解(带你手撸unet代码)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
学习笔记(代码理解加相关知识拓展):
1.UNet网络介绍
不同于CNN网络,UNet网络大致的结构就是:

(左边是重复下采样->卷积,右边是重复上采样->卷积)
卷积->下采样->卷积->下采样…->下采样->卷积->上采样->卷积->上采样…->上采样
实现相关参数的解码与编码(左边编码、右边解码)。
2.各文件的理解与相关知识点的介绍
(1).data文件
#相关配置 from torch.utils.data import Dataset import os from utils import * from torchvision import transforms transforms = transforms.Compose( { transforms.ToTensor() # 归一化 } ) class Mydata(Dataset): def __init__(self,path): self.path = path self.name = os.listdir(os.path.join(path,'SegmentationClass')) #合并文件路径 def __len__(self): return len(self.name) def __getitem__(self, index): #index为索引 Segment_name = self.name[index] Segment_path = os.path.join(self.path,'SegmentationClass',Segment_name) Image_path = os.path.join(self.path,'JPEGImages',Segment_name.replace('png','jpg')) Segment_image = keep_image_size_open(Segment_path) Image = keep_image_size_open(Image_path) return transforms(Image),transforms(Segment_image) #实现图片类型的转换,定义相关的存储路径 if __name__ == '__main__': data = Mydata('F:\Artificial Intelligence\\U_net\data') print(data[0][0].shape) print(data[0][1].shape) #此文件定义相关文件的保存路径,并引用utils文件进行图片的相关处理
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
(2).utils文件
#图片预处理
from PIL import Image
def keep_image_size_open(path,size=(256,256)):
img = Image.open(path)
temp = max(img.size)
#取最大的边,做mask矩形
mask = Image.new('RGB',(temp,temp),(0,0,0))
mask.paste(img,(0,0))
#贴附操作
mask = mask.resize(size)
return mask
'''
取最大的边做mask矩形,并将图片贴到矩形中进行等比缩放,保证图片不会变形
'''
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
(3).net文件
上、下采样:
这里用图像金字塔进行讲解:
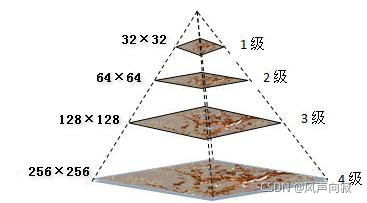
图像金子塔从下往上分辨率不断降低,即像素不断减小,最下层图像尺寸最大,分辨率最高。上一层图像是下一层图像的1/2,反过来下一层图像是上一层图像的2倍(图像的缩放)。
降采样:降采样之后图像大小是原图像MxN的M/2xN/2 ,就是对原图像删除偶数行与列,即得到降采样之后上一层的图片。
-对当前层进行高斯模糊
-删除当前层的偶数行与列
即可得到上一层的图像,这样上一层跟下一层相比,都只有它的1/4大小。
上采样:是与降采样相反,图像放大几乎都是采用内插值方法,即在原有图像像素的基础上在像素点之间采用合适的插值算法插入新的元素。
#实现UNet操作 import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import functional as F class Conv_Block(nn.Module): def __init__(self,in_channel,out_channel): super(Conv_Block, self).__init__() ''' torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True,padding_mode='zeros') in_channels(int):输入图像的channel(通道数),例如,RGB图像通道数为3 out_channels(int): 输出图像(特征层)的channel kernel_size(int or tuple):kernel(卷积核)的大小,kennel_size=5,意味着卷积大小(5,5)/5×5,kennel_size=(2,3),意味着卷积大小(2,3)/2×3 ,即非正方形卷积 stride(int or tuple,optional): 卷积的步长,默认为1,stride=2,意味着步长上下左右扫描皆为2, stride=(2,3),左右扫描步长为2、上下为3 padding(int or tuple,optional):四周pad的大小,默认为0,在卷积之前补0,四周都补0, dilation(int or tuple,optional): kernel元素间的距离,默认为1(dilation翻译为扩张,有时候也称为“空洞”1) groups(int ,optional):将原始输入channel划分成的组数,默认为1 bias(bool,optional):如果是True,则输出的bias可学,默认为True。卷积后是否加偏移量 padding_mode:默认为“zeros”,填充0 ''' self.layer=nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(in_channel,out_channel,3,1,1,padding_mode='reflect',bias=False), # 卷积 nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel), # 归一化 nn.Dropout2d(0.3), # 正则化,防止过拟合 nn.LeakyReLU(), # 解决神经元“死亡问题”,在输入为负值的时候给予很小的正斜率 nn.Conv2d(out_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, 1, padding_mode='reflect', bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel), nn.Dropout2d(0.3), nn.LeakyReLU() ) def forward(self,x): return self.layer(x) class DownSample(nn.Module): # 下采样 def __init__(self,channel): super(DownSample, self).