- 1信息系统项目管理师第一章_左人右龟上鹰
- 2一个完整的购物商城系统是一个庞大且复杂的任务,涉及到前端、后端、数据库等多个方面。
- 3docker 安装与使用日记_docker slim
- 4Unity优化大全(八)之 GPU-Ligh和其他_unity gpu opaque
- 5MySQL长时间事务_MySQL-长事务详解
- 6sql 前100条_在100,900之前的sql
- 7this beta version of Typora is expired, please download and install a newer version.Typora的保姆级最新解决方法_无法下载this beta version of typora is expired
- 8循环顺序队列_c语言请设计void clearqueue(seqqueue *q)函数。 该函数清除循环顺序队列q
- 9一文掌握大模型数据准备、模型微调、部署使用全流程_如何给大模型的数据
- 10OWASP固件安全性测试指南_fstm
Hbase中二级索引与Phoenix二级索引实现_phoinex如何设计hbase 二级索引
赞
踩
1、引入
HBase本身只提供基于行键和全表扫描的查询,而行键索引单一,对于多维度的查询困难。
所以我们引进一个二级索引的概念。二级索引的本质就是建立各列值与行键之间的映射关系 。
图解:

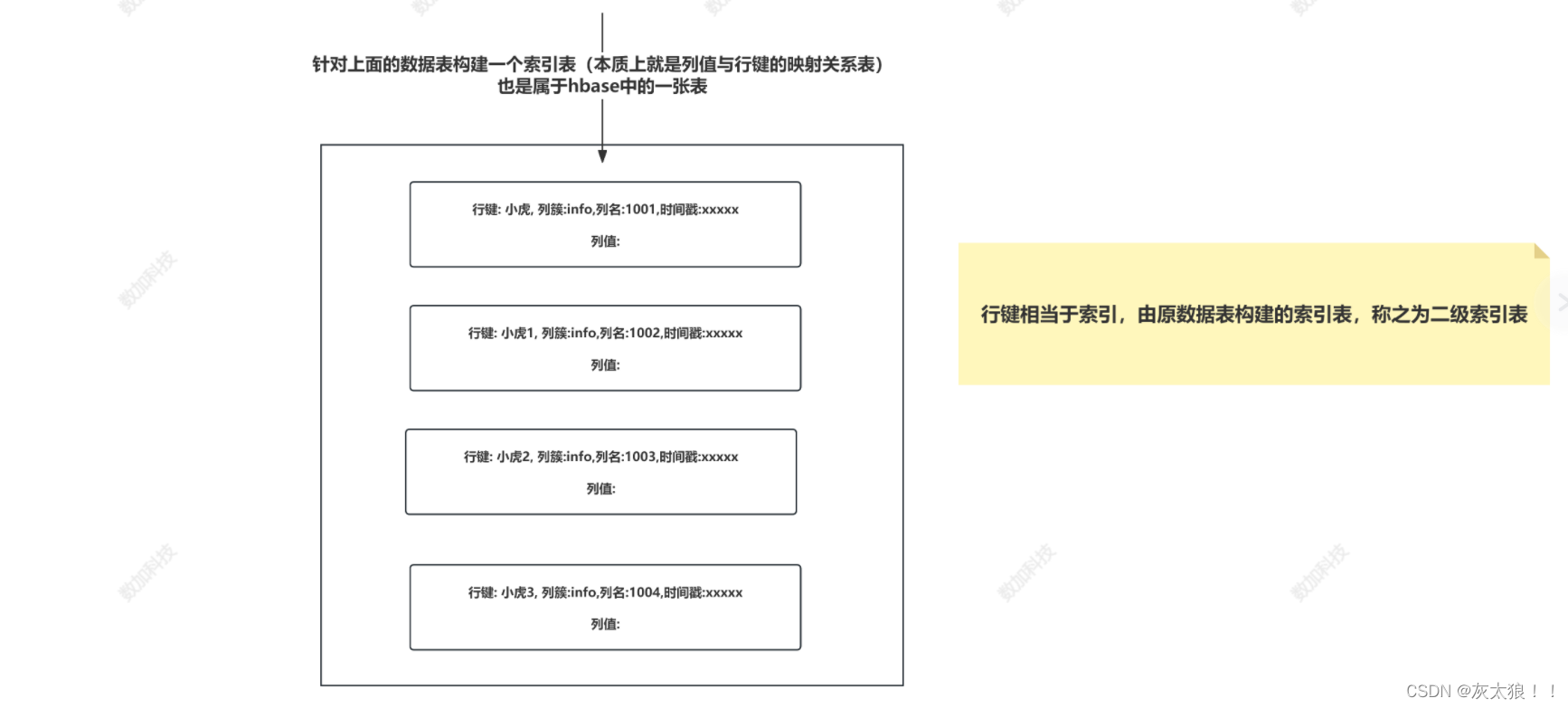
2、常见实现二级索引的方案:
HBase的一级索引就是rowkey,我们只能通过rowkey进行检索。如果我们相对hbase里面列族的列列进行一些组合查询,就需要采用HBase的二级索引方案来进行多条件的查询。
-
MapReduce方案
-
ITHBASE(Indexed-Transanctional HBase)方案
-
IHBASE(Index HBase)方案
-
Hbase Coprocessor(协处理器)方案
-
Solr+hbase方案或 redis+hbase 方案
-
CCIndex(complementalclustering index)方案
下面我们用代码来实现MapReduce方案与redis+hbase 方案
三、MapReduce方案实现
使用整合MapReduce的方式创建hbase索引。主要的流程如下:
1、扫描输入表,使用hbase继承类TableMapper
2、获取rowkey和指定字段名称和字段值
3、创建Put实例, value=” “, rowkey=班级,column=学号
4、使用IdentityTableReducer将数据写入索引表
- import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapReduceUtil;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapper;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableReducer;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.BloomType;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
- import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
- import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
-
- import java.io.IOException;
-
- /**
- * 使用整合MapReduce的方式创建hbase索引。主要的流程如下:
- * 1.1扫描输入表,使用hbase继承类TableMapper
- * 1.2获取rowkey和指定字段名称和字段值
- * 1.3创建Put实例, value=” “, rowkey=班级,column=学号
- * 1.4使用IdentityTableReducer将数据写入索引表
- */
- //因为我们现在要读取的数据来自于hbase中的hfile文件,与hdfs上普通的block块文件有所区别,不能直接继承Mapper类
- //要继承hbase读取数据专属的Mapper类 TableMapper
- //public abstract class TableMapper<KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> extends Mapper<ImmutableBytesWritable, Result, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>
- class MyIndexMapper extends TableMapper<Text, NullWritable> {
- @Override
- protected void map(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Result value, Mapper<ImmutableBytesWritable, Result, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- //ImmutableBytesWritable key --相当于是读取到一行的行键
- //Result value --相当于读取到一行多列的封装
- //获取行键
- String id = Bytes.toString(key.get());
- //获取姓名的列值
