- 1渗透测试之内网渗透(四):端口转发_socat 端口转发
- 2如何在VSCode上新建Flutter项目【两步搞定】_vscode fulltter项目
- 3内卷了!阿里 Java 八股文面试题“惨遭”泄露,导致 132 人面进大厂_阿里java八股文
- 4苹果手机支持鸿蒙,全球第三大手机系统「鸿蒙」上线,这19款能抢先用…
- 5Win10系统更新后【开机黑屏/白屏,不显示桌面,但是鼠标和任务管理器都好使】问题的解决_csdn win10更新黑屏
- 6java 子线程定时去更改主线程的变量
- 7大数据在金融行业的应用_大数据技术在商务银行的应用图表
- 8python坐标字符串_字符串坐标的numpy mgrid shapely
- 9linux kernel 5.1编译8723ds报错_vfs_internal_i_am_really_a_filesystem_and_am_not_a
- 10IOS MJRefresh:下拉刷新与上拉加载_ios开发 mjrefresh上拉加载
【OpenCV DNN】Flask 视频监控目标检测教程 02_flask部署目标检测模型
赞
踩
欢迎关注『OpenCV DNN @ Youcans』系列,持续更新中
【OpenCV DNN】Flask 视频监控目标检测教程 01
【OpenCV DNN】Flask 视频监控目标检测教程 02
【OpenCV DNN】Flask 视频监控目标检测教程 02
本系列从零开始,详细讲解使用 Flask 框架构建 OpenCV DNN 模型的 Web 应用程序。
本节介绍使用OpenCV+Flask将计算机视觉应用程序部署到Web端。
3.1 从URL地址读取图片进行处理
我们编写的第一个例程,从指定的URL地址读取图片,对图片进行处理,返回处理后的图片并在网页上显示。本例程在浏览器直接显示响应图片,没有使用HTML文档。
3.1.1 从指定的 url 地址读取图像
(1)首先从指定的 url 地址读取图像。
Flask中使用route()装饰器将应用程序的URL绑定到函数,可以接受URL参数实现路由访问。
@app.route('/enhance', methods=['GET'])
def detail_enhance():
# 从指定的 url 地址读取图像
with urllib.request.urlopen(request.args.get('url')) as url:
image_array = np.asarray(bytearray(url.read()), np.uint8)
# 从指定的内存缓存中读取数据,并把数据转换成图像格式
imgCV = cv2.imdecode(image_array, -1) # 转换为 OpenCV 图像
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
使用函数request.args.get(‘url’)来获取URL参数,构建一个变量URL。当我们访问/user/时,就可以接收到URL地址,然后从URL地址读取图片。
注意不能使用函数cv.imread()读取图像,而要使用函数cv.imdecode()从指定的内存缓存中读取数据,并将传输数据转换为OpenCV图像。
(2)图像处理。
简单地,例程使用边缘保护图像滤波和铅笔素描两种方法进行图像处理。
(3)将图像编码到内存缓冲区。
使用函数cv.imencode()将图像编码为流数据,存储到内存缓存中,方便网络传输。
(4)生成返回页面响应。
使用函数make_response()将缓存中的图像编码封装为响应对象,将页面响应返回到客户端。
3.1.2 例程:从指定的 url 读取图像
完整的例程如下。
