- 1UniPro、PingCode、禅道,CTO如何选择合适的项目管理软件_禅道和pingcode对比
- 2代码随想录算法训练营第37天| 738.单调递增的数字、968.监控二叉树
- 3TIDB 初级课程体验 7 (用户管理与权限,跳过密码)
- 4Android Studio引入framework.jar包
- 5mysql 单行函数
- 6谷歌浏览器没有添加flash选项_电脑谷歌浏览器没有flash设置
- 7将xml文件转yolov5训练数据txt标签文件_xml转yolo
- 8IO流详解及常用方法
- 9sample gpt 无限长上下文
- 10Python如何pip批量安装指定包 - 最简单方法_pip install 多个包
有手就行的自定义制作coco、voc、yolo格式数据集_voc数据集制作软件
赞
踩
目录
1. 准备工作
(1)安装软件labelme,自行安装,不再说明。
(2)准备好原始图片,本文以10张图片如下图所示,用labelme软件打标签

2. 开始打标注
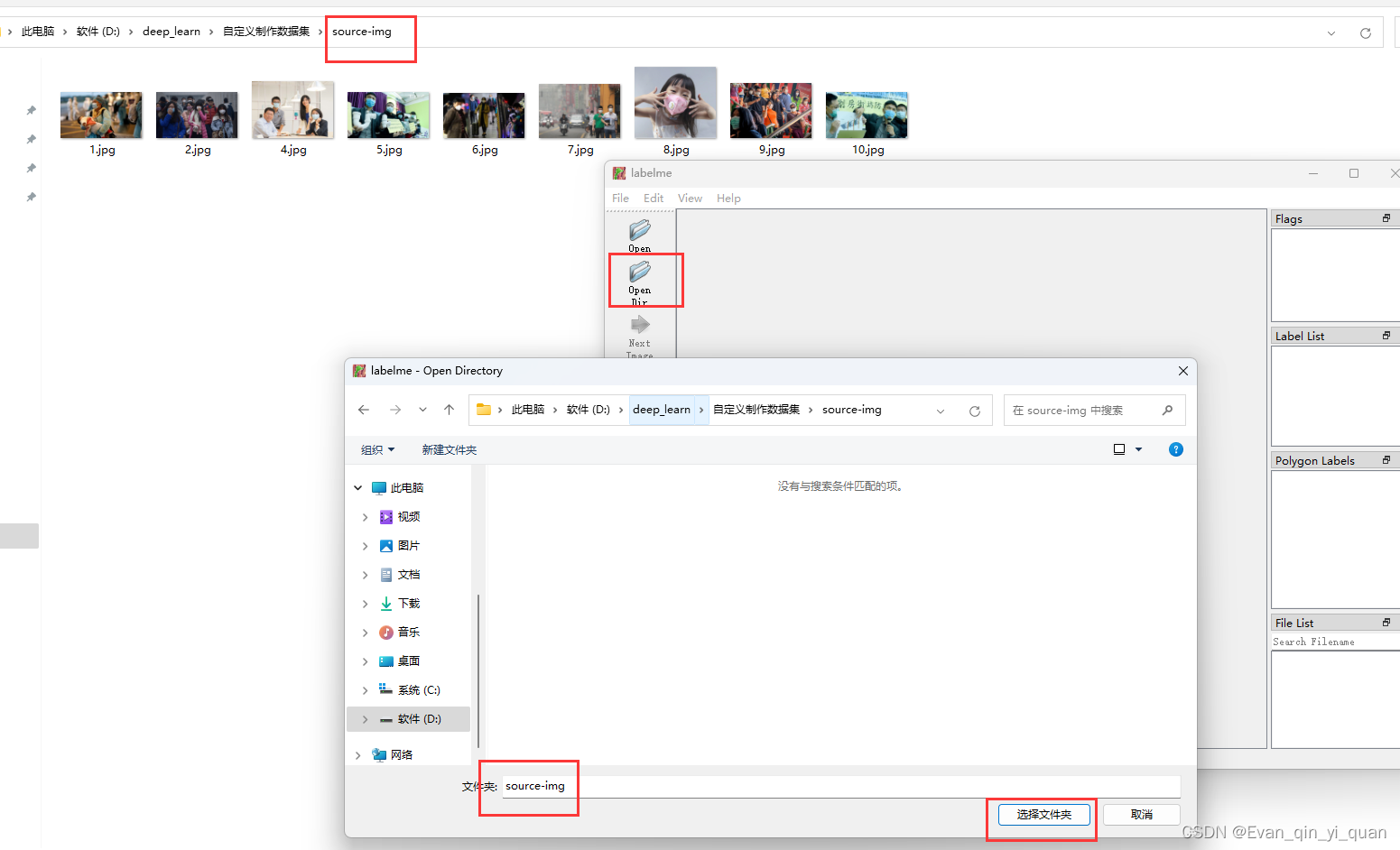
首先打开labelme软件 ,然后打开目录,定位到你数据源所在的文件夹

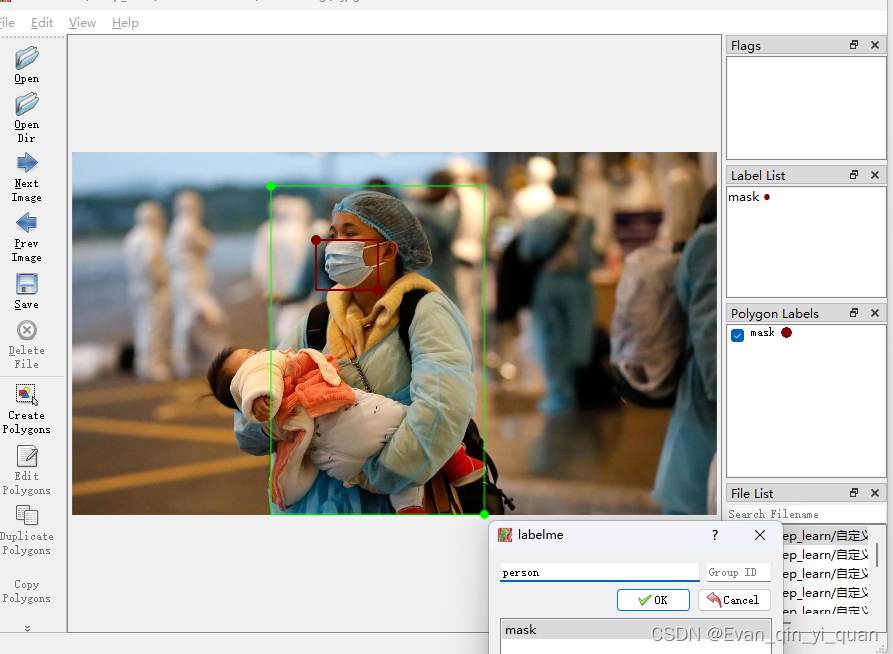
用矩形框打标注,这里只标注两个类别:mask、person
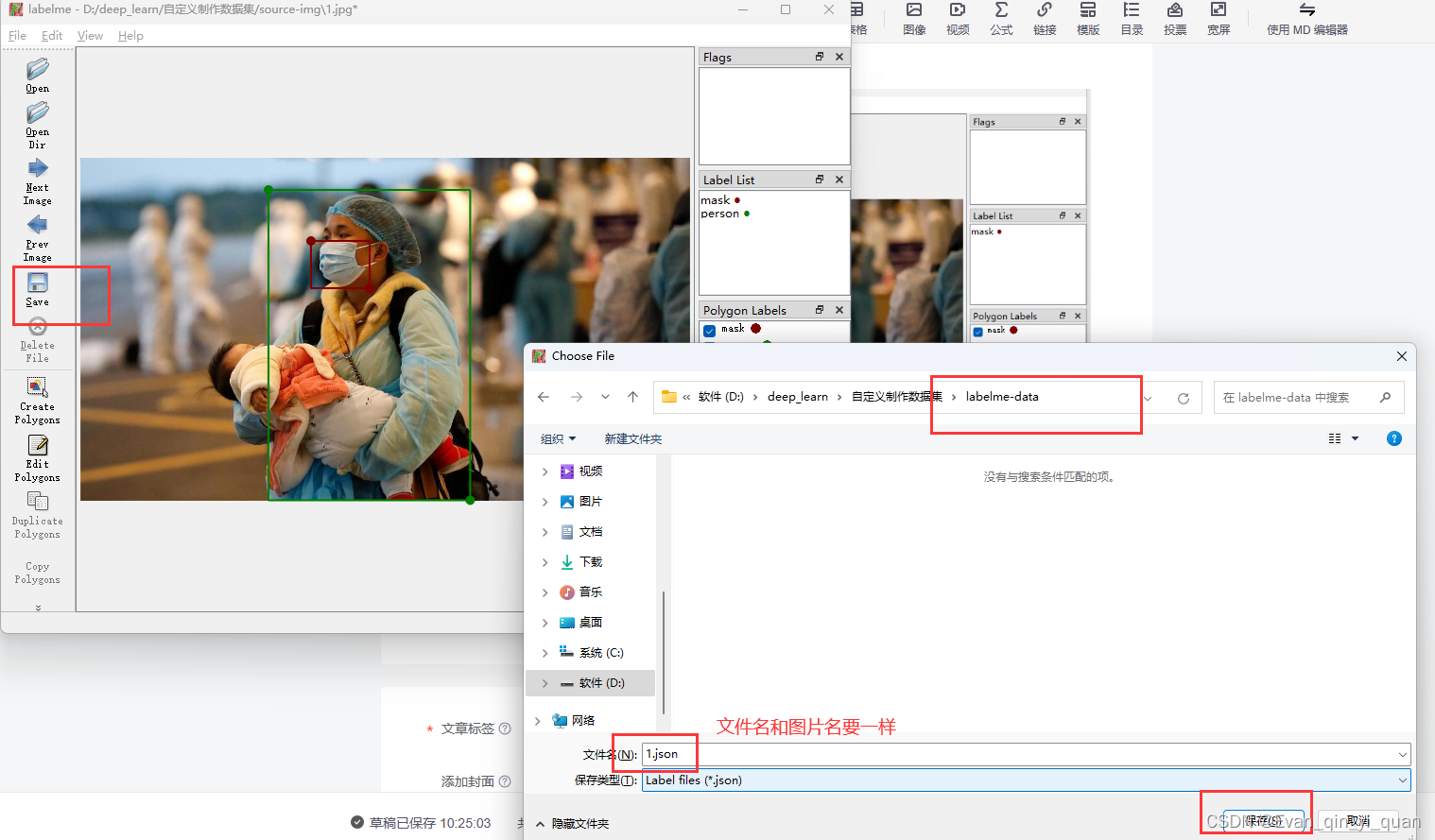
打完标注后保存图片,保存后得到的json文件名字要和图片名字一次,点击NextImage继续下一张图片打标注,直至所有图片打完标注。
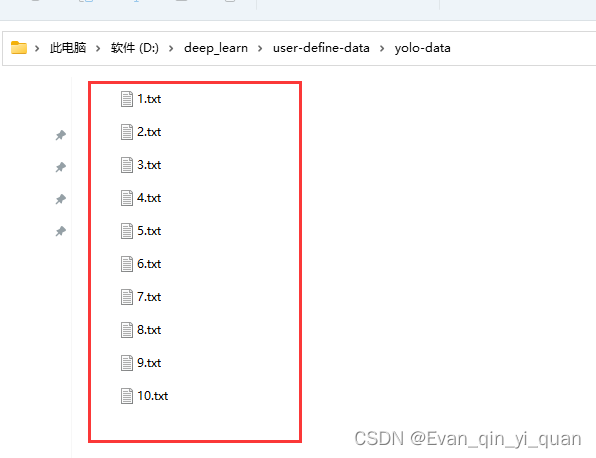
 待所有10张图片打完标签,得到如下结果,接着需要根据json文件分别转换为coco、voc、yolo格式的数据集。
待所有10张图片打完标签,得到如下结果,接着需要根据json文件分别转换为coco、voc、yolo格式的数据集。
3. 转换为coco格式
转换cooc格式,把上面的json文件复制到原来的图片文件夹source-ing中,因为需要把图片划分为训练集和验证集。
下面是转换代码json -> coco
- import os
- import json
- import numpy as np
- import glob
- import shutil
- import cv2
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
-
- np.random.seed(41)
-
- classname_to_id = {
- "mask": 0, #改成自己的类别
- "person": 1
- }
-
-
- class Lableme2CoCo:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.images = []
- self.annotations = []
- self.categories = []
- self.img_id = 0
- self.ann_id = 0
-
- def save_coco_json(self, instance, save_path):
- json.dump(instance, open(save_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8'), ensure_ascii=False, indent=1) # indent=2 更加美观显示
-
- # 由json文件构建COCO
- def to_coco(self, json_path_list):
- self._init_categories()
- for json_path in json_path_list:
- obj = self.read_jsonfile(json_path)
- self.images.append(self._image(obj, json_path))
- shapes = obj['shapes']
- for shape in shapes:
- annotation = self._annotation(shape)
- self.annotations.append(annotation)
- self.ann_id += 1
- self.img_id += 1
- instance = {}
- instance['info'] = 'spytensor created'
- instance['license'] = ['license']
