- 1Subscriber class xxx.xxx.xxx and its super classes have no public methods with the@Subscribe annotat_subscriber class com.topdon.tool.mainactivity and
- 2PyQt5快速开发与实战 4.13 菜单栏、工具栏与状态栏 and 4.14 QPrinter_qprinter qml
- 3tensorflow中prefetch最合适的用法_dataset prefetch
- 4MNE-Python | 开源生理信号分析神器(一)_python mne
- 5INT4和INT8_int4和int8区别
- 6Kubernetes 健康检查之 livenessProbe/readinessProbe_kubernetes livenessprobe
- 7HTTP常见状态码_.getrequest( code:1000
- 8搭建私有Nuget服务器(.Net Core框架)_nuget.server core
- 9各种假设检验用法汇总_假设检验的八种情况的公式
- 10再生资源回收系统 毕业设计 JAVA+Vue+SpringBoot+MySQL
谷歌移动UI框架Flutter教程之Widget_flutter widget return title: home
赞
踩
引言
在之间我已经介绍了关于Flutter的下载安装以及配置,还有开发工具Android Studio的配置,还不知道的同学可以看看我这篇博客——谷歌移动UI框架Flutter入门。这里为什么非要用Android Studio,我可以解释一下。Android Studio是Google的亲儿子,由谷歌一手开发,而Flutter也是谷歌推出的技术,所以在支持和兼容问题上,Android Studio是非常有优势的。老话说得好,肥水不流外人田,谷歌内部肯定是将Android Studio对Flutter的优化做到最佳的。
Widget基本组件
那么话不多说,我们先来熟悉一下关于Flutter的Widget组件,在Flutter中,一切皆组件,TextView、Image、Row、Column等等,都统称组件。
1.文本组件(Text)
首先,我们就来了解一下文本组件(Text)。学过前端的同学对UI部分应该都很了解,那Flutter当然也没有什么特别的,无非也就是文本内容、大小、字体样式、颜色等等的设置,那么首先我们就先来编写一个案例。找到lib目录下的main.dart,我们将在这个文件中编写代码。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyTextApp()); } /** * 文本组件(Text)的使用 */ class MyTextApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Text Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(title: Text('文本控件的使用'),), body: Center( child: Text( '这是一个文本控件', //文本内容 textAlign: TextAlign.center, //居中 maxLines: 1, //最大显示行数 style: TextStyle( fontSize: 25.0, //字体大小 color: Colors.lightBlue, //字体颜色 ), //样式 ), ), ), ); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
有语言基础的同学相信可以很好理解这些代码,第一行导入了Material相关的类库。程序会先执行main()方法,该方法又执行了runApp()方法,并将MyTextApp类作为参数传递。而MyTextApp类就是我们自定义的一个类,该类需要去继承StatelessWidget,并重写build()方法,该方法需要返回一个组件。具体的代码我就不一一介绍了,可以先不用理解每一行代码的意思。其中的Text便是文本组件,只需将值写入括号,便可以在文本框中显示,然后是文本框的一些属性。接下来我们运行起来看一下。

2.图片组件(Image)
接下来是图片组件,图片组件的作用无非就是显示图片,在Flutter中,Image有四种方式显示图片,我只介绍一种,就是显示网络图片,其它三种方式没有太大差别。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyImageApp()); } /** * 图片组件(Image)的使用 */ class MyImageApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Text Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(title: Text('图片组件的使用')), body: Center( child: Image.network( 'https://www.baidu.com/img/baidu_jgylogo3.gif', //图片地址 scale: 1.0, //缩放比 ), ), ), ); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
运行效果如下:

3.列表组件(ListView)
列表组件在移动端的开发中使用非常频繁,那么在Flutter中,该如何使用ListView呢?
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyListViewApp()); } /** * 列表组件(List)的使用 */ class MyListViewApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Text Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(title: Text('图片组件的使用')), body: Center( child: Container( height: 200.0, child: ListView( scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,,//列表方向(纵向) children: <Widget>[ Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.lightBlue, ), Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.amber, ), Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.deepOrange, ), Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.deepPurple, ), //Container ], //Widget[] ), ), ), ), ); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
有些同学看到这样的代码可能惊呆了,这么多层的嵌套维护起来岂不是很麻烦,其实这也是Dart语法的特点,避免不了,但是还是有办法的,我们可以把ListView单独抽出来,这样主体的代码将会简洁很多。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'FlutterApp', home: Scaffold( //主页 appBar: AppBar(title: Text('FlutterDemo')), //标题 body: Center( child: Container( height: 200.0, child: MyList(), //ListView ), //Container ), //主体 ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } } class MyList extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return ListView( scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal, children: <Widget>[ Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.lightBlue, ), Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.amber, ), Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.deepOrange, ), Container( width: 180.0, color: Colors.deepPurple, ), //Container ], //Widget[] ); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
现在运行看一下效果。
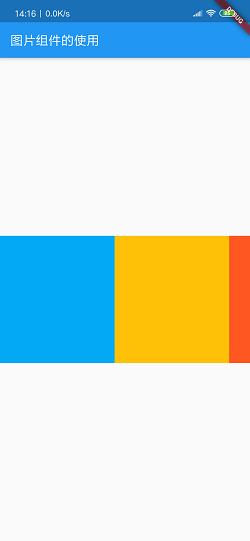
当然,这样编写列表在实际开发中是不现实的,我们应该让列表活起来,所以,下面介绍如何实现动态列表。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp( items: List < String>.generate(1000, (i) => "Item $i") ) ); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { final List<String> items; MyApp({Key key, @required this.items}) :super(key: key); @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'FlutterApp', home: Scaffold( //主页 appBar: AppBar(title: Text('FlutterDemo')), //标题 body: ListView.builder( itemCount: items.length, itemBuilder: (context, index) { return ListTile( title: Text('${items[index]}'), ); }, ), ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
这样就实现了动态列表,只不过这个数据还是自己提供的,只需要后期通过网络获取数据再封装成集合然后传递即可。不懂Dart语法的同学对于里面的某些代码可能会觉得难以理解,但是不用担心。即使没有一点Dart语言基础的同学也是可以很容易地学会Flutter的,只不过在某些Dart语法上就只能死记了,记住它,不用管为什么。那么现在来运行看下效果。
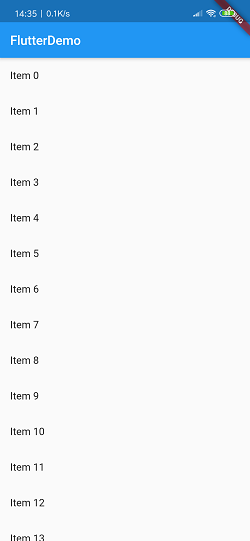
4.列表组件(GridView)
第二个列表组件,网格组件,该组件在如今的移动应用中也非常常见,最典型的便是系统相册。那么我们关心的是在Flutter中该如何去使用GridView呢?通过一个例子来了解一下。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'FlutterApp', home: Scaffold( //主页 appBar: AppBar(title: Text('FlutterDemo')), //标题 body: GridView( gridDelegate: SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount( crossAxisCount: 3, mainAxisSpacing: 2.0, //纵轴边距 crossAxisSpacing: 2.0, //横轴边距 childAspectRatio: 0.7 //缩放比例(宽高比) ), children: <Widget>[ Image.network( 'http://img5.mtime.cn/mg/2019/05/31/163641.36482297_270X405X4.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover), Image.network( 'http://img5.mtime.cn/mg/2019/07/01/091243.35485139_270X405X4.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover), Image.network( 'http://img5.mtime.cn/mg/2019/06/28/141449.40971533_270X405X4.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover), Image.network( 'http://img5.mtime.cn/mg/2019/05/31/163641.36482297_270X405X4.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover), Image.network( 'http://img5.mtime.cn/mg/2019/07/01/091243.35485139_270X405X4.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover), Image.network( 'http://img5.mtime.cn/mg/2019/06/28/141449.40971533_270X405X4.jpg', fit: BoxFit.cover), ], //Widget[] ) //GridView ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
网格组件其实也非常的简单,和ListView其实没有什么差别,最主要的就是它独特的属性,这些属性在官网文档中都有解释和示例。那么这段代码运行的效果如何呢?我们看一下:

布局
Flutter中基本的一些组件就介绍完了,但是光知道如何编写组件可远远不够,UI设计中的布局管理也尤为重要,那么,我们继续深入,了解一下Flutter中的布局。
1.水平布局(Row)
经过前面基本组件的学习,会发现Flutter无非就是一些组件的嵌套,但注意嵌套级别,不要被自己的代码搞晕了,那么布局其实是一样的。我们看一个例子。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Row Widget Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('水平方向布局'), ), //AppBar body: Row( children: <Widget>[ RaisedButton( onPressed: () {}, color: Colors.redAccent, child: Text('Red Button'), ),RaisedButton( onPressed: () {}, color: Colors.orangeAccent, child: Text('Orange Button'), ),RaisedButton( onPressed: () {}, color: Colors.lightBlue, child: Text('Blue Button'), ), ], //Widget[] ), //Row ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
Row即是水平布局,那么水平布局中我们放置了三个按钮,现在,运行看效果。

