热门标签
热门文章
- 1简单介绍DeepFaceLab(DeepFake)的使用以及容易被忽略的事项
- 2AIGC系列之:GroundingDNIO原理解读及在Stable Diffusion中使用_groundingdino
- 3Android Studio 导入frameworks源码_android stuido导入fw代码
- 4AMD CPU 的电脑运行 Android Studio 模拟器时报错 Failed to install Intel HAXM_intel haxm installation failed! for more details,
- 5TypeScript编程语言学习,为学习HarmonyOS开发做准备
- 6C语言编译全过程(有图有真相)
- 7Linux wget命令详解_wget -n --spider
- 8@@VMWARE@@ UTS_RELEASE
- 9数组----一维数组之插入删除(c++)(求关注666)_小明排队做操迟到
- 10RTL8380M管理型交换机系统软件操作指南三:VLAN
当前位置: article > 正文
Tensorflow2官方demo跑mnist数据集_tensorflow2 如何调用mnist
作者:花生_TL007 | 2024-04-01 21:50:17
赞
踩
tensorflow2 如何调用mnist
内容来源于网上教程,做个记录。
1.tensorflow1和tensorflow2的对比

2.在Pytorch和tensorflow中卷积后的矩阵尺寸大小计算公式区别
Pytorch中:

Tensorflow中:

在默认情况下,Padding=VALID。
当需要用Padding补0时,此时Padding=SAME,这样就不需要去操作Padding的过程,由tensorflow自动完成。
如若想自己控制Padding的过程,可以去调用tensoflow提供的Padding函数。
3.实例
①先下载mnist数据集,可视化查看下部分数据图像
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist # 手写数字识别数据集
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# 数据归一化处理
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
imgs = x_test[:3] # 查看测试集前3张图像
labs = y_test[:3] # 查看标签
print(labs)
# np.hstack():将图像在水平方向上平铺
plot_imgs = np.hstack(imgs)
plt.imshow(plot_imgs,cmap = 'gray')
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
输出:


②模型model.py
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras import Model
class MyModel(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu') # 卷积核个数32,卷积核大小3*3,激活函数ReLU
self.flatten = Flatten() # 将维度展平
self.d1 = Dense(128, activation='relu') # 全连接层1
self.d2 = Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 全连接层2
'''正向传播'''
def call(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x) # input[batch, 28, 28, 1] output[batch, 26, 26, 32]
x = self.flatten(x) # output [batch, 26*26*32=21632]
x = self.d1(x) # output [batch, 128]
return self.d2(x) # output [batch, 10]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
③main.py
a.tensorflow官网API查询
b.
@tf.function
# 作用:装饰器,构造高效的python代码
# 在@tf.function下面的代码变为静态图,不能进行断点调试,但运行速度快,提高运算性能。
# 相当于Pytorch中的with torch.no_grad()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
c.
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
from model import MyModel
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist # 手写数字识别数据集
# 下载和载入数据
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# 增加一个通道的维度
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
# 创建数据生成器
train_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(x_train, y_train)).shuffle(10000).batch(32)
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).batch(32)
# 创建模型
model = MyModel()
# 定义损失函数
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy()
# 定义优化器
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
# 定义训练集的损失函数和准确率
train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')
# 定义测试集的损失函数和准确率
test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
# 定义训练函数:计算损失、梯度和准确率
@tf.function
def train_step(images, labels):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = model(images)
loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
train_loss(loss)
train_accuracy(labels, predictions)
# 定义测试函数:计算损失、梯度和准确率
@tf.function
def test_step(images, labels):
predictions = model(images)
t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
test_loss(t_loss)
test_accuracy(labels, predictions)
EPOCHS = 5
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
# 每迭代一轮清空历史信息
train_loss.reset_states()
train_accuracy.reset_states()
test_loss.reset_states()
test_accuracy.reset_states()
for images, labels in train_ds:
train_step(images, labels)
for test_images, test_labels in test_ds:
test_step(test_images, test_labels)
template = 'Epoch {}, Loss: {}, Accuracy: {}, Test Loss: {}, Test Accuracy: {}'
print(template.format(epoch + 1,
train_loss.result(),
train_accuracy.result() * 100,
test_loss.result(),
test_accuracy.result() * 100))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
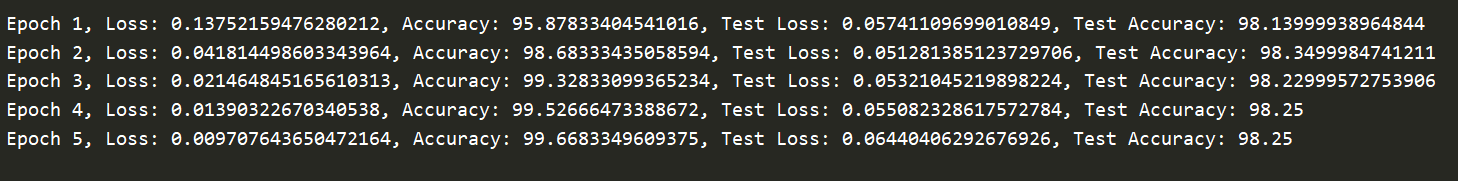
输出:
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/花生_TL007/article/detail/350233
推荐阅读
相关标签