- instance['images'] = self.images
- instance['annotations'] = self.annotations
- instance['categories'] = self.categories
- return instance
-
- # 构建类别
- def _init_categories(self):
- for k, v in classname_to_id.items():
- category = {}
- category['id'] = v
- category['name'] = k
- self.categories.append(category)
-
- # 构建COCO的image字段
- def _image(self, obj, path):
- image = {}
- from labelme import utils
- img_x = utils.img_b64_to_arr(obj['imageData'])
- h, w = img_x.shape[:-1]
- image['height'] = h
- image['width'] = w
- image['id'] = self.img_id
- image['file_name'] = os.path.basename(path).replace(".json", ".jpg")
- return image
-
- # 构建COCO的annotation字段
- def _annotation(self, shape):
- # print('shape', shape)
- label = shape['label']
- points = shape['points']
- annotation = {}
- annotation['id'] = self.ann_id
- annotation['image_id'] = self.img_id
- annotation['category_id'] = int(classname_to_id[label])
- annotation['segmentation'] = [np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()]
- annotation['bbox'] = self._get_box(points)
- annotation['iscrowd'] = 0
- annotation['area'] = 1.0
- return annotation
-
- # 读取json文件,返回一个json对象
- def read_jsonfile(self, path):
- with open(path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
- return json.load(f)
-
- # COCO的格式: [x1,y1,w,h] 对应COCO的bbox格式
- def _get_box(self, points):
- min_x = min_y = np.inf
- max_x = max_y = 0
- for x, y in points:
- min_x = min(min_x, x)
- min_y = min(min_y, y)
- max_x = max(max_x, x)
- max_y = max(max_y, y)
- return [min_x, min_y, max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
-
- #训练过程中,如果遇到Index put requires the source and destination dtypes match, got Long for the destination and Int for the source
- #参考:https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/issues/6706
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- labelme_path = "./source-img" #json和图片的存放目录
- saved_coco_path = "./data-" #生成coco格式数据的保存文件夹名字
- print('reading...')
- # 创建文件