- String name = Bytes.toString(value.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name")));
- //将学号和姓名拼接起来给到reduce,由reduce处理并写入到到索引表中
- context.write(new Text(id + "-" + name), NullWritable.get());
- }
- }
-
- //public abstract class TableReducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT> extends Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, Mutation>
- class MyIndexReducer extends TableReducer<Text, NullWritable, NullWritable> {
- @Override
- protected void reduce(Text value, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<Text, NullWritable, NullWritable, Mutation>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String string = value.toString();
- String id = string.split("-")[0];
- String name = string.split("-")[1];
-
- //将要添加的数据封装成Put类的对象
- Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(name));
- put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"),Bytes.toBytes(id),Bytes.toBytes(""));
-
- context.write(NullWritable.get(), put);
-
- }
- }
-
- public class HBaseIndexDemo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- //创建配置文件对象
- Configuration conf = new Configuration();
- //指定zookeeper的配置信息
- conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "master:2181,node1:2181,node2:2181");
- //创建Job作业对象
- Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
- job.setJobName("给学生表创建二级索引表");
-
- job.setJarByClass(HBaseIndexDemo1.class);
- //因为索引表的构建是建立列值与行键的映射关系,要获取所有的数据
- //scan扫描全表数据
- Scan scan = new Scan();
- //告诉输入的列值来自于哪一个列簇
- scan.addFamily(Bytes.toBytes("info"));
-
- //先将表名封装成一个TableName的对象
- Connection conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
- Admin admin = conn.getAdmin();
-
- //先将表名封装成一个TableName的对象
- TableName tn = TableName.valueOf("students2_index");
- if (!admin.tableExists(tn)) {
- TableDescriptorBuilder studentsIndex = TableDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(tn);
-
- //使用另外一种方式创建列簇并设置布隆过滤器
- ColumnFamilyDescriptor columnFamilyDescriptor = ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(Bytes.toBytes("info"))
- .setBloomFilterType(BloomType.ROW).build();
- studentsIndex.setColumnFamily(columnFamilyDescriptor);
- admin.createTable(studentsIndex.build());
- System.out.println(tn + "表创建成功!!!");
- } else {
- System.out.println(tn + "表已经存在!");
- }
-
-
- //索引表是执行完MR作业后产生的
- /**
- /**
- * Use this before submitting a TableMap job. It will appropriately set up
- * the job.
- *
- * @param table The table name to read from.
- * @param scan The scan instance with the columns, time range etc.