# opencvFlask01.py import cv2 import numpy as np from flask import Flask, request, make_response import urllib.request app = Flask(__name__) # 用当前脚本名称实例化Flask对象 @app.route('/enhance', methods=['GET']) def detail_enhance(): # 从指定的 url 地址读取图像 with urllib.request.urlopen(request.args.get('url')) as url: image_array = np.asarray(bytearray(url.read()), np.uint8) # 从指定的内存缓存中读取数据,并把数据转换成图像格式 imgCV = cv2.imdecode(image_array, -1) # 转换为 OpenCV 图像 # # 双边滤波增强图像 # dst = cv2.detailEnhance(imgCV, sigma_s=10, sigma_r=0.2) # 边缘保护滤波图像 dst = cv2.edgePreservingFilter(imgCV, sigma_s=50, sigma_r=0.4) # 将图像编码到内存缓冲区 ret, out_buf = cv2.imencode('.jpg', dst) # 生成返回页面响应 resp = make_response(out_buf.tobytes()) # 封装为响应对象 resp.headers['Content-Type'] = 'image/jpeg' # 设置响应头 return resp @app.route('/pencil', methods=['GET']) def pencil_sketch(): # 从指定的 url 地址读取图像 with urllib.request.urlopen(request.args.get('url')) as url: image_array = np.asarray(bytearray(url.read()), np.uint8) # 从指定的内存缓存中读取数据,并把数据转换成图像格式 imgCV = cv2.imdecode(image_array, -1) # 转换为 OpenCV 图像 # 铅笔画滤波图像 dst1, dst2 = cv2.pencilSketch(imgCV, sigma_s=100, sigma_r=0.15, shade_factor=0.02) # 将图像编码到内存缓冲区 ret, out_buf = cv2.imencode('.jpg', dst1) # 生成返回页面响应 resp = make_response(out_buf.tobytes()) # 封装为响应对象 resp.headers['Content-Type'] = 'image/jpeg' # 设置响应头 return resp if __name__ == '__main__': # 启动一个本地开发服务器,激活该网页 app.run(host='0.0.0.0', debug=True) # 绑定 IP 和端口
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
运行程序cvFlask01.py,启动Web服务器,控制台将显示如下消息。
* Serving Flask app 'cvFlask01'
* Debug mode: off
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000
* Running on http://192.168.3.249:5000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
在浏览器输入以下URL,调用GET请求。
http://192.168.3.249:5000/enhance?url=http://www.news.cn/photo/2023-03/29/1129476453_16800903517201n.jpg
http://192.168.3.249:5000/pencil?url=http://www.news.cn/photo/2023-03/29/1129476453_16800903517201n.jpg
- 1
- 2
- 3
不同网络设备运行时的IP地址不同,具体可以参考控制台显示输出的内容。其中参数url的值http://www.news.cn/photo/***.jpg是待处理图像的URL地址。通过route()装饰器的路由规则,将enhance绑定到函数detail_enhance(),将pencil绑定到函数pencil_sketch(),执行不同的图像处理任务。