- if not os.path.exists("%scoco/annotations/" % saved_coco_path):
- os.makedirs("%scoco/annotations/" % saved_coco_path)
- if not os.path.exists("%scoco/images/train/" % saved_coco_path):
- os.makedirs("%scoco/images/train" % saved_coco_path)
- if not os.path.exists("%scoco/images/val/" % saved_coco_path):
- os.makedirs("%scoco/images/val" % saved_coco_path)
- # 获取images目录下所有的joson文件列表
- print(labelme_path + "/*.json")
- json_list_path = glob.glob(labelme_path + "/*.json")
- print('json_list_path: ', len(json_list_path))
- # 数据划分,这里没有区分val2017和tran2017目录,所有图片都放在images目录下
- train_path, val_path = train_test_split(json_list_path, test_size=0.2, train_size=0.8)
- print("train_n:", len(train_path), 'val_n:', len(val_path))
-
- # 把训练集转化为COCO的json格式
- l2c_train = Lableme2CoCo()
- train_instance = l2c_train.to_coco(train_path)
- l2c_train.save_coco_json(train_instance, '%scoco/annotations/instances_train.json' % saved_coco_path)
- for file in train_path:
- # shutil.copy(file.replace("json", "jpg"), "%scoco/images/train2017/" % saved_coco_path)
- img_name = file.replace('json', 'jpg')
- temp_img = cv2.imread(img_name)
- try:
- cv2.imwrite("{}coco/images/train/{}".format(saved_coco_path, img_name.split('\\')[-1].replace('png', 'jpg')), temp_img)
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- print('Wrong Image:', img_name )
- continue
- print(img_name + '-->', img_name.replace('png', 'jpg'))
-
- for file in val_path:
- # shutil.copy(file.replace("json", "jpg"), "%scoco/images/val2017/" % saved_coco_path)
- img_name = file.replace('json', 'jpg')
- temp_img = cv2.imread(img_name)
- try:
- cv2.imwrite("{}coco/images/val/{}".format(saved_coco_path, img_name.split('\\')[-1].replace('png', 'jpg')), temp_img)
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- print('Wrong Image:', img_name)
- continue
- print(img_name + '-->', img_name.replace('png', 'jpg'))
-
- # 把验证集转化为COCO的json格式
- l2c_val = Lableme2CoCo()
- val_instance = l2c_val.to_coco(val_path)
- l2c_val.save_coco_json(val_instance, '%scoco/annotations/instances_val.json' % saved_coco_path)
