- 1Hadoop实践 | 58同城Hadoop2.6升级3.2实践_hadoop的3.3.0版本兼容2.6.0版本吗
- 2yum应用安装及使用,基础源和扩展源配置修改,文件解压缩,apache2.4源码安装_yum 基础源
- 3Apache Spark 的基本概念和在大数据分析中的应用_apache spark concept
- 4mysql begin commit_MySql之commit、rollback等事务控制命令
- 5计算机软考初级程序员教程,2013年计算机软考程序员教程
- 6bindIP: 0.0.0.0_bind 0.0.0.0
- 7移动应用开发实验四AlarmManager实现闹钟提醒_alarmanager 实现闹钟功能
- 8tkinter文件对话框
- 9web安全渗透测试十大常规项(二):web渗透测试之XSS跨站脚本攻击
- 10政府各种条件限制 用无人机送快递还不现实_petya和vasya被聘为快递员。在工作日期间,他们将提供包裹到线上的不同点。根据公
Java线程池七大参数详解和配置(面试重点!!!)_java线程池参数详解
赞
踩
1、ArrayBlockingQueue FIFO有界阻塞队列
2、LinkedBlockingQueue FIFO无限队列
七、handler超出线程数和工作队列时候的任务请求处理策略
策略1:ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy(默认)拒绝执行
策略2:ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy调用 execute 方法的线程本身运行任务
策略3:ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy执行程序未关闭,则删除工作队列头部的任务
策略4:ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy无法执行的任务被简单地删除
JDK1.8线程池参数源代码:
- public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
- int maximumPoolSize,
- long keepAliveTime,
- TimeUnit unit,
- BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue
- RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue
- Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
- }
一、corePoolSize核心线程数
指的是核心线程大小,线程池中维护一个最小的线程数量,即使这些线程处于空闲状态,也一直存在池中,除非设置了核心线程超时时间。
这也是源码中的注释说明。
- /** @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool,
- * even if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set.
- */
二、maximunPoolSize最大线程数
指的是线程池中允许的最大线程数量。当线程池中核心线程都处理执行状态,有新请求的任务:
1、工作队列未满:新请求的任务加入工作队列
2、工作队列已满:线程池会创建新线程,来执行这个任务。当然,创建新线程不是无限制的,因为会受到maximumPoolSize最大线程数量的限制。
三、keepAliveTime空闲线程存活时间
指的是空闲线程存活时间。具体说,当线程数大于核心线程数时,空闲线程在等待新任务到达的最大时间,如果超过这个时间还没有任务请求,该空闲线程就会被销毁。
可见官方注释:
- /** @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
- * the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
- * will wait for new tasks before terminating.
- */
四、unit空闲线程存活时间的单位
是指空闲线程存活时间的单位。keepAliveTime的计量单位。枚举类型TimeUnit类。
五、workQueue线程工作队列
1、ArrayBlockingQueue FIFO有界阻塞队列
基于数组的有界阻塞队列,特点FIFO(先进先出)。
当线程池中已经存在最大数量的线程时候,再请求新的任务,这时就会将任务加入工作队列的队尾,一旦有空闲线程,就会取出队头执行任务。因为是基于数组的有界阻塞队列,所以可以避免系统资源的耗尽。
那么如果出现有界队列已满,最大数量的所有线程都处于执行状态,这时又有新的任务请求,怎么办呢?
这时候会采用Handler拒绝策略,对请求的任务进行处理。后面会详细介绍。
2、LinkedBlockingQueue FIFO无限队列
基于链表的无界阻塞队列,默认最大容量Integer.MAX_VALUE( ),可认为是无限队列,特点FIFO。
关于maximumPoolSize参数在工作队列为LinkedBlockingQueue时候,是否起作用这个问题,我们需要视情况而定!
