- 1计算机主机一闪一闪的无法启动,电脑启动不了灯一闪一闪的
- 2【JavaScript】如何使用正则表达式_javascript使用正则
- 3Android7.1 动态显示和隐藏导航栏和状态栏 广播_android 设置状态栏覆盖在布局之上,并动态的显示和隐藏状态栏
- 4Python实现AES算法和国密SM4算法_python sm4
- 5linux “大脏牛”漏洞分析(CVE-2017-1000405)_脏牛漏洞
- 6微软的反面:错过了AI时代最大机遇的亚马逊
- 7stm32学习——定时器部分2(输出比较)_output compare no output
- 8手把手教你用 ComfyUI 部署 最新开源的Stable diffusion 3,目前最强的AI绘画模型!(附报错和解决方法)
- 9Three.js——tween动画、光线投射拾取、加载.obj/.mtl外部文件、使用相机控制器_three 加载obj和mtl
- 10python udp sendto_Python中UDP协议的理解
情感分析基于词典(算例代码)_基于词典的情感分析
赞
踩
基于词典的情感分析
情感分析是指挖掘文本表达的观点,识别主体对某客体的评价是褒还是贬,褒贬根据进态度行倾向性研究。文本情感分析可以分为基于机器学习的情感分类方法和基于语义理解的情感分析。基于机器学习进行语义分析的话需要大量的训练集,同时需要人工对其进行分类标注。本文采用基于词典的方法的进行情感分析。
词典情感分析流程图如下:大致意思就是将输入的文本进行分词,将分的词和词典数据库的的词进行匹配。看是属于积极还是消极,否定,还是程度词。然后按照人为定义的打分公式对每个词进行情感打分。每个词汇的情感平均值作为整个句子的情感得分。本文定义的打分公式为:
emotion_value = 1 * ((-1) ** not_num) * emotion_times
式子中not_num为否定词,如果一个词为积极词,则not_num=0.否定词则not_num=1.。emotion_times为程度初始值,初始值为1,如果一个词汇前面出现一个程度副词,emotion_times应加上这个程度副词得数值。

由于是基于词典的情感分析方法。首先准备好几个本地词汇文件。
积极词汇.txt, 消极词汇txt, 否定词汇.txt ,程度副词1.txt,,程度副词2.txt,,程度副词3.txt,,程度副词4.txt,,程度副词5.txt,,程度副词6.txt,。程度副词由于有多种程度不一的程度副词如好,非常好。所以准备多个文件。
读取词汇文件并添加进各自数组:
# part 1:情感词典录入
positive_emotion = []#积极词汇数据库
negative_emotion = []#消极词汇数据库
extreme = []#程度副词1
very = []#程度副词2
more = []#程度副词3
alittlebit = []#程度副词4
insufficiently = []#程度副词5
over = []#程度副词6
no = []#否定词
d = open("positive-emotion.txt", encoding='utf-8')#积极词汇
d2 = open("positive_evaluate.txt", encoding='utf-8')#积极词汇
n = open("negative-emotion.txt", encoding='utf-8')#否定词汇
n22 = open("negative_evaluate.txt", encoding='utf-8')#否定词汇
e = open("extreme-6.txt", encoding='utf-8')#程度副词1
v = open("very-5.txt", encoding='utf-8')#程度副词2
m = open("more-4.txt", encoding='utf-8')#程度副词3
a = open("alittlebit-3.txt", encoding='utf-8')#程度副词4
i = open("insufficiently-2.txt", encoding='utf-8')#程度副词5
o = open("over-1.txt", encoding='utf-8')#程度副词6
n2 = open("no.txt", encoding='utf-8')#否定词
for line in d.readlines():
positive_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进积极词汇数据库
for line in d2.readlines():
positive_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进积极词汇数据库
for line in n.readlines():
negative_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进消极词汇数据库
for line in n22.readlines():
negative_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进消极词汇数据库
for line in e.readlines():
extreme.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词1
for line in v.readlines():
very.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词2
for line in m.readlines():
more.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词3
for line in a.readlines():
alittlebit.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词4
for line in i.readlines():