-

生成的coco数据集文件夹为data-coco,原代码中train和val的比例为8:2(比例可在代码中修改),所以train有8张图片,val有2张图片。

4. 转换为voc格式
转换代码在本小节最下面,需要给脚本传递3个参数:
输入数据集数据文件夹 转换结果存放的文件夹名字 --labels label文件
输入数据集数据文件夹:就是上面source-img
转换结果存放的文件夹名字: 就是转换成voc格式后的数据保存路径名字,这个路径是程序自己创建的,不需要我们事先创建,我们只是传递名字给脚本。
label文件:内容是类别的名字,格式如下
以本文为例,传递参数这样写 source-img voc-data --labels labels.txt
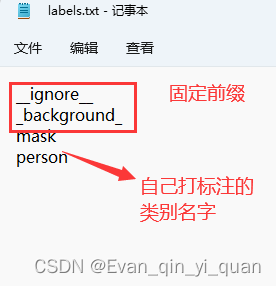
pycharm 编译配置参数:
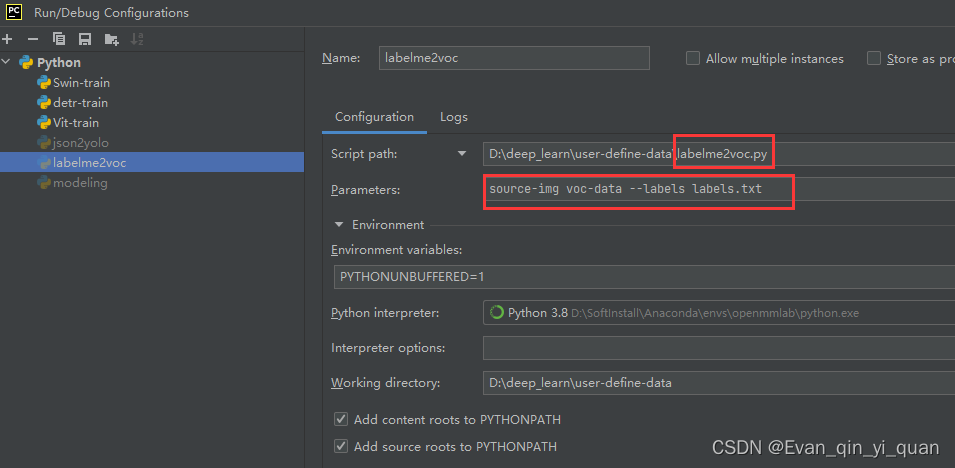
label文件内容
- __ignore__
- _background_
- mask
- person
转换成voc脚本代码
- #!/usr/bin/env python
-
- from __future__ import print_function
-
- import argparse
- import glob
- import os
- import os.path as osp
- import sys
-
- import imgviz
- import numpy as np
-
- import labelme
-
- #传递参数3个: 输入数据文件夹 转换结果文件夹名字 --labels label文件
- #如 source-img voc-data --labels labels.txt
- def main():
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
- formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
- )
- parser.add_argument("input_dir", help="input annotated directory")
- parser.add_argument("output_dir", help="output dataset directory")
- parser.add_argument("--labels", help="labels file", required=True)
- parser.add_argument(
- "--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
- )
- args = parser.parse_args()
-
- if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
- print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
- sys.exit(1)
- os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
- os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
- os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass"))
- os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassPNG"))
- if not args.noviz:
- os.makedirs(
- osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassVisualization")
- )
- os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationObject"))
- os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationObjectPNG"))
- if not args.noviz:
- os.makedirs(
- osp.join(args.output_dir, "SegmentationObjectVisualization")
