热门标签
热门文章
- 1利用Java8新特性stream流给集合中的某个属性赋值_用stream流给数组的多个属性赋值
- 2片上网络(NoC)技术的背景、意义以及发展_片上网络与总线对比
- 3JAVA获得真正IP过滤虚拟机IP_根据网卡名称获取ip时不获取虚ip java
- 4PAT乙级_每个输入包含一个测试用例。每个测试用例先给出一个不超过 1000 的正整数 n 表示
- 5BP神经网络_bp神经网络结构
- 6计划任务ScheduledExecutorService的使用总结
- 7uview组件使用笔记_uview组件中的步骤条样式颜色怎么改
- 8【ArcGIS】批量对栅格图像按要素掩膜提取_arcmap批量掩膜提取idle
- 9Unity 使用JSON实现本地数据保存和读取_unity json get set
- 10CSDN IT冷知识(每日更新)_在 19 世纪至 20 世纪有一对同名同姓的父子,他们在唱片、办公设备、打字机到计算
当前位置: article > 正文
Tensorflow2.0笔记 - where,scatter_nd, meshgrid相关操作
作者:键盘狂人 | 2024-02-01 10:52:43
赞
踩
Tensorflow2.0笔记 - where,scatter_nd, meshgrid相关操作
本笔记记录tf.where进行元素位置查找,scatter_nd用于指派元素到tensor的特定位置,meshgrid用作绘图的相关操作。
- import tensorflow as tf
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
- tf.__version__
-
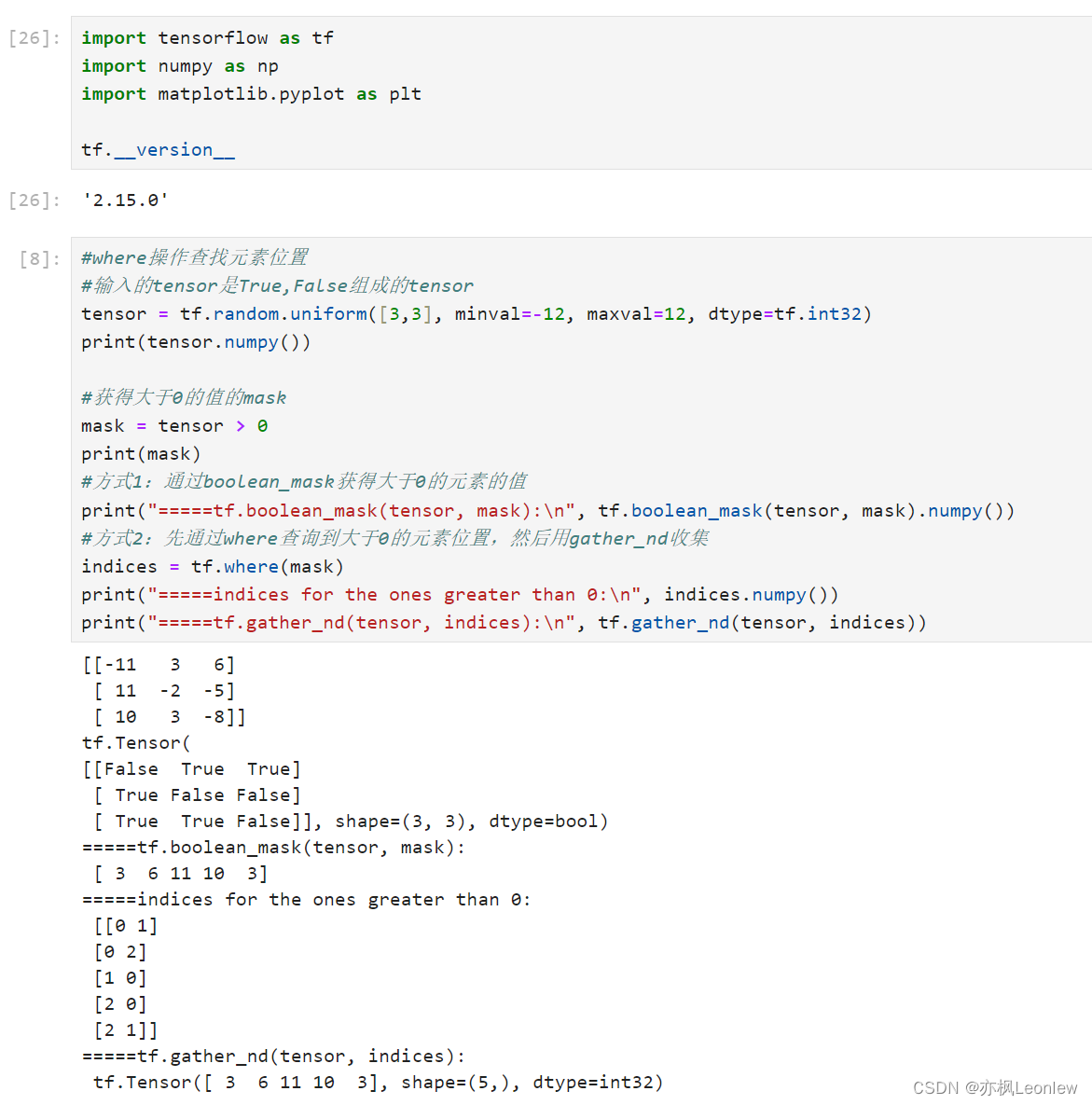
- #where操作查找元素位置
- #输入的tensor是True,False组成的tensor
- tensor = tf.random.uniform([3,3], minval=-12, maxval=12, dtype=tf.int32)
- print(tensor.numpy())
-
- #获得大于0的值的mask