情况①:如果指定了工作队列大小,比如core=2,max=3,workQueue=2,任务数task=5,这种情况的最大线程数量的限制是有效的。
情况②:如果工作队列大小默认,这时maximumPoolSize不起作用,因为新请求的任务一直可以加到队列中。
3、PriorityBlockingQueue VIP
优先级无界阻塞队列,前面两种工作队列特点都是FIFO,而优先级阻塞队列可以通过参数Comparator实现对任务进行排序,不按照FIFO执行。
4、SynchronousQueue不缓存任务的阻塞队列
不缓存任务的阻塞队列,它实际上不是真正的队列,因为它没有提供存储任务的空间。生产者一个任务请求到来,会直接执行,也就是说这种队列在消费者充足的情况下更加适合。因为这种队列没有存储能力,所以只有当另一个线程(消费者)准备好工作,put(入队)和take(出队)方法才不会是阻塞状态。
以上四种工作队列,跟线程池结合就是一种生产者-消费者 设计模式。生产者把新任务加入工作队列,消费者从队列取出任务消费,BlockingQueue可以使用任意数量的生产者和消费者,这样实现了解耦,简化了设计。
六、threadFactory线程工厂
线程工厂,创建一个新线程时使用的工厂,可以用来设定线程名、是否为daemon线程等。
守护线程(Daemon Thread) 在Java中有两类线程:用户线程 (User Thread)、守护线程 (DaemonThread)。
一般建议自定义线程工厂,构建线程的时候设置线程的名称,这样就在查日志的时候就方便知道是哪个线程执行的代码。
官方使用默认的线程工厂源码如下:
- /**
- * The default thread factory
- */
- static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
- private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
- private final ThreadGroup group;
- private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
- private final String namePrefix;
- DefaultThreadFactory() {
- SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
- group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
- Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
- namePrefix = "pool-" +
- poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
- "-thread-";
-
- }
-
- public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
-
- Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
-
- namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),
-
- 0);
- if (t.isDaemon()) t.setDaemon(false);
- if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
-
- t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
- return t
-
- }
- }
七、handler超出线程数和工作队列时候的任务请求处理策略
Java 并发超出线程数和工作队列时候的任务请求处理策略,使用了策略设计模式。
策略1:ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy(默认)拒绝执行
在默认的处理策略。该处理在拒绝时抛出RejectedExecutionException,拒绝执行。
- public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
-
-
-
- /**
- * Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
- */
- public AbortPolicy() { }
- /** * Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
- *
- * @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
- * @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
- * @throws RejectedExecutionException always
- */
- public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
- throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
- " rejected from " +
- e.toString());
- }
- }
策略2:ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy调用 execute 方法的线程本身运行任务
调用 execute 方法的线程本身运行任务。这提供了一个简单的反馈控制机制,可以降低新任务提交的速度。
- public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
- /**
- * Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
- */
- public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
- /**
- * Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
- * has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
- *
- * @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
- * @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