- )
- print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
-
- class_names = []
- class_name_to_id = {}
- for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
- class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
- class_name = line.strip()
- class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
- if class_id == -1:
- assert class_name == "__ignore__"
- continue
- elif class_id == 0:
- assert class_name == "_background_"
- class_names.append(class_name)
- class_names = tuple(class_names)
- print("class_names:", class_names)
- out_class_names_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "class_names.txt")
- with open(out_class_names_file, "w") as f:
- f.writelines("\n".join(class_names))
- print("Saved class_names:", out_class_names_file)
-
- for filename in glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json")):
- print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
-
- label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
-
- base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
- out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
- out_cls_file = osp.join(
- args.output_dir, "SegmentationClass", base + ".npy"
- )
- out_clsp_file = osp.join(
- args.output_dir, "SegmentationClassPNG", base + ".png"
- )
- if not args.noviz:
- out_clsv_file = osp.join(
- args.output_dir,
- "SegmentationClassVisualization",
- base + ".jpg",
- )
- out_ins_file = osp.join(
- args.output_dir, "SegmentationObject", base + ".npy"
- )
- out_insp_file = osp.join(
- args.output_dir, "SegmentationObjectPNG", base + ".png"
- )
- if not args.noviz:
- out_insv_file = osp.join(
- args.output_dir,
- "SegmentationObjectVisualization",
- base + ".jpg",
- )
-
- img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
- imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img)
-
- cls, ins = labelme.utils.shapes_to_label(
- img_shape=img.shape,
- shapes=label_file.shapes,
- label_name_to_value=class_name_to_id,
- )
- ins[cls == -1] = 0 # ignore it.