__init__() self.layer=nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(channel,channel,3,2,1,padding_mode='reflect',bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(channel), nn.LeakyReLU() ) # padding_mode='reflect'填充像素矩阵中对称轴元素的像素点,加强图像的特征 def forward(self,x): return self.layer(x) class UpSample(nn.Module): # 上采样 def __init__(self,channel): super(UpSample, self).__init__() self.layer=nn.Conv2d(channel,channel//2,1,1) def forward(self,x,feature_map): up=F.interpolate(x,scale_factor=2,mode='nearest') # 上采样函数 scale_factor为空间大小 mode则是用于采样的算法 # 最近临插值算法的原理是在原图像中找到最近临的一个点,然后把这个点的像素值插入到目标图像中 out=self.layer(up) return torch.cat((out,feature_map),dim=1) #将输出矩阵与特征图拼接起来 class UNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self): #实现 卷积 下采样....卷积 下采样 卷积 上采样...卷积 上采样 super(UNet, self).__init__() self.c1 = Conv_Block(3,64) self.d1 = DownSample(64) self.c2 = Conv_Block(64,128) self.d2 = DownSample(128) self.c3 = Conv_Block(128,256) self.d3 = DownSample(256) self.c4 = Conv_Block(256,512) self.d4 = DownSample(512) self.c5 = Conv_Block(512,1024) self.u1 = UpSample(1024) self.c6 = Conv_Block(1024,512) self.u2 = UpSample(512) self.c7 = Conv_Block(512, 256) self.u3 = UpSample(256) self.c8 = Conv_Block(256, 128) self.u4 = UpSample(128) self.c9 = Conv_Block(128, 64) self.out = nn.Conv2d(64,3,3,1,1) self.Th = nn.Sigmoid() #Sigmoid是激活函数的一种,它会将样本值映射到0到1之间。 def forward(self,x): R1 = self.c1(x) R2 = self.c2(self.d1(R1)) R3 = self.c3(self.d2(R2)) R4 = self.c4(self.d3(R3)) R5 = self.c5(self.d4(R4)) O1 = self.c6(self.u1(R5,R4)) O2 = self.c7(self.u2(O1, R3)) O3 = self.c8(self.u3(O2, R2)) O4 = self.c9(self.u4(O3, R1)) return self.Th(self.out(O4)) if __name__ == '__main__': x = torch.randn(2,3,256,256) """ torch.randn()返回一个符合均值为0,方差为1的正态分布(标准正态分布)中填充随机数的张量 """ net = UNet() print(net(x).shape)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
(4).train文件
#训练函数 import os from torch import nn,optim import torch from torch.utils.data import DataLoader from data import * from net import * from torchvision.utils import save_image device=torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') # 调用GPU weight_path='params/unet.pth' # 权重保存路径 data_path=r'F:\Artificial Intelligence\U_net\data' # 数据集路径 save_path='train_image' # 训练结果保存路径 if __name__ == '__main__': data_loader=DataLoader(Mydata(data_path),batch_size=2,shuffle=True) # 读取图片 batch_size训练批大小 shuffle是否乱序 net=UNet().to(device) # 模型导入GPU或CPU # 判断权重文件是否存在 if os.path.exists(weight_path): net.load_state_dict(torch.load(weight_path)) print('successful load weight!') else: print('not successful load weight') #优化器 opt=optim.Adam(net.parameters()) loss_fun=nn.BCELoss() epoch=1 while True: for i,(image,segment_image) in enumerate(data_loader): # 数据导入GPU或CPU image, segment_image=image.to(device),segment_image.to(device) out_image=net(image) train_loss=loss_fun(out_image,segment_image) opt.zero_grad() # 模型中参数的梯度设为0 train_loss.backward() opt.step() # 更新优化器学习率 if i%5==0: print(f'{epoch}-{i}-train_loss===>>{train_loss.item()}') # 每五轮输出一次 loss if i%50==0: torch.save(net.state_dict(),weight_path) # 每50轮保存一次权重 _image=image[0] _segment_image=segment_image[0] _out_image=out_image[0] img=torch.stack([_image,_segment_image,_out_image],dim=0) # 沿着一个新维度对输入张量序列进行连接。,要保证张量都为相同形状 save_image(img,f'{save_path}/{i}.png') epoch+=1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
训练函数跟大多数训练函数相同,在此就不多讲解。
在此附上训练效果:


10.7学习笔记
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/花生_TL007/article/detail/351122
推荐阅读
相关标签