- * @param mapper The mapper class to use.
- * @param outputKeyClass The class of the output key.
- * @param outputValueClass The class of the output value.
- * @param job The current job to adjust. Make sure the passed job is
- * carrying all necessary HBase configuration.
- * @throws IOException When setting up the details fails.
- *public static void initTableMapperJob
- * (String table,Scan scan,Class<? extends TableMapper> mapper,Class<?> outputKeyClass,Class<?> outputValueClass,Job job)
- */
- TableMapReduceUtil.initTableMapperJob("students2", scan, MyIndexMapper.class, Text.class, NullWritable.class, job);
-
- TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob("students2_index", MyIndexReducer.class, job);
-
- //提交作业到集群中允许
- boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
- if (b) {
- System.out.println("================== students2索引表构建成功!!!============================");
- } else {
- System.out.println("================== students2索引表构建失败!!!============================");
- }
-
- }
- }

四、使用redis第三方的存储工具存储hbase索引
- import com.shujia.utils.HBaseUtil;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.CompareOperator;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.BinaryComparator;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.filter.ValueFilter;
- import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
- import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
-
- import java.util.Scanner;
- import java.util.Set;
-
- /*
- 使用redis第三方的存储工具存储hbase索引(本质依旧是列值与行键产生映射关系)
- */
- public class HBaseWithRedisIndex {
- //1、获取hbase数据库连接对象和操作对象
- static Connection conn = HBaseUtil.CONNECTION;
- static Admin admin = HBaseUtil.ADMIN;
-
- //获取redis连接对象
- static Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.19.100", 12346);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- //步骤1:在redis中构建映射关系(性别:学号)
- // buildIndexInRedis();
-
- //使用:先通过查询redis中性别对应的学号,拿着学号去hbase原表中查询获取结果
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入您要查询的性别:");
- String gender = sc.next();
- selectGenderFromHbase(gender);
- }
-
- public static void selectGenderFromHbase(String gender) throws Exception {
- if ("男".equals(gender)) {
- selectIdFromRedis(gender);
- } else if ("女".equals(gender)) {
- selectIdFromRedis(gender);
- } else {
- System.out.println("没有该性别");
- }
- }
-
- //单独编写一个方法查询redis
- public static void selectIdFromRedis(String gender) throws Exception {
- Table students2 = conn.getTable(TableName.valueOf("students2"));
-
- Set<String> ids = jedis.smembers("性别:"+gender);
- for (String id : ids) {
- Result result = students2.get(new Get(Bytes.toBytes(id)).addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name")));
- String name = Bytes.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name")));
- System.out.println("学号:" + id + ",姓名:" + name);
- }
- }
-
- public static void buildIndexInRedis() throws Exception {
-
- //获取要构建索引的原表
- Table students2 = conn.getTable(TableName.valueOf("students2"));
-
- Scan scan = new Scan();
- //获取男生的学号,放入到redis中
- //创建列值过滤器
- ValueFilter filter1 = new ValueFilter(CompareOperator.EQUAL, new BinaryComparator(Bytes.toBytes("男")));
- scan.setFilter(filter1);
- ResultScanner resultScanner = students2.getScanner(scan);
- for (Result result : resultScanner) {
- //获取每一行的行键即可
- String id = Bytes.toString(result.getRow());
- //将学号以值的方式添加到redis键对应的值中
- //因为男生的学号有很多个,且不重复,所以我们在redis中采用set的数据类型存储
- jedis.sadd("性别:男", id);
- }
-
- //获取男生的学号,放入到redis中
- //创建列值过滤器
- ValueFilter filter2 = new ValueFilter(CompareOperator.EQUAL, new BinaryComparator(Bytes.toBytes("女")));
- scan.setFilter(filter2);
- ResultScanner resultScanner2 = students2.getScanner(scan);
- for (Result result : resultScanner2) {
- //获取每一行的行键即可
- String id = Bytes.toString(result.getRow());
- //将学号以值的方式添加到redis键对应的值中
- //因为男生的学号有很多个,且不重复,所以我们在redis中采用set的数据类型存储
- jedis.sadd("性别:女", id);