insufficiently.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词5
for line in o.readlines():
over.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词6
for line in n2.readlines():
no.append(line.strip().encode('utf-8'))#添加进否定词
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
句子的情感分析与识别
# 句子情感的识别与分析
line = self.textbox.toPlainText()#读取用户输入
aline = jieba.cut(line, cut_all=False)#对输入进行分词
emotions = []#情感词汇数组
emotion_value = 0#初始情感值
not_num = 0#初始否定值为0
emotion_times = 1#初始程度副词权重
for word in aline:
# print(word)
if word in positive_emotion:
emotion_value = 1 * ((-1) ** not_num) * emotion_times
emotions.append(emotion_value)
not_num = 0
emotion_times = 1
# positive
elif word in negative_emotion:
not_num = not_num + 1
emotion_value = 1 * ((-1) ** not_num) * emotion_times
emotions.append(emotion_value)
not_num = 0
emotion_times = 1
# negative
elif word in extreme:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 2
elif word in very:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 1.4
elif word in more:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 1
elif word in alittlebit:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 0.4
elif word in insufficiently:
emotion_times = emotion_times - 0.2
elif word in over:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 1.2
elif word in no:
not_num += 1
elif word == "!":#如果是标点!,程度加1
if emotions[len(emotions) - 1] > 0:
emotions[len(emotions) - 1] += 1
else:
emotions[len(emotions) - 1] -= 1
mean_zhi=str(sum(emotions) / len(emotions))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
建立pyqt5的简单页面
页面
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Qt5Agg')
# 使用 matplotlib中的FigureCanvas (在使用 Qt5 Backends中 FigureCanvas继承自QtWidgets.QWidget)
from matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5agg import FigureCanvasQTAgg as FigureCanvas
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class App(QtWidgets.QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
# 父类初始化方法
super(App, self).__init__(parent)
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle('情感分析系统by(yudengwu)')
# 几个QWidgets
self.lb1 = QLabel("情感分析")
self.lb2 = QLabel("情感分析均值(积极为正值,消极为负值):")
self.lb3 = QLabel()
self.lb4=QLabel("情绪波动方差:")
self.lb5=QLabel()
self.lb6 = QLabel("情绪波动曲线")
self.textbox = QTextEdit()
self.figure = plt.figure()
self.canvas = FigureCanvas(self.figure)
self.button_plot = QtWidgets.QPushButton("点击情感分析")
# 连接事件
#self.button_plot.clicked.connect(self.plot_)
# 设置布局
layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
layout.addWidget(self.lb1)
layout.addWidget(self.textbox )
layout.addWidget(self.lb2)
layout.addWidget(self.lb3)
layout.addWidget(self.lb4)
layout.addWidget(self.lb5)
layout.addWidget(self.lb6)
