- 1Gradle配置国内镜像_gradle 国内镜像
- 2STM32 HAL库 STM32CubeMX -- SPI_stm32cubemx spi
- 3VMware虚拟机软件安装国产操作系统 统信 UOS V20 1050e 手把手保姆教程_uos-1050e
- 4Docker如何删除指定镜像的所有容器?_删除docker一个镜像的所有容器
- 5Android计算器——入门
- 6一个 bug ,罚款 200,我真待过这样的公司
- 7让你的3D建模技能瞬间提升的AI工具
- 8$(":submit[id=submit01]").click(function(check){_"$(\"#submit\").click()"
- 9【工业物联网基础】什么是SCADA?
- 10批量归一化与残差网络、凸优化、梯度下降法_对二值图像批量归一化效果变差
基于TF2的DQN算法详解与源码_dqn源码
赞
踩
前言
DQN算法是一种深度强化学习算法(Deep Reinforcement Learning,DRL),DQN算法是深度学习(Deep Learning)与强化学习(Reinforcement learning)结合的产物,利用深度学习的感知能力与强化学习的决策能力,实现了从感知到动作的端到端(End to End)的革命性算法。DQN算法由谷歌的DeepMind团队在NIPS 2013上首次发表,并在Nature 2015上提出由两个网络组成的Nature DQN。
由于tensorflow2相对于tensorflow1更加简介,因此本文代码部分参照莫烦老师的maze环境,将tensorflow1版本的DQN算法修改为tensorflow2版本的DQN算法。
一、DQN算法原理
DQN算法是Q-Learning算法与卷积神经网络结合,解决了Q-Learning在决策时容易产生维度灾难问题。在Q-Learning中有一个状态动作的表格Q-table,主要进行查表操作,当机器人处于某个状态时,通过查表选择Q值最大的动作来执行。Q-Learning的本质就是不断的对Q-table进行更新操作。
与Q-Learning算法相比,DQN算法做了如下改进:
1.使用卷积神经网络来逼近行为值函数来解决维度灾难的问题;
2.使用target Q network来更新target Q解决相关性的问题;
3.使用经验回访Experience Replay来解决样本相关性及非静态分布问题。
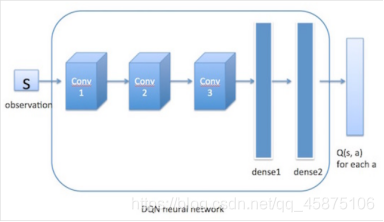
DQN算法是Q-Learning在深度学习领域的应用。因此,DQN算法需要有个值函数网络,值网络的主要作用就是在高维空间下对Q-table做函数拟合,一个状态动作对(s, a)对应于一个值函数Q(s, a)。Q(s, a)是通过将状态s输入到神经网络中,然后经过神经网络的近似拟合来得出Q(s, a),然后DQN算法通过e-greedy策略来选择动作a。动作a确定以后,环境对于该动作a会给出一个奖励值r和下一个状态s,依次不断循环,直到训练出一个好的神经网络。
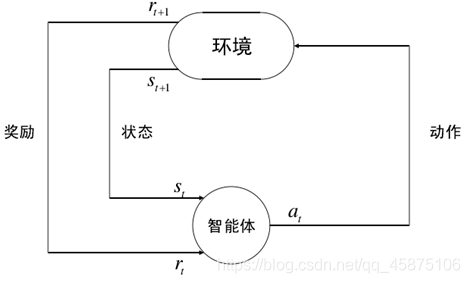
greedy策略是一种贪婪策略,他会选择Q值最大的动作a,但是对于没有出现的状态动作对(s, a),他没有办法进行选择。因此引入了e-greedy策略,e-greedy策略能够兼顾探索(Exploration)和利用(Exploitation),探索能够获取环境中更多的信息,不会拘泥于现有的信息;利用是指从现有的信息中获取最大的奖励。e-greedy策略以e的概率从环境中的所有动作中随机抽取一个,以(1-e)的概率选取Q值最大的动作。正是因为兼顾了探索和利用,强化学习才能表现出类人脑的表现。
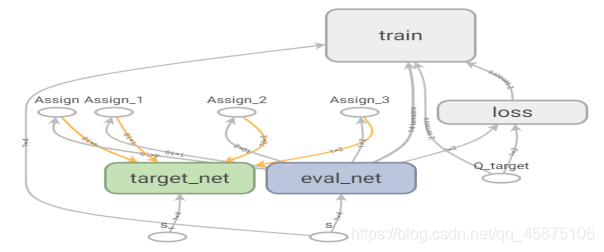
Nature DQN中引入了两个结构、初始参数完全相同的网络结构来打乱相关性。Main网络中的参数是通过Loss Function,随着反向传播来进行实时更新的,Target网络中的参数则是通过设定的参数每隔多少步来进行更新(在此期间,参数保持不变),将Main网络中的参数复制到Target网络中。Q(s, a; w)是Main网络输出的Q值,Q(s’, a’; w-)是Target网络输出的Q值。通过两个网络可以降低Q值与目标Q值之间的相关性,提高了算法的稳定性。
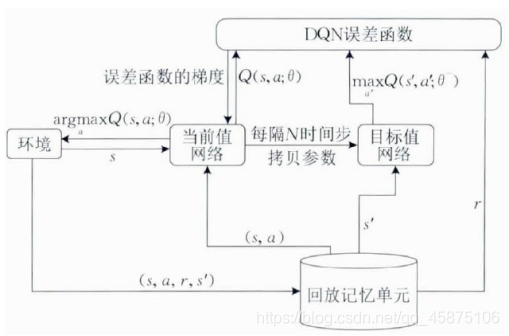
DQN算法跟Q-Learning算法一样,也是一种off-policy的的学习算法,既可以学习当前的经历,也可以学习过去的经历、学习别人的经历。经验池(Experience Replay)用来记录这些学习的经历,在训练的时候,随机拿出一些experience来进行学习,从而打乱经历之间的相关性。
DQN算法的损失函数:
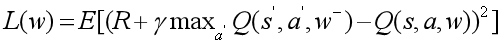
DQN算法的伪代码

二、DQN算法代码部分
本文代码的环境部分是使用莫烦老师的maze环境,将DQN算法的代码修改为tensorflow2的版本,tensorflow2相对与tensorflow1更加简洁易懂。
1.网络结构
代码如下(示例):
class NetWork(tf.keras.Model): def __init__(self): super(NetWork, self).__init__() self.wc1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2, 10], mean=0.0, stddev=0.30, dtype='float32')) self.bc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[1, 10], dtype='float32')) self.wc2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([10, 20], mean=0.0, stddev=0.30, dtype='float32')) self.bc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[1, 20], dtype='float32')) self.wc3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([20, 4], mean=0.0, stddev=0.30, dtype='float32')) self.bc3 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[1, 4], dtype='float32')) def call(self, x, training=None): x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(x, self.wc1) + self.bc1) l2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(l1, self.wc2) + self.bc2) out = tf.matmul(l2, self.wc3) + self.bc3 return out
