- 1Elasticsearch - Docker安装Elasticsearch8.12.2
- 2Flutter入门之Row、Column、Container布局_flutter container和row
- 3如何修改YOLOV8?(从这8方面入手帮你提升精度)_yolov8改进
- 476. 最小覆盖子串 滑动窗口
- 5【运维】MacOS Wifi热点设置
- 6Java导出Excel里包含图片(包括GIF)_java excel导出图片
- 7解决将IDEA中的项目上传到Gitee平台时报错:Failed to connect to 127.0.0.1 port XXXX: Connection refused_idea failed to connect to 127.0.0.1 port 15732 aft
- 8最小二乘法(LSM)入门详解(原理及公式推导),MATLAB实现及应用_最小二乘法原理和公式
- 9Android Studio 自定义Gradle Plugin_android studio process release agcpligin
- 10LlamaIndex:轻松构建索引查询本地文档的神器_spacytextsplitter
AI发展史:AI发展还会陷入寒冬吗_ai development
赞
踩
Summarize the history of AI development
suffer many mishaps(命运多舛)! have a great future(前途无量)?
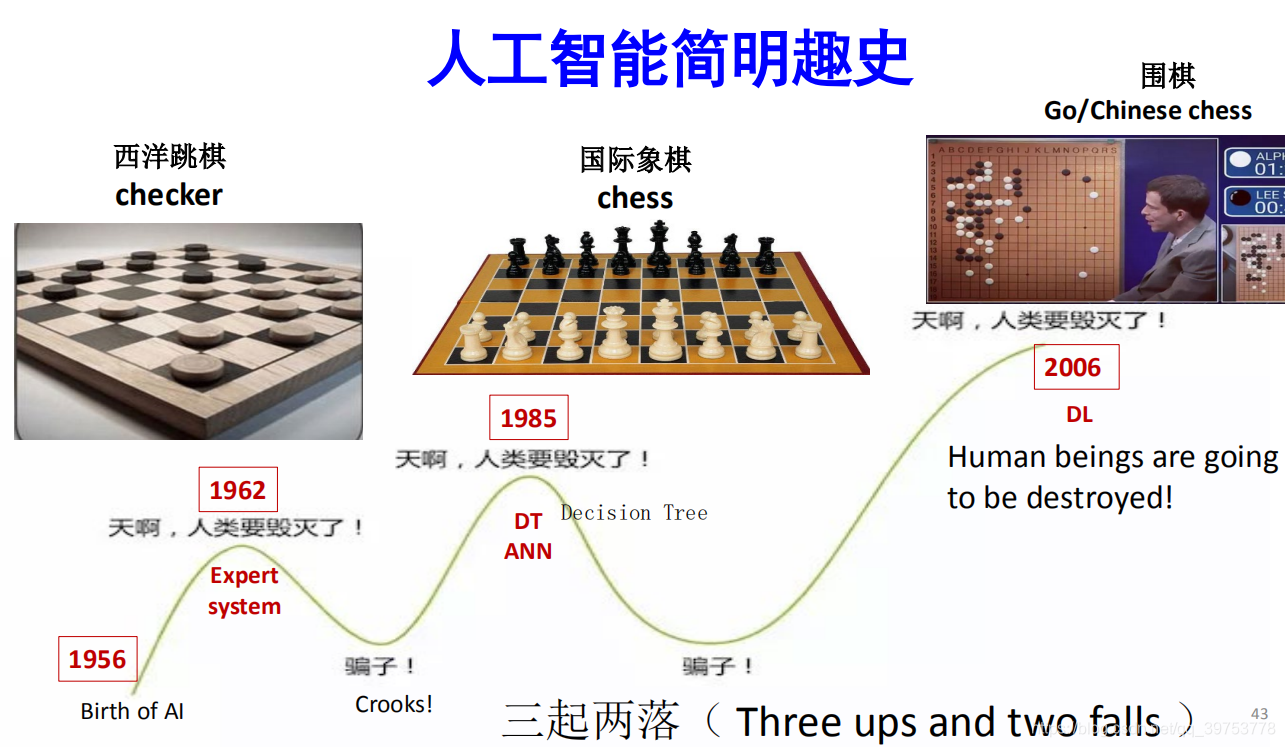
三起两落( Three ups and two falls ),命运多舛
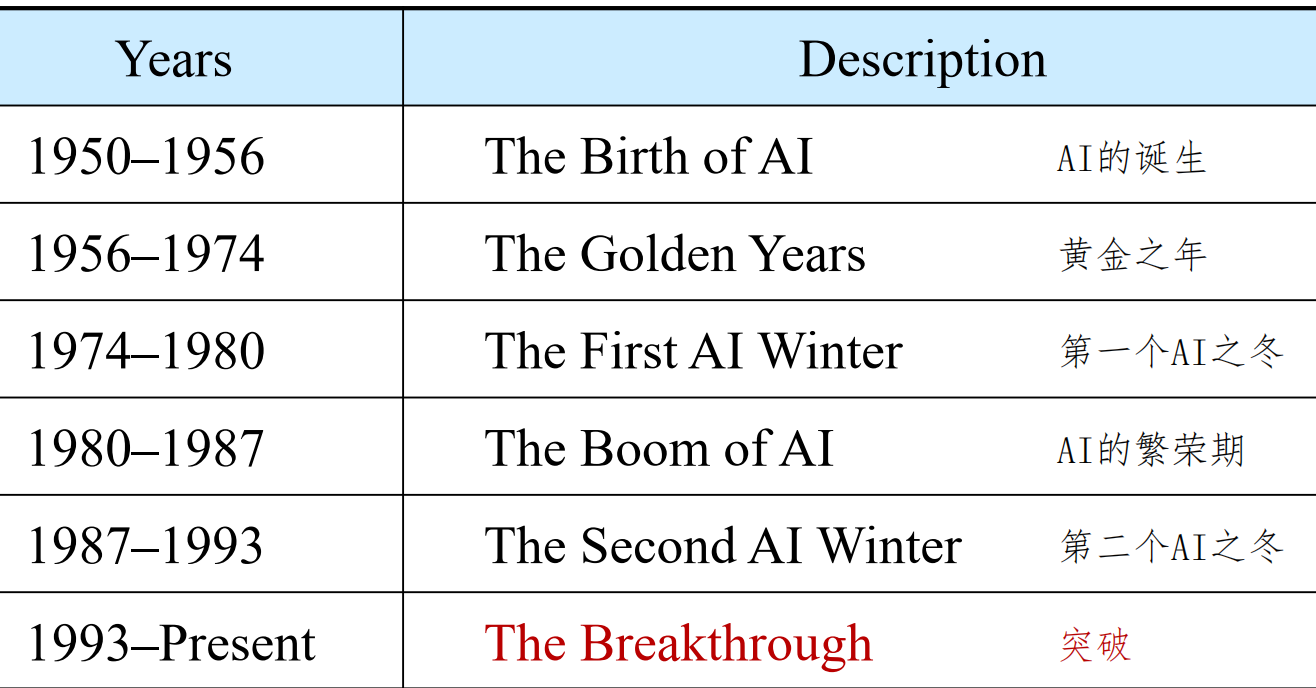
1950–1956, The Birth of AI
- 1950, Alan Turing proposes the Turing Test as a measure of machine intelligence.
1950年,艾伦·图灵提出了图灵测试,将其作为机器智能的度量。
-1956, the field of AI research was founded at a conference on Dartmouth College. 1956年,在美国达特茅斯学院的会议上,人工智能研究领域正式诞生。

- Professor Atanasoff of Iowa State University and his graduate student Berry built the world’s first electronic computer, Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC,“阿塔纳索夫-贝瑞计算机), from 1937 to 1941.
- It laid the material foundation for the study of AI.
- Not the American mathematician Mokley and Echo invented in 1946!

1956–1974, The Golden Years
- After the Dartmouth Conference, the United States formed a number of AI research organizations, such as
- Carnegie RAND Co-working Group led by Newell and Simon ,
- the MIT Research Group led by Minsky and McCarthy,
- the IBM Engineering Research Group led by Samuel.
达特茅斯会议后,美国形成了多个人工智能研究组织,如:
纽厄尔和西蒙的Carnegie RAND协作组,
明斯基和麦卡锡的MIT研究组,
塞缪尔的IBM工程研究组等。 - In 1958, Rosenblatt developed a perceptron , a system that uses neurons for recognition. Its learning function has aroused wide interest and promoted the research of connection mechanism. However, the limitation of perceptron is quickly discovered, which can not solve the complex problem of recognition, so the research of connection mechanism has entered a low tide.