layout.addWidget(self.canvas)
layout.addWidget(self.button_plot)
self.setLayout(layout)
# 运行程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = App()
main_window.show()
app.exec()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
将情感分析部分添加进去作为事件:
总代码如下
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import jieba
import sys
import numpy as nm
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Qt5Agg')
# 使用 matplotlib中的FigureCanvas (在使用 Qt5 Backends中 FigureCanvas继承自QtWidgets.QWidget)
from matplotlib.backends.backend_qt5agg import FigureCanvasQTAgg as FigureCanvas
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtWidgets, QtGui
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class App(QtWidgets.QDialog):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
# 父类初始化方法
super(App, self).__init__(parent)
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle('情感分析系统by(yudengwu)')
# 几个QWidgets
self.lb1 = QLabel("情感分析")
self.lb2 = QLabel("情感分析均值(积极为正值,消极为负值):")
self.lb3 = QLabel()
self.lb4=QLabel("情绪波动方差:")
self.lb5=QLabel()
self.lb6 = QLabel("情绪波动曲线")
self.textbox = QTextEdit()
self.figure = plt.figure()
self.canvas = FigureCanvas(self.figure)
self.button_plot = QtWidgets.QPushButton("点击情感分析")
# 连接事件
self.button_plot.clicked.connect(self.plot_)
# 设置布局
layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
layout.addWidget(self.lb1)
layout.addWidget(self.textbox )
layout.addWidget(self.lb2)
layout.addWidget(self.lb3)
layout.addWidget(self.lb4)
layout.addWidget(self.lb5)
layout.addWidget(self.lb6)
layout.addWidget(self.canvas)
layout.addWidget(self.button_plot)
self.setLayout(layout)
def plot_(self):
# part 1:情感词典录入
positive_emotion = []#积极词汇数据库
negative_emotion = []#消极词汇数据库
extreme = []#程度副词1
very = []#程度副词2
more = []#程度副词3
alittlebit = []#程度副词4
insufficiently = []#程度副词5
over = []#程度副词6
no = []#否定词
d = open("positive-emotion.txt", encoding='utf-8')
d2 = open("positive_evaluate.txt", encoding='utf-8')
n = open("negative-emotion.txt", encoding='utf-8')
n22 = open("negative_evaluate.txt", encoding='utf-8')
e = open("extreme-6.txt", encoding='utf-8')
v = open("very-5.txt", encoding='utf-8')
m = open("more-4.txt", encoding='utf-8')
a = open("alittlebit-3.txt", encoding='utf-8')
i = open("insufficiently-2.txt", encoding='utf-8')
o = open("over-1.txt", encoding='utf-8')
n2 = open("no.txt", encoding='utf-8')
for line in d.readlines():
positive_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进积极词汇数据库
for line in d2.readlines():
positive_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进积极词汇数据库
for line in n.readlines():
negative_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进消极词汇数据库
for line in n22.readlines():