- mask = tensor > 0
- print(mask)
- #方式1:通过boolean_mask获得大于0的元素的值
- print("=====tf.boolean_mask(tensor, mask):\n", tf.boolean_mask(tensor, mask).numpy())
- #方式2:先通过where查询到大于0的元素位置,然后用gather_nd收集
- indices = tf.where(mask)
- print("=====indices for the ones greater than 0:\n", indices.numpy())
- print("=====tf.gather_nd(tensor, indices):\n", tf.gather_nd(tensor, indices))
-
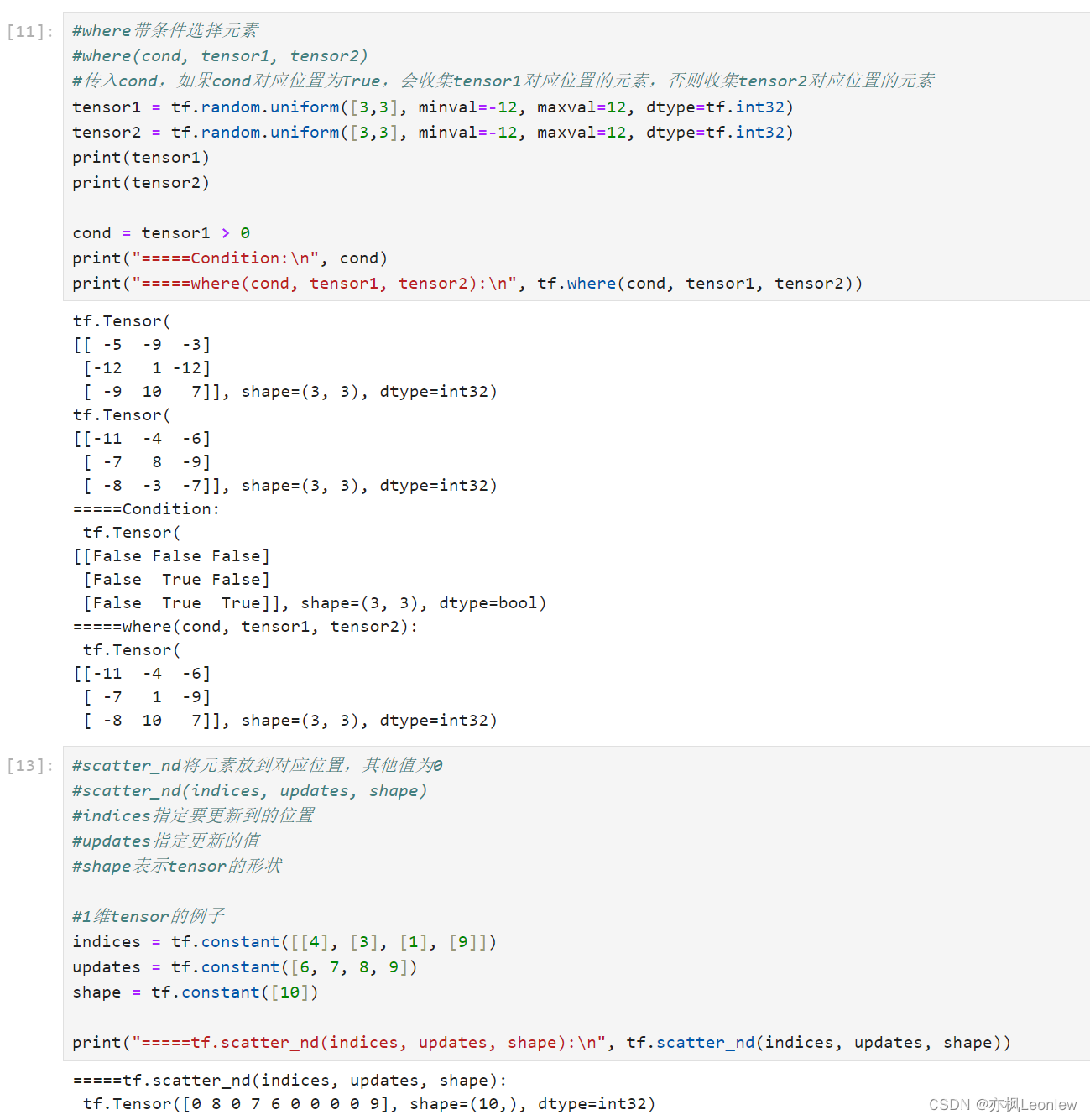
- #where带条件选择元素
- #where(cond, tensor1, tensor2)
- #传入cond,如果cond对应位置为True,会收集tensor1对应位置的元素,否则收集tensor2对应位置的元素
- tensor1 = tf.random.uniform([3,3], minval=-12, maxval=12, dtype=tf.int32)
- tensor2 = tf.random.uniform([3,3], minval=-12, maxval=12, dtype=tf.int32)
- print(tensor1)
- print(tensor2)
-
- cond = tensor1 > 0
- print("=====Condition:\n", cond)
- print("=====where(cond, tensor1, tensor2):\n", tf.where(cond, tensor1, tensor2))
-
-
- #scatter_nd将元素放到对应位置,其他值为0
- #scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape)
- #indices指定要更新到的位置
