- 1基础算法——位运算(解决你初学位运算的所有疑惑)
- 2常见的基础算法_基础算法有哪些
- 3封装python函数判断成绩等级_python判断成绩等级思路与实现
- 4Git配置SSH及通过IDEA连接GitLab方法总结_idea添加gitlab用户名
- 5关于js中操作数组的13种方法_js操作数组的方法
- 6加速计算卡设计资料:基于ZU19EG的4路100G 网络 DPU的PCIe 加速计算卡_基于 zu19eg 的 4 路 100g网络dpu
- 7谷歌浏览器Chrome安装GitHunt插件_githunt插件下载
- 8d3.js mysql_d3js是什么
- 9已解决com.rabbitmq.client.ShutdownSignalException: 关闭信号异常的正确解决方法,亲测有效!!!_caused by: com.rabbitmq.client.shutdownsignalexcep
- 10C# 使用SQLite
Java接口自动化测试框架学习(三)_java 关联接口自动化测试框架
赞
踩
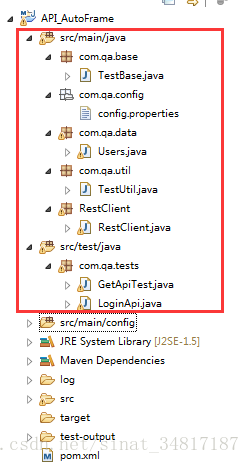
前面项目已创建好,依赖包添加完成,testng也已添加
项目结构如下:
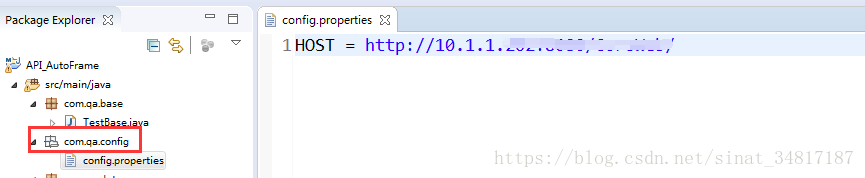
1.设计配置文件
在src/main/java下新建一个包:com.qa.config,然后在新包下新建一个config.properties文件,文件内容如下
2.加载读取properties文件
然后在src/main/java下新建一个包:com.qa.base,新建一个TestBase.java,这个类作为所有接口请求测试的父类,都需要继承这个父类,目前我们就写一个构造方法,实现加载读取properties文件。
我们不想在代码里写死例如像HTTP响应状态码200这样的硬编码,所以,这里我们在TestBase.java里把状态码给用常量写出来,方便每一个TestNG测试用例去调用去断言
package com.qa.base; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Properties; //接口请求测试的父类 public class TestBase { public Properties prop; //写一个构造函数 public TestBase() { try { prop = new Properties(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(System.getProperty("user.dir")+ "/src/main/java/com/qa/config/config.properties"); prop.load(fis); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
3. 新建一个log4j.properties文件
在Eclipse上点击当前项目名,右键new -source folder,输出src/main/config,点击确定,然后在src/main/config下新建一个log4j.properties文件,内容如下。
### set log levels ### log4j.rootLogger = INFO, stdout, file log4j.appender.stdout = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.Target = System.out log4j.appender.stdout.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern = %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n log4j.appender.file = org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender log4j.appender.file.File = ./log/apilog.log # overwirte the old log file log4j.appender.file.Append = false ## log4j.appender.file.Threshold = INFO log4j.appender.file.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern = %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS} %-5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
在项目根目录下新建log文件夹:用于日志输出存放
新建这个文件夹是上面log4j.properties文件我们设置的日志保存文件路径是在./log文件夹下。
4.写一个JSON解析的工具类
在src/main/java下新建一个包:com.qa.util,然后在新包下创建一个TestUtil.java类。
package com.qa.util; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; public class TestUtil { /** * * @param responseJson ,这个变量是拿到响应字符串通过json转换成json对象 * @param jpath,这个jpath指的是用户想要查询json对象的值的路径写法 * jpath写法举例:1) per_page 2)data[1]/first_name ,data是一个json数组,[1]表示索引 * /first_name 表示data数组下某一个元素下的json对象的名称为first_name * @return,返回first_name这个json对象名称对应的值 */ //1 json解析方法 public static String getValueByJPath(JSONObject responseJson, String jpath){ Objectobj = responseJson; for(String s : jpath.split("/")) { if(!s.isEmpty()) { if(!(s.contains("[") || s.contains("]"))) { obj = ((JSONObject) obj).get(s); }else if(s.contains("[") || s.contains("]")) { obj =((JSONArray)((JSONObject)obj).get(s.split("\\[")[0])).get(Integer.parseInt(s.split("\\[")[1].replaceAll("]", ""))); } } } return obj.toString(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
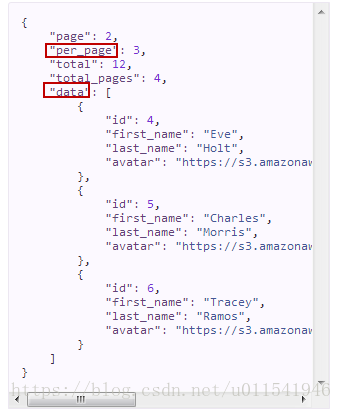
简单解释下上面的代码,主要是查询两种json对象的的值,第一种最简单的,这个json对象在整个json串的第一层,例如上面截图中的per_page,这个per_page就是通过jpath这个参数传入,返回的结果就是3. 第二种jpath的查询,例如我想查询data下第一个用户信息里面的first_name的值,这个时候jpath的写法就是data[0]/first_name,查询结果应该是Eve。
4.请求方法代码封装
在src/main/java下新建一个包:com.qa.restclient,然后新建一个RestClient.java文件,下面是具体代码,已加日志输出
这个Java接口自动化测试框架的核心就是Get和POST请求方法的封装过程。