negative_emotion.append(line.strip())#添加进消极词汇数据库
for line in e.readlines():
extreme.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词1
for line in v.readlines():
very.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词2
for line in m.readlines():
more.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词3
for line in a.readlines():
alittlebit.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词4
for line in i.readlines():
insufficiently.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词5
for line in o.readlines():
over.append(line.strip())#添加进程度副词6
for line in n2.readlines():
no.append(line.strip().encode('utf-8'))#添加进否定词
# 句子情感的识别与分析
# input =open(input.txt)
# for line in open("out.txt").readlines():
line = self.textbox.toPlainText()#读取用户输入
aline = jieba.cut(line, cut_all=False)#对输入进行分词
emotions = []#情感词汇数组
emotion_value = 0#初始情感值
not_num = 0#初始否定值为0
emotion_times = 1#初始程度副词权重
for word in aline:
# print(word)
if word in positive_emotion:
emotion_value = 1 * ((-1) ** not_num) * emotion_times
emotions.append(emotion_value)
not_num = 0
emotion_times = 1
# positive
elif word in negative_emotion:
not_num = not_num + 1
emotion_value = 1 * ((-1) ** not_num) * emotion_times
emotions.append(emotion_value)
not_num = 0
emotion_times = 1
# negative
elif word in extreme:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 2
elif word in very:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 1.4
elif word in more:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 1
elif word in alittlebit:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 0.4
elif word in insufficiently:
emotion_times = emotion_times - 0.2
elif word in over:
emotion_times = emotion_times + 1.2
elif word in no:
not_num += 1
elif word == "!":
if emotions[len(emotions) - 1] > 0:
emotions[len(emotions) - 1] += 1
else:
emotions[len(emotions) - 1] -= 1
mean_zhi=str(sum(emotions) / len(emotions))
self.lb3.setText(mean_zhi)
qingxustd=str(nm.cov(emotions))
self.lb5.setText(qingxustd)
x1 = range(0, len(emotions))
ax = self.figure.add_axes([0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8])
ax.clear() # 每次绘制一个函数时清空绘图
ax.plot(x1, emotions, label='emotion values', marker='.', markerfacecolor='red', markersize=12)
ax.set_xlabel('emotion_words_apper_times')
ax.set_ylabel('emotion_value')
#ax.legend()
#ax.ylim(-10, 10)
self.canvas.draw()
# 解析上传文件
# 运行程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
main_window = App()
main_window.show()
app.exec()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
运行结果示范:
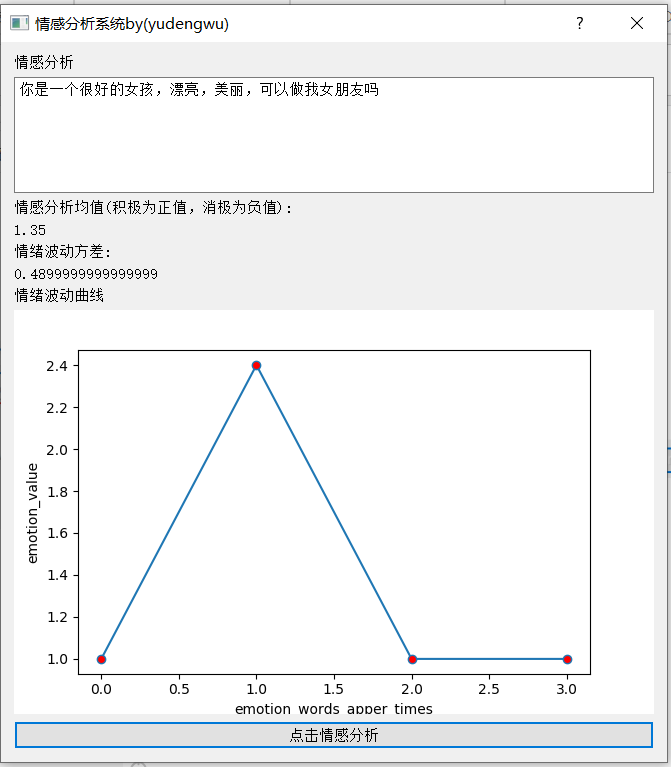
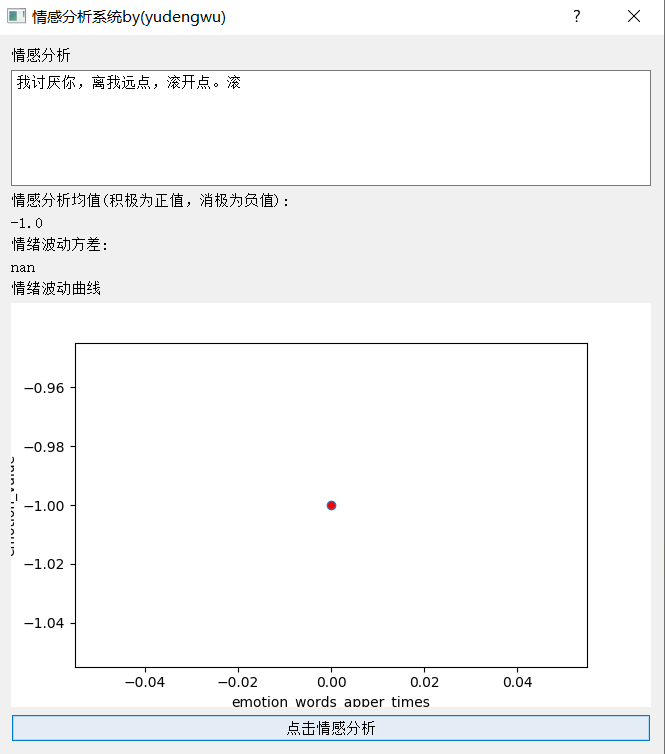
词典的优劣决定着模型的好坏。
数据集链接:
中文情感分析词典数据集(基于词典).zip
电气专业的计算机小白: 余登武,写博文不容易,如果你觉得本文对你有用,请点个赞支持下,谢谢。