- #updates指定更新的值
- #shape表示tensor的形状
-
- #1维tensor的例子
- indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [9]])
- updates = tf.constant([6, 7, 8, 9])
- shape = tf.constant([10])
-
- print("=====tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape):\n", tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape))
-
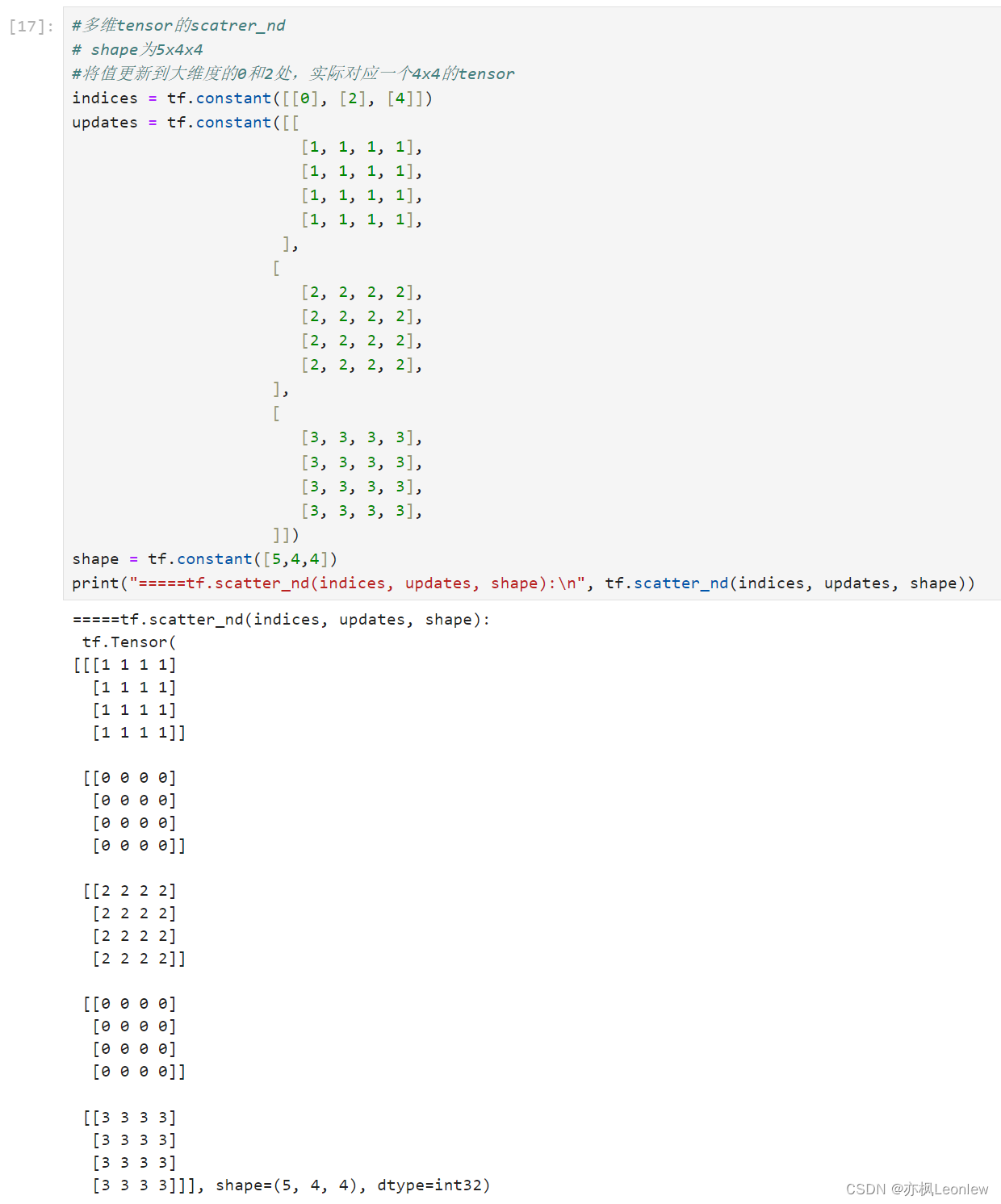
- #多维tensor的scatrer_nd
- # shape为5x4x4
- #将值更新到大维度的0和2处,实际对应一个4x4的tensor
- indices = tf.constant([[0], [2], [4]])
- updates = tf.constant([[
- [1, 1, 1, 1],
- [1, 1, 1, 1],
- [1, 1, 1, 1],
- [1, 1, 1, 1],
- ],
- [
- [2, 2, 2, 2],
- [2, 2, 2, 2],
- [2, 2, 2, 2],
- [2, 2, 2, 2],
- ],
- [
- [3, 3, 3, 3],
- [3, 3, 3, 3],
- [3, 3, 3, 3],
- [3, 3, 3, 3],
- ]])
- shape = tf.constant([5,4,4])
- print("=====tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape):\n", tf.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape))
-
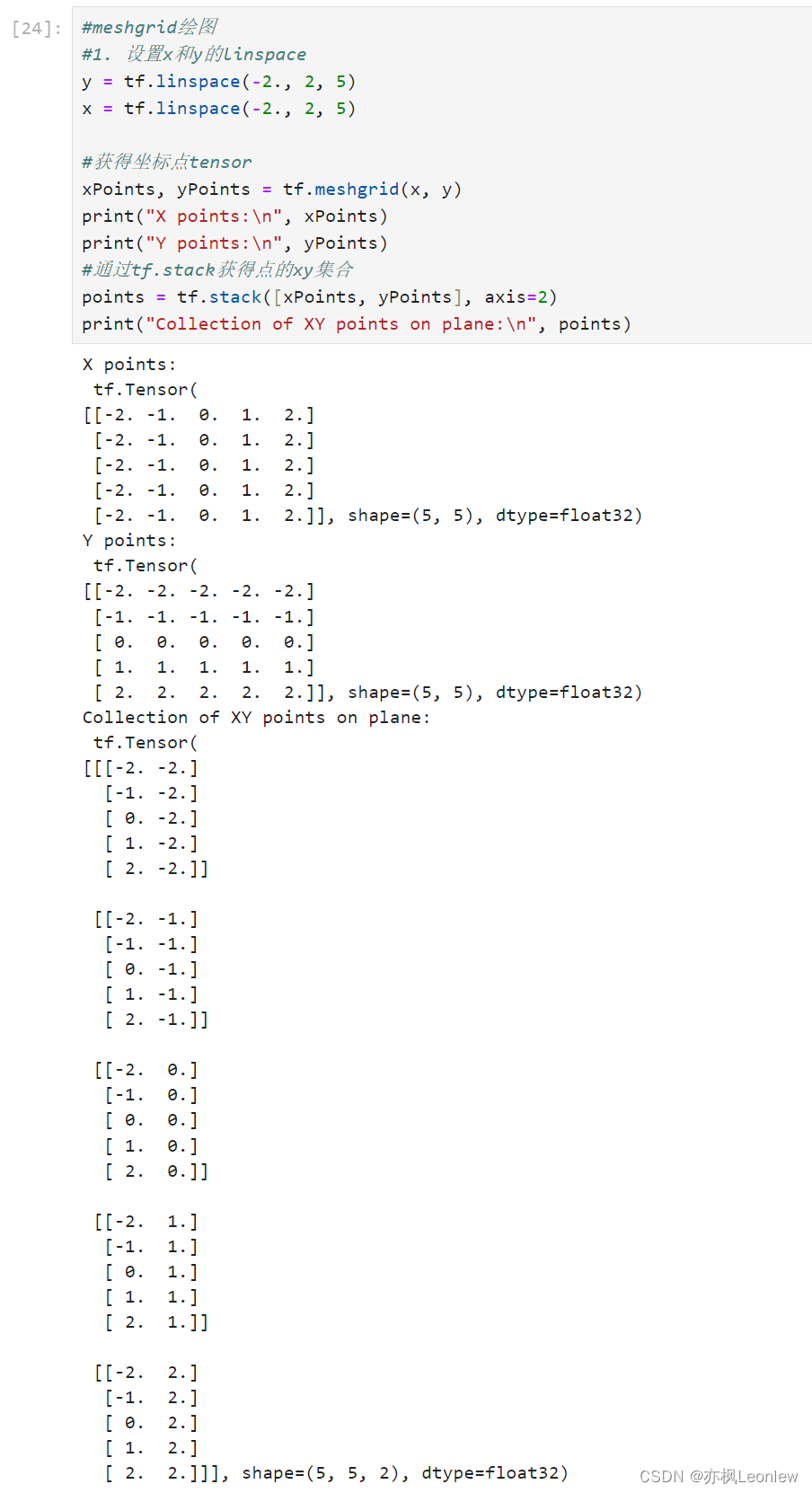
- #meshgrid绘图