package com.qa.restclient; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.http.ParseException; import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpDelete; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPut; import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity; import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; public class RestClient { final static Logger Log = Logger.getLogger(RestClient.class); /** * 不带请求头的get方法封装 * @param url * @return 返回响应对象 * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public CloseableHttpResponse get (String url) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { //创建一个可关闭的HttpClient对象 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); //创建一个HttpGet的请求对象 HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(url); //执行请求,相当于postman上点击发送按钮,然后赋值给HttpResponse对象接收 Log.info("开始发送get请求..."); CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = httpclient.execute(httpget); Log.info("发送请求成功!开始得到响应对象。"); return httpResponse; } /** * 带请求头信息的get方法 * @param url * @param headermap,键值对形式 * @return 返回响应对象 * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public CloseableHttpResponse get (String url,HashMap<String,String> headermap) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { //创建一个可关闭的HttpClient对象 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); //创建一个HttpGet的请求对象 HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(url); //加载请求头到httpget对象 for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : headermap.entrySet()) { httpget.addHeader(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } //执行请求,相当于postman上点击发送按钮,然后赋值给HttpResponse对象接收 CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = httpclient.execute(httpget); Log.info("开始发送带请求头的get请求..."); return httpResponse; } /** * 封装post方法 * @param url * @param entityString,其实就是设置请求json参数 * @param headermap,带请求头 * @return 返回响应对象 * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public CloseableHttpResponse post (String url, String entityString, HashMap<String,String> headermap) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { //创建一个可关闭的HttpClient对象 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); //创建一个HttpPost的请求对象 HttpPost httppost = new HttpPost(url); //设置payload httppost.setEntity(new StringEntity(entityString)); //加载请求头到httppost对象 for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : headermap.entrySet()) { httppost.addHeader(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } //发送post请求 CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = httpclient.execute(httppost); Log.info("开始发送post请求"); return httpResponse; } /** * 封装 put请求方法,参数和post方法一样 * @param url * @param entityString,这个主要是设置payload,一般来说就是json串 * @param headerMap,带请求的头信息,格式是键值对,所以这里使用hashmap * @return 返回响应对象 * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public CloseableHttpResponse put (String url, String entityString, HashMap<String,String> headerMap) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); HttpPut httpput = new HttpPut(url); httpput.setEntity(new StringEntity(entityString)); for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : headerMap.entrySet()) { httpput.addHeader(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } //发送put请求 CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = httpclient.execute(httpput); return httpResponse; } /** * 封装 delete请求方法,参数和get方法一样 * @param url, 接口url完整地址 * @return,返回一个response对象,方便进行得到状态码和json解析动作 * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public CloseableHttpResponse delete (String url) throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); HttpDelete httpdel = new HttpDelete(url); //发送delete请求 CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = httpclient.execute(httpdel); return httpResponse; } /** * 获取响应状态码,常用来和TestBase中定义的状态码常量去测试断言使用 * @param response * @return 返回int类型状态码 */ public int getStatusCode (CloseableHttpResponse response) { int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); Log.info("解析,得到响应状态码:"+ statusCode); return statusCode; } /** * * @param response, 任何请求返回返回的响应对象 * @return, 返回响应体的json格式对象,方便接下来对JSON对象内容解析 * 接下来,一般会继续调用TestUtil类下的json解析方法得到某一个json对象的值 * @throws ParseException * @throws IOException */ public JSONObject getResponseJson (CloseableHttpResponse response) throws ParseException, IOException { Log.info("得到响应对象的String格式"); String responseString = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),"UTF-8"); JSONObject responseJson = JSON.parseObject(responseString); Log.info("返回响应内容的JSON格式"); return responseJson; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
