- 1Linux内核
- 2共识算法 PBFT浅析_pbft共识
- 3MySQL Column count doesn't match value count at row 1_为什么mybaits的insert方法column count doesn't match valu
- 4移动边缘计算在人工智能有哪些应用?_ai应用+边缘计算+智能驾驶
- 5springboot配置 spring.profiles.active spring.profiles.include @profile
- 6python基于Spark的共享单车数据存储系统的设计与实现flask-django-php-nodejs_python spark
- 7面向开发人员的 ChatGPT 提示词教程中文版_chatgpt提示词模板怎么让结果输出为固定的语言
- 8IT行业的现状与未来发展趋势:重塑生活与工作的无限可能
- 9双目立体视觉测量_双目视觉测量
- 10双目视觉下空间坐标计算/双目测距_description:将世界坐标系中的点投影到左右相机成像坐标系中
【我的C/C++语言学习进阶之旅】 通过C++跨平台的预编译宏来区分不同的操作系统:Win32/Win64/Unix/Linux/MacOS/iOS/Android等_c++编译32位宏
赞
踩
一、需求
因为C++具有跨平台的特性,所以有些需求一套代码就多端使用,比如我最近在学习的OpenGL ES。
但是,不同平台还是具有一定差异性,所以我们首先得判断出是什么平台? 比如iOS系统和Android系统。
那么如何判断呢?我们接着往下看!
二、了解操作系统宏定义
要检查 C 或 C 代码中主机的操作系统,我们需要检查编译器(GNU GCC 或 G )定义的宏。 例如,在 Windows 平台上,编译器定义了一个名为 _WIN32 的特殊宏。 因此,如果定义了宏 _WIN32,我们就在 Windows 上。 同样,其他操作系统也有编译器定义的特定宏。
C++ 编译器预定义了某些全局标识符,称为 manifest constants 。大多数全局标识符以两个下划线 (__) 开头和结尾。
检查 Windows 操作系统的示例:
#ifdef _WIN32
printf("You have Windows Operating System");
#endif
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.1 宏定义列表
以下是基于操作系统定义的宏列表:
| 操作系统 | 宏定义 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 32 bit + 64 bit | _WIN32 | for all Windows OS |
| Windows 64 bit | _WIN64 | Only for 64 bit Windows |
| Apple | __APPLE__ | for all Apple OS |
| Apple | __MACH__ | alternative to above |
| iOS embedded | TARGET_OS_EMBEDDED | include TargetConditionals.h |
| iOS stimulator | TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR | include TargetConditionals.h |
| iPhone | TARGET_OS_IPHONE | include TargetConditionals.h |
| MacOS | TARGET_OS_MAC | include TargetConditionals.h |
| Android | __ANDROID__ | subset of linux |
| Unix based OS | __unix__ | |
| Linux | __linux__ | subset of unix |
| POSIX based | _POSIX_VERSION | Windows with Cygwin |
| Solaris | __sun | |
| HP UX | __hpux | |
| BSD | BSD | all BSD flavors |
| DragonFly BSD | __DragonFly__ | |
| FreeBSD | __FreeBSD__ | |
| NetBSD | __NetBSD__ | |
| OpenBSD | __OpenBSD__ |
请注意,宏对 GNU GCC 和 G++ 有效,并且可能因其他编译器而异。 我们将通过一些基本示例,并探讨这些功能在现实生活中的使用。
关于更多的宏定义可以参考下面的两个链接:
2.2 示例: 检测 64 位 Windows 操作系统或 32 位 Windows 操作系统
在下面的示例中,我们专注于检测我们正在运行的 Windows 的风格,它可以是 64 位或 32 位。对于 Windows,我们的表格将是:
| 操作系统 | 宏定义 |
|---|---|
| Windows OS 32 bit + 64 bit | _WIN32 |
| Windows OS 64 bit | _WIN64 |
由于 _WIN32 在 32 位和 64 位 Windows 操作系统中都存在,
所以我们需要先检查 _WIN32 的存在以确认它是 Windows 操作系统,
然后再检查 _WIN64 的存在以确认它是否是 64 位 Windows 操作系统或 32 位 Windows 操作系统。
以下是检查您的 Windows 操作系统的代码:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { #ifdef _WIN32 // Includes both 32 bit and 64 bit #ifdef _WIN64 printf("Windows 64 bit\n"); #else printf("Windows 32 bit\n"); #endif #else printf("Not a Windows OS\n"); #endif return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