- #1. 设置x和y的linspace
- y = tf.linspace(-2., 2, 5)
- x = tf.linspace(-2., 2, 5)
-
- #获得坐标点tensor
- xPoints, yPoints = tf.meshgrid(x, y)
- print("X points:\n", xPoints)
- print("Y points:\n", yPoints)
- #通过tf.stack获得点的xy集合
- points = tf.stack([xPoints, yPoints], axis=2)
- print("Collection of XY points on plane:\n", points)
-
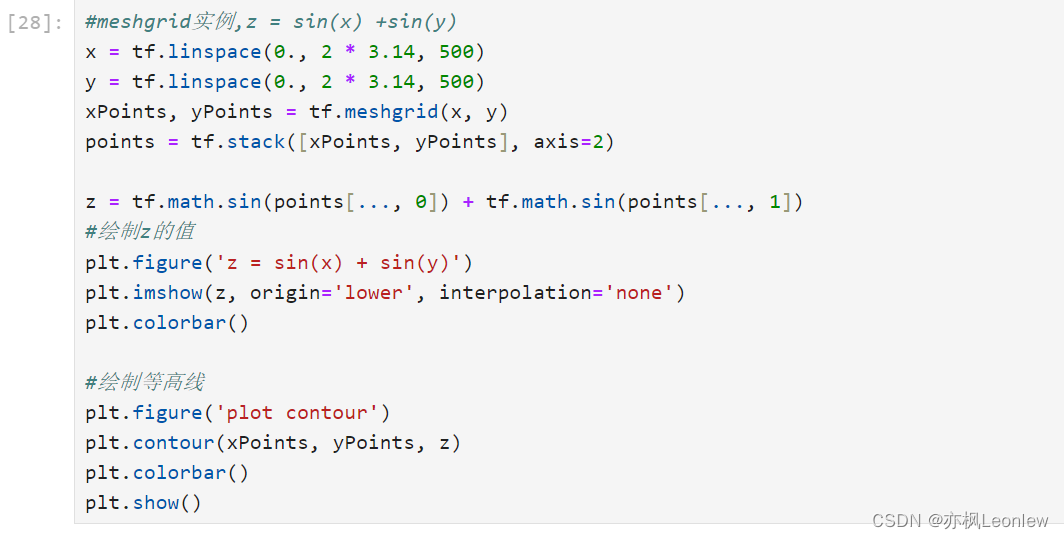
- #meshgrid实例,z = sin(x) +sin(y)
- x = tf.linspace(0., 2 * 3.14, 500)
- y = tf.linspace(0., 2 * 3.14, 500)
- xPoints, yPoints = tf.meshgrid(x, y)
- points = tf.stack([xPoints, yPoints], axis=2)
-
- z = tf.math.sin(points[..., 0]) + tf.math.sin(points[..., 1])
- #绘制z的值
- plt.figure('z = sin(x) + sin(y)')
- plt.imshow(z, origin='lower', interpolation='none')
- plt.colorbar()
-
- #绘制等高线
- plt.figure('plot contour')
- plt.contour(xPoints, yPoints, z)
- plt.colorbar()
- plt.show()

运行结果:

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/blog/article/detail/53390
推荐阅读
