热门标签
热门文章
- 1邮箱投递简历注意哪些礼仪?
- 2STM32标准库FLASH读写_stm32 flash读写 库函数版
- 3程序媛的mac修炼手册-- 2024如何彻底卸载Python_mac系统如何清除python安装环境
- 4如何保证RabbitMQ消息的顺序性_rabbitmq如何保证消息的顺序性
- 5cuda9.1+torch0.4.0+torchvision.0.2.2+python3.6.x配置_wincuda9.1安装torch
- 6语言模型在新闻媒体中的应用
- 7Python数据可视化工具matpoltlib使用_python matpoltlab
- 8Pytorch-Lightning--v1.9中的训练器--Trainer
- 9必读!信息抽取(Information Extraction)【命名实体识别】_信息抽取作用
- 10flink NoSuchMethodException: org.apache.hadoop.hive.metastore.RetryingMetaStoreClient.getProxy
当前位置: article > 正文
RabbitMQ消息模型之Fanout消息模型
作者:AllinToyou | 2024-04-13 05:40:00
赞
踩
RabbitMQ消息模型之Fanout消息模型
Fanout消息模型
* 广播模型:
* 一个交换机绑定多个队列
* 每个队列都有一个消费者
* 每个消费者消费自己队列中的消息,每个队列的信息是一样的
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
生产者
package com.example.demo02.mq.fanout;
import com.example.demo02.mq.util.ConnectionUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Allen
* 4/11/2024 8:24 AM
* @version 1.0
* @description: 广播模型发送者
*
* 广播模型:
* 一个交换机绑定多个队列
* 每个队列都有一个消费者
* 每个消费者消费自己队列中的消息,每个队列的信息是一样的
*/
public class FanoutSender {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1:获取连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
// 2:创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3:声明交换机
// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:交换机类型 (fanout direct topic) 参数3:是否持久化
/*
fanout:广播模式
绑定了这个交换机的队列都会收到消息
direct:路由模式
通过路由键完全匹配的队列会收到消息
topic:通配符模式
通过通配符匹配的队列会收到消息
*/
channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,false);
// 交换机不会存储消息,只是负责消息的转发,如果没有队列绑定到交换机上,消息会丢失
// 4:发送消息到交换机:需要消费信息的消费者自己声明自己的队列绑定到当前交换机上
String msg = "fanout message";
channel.basicPublish("fanout.exchange", "", null, msg.getBytes());
// 5:关闭通道
channel.close();
// 6:关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
消费者1
package com.example.demo02.mq.fanout;
import com.example.demo02.mq.util.ConnectionUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Allen
* 4/11/2024 8:55 AM
* @version 1.0
* @description: 广播模型接收者
*/
public class FanoutReceiver1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1:获取连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
// 2:创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3:声明交换机
//为什么消费者也得声明交换机?如果消费者先启动,那么交换机还没有声明,消费者就会报错,所以消费者也得声明交换机
// 参数1:交换机名称 参数2:交换机类型 参数3:是否持久化
channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,false);
// 4:声明队列
// 参数1:队列名称 参数2:是否持久化 参数3:是否排他性 参数4:是否自动删除 参数5:其他参数
channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue1", false, false, false, null);
// 5:绑定自己的队列到交换机
channel.queueBind("fanout.queue1", "fanout.exchange", "");
// 6:消费消息
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
// 参数1:消费者标签 参数2:消息传递参数 参数3: 参数4:消息内容
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 消费消息
System.out.println("Fanout1接收到的消息是:" + new String(body));
// 手动确认消息
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);
}
};
channel.basicConsume("fanout.queue1",false,consumer);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
消费者2
package com.example.demo02.mq.fanout;
import com.example.demo02.mq.util.ConnectionUtils;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author Allen
* 4/11/2024 8:55 AM
* @version 1.0
* @description: 广播模型接收者
*/
public class FanoutReceiver2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1:获取连接
Connection connection = ConnectionUtils.getConnection();
// 2:创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 3:声明交换机
//为什么消费者也得声明交换机?如果消费者先启动,那么交换机还没有声明,消费者就会报错,所以消费者也得声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,false);
// 4:声明队列
// 参数1:队列名称 参数2:是否持久化 参数3:是否排他性 参数4:是否自动删除 参数5:其他参数
channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue2", false, false, false, null);
// 5:绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind("fanout.queue2", "fanout.exchange", "");
// 6:消费消息
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
// 参数1:消费者标签 参数2:消息传递参数 参数3: 参数4:消息内容
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 消费消息
System.out.println("Fanout2接收到的消息是:" + new String(body));
// 手动确认消息
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);
}
};
channel.basicConsume("fanout.queue2",false,consumer);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
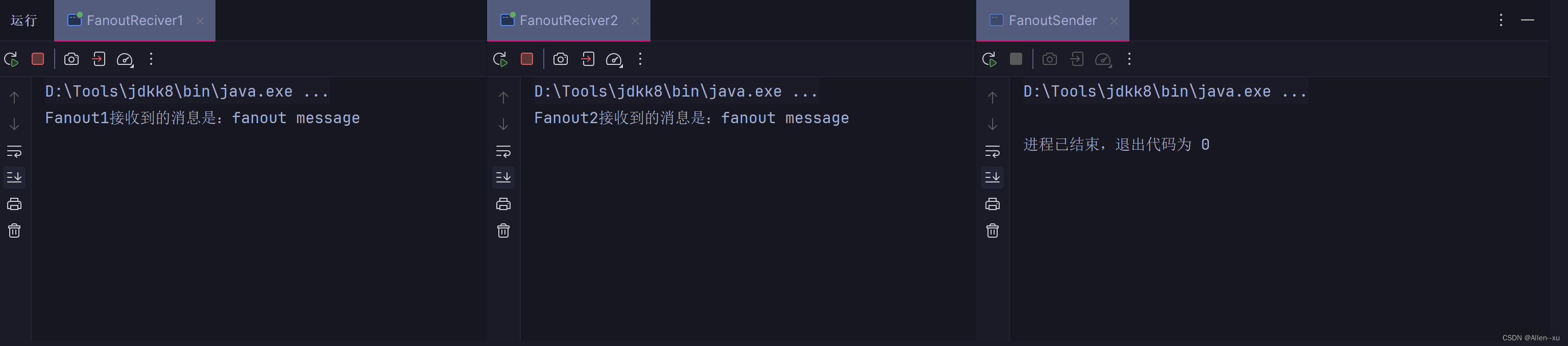
结果
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/AllinToyou/article/detail/414696
推荐阅读
相关标签