- }
-
- }
- }

五、Phoenix二级索引
1、开启索引支持
# 在hbase-site.xml中增加如下配置
<property>
<name>hbase.regionserver.wal.codec</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.wal.IndexedWALEditCodec</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.rpc.timeout</name>
<value>60000000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period</name>
<value>60000000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>phoenix.query.timeoutMs</name>
<value>60000000</value>
</property>
# 同步到所有节点
scp hbase-site.xml node1:`pwd`
scp hbase-site.xml node2:`pwd`# 修改phoenix目录下的bin目录中的hbase-site.xml
<property>
<name>hbase.rpc.timeout</name>
<value>60000000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period</name>
<value>60000000</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>phoenix.query.timeoutMs</name>
<value>60000000</value>
</property>-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 启动hbase
start-hbase.sh
# 重新进入phoenix客户端
sqlline.py master,node1,node2
2、索引的种类及其实现方式
2.1、全局索引
全局索引适合读多写少的场景。如果使用全局索引,读数据基本不损耗性能,所有的性能损耗都来源于写数据。数据表的添加、删除和修改都会更新相关的索引表(数据删除了,索引表中的数据也会删除;数据增加了,索引表的数据也会增加)
注意: 对于全局索引在默认情况下,在查询语句中检索的列如果不在索引表中,Phoenix不会使用索引表将,除非使用hint
手机号 进入网格的时间 离开网格的时间 区县编码 经度 纬度 基站标识 网格编号 业务类型
# 创建DIANXIN.sql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DIANXIN (
mdn VARCHAR ,
start_date VARCHAR ,
end_date VARCHAR ,
county VARCHAR,
x DOUBLE ,
y DOUBLE,
bsid VARCHAR,
grid_id VARCHAR,
biz_type VARCHAR,
event_type VARCHAR ,
data_source VARCHAR ,
CONSTRAINT PK PRIMARY KEY (mdn,start_date)
) column_encoded_bytes=0;# 上传数据DIANXIN.csv
# 导入数据
psql.py master,node1,node2 DIANXIN.sql DIANXIN.csv# 创建全局索引
CREATE INDEX DIANXIN_INDEX ON DIANXIN ( end_date );# 查询数据 ( 索引未生效)
select * from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014';# 强制使用索引 (索引生效) hint 语法糖
select /*+ INDEX(DIANXIN DIANXIN_INDEX) */ * from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014';select /*+ INDEX(DIANXIN DIANXIN_INDEX) */ * from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014' and start_date = '20180503154614';
# 取索引列,(索引生效)
select end_date from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014';# 创建多列索引
CREATE INDEX DIANXIN_INDEX1 ON DIANXIN ( end_date,COUNTY );# 多条件查询 (索引生效)
select end_date,MDN,COUNTY from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014' and COUNTY = '8340104';# 查询所有列 (索引未生效)
select * from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014' and COUNTY = '8340104';# 查询所有列 (索引生效)
select /*+ INDEX(DIANXIN DIANXIN_INDEX1) */ * from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014' and COUNTY = '8340104';# 单条件 (索引未生效)
select end_date from DIANXIN where COUNTY = '8340103';
# 单条件 (索引生效) end_date 在前
select COUNTY from DIANXIN where end_date = '20180503154014';# 删除索引
drop index DIANXIN_INDEX on DIANXIN;
2.2、本地索引
本地索引适合写多读少的场景,或者存储空间有限的场景。和全局索引一样,Phoenix也会在查询的时候自动选择是否使用本地索引。本地索引因为索引数据和原数据存储在同一台机器上,避免网络数据传输的开销,所以更适合写多的场景。由于无法提前确定数据在哪个Region上,所以在读数据的时候,需要检查每个Region上的数据从而带来一些性能损耗。
注意:对于本地索引,查询中无论是否指定hint或者是查询的列是否都在索引表中,都会使用索引表。
# 创建本地索引
CREATE LOCAL INDEX DIANXIN_LOCAL_IDEX ON DIANXIN(grid_id);# 索引生效
select grid_id from dianxin where grid_id='117285031820040';# 索引生效
select * from dianxin where grid_id='117285031820040';
2.3、覆盖索引
覆盖索引是把原数据存储在索引数据表中,这样在查询时不需要再去HBase的原表获取数据就,直接返回查询结果。
注意:查询是 select 的列和 where 的列都需要在索引中出现。
# 创建覆盖索引
CREATE INDEX DIANXIN_INDEX_COVER ON DIANXIN ( x,y ) INCLUDE ( county );# 查询所有列 (索引未生效)
select * from DIANXIN where x=117.288 and y =31.822;# 强制使用索引 (索引生效)
select /*+ INDEX(DIANXIN DIANXIN_INDEX_COVER) */ * from DIANXIN where x=117.288 and y =31.822;# 查询索引中的列 (索引生效) mdn是DIANXIN表的RowKey中的一部分
select x,y,county from DIANXIN where x=117.288 and y =31.822;
select mdn,x,y,county from DIANXIN where x=117.288 and y =31.822;# 查询条件必须放在索引中 select 中的列可以放在INCLUDE (将数据保存在索引中)
select /*+ INDEX(DIANXIN DIANXIN_INDEX_COVER) */ x,y,count(*) from DIANXIN group by x,y;