运行输出
Windows 32 bit
- 1
2.3 示例:检测苹果操作系统是MacOS 还是 iPhone
在此示例中,我们使用 Apple OS 的宏来检测正在使用的 Apple OS,如 MacOS 或 iPhone。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { #if __APPLE__ #include "TargetConditionals.h" #if TARGET_OS_IPHONE && TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR printf("iPhone stimulator\n"); #elif TARGET_OS_IPHONE printf("iPhone\n"); #elif TARGET_OS_MAC printf("MacOS\n"); #else printf("Other Apple OS\n"); #endif #else printf("Not an Apple OS\n"); #endif return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
运行输出
MacOS
- 1
2.4 普通示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
#ifdef _WIN32
printf("Windows\n");
#elif __linux__
printf("Linux\n");
#elif __unix__
printf("Other unix OS\n");
#else
printf("Unidentified OS\n");
#endif
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2.5 作用
凭借检测语言(在我们的案例中为 C 和 C++)中的操作系统的能力,我们可以编写一个跨平台代码,通过分离平台相关代码来在所有平台上运行。
#include <stdio.h> int main() { #if __APPLE__ // apple specific code #elif _WIN32 // windows specific code #elif __LINUX__ // linux specific code #elif BSD // BSD specific code #else // general code or warning #endif // general code return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
同时,我们可以编写针对特定平台优化的代码。
例如,一个函数调用可能在所有平台上都受支持,但我们可以针对特定平台(例如 Linux)对其进行大幅优化,但是这个新代码会在其他平台上引发错误。 在这种情况下,我们可以使用宏来检测它是否是 Linux,对于这种情况,我们可以轻松地使用其他替代优化代码。
例如:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
#if __linux__
// linux optimized code (will fail in other platforms)
#else
// general code for all platforms
#endif
// general code
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
三、实际示例
3.1 一个简单的判断
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(__WIN32__) || defined(__NT__) //define something for Windows (32-bit and 64-bit, this part is common) #ifdef _WIN64 //define something for Windows (64-bit only) #else //define something for Windows (32-bit only) #endif #elif __APPLE__ #include <TargetConditionals.h> #if TARGET_IPHONE_SIMULATOR // iOS, tvOS, or watchOS Simulator #elif TARGET_OS_MACCATALYST // Mac's Catalyst (ports iOS API into Mac, like UIKit). #elif TARGET_OS_IPHONE // iOS, tvOS, or watchOS device #elif TARGET_OS_MAC // Other kinds of Apple platforms #else # error "Unknown Apple platform" #endif #elif __linux__ // linux #elif __unix__ // all unices not caught above // Unix #elif defined(_POSIX_VERSION) // POSIX #else # error "Unknown compiler" #endif
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
3.2 优秀的googletest的示例
https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/main/googletest/include/gtest/internal/gtest-port-arch.h