- 如果你想让模型在两个GPU上进行训练,你需要使用分布式训练。在PyTorch中,可以使用。这样,你就可以在两个GPU上进行训练了。注意,你需要在命令行中使用。指定每个节点使用的GPU数量。指定使用哪些GPU进行训练,指定输出设备的GPUID... [详细]
赞
踩
- Spring表达式语言最初是为Spring社区创建的,它拥有一种受良好支持的表达式语言,可用于Spring产品组合中的所有产品。虽然SpEL是Spring产品组合中表达式评估的基础,但它不直接与Spring绑定,可以独立使用。Spring表... [详细]
赞
踩
- title:JDK1.8特性date:2022-06-0322:26:52categories:Java8允许我们给接口添加一个非抽象的方法实现,只需要使用default关键字即可,这个特征又叫做扩展方法,代码如下:代码如下:文中的form... [详细]
赞
踩
- 路径规划方法综述概述主要方法基于图搜索的方法DijkstraA*状态栅格法基于采样的搜索方法Rapidly-ExploringRandomTree(RRT)概述路径规划的过程大致如下图所示,信息获取-感知-通信-决策-控制-执行。主要方法基... [详细]
赞
踩
- JDK8新特性详解_jdk8jdk8JDK8新特性1.了解Java发展史2.Lambda表达式3.接口的增强4.函数式接口5.方法引用6.StreamAPI7.Optional8.新时间日期API9.其他新特性一、Java发展历史1.Jav... [详细]
赞
踩
- win10已经发布一周年了,JDK8也比较成熟了,越来越多的小伙伴想在win10上安装JDk8,可是很多小伙伴对安装与配置JDK8还是不熟悉,为解决安装与配置问题,本文详细说明怎么在win10上安装JDK8,方便小伙伴们快速学会安装与配置J... [详细]
赞
踩
- SpringSecurity是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。提供了完善的认证机制和方法级的授权功能。是一款非常优秀的权限管理框架。它的核心是一组过滤器链,不同的功能经由不同的过滤器。这篇文章就是想通过一个小案例将Spri... [详细]
赞
踩