会发现 ,这个按钮的右边空出了一块,这是为什么呢?其实是因为我们使用的是一个不灵活的水平布局,那么既然有不灵活的水平布局,那就肯定会有灵活的水平布局。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Row Widget Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('水平方向布局'), ), //AppBar body: Row( children: <Widget>[ Expanded(child: RaisedButton( onPressed: () {}, color: Colors.redAccent, child: Text('Red Button'), )), Expanded(child: RaisedButton( onPressed: () {}, color: Colors.orangeAccent, child: Text('Orange Button'), )), Expanded(child: RaisedButton( onPressed: () {}, color: Colors.lightBlue, child: Text('Blue Button'), )), ], //Widget[] ), //Row ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
我们并没有对代码进行过多的修改,只是在每个按钮外部包了一个Expanded组件,那么现在我们来看一下运行效果:

会发现,按钮成功自适应屏幕了,这才是我们想要的效果。
2.垂直布局(Column)
既然有水平布局,当然就有垂直布局。现在通过一个例子来理解一下垂直布局。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Row Widget Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('水平方向布局'), ), //AppBar body: Column( children: <Widget>[ Text('Column 1'), Text('This is Column 2'), Text('Column 3'), ], //Widget ) //Column ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
应该不难理解,道理是一样的,现在看一下效果:

细心的同学会发现,它默认会有一个居中的对齐方式。但有同学提出疑问了,这也没居中啊,这不还是在屏幕的左侧吗?其实这个对齐是相对Column来说的,这个Column的大小是由最长的Text组件决定的。通过crossAxisAlignment属性可以设置Column的对齐方式。
3.层叠布局(Stack)
使用水平布局和垂直布局虽然可以实现大部分的布局效果,但是如果要在一张图片上显示一段文字,这两种布局将无法实现。所以,这里我们学习一种层叠布局,它能够很轻松地实现这个效果。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { var stack = Stack( alignment: const FractionalOffset(0.5, 0.8), children: <Widget>[ CircleAvatar( backgroundImage: NetworkImage( 'https://i0.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/79c30cf5850cb9ec9d6129b200145e1644f696f8.jpg@880w_440h.jpg'), radius: 100.0, ), //CircleAvatar Container( decoration: BoxDecoration( color: Colors.lightBlue ), padding: EdgeInsets.all(5.0), child: Text('层叠布局'), ) ], //Widget[] ); //Stack return MaterialApp( title: 'Row Widget Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('水平方向布局'), ), //AppBar body: Center( child: stack, ) ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
我们首先创建一个组件变量,将我们的图片和文字都定义在里面,然后通过alignment属性可以决定文本组件的相对位置,看一下效果:

4.卡片布局(Card)
最后一个布局,卡片布局。来看例子。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp(MyApp()); } class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { var card = Card( child: Column( children: <Widget>[ ListTile( title: Text( '江西省南昌市青云谱区', style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.w500),), subtitle: Text('Temptation:123456789'), leading: Icon(Icons.account_box, color: Colors.lightBlue,), ), new Divider(), ListTile( title: Text( '北京市海淀区中国科技大学', style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.w500),), subtitle: Text('Temptation:123456789'), leading: Icon(Icons.account_box, color: Colors.lightBlue,), ), new Divider(), ListTile( title: Text( '河南省濮阳市百姓办公楼', style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.w500),), subtitle: Text('Temptation:123456789'), leading: Icon(Icons.account_box, color: Colors.lightBlue,), ) //ListTile ], //Widget[] ), //Column ); //Card return MaterialApp( title: 'Row Widget Demo', home: Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text('水平方向布局'), ), //AppBar body: Center( child: card ) ), //Scaffold ); //MaterialApp } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
运行看效果:
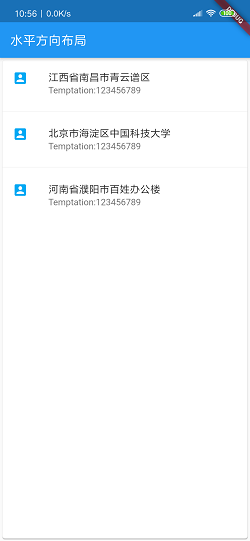
篇幅有限,关于Flutter的组件和布局就介绍到这里,接下来还会有一篇关于Flutter的进阶博客,感兴趣的同学可以看一看。