5.TestNG测试用例测试get方法
在src/test/java下新建一个包:com.qa.tests,然后新建一个GetApiTest.java类,写一个TestNG的测试用例来测试下我们上面写的Get请求方法
简单提一下TestNG的断言方法,我们一般测试都需要写断言的代码,否则这样的单元测试代码就没有意义。下面,我在statusCode和json解析的first_name进行断言。
package com.qa.tests; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.testng.Assert; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.qa.base.TestBase; import com.qa.restclient.RestClient; import com.qa.util.TestUtil; public class GetApiTest extends TestBase { TestBase testBase; String host; String url; RestClient restClient; CloseableHttpResponse closeableHttpResponse; final static Logger Log = Logger.getLogger(GetApiTest.class); @BeforeClass public void setUp() { testBase = new TestBase(); //Log.info("测试服务器地址为:"+ host.toString()); host = prop.getProperty("HOST"); //Log.info("当前测试接口的完整地址为:"+url.toString()); url = host + "/api/users?page=2"; } @Test public void getAPITest() throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { Log.info("开始执行用例..."); restClient = new RestClient(); closeableHttpResponse = restClient.get(url); //断言状态码是不是200 Log.info("测试响应状态码是否是200"); int statusCode = restClient.getStatusCode(closeableHttpResponse); Assert.assertEquals(statusCode, RESPNSE_STATUS_CODE_200, "response status code is not 200"); JSONObject responseJson = restClient.getResponseJson(closeableHttpResponse); //System.out.println("respon json from API-->" + responseJson); //json内容解析 String s = TestUtil.getValueByJPath(responseJson,"data[0]/first_name"); Log.info("执行JSON解析,解析的内容是 " + s); //System.out.println(s); Log.info("接口内容响应断言"); Assert.assertEquals(s, "Eve","first name is not Eve"); Log.info("用例执行结束..."); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
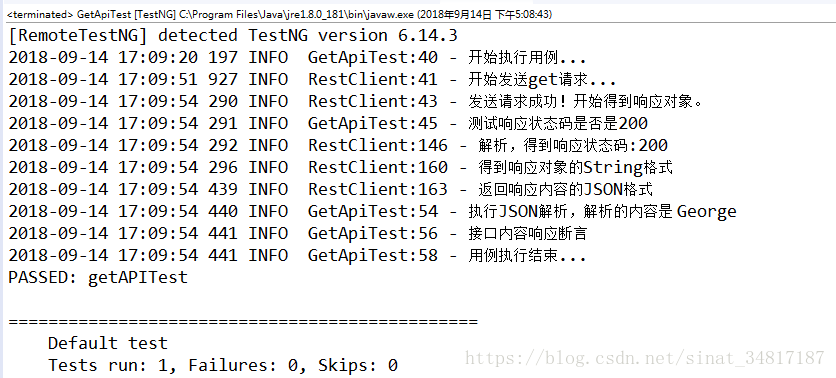
执行日志输出如下:
经常使用的测试断言:
Assert.assertEquals(“现实结果”, “期待结果”,“断言失败时候打印日志消息”);
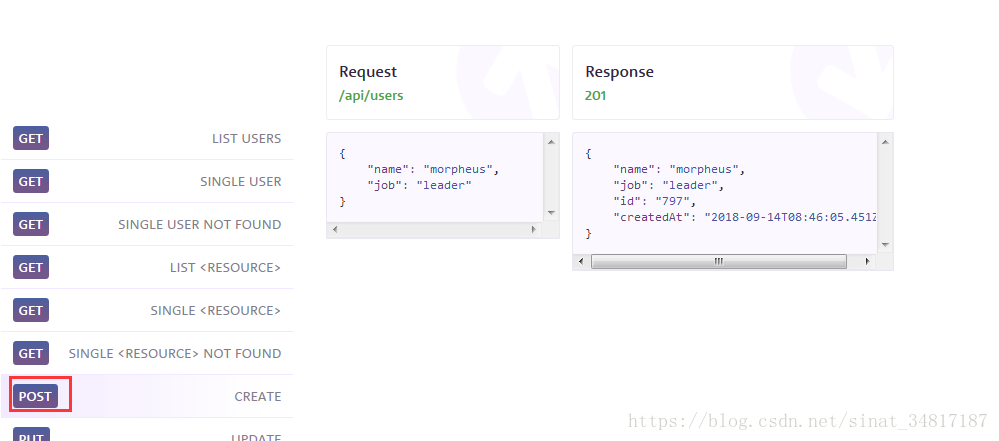
6.TestNG测试用例测试post方法
post接口示例:
这个接口的作用是创建用户,参数是一个json类型的数据,一个name一个job,两个JSON对象。发送请求之后,返回的JSON数据有name和job和id,以及创建时间这几个数据。
JAVA Bean类
写测试用例之前,我们需要提前准备好json数据【上边的name和job】,一般来说,在Java中JSON数据都是放在JAVA Bean类中,通过JSON把高级对象序列化成JSON对象。
在src/main/java中新建包:com.qa.data,然后新建一个Users.java,这个命名就参考接口的url单词就行。在postman或者网站该post方法,我们知道,需要name和job这两个json对象。我们新建一个bean类,同alt+shift+s,然后选择生成构造方法和set和get方法。
package com.qa.data; public class Users { private String name; private String pwd; private String srv_name; public Users() { super(); } public Users(String name, String job,String srv_name) { super(); this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.srv_name = srv_name; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public String getSrv_name() { return srv_name; } public void setSrv_name(String srv_name) { this.srv_name = srv_name; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
TestNG用例测试
在src/test/java下的com.qa.tests我们新建一个POST测试用例,现在我们的TestNG测试类代码如下:
package com.qa.tests; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import org.testng.Assert; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.qa.base.TestBase; import com.qa.data.Users; import com.qa.restclient.RestClient; import com.qa.util.TestUtil; public class PostApiTest extends TestBase { TestBase testBase; String host; String url; RestClient restClient; CloseableHttpResponse closeableHttpResponse; @BeforeClass public void setUp() { testBase = new TestBase(); host = prop.getProperty("HOST"); url = host + "/api/users"; } @Test public void postApiTest() throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { restClient = new RestClient(); //准备请求头信息 HashMap<String,String> headermap = new HashMap<String,String>(); headermap.put("Content-Type", "application/json"); //这个在postman中可以查询到 //对象转换成Json字符串 Users user = new Users("Anthony","tester"); String userJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user); //System.out.println(userJsonString); closeableHttpResponse = restClient.post(url, userJsonString, headermap); //验证状态码是不是200 int statusCode = closeableHttpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); Assert.assertEquals(statusCode, RESPNSE_STATUS_CODE_201,"status code is not 201"); //断言响应json内容中name和job是不是期待结果 String responseString = EntityUtils.toString(closeableHttpResponse.getEntity()); JSONObject responseJson = JSON.parseObject(responseString); //System.out.println(responseString); String name = TestUtil.getValueByJPath(responseJson, "name"); String job = TestUtil.getValueByJPath(responseJson, "job"); Assert.assertEquals(name, "Anthony","name is not same"); Assert.assertEquals(job, "tester","job is not same"); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
7.TestNG测试用例测试put方法
package com.qa.tests; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import org.testng.Assert; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.qa.base.TestBase; import com.qa.data.Users; import com.qa.restclient.RestClient; import com.qa.util.TestUtil; public class PutApiTest extends TestBase { TestBase testBase; String host; String url; RestClient restClient; CloseableHttpResponse closeableHttpResponse; @BeforeClass public void setUp() { testBase = new TestBase(); host = prop.getProperty("HOST"); url = host + "/api/users/2"; } @Test public void putTest() throws ClientProtocolException, IOException{ restClient = new RestClient(); HashMap<String,String> headermap = new HashMap<String,String>(); headermap.put("Content-Type", "application/json"); //这个在postman中可以查询到 //对象转换成Json字符串 Users user = new Users("Anthony","automation tester"); String userJsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user); //System.out.println(userJsonString); closeableHttpResponse = restClient.put(url, userJsonString, headermap); //验证状态码是不是200 int statusCode = closeableHttpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); Assert.assertEquals(statusCode, RESPNSE_STATUS_CODE_200,"response status code is not 200"); //验证名称为Anthony的jon是不是 automation tester String responseString = EntityUtils.toString(closeableHttpResponse.getEntity()); JSONObject responseJson = JSON.parseObject(responseString); String jobString = TestUtil.getValueByJPath(responseJson, "job"); System.out.println(jobString); Assert.assertEquals(jobString, "automation tester","job is not same"); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
8.TestNG测试用例测试Delete方法
package com.qa.tests; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.testng.Assert; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Test; import com.qa.base.TestBase; import com.qa.restclient.RestClient; public class DeleteApiTest extends TestBase { TestBase testBase; String host; String url; RestClient restClient; CloseableHttpResponse closeableHttpResponse; @BeforeClass public void setUp() { testBase = new TestBase(); host = prop.getProperty("HOST"); url = host + "/api/users/2"; //直接在这个网站可以找到delete的api } @Test public void deleteApiTest() throws ClientProtocolException, IOException { restClient = new RestClient(); closeableHttpResponse = restClient.delete(url); int statusCode = closeableHttpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); System.out.println(statusCode); Assert.assertEquals(statusCode, 204,"status code is not 204"); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
源码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dUYQBZFJrlDSkR4EYApBUA 提取码:4RT8