Flask获取GET请求后,进行图像处理,并在浏览器显示响应图片如下。
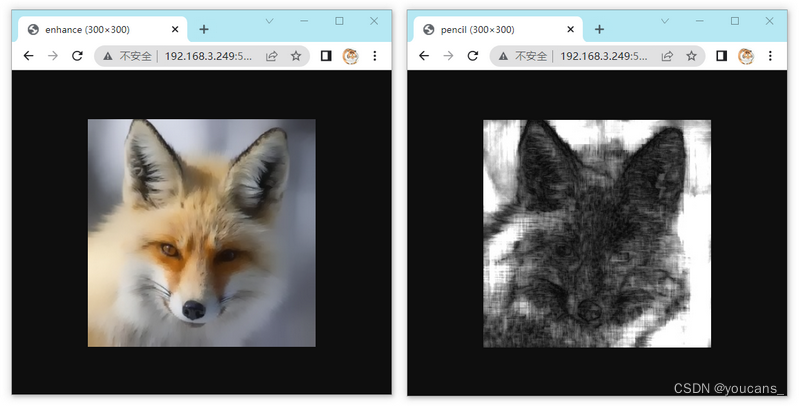
3.2 上传本地图片进行卡通处理
我们的第二个例程,上传本地图片,对图片进行处理,返回处理图片并在网页上进行格式化显示。
3.2.1 建立 Flask 项目
为了处理本地图片上传和格式化显示处理的图片,我们需要建立一个Flask项目,并编写简单的HTML文档。具体步骤如下。
(1)新建一个Flask项目。
项目默认配置建立static和templates目录,static目录用来存放静态资源,例如图片、js、css文件等,templates目录存放模板文件。网站逻辑由Python程序文件cvFlask02.py实现,保存在项目的根目录。项目cvFlask02的文件树如下。
---项目文件名\
|---static\
|---templates\
| |---processed.html
| |---upload.html
|--- cvFlask02.py
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.2.2 编写 HTML 文档
(2)编写upload.html文档,用于上传本地图片,保存在templates目录。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>OpenCV+Flask 上传图片</title> </head> <body> <h1 align="center">OpenCV+Flask 例程:上传本地图片处理</h1> <p align="center">Developed by youcans@xupt,2023</p> <form action="" enctype='multipart/form-data' method='POST'> <label>选择按钮:</label> <input type="file" name="file" style="margin-top:25px;"/> <br> <label>选中文件:</label> <input type="text" class="txt_input" name="name" value="png/jpg/jpeg/bmp" style="margin-top:20px;"/> <br> <label>上传按钮:</label> <input type="submit" value="上传图片" class="button-new" style="margin-top:20px;"/> <br> </form> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
(3)编写processed.html文档,用于显示上传图片和处理图片,保存在templates目录。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>OpenCV+Flask 上传图片</title> </head> <body> <h1 align="center">OpenCV+Flask 例程:上传本地图片进行处理</h1> <p align="center">Developed by youcans@xupt, 2023</p> <form action="" enctype='multipart/form-data' method='POST'> <label>选中文件:</label> <input type="text" class="txt_input" name="name" value={{userinput}} style="margin-top:10px;"/> <br> </form> <h2 align="center">图片处理结果</h2> <table width="700" height="350" border="5" align="center" frame=void> <tr> <td align="center" valign="middle">原始图片</td> <td align="center" valign="middle">处理结果</td> </tr> <tr> <td