- 1层与特征融合_每日一读:融合词性的双注意力 BiLSTM 情感分析
- 2多通路fpga 通信_【论文精选】基于FPGA的EtherCAT从站通信链路分析与验证
- 3手机访问电脑文件_【手机篇】巧借局域网,便捷实现手机电脑间的文件传输
- 4基于ERNIEPRO的文本分类与命名实体识别
- 5centos7使用rpmbuild制作rpm包_centos7 rpmbuild
- 6window 上跑hadoop问题之java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: org.apache.hadoop.io.nativeio.NativeIO$Windows._windows hadoop start_all.cmd java.lang.unsatisfied
- 7雷电模拟器一直android正在启动,雷电安卓模拟器启动后没反应、无法启动、闪退的3种解决办法-针对2020年4月4号出现的...
- 8等保2.0 MySQL数据库测评_等保测评mysql数据库
- 9布隆过滤器C语言代码_bloom_filter_init(
- 10基于FPGA状态机设计实现EtherCAT从站基本通信链路并验证_基于fpga的ethercat从站通信
pytorch学习笔记1-Dataset类代码实战_python dataset
赞
踩
本人在b站上学习PyTorch深度学习快速入门教程以及python学习中所做的笔记,教程链接在末尾。
从dataset数据集中主要获得数据(比如图片)、标签等,还有数据集总数。
准备工作:
蜜蜂蚂蚁数据集:
https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/hymenoptera_data.zip
把要制作的数据集移动到当前项目中:
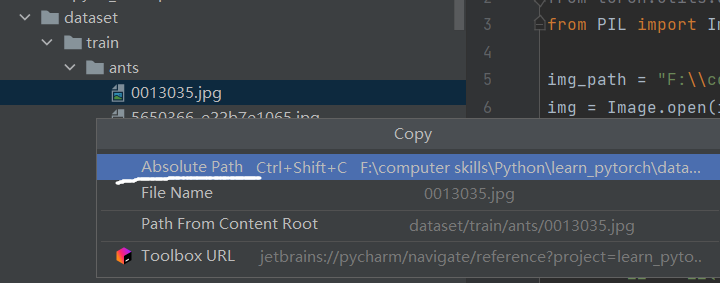
右键点击图片,选择复制路径,上面的absolute是绝对路径,下面path from content root是相对路径。在一个工程文件中最好使用相对路径,部署和移植不容易出错。
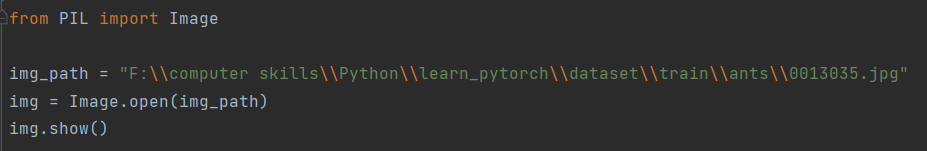
注意使用转义字符,或者直接在引号前加r。
复制相对路径的话是正斜杠/,就不需要前面防转义了。
(复制绝对路径时因为原字符串中有\会使发生转义,所以要防止转义,可以用r""防止转义也可以用两个\\,如下图所示。)
写一个类用来获取图片的地址和label:
- from torch.utils.data import Dataset
- from PIL import Image
- import os
-
-
- class MyData(Dataset):
-
- def __init__(self, root_dir, label_dir):
- self.root_dir = root_dir # "dataset/train",用self方法相当于创建全局变量
- self.label_dir = label_dir # "ants"