- */
- public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e)
- if (!e.isShutdown()) {
- r.run();
- }
- }
- }
策略3:ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy执行程序未关闭,则删除工作队列头部的任务
- public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
-
-
-
- /**
- * Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
-
-
-
- */
- public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
-
-
- /**
- * Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
- * * would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
- * and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
- * is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded. *
- * @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
- * @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
- */
- public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
- if (!e.isShutdown()) {
-
- e.getQueue().poll();
-
- e.execute(r);
-
- }
- }
如果执行程序未关闭,则删除工作队列头部的任务,然后重试执行(可能再次失败,导致重复执行)。
策略4:ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy无法执行的任务被简单地删除
无法执行的任务被简单地删除,将会丢弃当前任务,通过源码可以看出,该策略不会执行任务操作。
- public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
-
-
-
- /**
-
- * Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
-
- */
-
- public DiscardPolicy() { }
- /**
-
- * Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
- *
- * @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
- * @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
- */
- public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
-
- } }
八 ThreadPoolExecutor线程池参数设置技巧
1、ThreadPoolExecutor的重要参数
- corePoolSize:核心线程数
- 核心线程会一直存活,及时没有任务需要执行
- 当线程数小于核心线程数时,即使有线程空闲,线程池也会优先创建新线程处理
- 设置allowCoreThreadTimeout=true(默认false)时,核心线程会超时关闭
- queueCapacity:任务队列容量(阻塞队列)
当核心线程数达到最大时,新任务会放在队列中排队等待执行
- maxPoolSize:最大线程数
当线程数>=corePoolSize,且任务队列已满时。线程池会创建新线程来处理任务
当线程数=maxPoolSize,且任务队列已满时,线程池会拒绝处理任务而抛出异常
- keepAliveTime:线程空闲时间
当线程空闲时间达到keepAliveTime时,线程会退出,直到线程数量=corePoolSize
如果allowCoreThreadTimeout=true,则会直到线程数量=0
- allowCoreThreadTimeout:允许核心线程超时
- rejectedExecutionHandler:任务拒绝处理器
两种情况会拒绝处理任务:
当线程数已经达到maxPoolSize,切队列已满,会拒绝新任务
当线程池被调用shutdown()后,会等待线程池里的任务执行完毕,再shutdown。如果在调用shutdown()和线程池真正shutdown之间提交任务,会拒绝新任务
线程池会调用rejectedExecutionHandler来处理这个任务。如果没有设置默认是AbortPolicy,会抛出异常
ThreadPoolExecutor类有几个内部实现类来处理这类情况:
AbortPolicy 丢弃任务,抛运行时异常
CallerRunsPolicy 执行任务
DiscardPolicy 忽视,什么都不会发生
DiscardOldestPolicy 从队列中踢出最先进入队列(最后一个执行)的任务
实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口,可自定义处理器
2、ThreadPoolExecutor执行顺序:
线程池按以下行为执行任务
- 当线程数小于核心线程数时,创建线程。
- 当线程数大于等于核心线程数,且任务队列未满时,将任务放入任务队列。
- 当线程数大于等于核心线程数,且任务队列已满
- 若线程数小于最大线程数,创建线程
- 若线程数等于最大线程数,抛出异常,拒绝任务
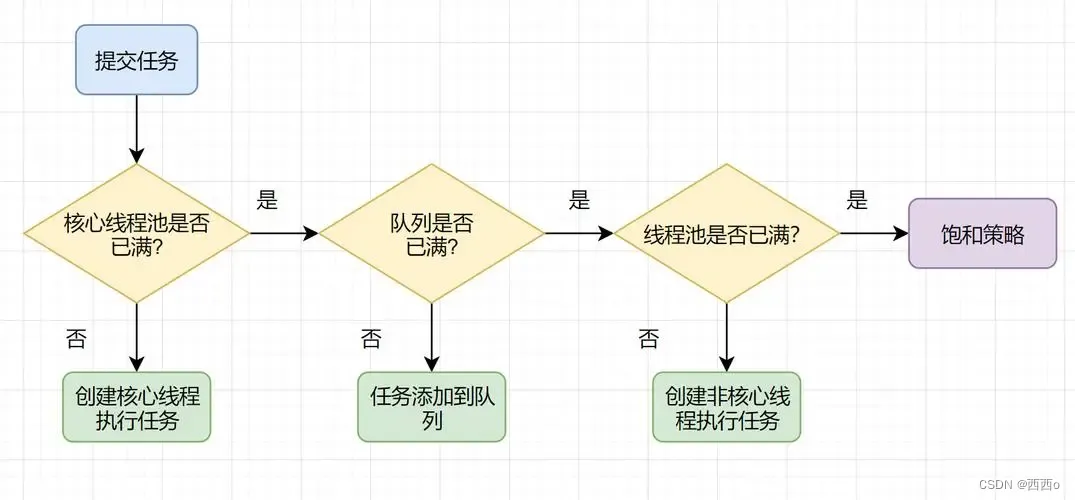
3、如何设置参数
默认值
- corePoolSize=1
- queueCapacity=Integer.MAX_VALUE
- maxPoolSize=Integer.MAX_VALUE
- keepAliveTime=60s
- allowCoreThreadTimeout=false
- rejectedExecutionHandler=AbortPolicy()
如何来设置
- 需要根据几个值来决定
tasks :每秒的任务数,假设为500~1000
taskcost:每个任务花费时间,假设为0.1s
responsetime:系统允许容忍的最大响应时间,假设为1s
- 做几个计算
- corePoolSize = 每秒需要多少个线程处理?