-
- # class label
- labelme.utils.lblsave(out_clsp_file, cls)
- np.save(out_cls_file, cls)
- if not args.noviz:
- clsv = imgviz.label2rgb(
- cls,
- imgviz.rgb2gray(img),
- label_names=class_names,
- font_size=15,
- loc="rb",
- )
- imgviz.io.imsave(out_clsv_file, clsv)
-
- # instance label
- labelme.utils.lblsave(out_insp_file, ins)
- np.save(out_ins_file, ins)
- if not args.noviz:
- instance_ids = np.unique(ins)
- instance_names = [str(i) for i in range(max(instance_ids) + 1)]
- insv = imgviz.label2rgb(
- ins,
- imgviz.rgb2gray(img),
- label_names=instance_names,
- font_size=15,
- loc="rb",
- )
- imgviz.io.imsave(out_insv_file, insv)
-
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- main()

5. 转换为yolo格式
指定类别,labelme生成的json文件所在路径,和输出保存的路径即可,直接在代码里写,然后直接编译即可


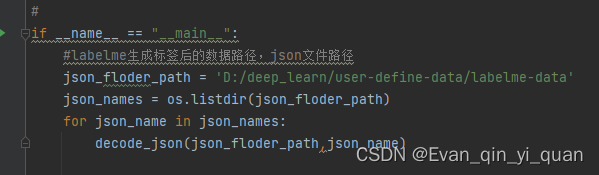
-
- import json
- import os
- #自己打标签有多少类别就写在这里
- name2id = {'mask':0,'person':1}
-
- def convert(img_size, box):
- dw = 1./(img_size[0])
- dh = 1./(img_size[1])
- x = (box[0] + box[2])/2.0 - 1
- y = (box[1] + box[3])/2.0 - 1
- w = box[2] - box[0]
- h = box[3] - box[1]
- x = x*dw
- w = w*dw
- y = y*dh
- h = h*dh
- return (x,y,w,h)
-
- #
- def decode_json(json_floder_path,json_name):
- #转换好的标签放哪里
- txt_name = 'D:/deep_learn/user-define-data/yolo-data/' + json_name[0:-5] + '.txt'
- txt_file = open(txt_name, 'w')
-
- json_path = os.path.join(json_floder_path, json_name)
- data = json.load(open(json_path, 'r', encoding='gb2312'))
-
- img_w = data['imageWidth']
- img_h = data['imageHeight']
-
- for i in data['shapes']:
-
- label_name = i['label']
- if (i['shape_type'] == 'rectangle'):
-
- x1 = int(i['points'][0][0])
- y1 = int(i['points'][0][1])
- x2 = int(i['points'][1][0])
- y2 = int(i['points'][1][1])
-
- bb = (x1,y1,x2,y2)
- bbox = convert((img_w,img_h),bb)
- txt_file.write(str(name2id[label_name]) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox]) + '\n')
- #
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- #labelme生成标签后的数据路径,json文件路径
- json_floder_path = 'D:/deep_learn/user-define-data/labelme-data'
- json_names = os.listdir(json_floder_path)
- for json_name in json_names:
- decode_json(json_floder_path,json_name)

下面就是转换完成后的yolo格式数据