- 本篇一句话总结:Java实现分布式通信,可以基于JavaAPI、开源框架和远程通信技术三种方式实现。正文开始:通过上一篇文章《分布式专题(1)-计算机网络》我们知道了计算机之间之所以能够进行通信的原理。如果对计算机网络还不是很清楚的同学可以... [详细]
赞
踩
- linux下PHP环境搭建重点内容linux下环境搭建第一步安装Apache2sudoapt-getinstallapache2第二步安装PHP模块sudoapt-getinstallphp5第三步安装Mysqlsudoapt-getins... [详细]
赞
踩
- article
zookeeper的配置(Windows环境和Linux环境下)常见问题(zookeeper_server.pid: No such file or directory)解决_zookeeper 启动no such file
Zookeeper作为一款优秀的注册中心,其安装和配置都十分简单,单机模式、集群模式配置方便,而且其安装包windows和linux下通用,下载地址如下:http://zookeeper.apache.org/releases.html--... [详细]赞
踩
- 上篇博文,我们成功的安装和启动了zookeeper服务器,zookeeper还提供了很多方便的功能,方便我们查看服务器的状态,增加,修改,删除数据(入口是zkServer.sh和zkCli.sh)。还提供了一系列四字命令,方便我们跟服务器进... [详细]
赞
踩
- 备份好/etc/apt/sources.list文件后,将sources.list里面的内容修改为清华镜像源:#默认注释了源码镜像以提高aptupdate速度,如有需要可自行取消注释debhttps://mirrors.tuna.tsing... [详细]
赞
踩
- 通过命令:ZkServer.shstatus查看zookeeper状态显示以下错误1.Mode:standalonezookeeper处于单机模式,说明此时zookeeper的zoo.cfg文件配置有问题2.Errorcontactings... [详细]
赞
踩
