热门标签
热门文章
- 1Haproxy集群
- 2《数据结构》-第八章 排序(习题)_对任意7个关键字进行基于比较的排序
- 3OpenCV视觉--视频人脸微笑检测(超详细,附带检测资源)_opencv笑脸识别
- 4阿里云百炼模型训练实战流程:从入门到实战应用_阿里云百炼 流程怎么使用
- 5算法力扣刷题记录 六十三【回溯章节开篇】
- 6web.xml中的Security Constraint元素
- 7六自由度机器人逆向运动学_【课程笔记】Notes for Robotics/机器人学 (Part1)
- 8Redis Cluster基于客户端对mget的性能优化_redis cluster mget
- 9Python 比特币编程实用指南(全)_python 比特币包
- 10Nature重磅!Google DeepMind推出AlphaDev,用AI打破十年算法封印!_ai.google.dev
当前位置: article > 正文
windows10安装Tensorflow-gpu 2.10.0_tensorflow2.10.0对应tensorflow intel版本
作者:运维做开发 | 2024-08-06 19:04:21
赞
踩
tensorflow2.10.0对应tensorflow intel版本
windows10安装Tensorflow-gpu 2.10.0
本文主要目的是 从0开始演示 在windows10 平台安装Tensorflow-gpu 2.10.0。
Tensorflow-gpu 2.10.0 之后的版本,不再支持这样的安装方式,如果有需要,请参考wsl安装ubuntu的方式,进行安装。
1.安装miniconda
https://docs.anaconda.com/free/miniconda/index.html

2.安装CUDA
tensorflow-cuda-cudnn对应版本
tensorflow-cuda-cudnn

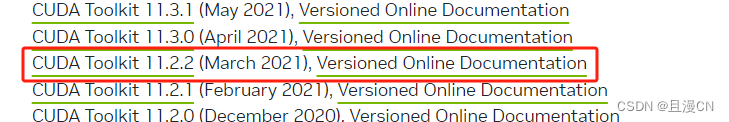
下载 CUDA 11.2.2
cuda11.2.2 | https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive
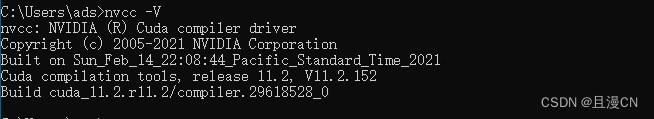
cuda安装完之后,已经配置好环境路径了,直接在cmd中查看
nvcc -V
- 1
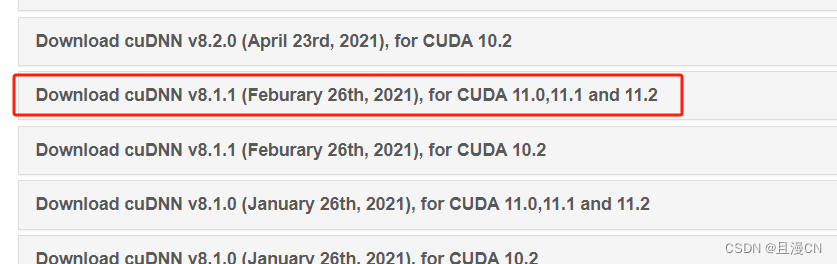
下载cudnn 8.1.1
cudnn 8.1.1 | https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive
把cudnn8.10解压出来的文件,拷贝到cuda下,有对应的文件下名称,对应拷贝过去。
3.创建python环境
conda create --name tf2.10 python==3.10.14
conda activate tf2.10
- 1
- 2
- 3
4.安装Tensorflow-GPU 2.10.0
Tensorflow-GPU 2.10.0
pip install tensorflow-gpu==2.10.0 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
- 1
安装一些常用常用包
pip install scikit-learn einops ipywidgets pandas tqdm jupyterlab matplotlib seaborn -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
- 1
测试
python ./mnist.py
import tensorflow as tf
print(tf.__version__)
print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))
print(tf.test.is_built_with_cuda())
import tensorflow as tf
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
print(tf.__version__)
print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data(path="mnist.npz")
input_shape = (28, 28, 1)
x_train=x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0], x_train.shape[1], x_train.shape[2], 1)
x_train=x_train / 255.0
x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0], x_test.shape[1], x_test.shape[2], 1)
x_test=x_test/255.0
y_train = tf.one_hot(y_train.astype(np.int32), depth=10)
y_test = tf.one_hot(y_test.astype(np.int32), depth=10)
batch_size = 64
num_classes = 10
epochs = 5
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (5,5), padding='same', activation='relu', input_shape=input_shape),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, (5,5), padding='same', activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.25),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3,3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, (3,3), padding='same', activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(strides=(2,2)),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.25),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(epsilon=1e-08), loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['acc'])
class myCallback(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs={}):
if(logs.get('acc')>0.995):
print("\nReached 99.5% accuracy so cancelling training!")
self.model.stop_training = True
callbacks = myCallback()
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_split=0.1,
callbacks=[callbacks])
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/运维做开发/article/detail/938886
推荐阅读
相关标签