align="center" valign="middle"> <img src="{{ url_for('static', filename= './images/upload.jpg',_t=val1) }}" width="300" height="300" alt="上传的原始图片"/> </td> <td align="center" valign="middle"> <img src="{{ url_for('static', filename= './images/processed.jpg',_t=val1) }}" width="300" height="300" alt="处理完成的图片"/> </td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
(4)编写Python程序文件cvFlask02.py,保存在项目根目录下。
3.2.3 Python程序实现业务逻辑
Python程序实现如下的业务逻辑:
1)启动一个本地开发服务器,激活upload.html网页。
2)接收upload.html页面上传的图像文件,并进行检查。
3)将上传的图片保存到 upload_path 路径。
4)调用图像处理子程序,对上传的图像进行处理。
5)激活processed.html网页,显示原始图像和处理后的图像。
本例程的图像处理子程序,使用cv. Stylization()函数对上传的图片进行卡通化处理,也可以根据需要实现其它图片处理方法。
cvFlask02.py完整的程序代码如下。
# cvFlask02.py # OpenCV+Flask 图像处理例程 02 # 上传本地图片进行处理,在网页上显示处理结果 # Copyright 2023 Youcans, XUPT # Crated:2023-4-25 # coding:utf-8 import cv2 import os, time from flask import Flask, render_template, request, make_response, jsonify from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename from datetime import timedelta # 设置允许的文件格式 ALLOWED_EXTENSIONS = set(['png', 'jpg', 'JPG', 'PNG', 'bmp']) app = Flask(__name__) # 用当前脚本名称实例化Flask对象 app.send_file_max_age_default = timedelta(seconds=1) # 设置静态文件缓存过期时间 @app.route('/upload', methods=['POST', 'GET']) # 添加路由 def upload(): if request.method == 'POST': f = request.files['file'] # 从表单的 file 字段获取文件,file为该表单的name值 print("user_input:", f.filename) # tiger02.png if not (f and allowed_file(f.filename)): # 检查图片类型 return jsonify({"error": 1001, "msg": "上传图片必须是 png/jpg/jpeg/bmp 类型"}) user_input = request.form.get("name") # 获取表单输入的 name 值, png/jpg/jpeg/bmp basepath = os.path.dirname(__file__) # 当前文件所在路径 C:\Users\David\cvFlask\ # upload_filepath = os.path.join(basepath, 'static\images', secure_filename(f.filename)) upload_filepath = os.path.join(basepath, 'static\images', 'upload.jpg') # 合成上传图片的保存路径 