// Copyright 2015, Google Inc. // All rights reserved. // // Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without // modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are // met: // // * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright // notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. // * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above // copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer // in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the // distribution. // * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its // contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from // this software without specific prior written permission. // // THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS // "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT // LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR // A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT // OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, // SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT // LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, // DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY // THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT // (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE // OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. // The Google C++ Testing and Mocking Framework (Google Test) // // This header file defines the GTEST_OS_* macro. // It is separate from gtest-port.h so that custom/gtest-port.h can include it. #ifndef GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_ARCH_H_ #define GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_ARCH_H_ // Determines the platform on which Google Test is compiled. #ifdef __CYGWIN__ #define GTEST_OS_CYGWIN 1 #elif defined(__MINGW__) || defined(__MINGW32__) || defined(__MINGW64__) #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MINGW 1 #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS 1 #elif defined _WIN32 #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS 1 #ifdef _WIN32_WCE #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_MOBILE 1 #elif defined(WINAPI_FAMILY) #include <winapifamily.h> #if WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_DESKTOP) #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 #elif WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_PHONE_APP) #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE 1 #elif WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_APP) #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_RT 1 #elif WINAPI_FAMILY_PARTITION(WINAPI_PARTITION_TV_TITLE) #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_PHONE 1 #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_TV_TITLE 1 #else // WINAPI_FAMILY defined but no known partition matched. // Default to