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
NetWork类为DQN算法的网络结构,maze环境中的状态为2,动作为4个方向。为了方便收敛,本文使用了三个全连接层,前两个全连接层使用relu激活函数。
2.经验存储函数
代码如下(示例):
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
if not hasattr(self, 'memory_counter'):
self.memory_counter = 0
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
# replace the old memory with new memory
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
定义一个store_transition函数用来存储experience,将数据(s,a,r,a’)存入到经验池中,打乱数据之间的关联性。如果self.memory_counter超过经验池的容量,那么从经验池开始覆盖原有部分。
3.动作选择函数
代码如下(示例):
def choose_action(self, observation):
# to have batch dimension when feed into tf placeholder
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# forward feed the observation and get q value for every actions
actions_value = mainQN.call(observation)
action = np.argmax(actions_value)
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
定义一个choose_action函数来选择动作,动作选择遵循e-greedy策略。以(1-e)的概率从环境中的所有动作中随机抽取一个,以e的概率选取Q值最大的动作。
4.DQN算法训练
代码如下(示例):
def train(self): # replace target params if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0: mainQN_weights = mainQN.get_weights() targetQN.set_weights(mainQN_weights) print("\ntargetQN_params_replaced\n") # select batchsz sample if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size: sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size=self.batch_size) else: sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size=self.batch_size) batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :] # loss with tf.GradientTape() as tape: q_next = targetQN.call(batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:], training=False) q_eval = mainQN.call(batch_memory[:, :self.n_features], training=True) q_target = q_eval.numpy().copy() batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype=np.int32) eval_act_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int) reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1] q_target[batch_index, eval_act_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis=1) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(q_target - q_eval)) grads = tape.gradient(loss, mainQN.trainable_variables) optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(lr=self.lr) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, mainQN.trainable_variables)) self.cost.append(loss) # increasing epsilon self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max self.learn_step_counter += 1 if self.learn_step_counter % 500 == 0: print("step:", self.learn_step_counter, "loss:", float(loss)) with summary_writer.as_default(): tf.summary.scalar("loss", float(loss), step=len(self.cost))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
DQN算法在进行训练的时候,首先需要判断Target网络中的参数是否需要更新,如果需要更新,则按照上述公式对Target网络中的参数进行更新。然后从经验池中随机选取minibatch数量的样本来进行训练。随后计算loss进行梯度下降并且更新Main网络的参数。随后增加e的值,减少随机获取动作的概率,提高选取最大Q值动作的概率,最后每隔100个step将loss写入tensorboard,以便实时查看loss的曲线。
关注微信公众号提取源码:深度学习与路径规划