- self.path = os.path.join(root_dir, label_dir) # 把地址拼接起来,"dataset/train\\ants"
- self.img_path = os.listdir(self.path) # 获得所选路径所有的label,储存在列表里,这里是所有图片名称
-
- def __getitem__(self, idx):
- img_name = self.img_path[idx]
- img_item_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir, img_name) # 每个图片对应的相对路径
- img = Image.open(img_item_path) # 只是保持文件打开,在对图像进行操作之前不会读取图像数据
- label = self.label_dir
- return img, label
-
- def __len__(self):
- return len(self.img_path)
-
-
- root_dir = "dataset/train"
- ants_label_dir = "ants_image"
- bees_label_dir = "bees_image"
- ants_dataset = MyData(root_dir, ants_label_dir)
- bees_dataset = MyData(root_dir, bees_label_dir)
- train_dataset = ants_dataset + bees_dataset
- img, label = train_dataset[0]
- img.show()

两个需要注意的地方:
___getitem___:可以使用[]索引,如上面代码块中的第31行,在对这个类进行索引时就调用了这个函数,该方法的作用是使这个类可以作为迭代对象访问。
__len__:定义该方法后可以直接使用len(实例化对象的类名)输出长度,如果不定义该方法,只能使用len(对象.方法)输出长度。
采用python中的文件操作,给每张图片打标签,存到ants_label和bees_label文件夹中,文件名为对应图片的文件名,后缀为“txt”,内容为ants/bees。
- import os
- # 创建ants的label
- root_dir = "dataset/train"
- ants_dir = "ants_image"
- ants_img_path = os.listdir(os.path.join(root_dir, ants_dir))
- ants_label = ants_dir.split("_")[0]
- ants_out_dir = "ants_label"
-
- for i in ants_img_path:
- file_name = i.split(".jpg")[0]
- # 使用with … as…结构读写文件,就不用使用close关闭文件对象
- with open(os.path.join(root_dir, ants_out_dir, "{}.txt".format(file_name)), "w") as f:
- #(.write(s)向文件写入一个字符串或字节流(b模式下),不能直接写入数字)