desktop. #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 #endif #else #define GTEST_OS_WINDOWS_DESKTOP 1 #endif // _WIN32_WCE #elif defined __OS2__ #define GTEST_OS_OS2 1 #elif defined __APPLE__ #define GTEST_OS_MAC 1 #include <TargetConditionals.h> #if TARGET_OS_IPHONE #define GTEST_OS_IOS 1 #endif #elif defined __DragonFly__ #define GTEST_OS_DRAGONFLY 1 #elif defined __FreeBSD__ #define GTEST_OS_FREEBSD 1 #elif defined __Fuchsia__ #define GTEST_OS_FUCHSIA 1 #elif defined(__GNU__) #define GTEST_OS_GNU_HURD 1 #elif defined(__GLIBC__) && defined(__FreeBSD_kernel__) #define GTEST_OS_GNU_KFREEBSD 1 #elif defined __linux__ #define GTEST_OS_LINUX 1 #if defined __ANDROID__ #define GTEST_OS_LINUX_ANDROID 1 #endif #elif defined __MVS__ #define GTEST_OS_ZOS 1 #elif defined(__sun) && defined(__SVR4) #define GTEST_OS_SOLARIS 1 #elif defined(_AIX) #define GTEST_OS_AIX 1 #elif defined(__hpux) #define GTEST_OS_HPUX 1 #elif defined __native_client__ #define GTEST_OS_NACL 1 #elif defined __NetBSD__ #define GTEST_OS_NETBSD 1 #elif defined __OpenBSD__ #define GTEST_OS_OPENBSD 1 #elif defined __QNX__ #define GTEST_OS_QNX 1 #elif defined(__HAIKU__) #define GTEST_OS_HAIKU 1 #elif defined ESP8266 #define GTEST_OS_ESP8266 1 #elif defined ESP32 #define GTEST_OS_ESP32 1 #elif defined(__XTENSA__) #define GTEST_OS_XTENSA 1 #endif // __CYGWIN__ #endif // GOOGLETEST_INCLUDE_GTEST_INTERNAL_GTEST_PORT_ARCH_H_
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
这个示例通过判断系统预定的宏定义,然后重新定义了一些宏定义,方便后续业务直接判断,如下所示:
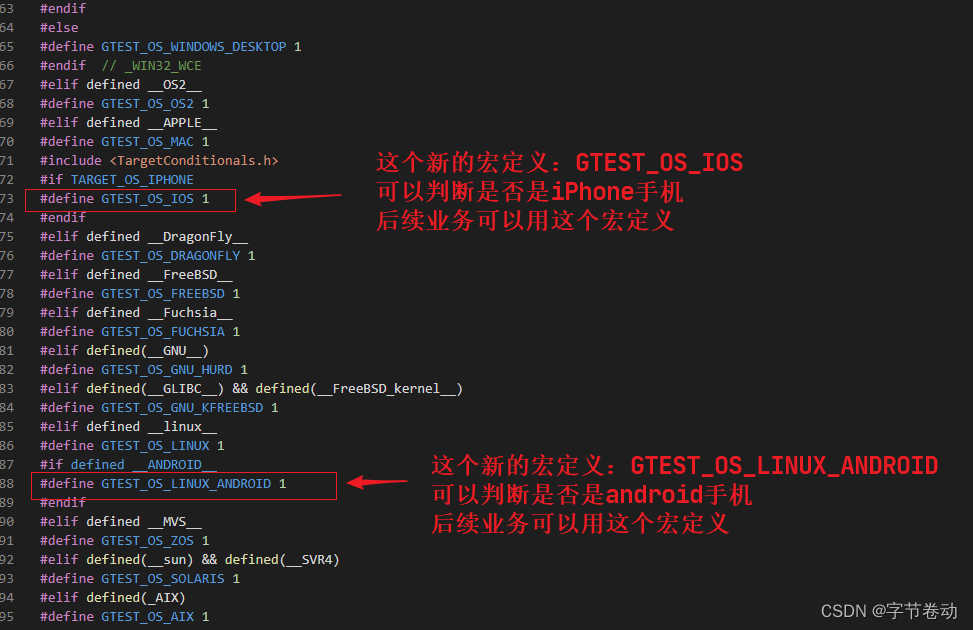
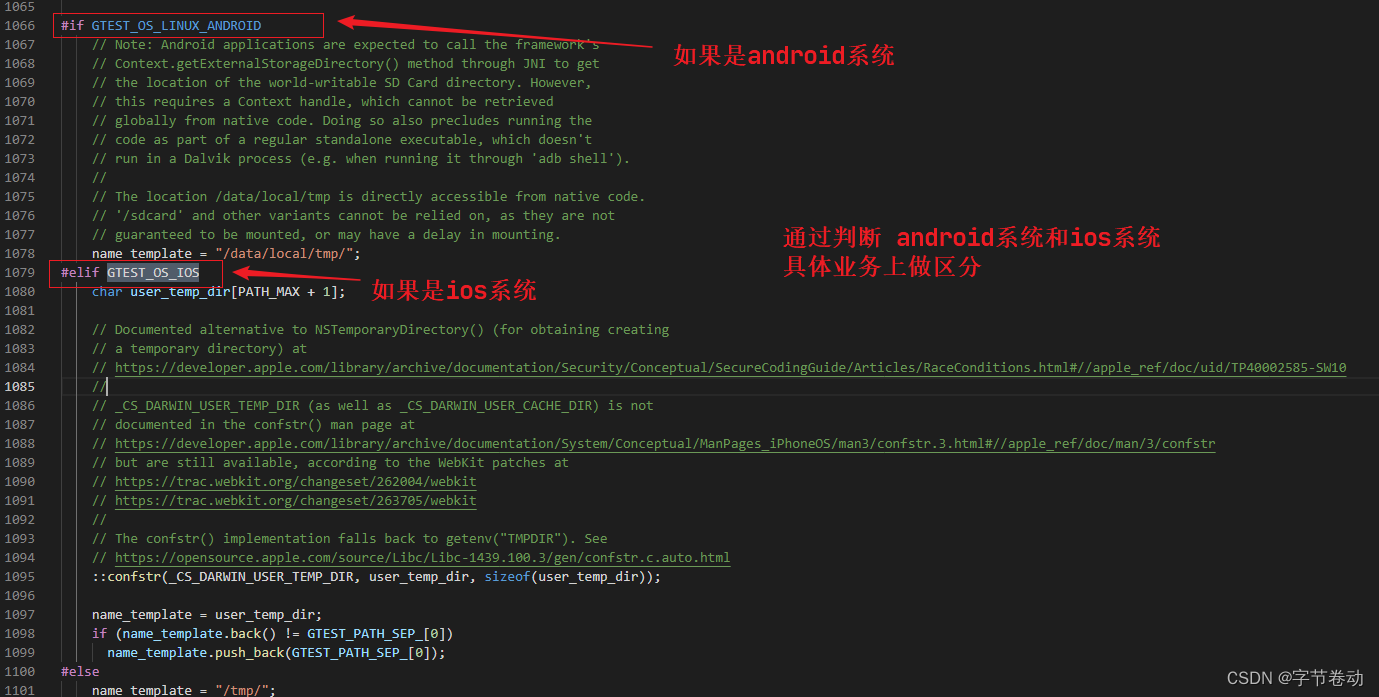
通过以上的知识,我们知道了C++如何通过宏定义来判断不同的操作系统,方便后续对不同的平台做一些差异性的业务。
四、CMake相关的宏定义
CMake 能够用来在 Window、Linux、Mac 平台下进行编译,在它的内部也定义了和这些平台相关的变量。
具体查看 官方文档 。
列举一些常见的:
- WIN32
- 如果编译的目标系统是 Window, 包括WIN64,那么 WIN32 为 True 。
- UNIX
- 如果编译的目标系统是 Unix 或者类 Unix 也就是 Linux ,那么 UNIX 为 True 。
- MSVC
- 如果编译器是 Window 上的 Visual C++ 之类的,那么 MSVC 为 True 。
- ANDROID
- Set to 1 when the target system (CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME) is Android.
- APPLE
- Set to True when the target system is an Apple platform (macOS, iOS, tvOS or watchOS).
有了这些常量做区分,就可以在一份 CMake 文件中编写不同平台的编译选项。
if(ANDROID){
# do something
}elseif(APPLE){
# do something
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
更多可以参考链接:
五、参考链接
- https://docwiki.embarcadero.com/RADStudio/Sydney/en/Predefined_Macros
- https://sourceforge.net/p/predef/wiki/OperatingSystems/
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5919996/how-to-detect-reliably-mac-os-x-ios-linux-windows-in-c-preprocessor
- https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/main/googletest/include/gtest/internal/gtest-port-arch.h
- https://iq.opengenus.org/detect-operating-system-in-c/