threadcount = tasks/(1/taskcost) =tasks*taskcout = (500~1000)*0.1 = 50~100 个线程。corePoolSize设置应该大于50
根据8020原则,如果80%的每秒任务数小于800,那么corePoolSize设置为80即可
- queueCapacity = (coreSizePool/taskcost)*responsetime
计算可得 queueCapacity = 80/0.1*1 = 80。意思是队列里的线程可以等待1s,超过了的需要新开线程来执行
切记不能设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE,这样队列会很大,线程数只会保持在corePoolSize大小,当任务陡增时,不能新开线程来执行,响应时间会随之陡增。
- maxPoolSize = (max(tasks)- queueCapacity)/(1/taskcost)
计算可得 maxPoolSize = (1000-80)/10 = 92
(最大任务数-队列容量)/每个线程每秒处理能力 = 最大线程数
- rejectedExecutionHandler:
根据具体情况来决定,任务不重要可丢弃,任务重要则要利用一些缓冲机制来处理
- keepAliveTime和allowCoreThreadTimeout
采用默认通常能满足
以上都是理想值,实际情况下要根据机器性能来决定。如果在未达到最大线程数的情况机器cpu load已经满了,则需要通过升级硬件(呵呵)和优化代码,降低taskcost来处理。
九 真实环境实践
-
- import org.apache.commons.lang3.concurrent.BasicThreadFactory;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
- import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
-
- import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
- import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
- import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
- import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
-
- /**
- * 线程池配置
- *
- * @author oldlu
- **/
- @Configuration
- public class ThreadPoolConfig {
-
- // 核心线程池大小
- @Value("${threadPoolConfig.corePoolSize}")
- private int corePoolSize;
-
- // 最大可创建的线程数
- @Value("${threadPoolConfig.maxPoolSize}")
- private int maxPoolSize;
-
- // 队列最大长度
- @Value("${threadPoolConfig.queueCapacity}")
- private int queueCapacity;
-
- // 线程池维护线程所允许的空闲时间
- @Value("${threadPoolConfig.keepAliveSeconds}")
- private int keepAliveSeconds;
-
- // 线程池对拒绝任务(无线程可用)的处理策略
- @Value("${threadPoolConfig.rejectedExecutionHandler}")
- private String rejectedExecutionHandler;
-
- @Bean(name = "threadPoolTaskExecutor")
- @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "threadPoolTaskExecutor", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
- public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadPoolTaskExecutor() {
- ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
- executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
- executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
- executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
- executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
- RejectedExecutionHandler handler;
- if (rejectedExecutionHandler.equals("CallerRunsPolicy")) {
- handler = new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy();
- } else if (rejectedExecutionHandler.equals("DiscardOldestPolicy")) {
- handler = new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy();
- } else if (rejectedExecutionHandler.equals("DiscardPolicy")) {
- handler = new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy();
- } else {
- handler = new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy();
- }
- executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(handler);
- return executor;
- }
-
- /**
- * 执行周期性或定时任务
- */
- @Bean(name = "scheduledExecutorService")
- protected ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService() {
- return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize,
- new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("schedule-pool-%d").daemon(true).build()) {
- @Override
- protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
- super.afterExecute(r, t);
- Threads.printException(r, t);
- }
- };
- }
- }
-
十 个人总结
Java-如何合理的设置线程池大小
想要合理配置线程池线程数的大小,需要分析任务的类型,任务类型不同,线程池大小配置也不同。
配置线程池的大小可根据以下几个维度进行分析来配置合理的线程数:
任务性质可分为:CPU密集型任务,IO密集型任务,混合型任务。
任务的执行时长。
任务是否有依赖——依赖其他系统资源,如数据库连接等。
CPU密集型任务(普通计算):
尽量使用较小的线程池,一般为CPU核心数+1。
因为CPU密集型任务使得CPU使用率很高,若开过多的线程数,只能增加上下文切换的次数,因此会带来额外的开销。
IO密集型任务(文件,数据库操作):
可以使用稍大的线程池,一般为2*CPU核心数+1。
因为IO操作不占用CPU,不要让CPU闲下来,应加大线程数量,因此可以让CPU在等待IO的时候去处理别的任务,充分利用CPU时间。
混合型任务:
可以将任务分成IO密集型和CPU密集型任务,然后分别用不同的线程池去处理。
只要分完之后两个任务的执行时间相差不大,那么就会比串行执行来的高效。
因为如果划分之后两个任务执行时间相差甚远,那么先执行完的任务就要等后执行完的任务,最终的时间仍然取决于后执行完的任务,而且还要加上任务拆分与合并的开销,得不偿失
依赖其他资源
如某个任务依赖数据库的连接返回的结果,这时候等待的时间越长,则CPU空闲的时间越长,那么线程数量应设置得越大,才能更好的利用CPU。
借鉴别人的文章 对线程池大小的估算公式:
最佳线程数目 = ((线程等待时间+线程CPU时间)/线程CPU时间 )* CPU数目
比如平均每个线程CPU运行时间为0.5s,而线程等待时间(非CPU运行时间,比如IO)为1.5s,CPU核心数为8,那么根据上面这个公式估算得到:((0.5+1.5)/0.5)*8=32。
可以得出一个结论:
线程等待时间所占比例越高,需要越多线程。线程CPU时间所占比例越高,需要越少线程。