- os.environ[“CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER”]=“PCI_BUS_ID”#按照PCI_BUS_ID顺序从0开始排列GPU设备os.environ[“CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES”]=“0”#设置当前使用的GPU设... [详细]
赞
踩
- tensorflow安装2.12版本开始,GPU的包名发生变化,安装方法略有不同_tensorflow版本tensorflow版本tensorflow1和2的安装部署,演示2.14版本(最新是2.15版本)windows和linux用法一致... [详细]
赞
踩
- 刷题记录:牛客NC21472[NOIP2018]对称二叉树_现在给出一棵二叉树,希望你找出它的一棵子树,该子树为对称二叉树,且节点数最多。现在给出一棵二叉树,希望你找出它的一棵子树,该子树为对称二叉树,且节点数最多。NOIP2018普及组的... [详细]
赞
踩
- 题意:给你一个有n(2思路:不难发现,最后一定要正好去掉k-1条边才能使他们互不连通,对于这k-1条边我们希望他们的权值之和最小,更进一步,我们希望选取的每条边都尽量小。正常来想,应该是边权递增排序,每次去掉一条边,看是否不连通的数目加... [详细]
赞
踩
- Ubuntu16.04安装NVIDIA驱动时的一些坑与解决方案_ubuntu16.04安装nvidia驱动的坑ubuntu16.04安装nvidia驱动的坑Ubuntu16.04安装NVIDIA驱动时的一些坑与解决方案参考文章:(1)Ubu... [详细]
赞
踩
- SpringBoot注册自己的Servlet(三种方式)(内含源代码)方法1:使用servlet3.0规范提供的注解方式注册Servlet1,声明servlet及映射2,加上@ServletComponentScan才会扫描加了这个注解运行... [详细]
赞
踩
- Git的常用命令与含义及各种方法简记GitGit与SVN区别简述状态转换图命令与含义一、新建代码库二、配置三、增加/删除文件四、代码提交五、分支六、标签七、查看信息八、远程同步九、撤销十、其他Git分支管理策略一、主分支Master二、开发... [详细]
赞
踩
相关标签