- f.write(ants_label)
-
- # 创建bees的label文件
- bees_dir = "bees_image"
- bees_img_path = os.listdir(os.path.join(root_dir, bees_dir))
- bees_label = bees_dir.split("_")[0]
- bees_out_dir = "bees_label"
-
- for i in bees_img_path:
- bees_file_name = i.split(".jpg")[0]
- # 覆盖写模式,文件不存在则创建,存在则完全覆盖源文件。
- fo = open(os.path.join(root_dir, bees_out_dir, "{}.txt".format(bees_file_name)), "w")
- fo.write(bees_label)
- fo.close()

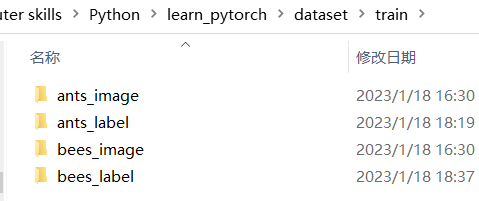
结果:
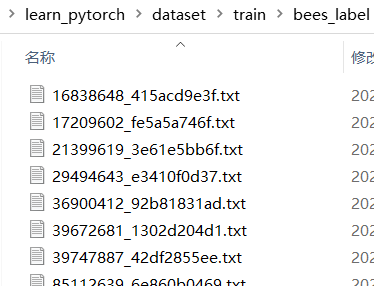
知识总结:
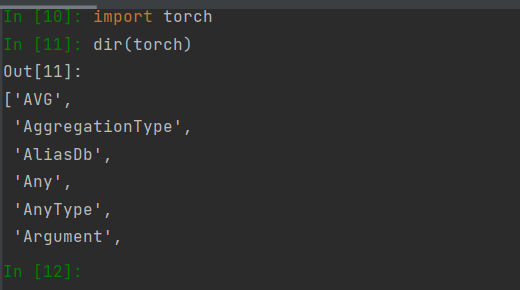
活用两个函数:dir()和help()
dir()函数的参数是你传入的对象,它会返回对象的属性和方法。比如字符串,当你不记得某个方法的拼写就可以用该函数查询字符串的所有方法。
help()函数可以查看某函数的帮助文档,当你不知道某个函数是干啥的时候可用。
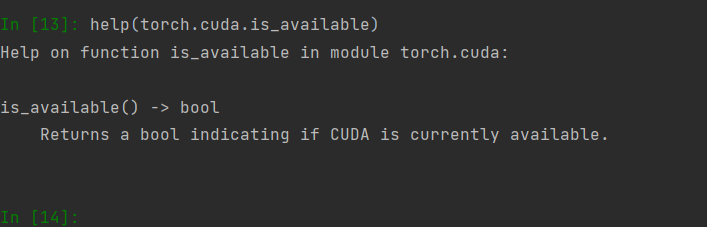
显示帮助文档的方法:
1.打开jupyter notebook(可以在pycharm下面的终端打开jupyter notebook。)
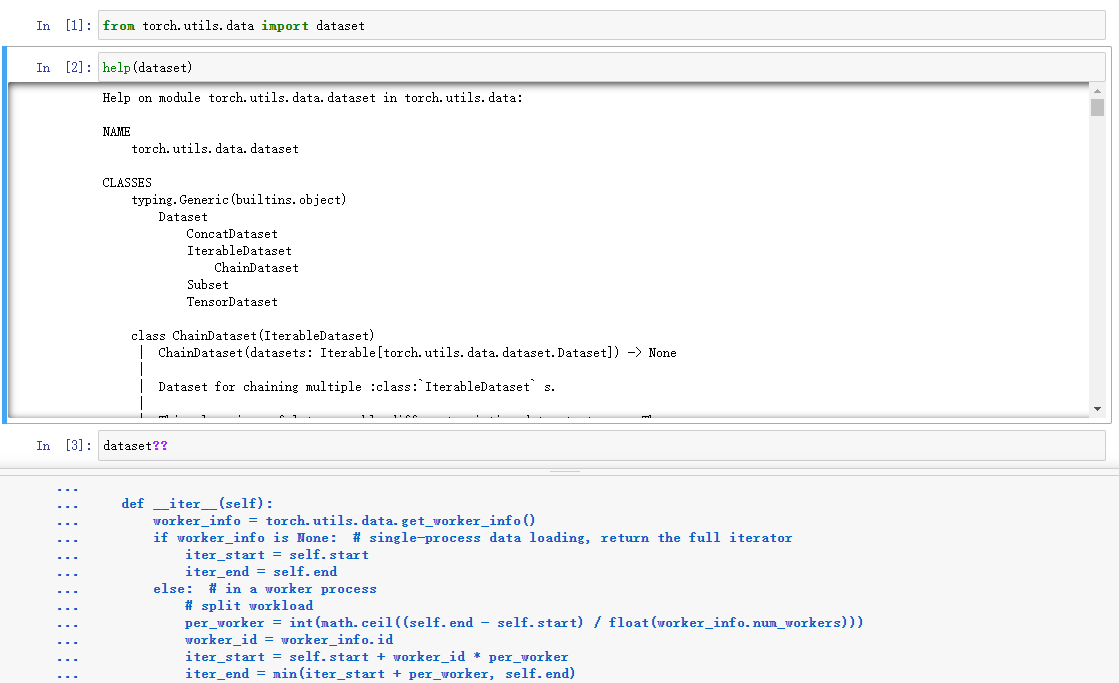
2.pycharm中将光标放在要查看文档的函数上,按住Ctrl+b(或Ctrl+点击),就会打开这个函数。
python中class中的方法
__init__
__init__(self)是类的初始化方法,在实例化后,会自动调用,而不用手动调用,所以一般把属性设置在__init__()里。
__getitem__
凡是在类中定义了这个__getitem__ 方法,那么它的实例对象(假定为p),可以像这样p[key] 取值,当实例对象做p[key] 运算时,会调用类中的方法__getitem__。一般如果想使用索引访问元素时,就可以在类中定义这个方法(__getitem__(self, key) )。
上面第一个代码中img, label = train_dataset[0]就是实例对象train_dataset做索引,这样就调用了类方法中的__getitem__,并返回return值。
PyTorch深度学习快速入门教程(绝对通俗易懂!)【小土堆】:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hE411t7RN?p=7&vd_source=759a4e59a9e315c4575a2b4d97dfae44