print("upload_filepath", upload_filepath) # upload_path, C:\Users\David\cvFlask\static\images\upload.jpg f.save(upload_filepath) # 将上传的图片保存到 upload_path 路径 # OpenCV 图像处理 dst = imageProcessing(upload_filepath) # 调用图片处理子程序 cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(basepath, 'static/images', 'processed.jpg'), dst) # 保存处理后的图片 user_input = f.filename # 上传图片的文件名 return render_template('processed.html', userinput=user_input, val1=time.time()) return render_template('upload.html') def imageProcessing(filepath): # 图片处理子程序 imgCV = cv2.imread(filepath) # 从 filepath 路径读取图片 dst = cv2.stylization(imgCV, sigma_s=60, sigma_r=0.07) # 图片卡通化处理 return dst def allowed_file(filename): return '.' in filename and filename.rsplit('.', 1)[1] in ALLOWED_EXTENSIONS if __name__ == '__main__': # 启动一个本地开发服务器,激活该网页 app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000, debug=True) # 绑定 IP 和端口
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
3.2.4 运行脚本
(5)接下来运行此脚本。
进入cvFlask02项目的根目录,运行程序cvFlask02.py,启动流媒体服务器。控制台将显示如下消息。
* Serving Flask app 'cvFlask02'
* Debug mode: on
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000
* Running on http://192.168.3.249:5000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
在浏览器输入URL(http://192.168.3.249:5000/upload),打开upload.html网页,显示如下。
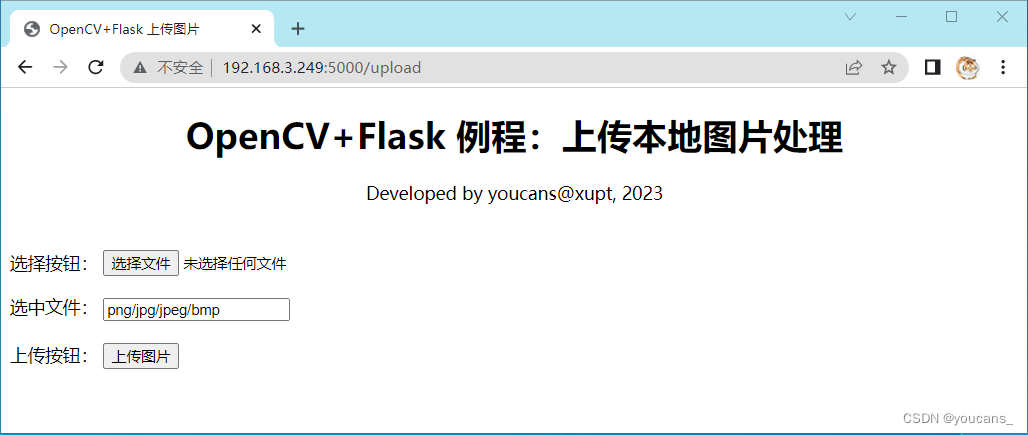
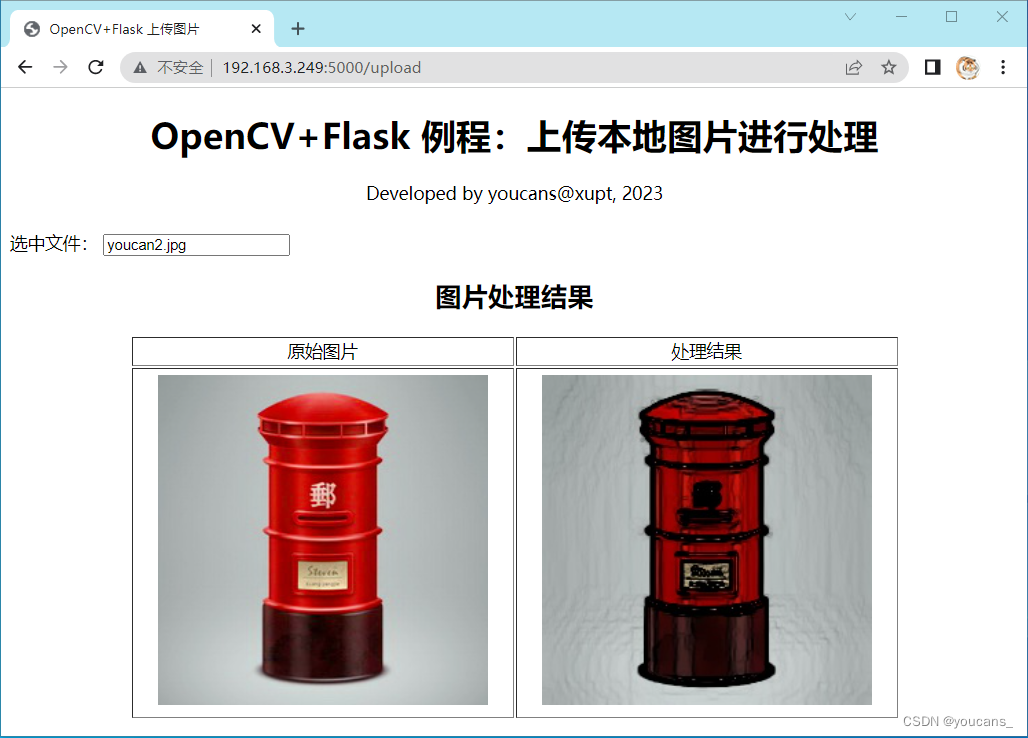
在浏览器点击页面上的选择按钮,选择本地的图片上传,上传的图片保存到static\images目录。
程序cvFlask02.py对上传的图片进行卡通化处理,然后激活processed.html网页,显示原始图像和处理后的图像。
在移动手机打开浏览器,输入URL(http://192.168.3.249:5000/upload),也可以上传手机中的图片进行处理,结果如下图所示。不同网络设备运行时的IP地址不同,具体可以参考控制台显示输出的内容。
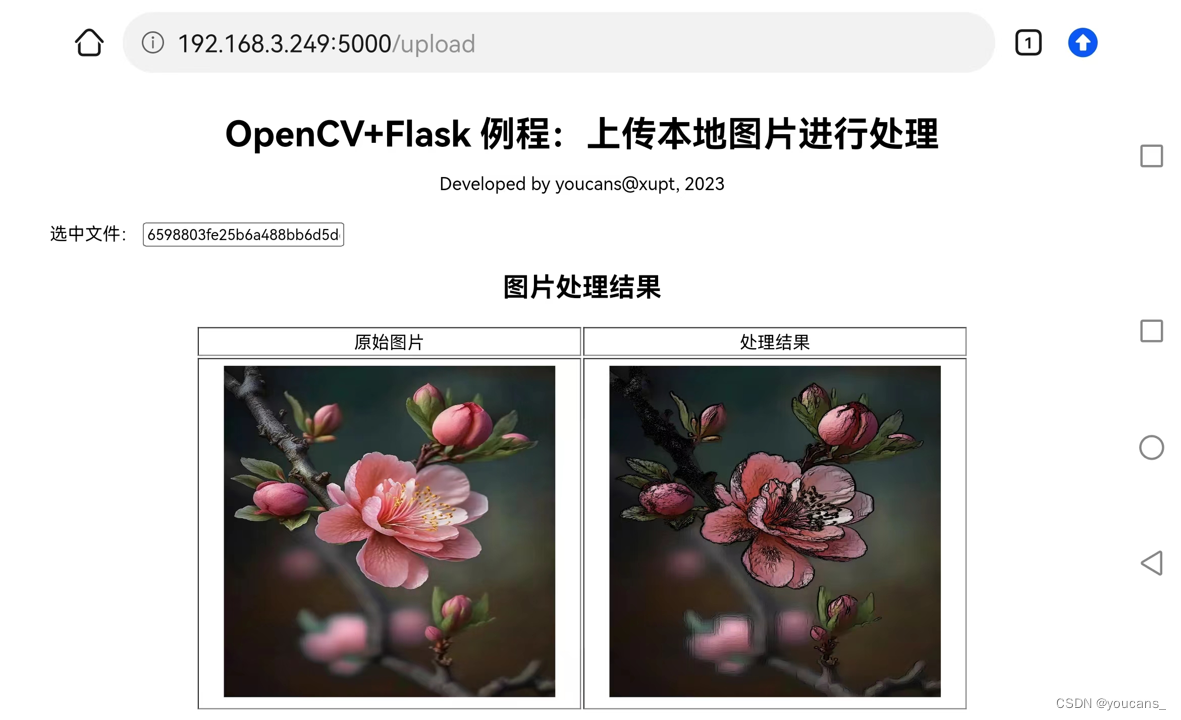
【本节完】
下节我们将讨论:在浏览器运行 OpenCV DNN 人脸检测。
欢迎关注『OpenCV DNN @ Youcans』系列,持续更新中
版权声明:
youcans@xupt 原创作品,转载必须标注原文链接:
【OpenCV DNN】Flask 视频监控目标检测教程 02(https://blog.csdn.net/youcans/article/details/130809121)
Copyright 2023 youcans, XUPT
Crated:2023-05-22