1958年,Rosenblatt研制了感知机,这是一种将神经元用于识别的系统,它的学习功能引起了广泛的兴趣,推动了连接机制的研究。但很快就发现了感知机的局限性,不能解决复杂的识别问题,从而连接机制的研究进入低潮。(感知机:单个神经元,线性不可分问题,如异或问题,现实世界大部分问题线性不可分) - In 1958, Herbert Simon and Allen Newell demonstrated the first AI program, Logic Theorist (LT). 1958年赫尔伯特.西蒙和艾伦·纽厄尔演示了第一个AI程序,名称为逻辑理论家。
- 1958, John McCarthy (MIT) invented LISP programming language, which was developed as an important tool to build expert system.
1958年麦卡锡发明了LISP (List Processing列表处理缩写)编程语言,成为建造专家系统的重要工具。 - 1960s, M. Masterman and his colleagues at University of Cambridge design semantic nets for machine translation.
1960年代,M·马斯特曼与剑桥大学的同事们设计了语义网络,用于机器翻译。 - 1963, Leonard Uhrand Charles Vossler published “A Pattern Recognition Program That Generates, Evaluates, and Adjusts Its Own Operators”, which described one of the first machine learning programs.
1963年伦纳德·武赫和查尔斯·瓦斯勒发表了关于模式识别的论文,描述了第一个机器学习程序。
-1965, E. Feigenbaum initiated DENDRAL, a software to deduce the molecular structure of organic compounds. It was the first expert systems.
1965年,E·费根鲍姆开创了Dendral,一个推断有机化合物分子结构的软件。这是首套专家系统。

- In 1970 s, Holland proposed genetic algorithm, which marked the beginning of evolutionary computing.
In 1970s, Holland 提出了遗传算法,标志着演化计算研究的开始。 - In 1972, A.Comerauer of the University of Marseille, France, proposed and implemented the logical programming language PROLOG.
1972年法国马赛大学的科麦瑞尔提出并实现了逻辑程序设计语言PROLOG。
-1974, T. Shortliffe demonstrated MYCIN program, a very practical rule-based approach to medical diagnoses.
1974年,肖特列夫演示了MYCIN程序,一个非常实用的基于规则的医学诊断方法。 - Since 1956, the study of AI has achieved many remarkable achievements in machine learning, theorem proving, pattern recognition, problem solving, expert systems and artificial intelligence languages.
1956年以后,人工智能的研究在机器学习、定理证明、模式识别、问题求解、专家系统及人工智能语言等方面都取得了许多引人瞩目的成就 。 - In 1969, the International Joint Conference on Artificial
Intelligence(IJCAI) was established. (国际人工智能联合会
议)
-In 1970, the International Journal named 《Artificial Intelligence》
started its publication.
1974–1980, The First AI Winter
- In the late 1960s, AI research encountered difficulties, such as machine translation.
20世纪60年代末,人工智能研究遇到困难,如机器翻译。
-1966, the machine translation failed. 1966年,机器翻译失败了。
-The report of the US Advisory Board in 1966 affirmed that there is no universal scientific text machine translation, and the short term outlook for success remains gloomy.
1966年美国顾问委员会的报告裁定:还不存在通用的科学文本机器翻译,有很近的实现前景。
-The United Kingdom and the United States suspended funding for most machine translation projects.
英国、美国中断了大部分机器翻译项目的资助。
-1970, the connectionism was abandoned. 1970年,连接主义遭到遗弃。
AI两大学派
——连接主义:采用神经网络结构不是知识
——符号主义:采用符号表示知识(广义表、LISP)
-1971–1975, DARPA(美国国防部高级研究计划局)felt frustrated at the Speech Understanding Research program at Carnegie Mellon University.
1971年至75年,美国DARPA对卡内基梅隆大学的语音理解研究项目感到沮丧。
-1973, the large decrease in AI research in the United Kingdom, in response to the Lighthill report “Artificial Intelligence: A General Survey”.
1973年,受莱特希尔的“人工智能:综合调查”报告的影响,英国大幅度缩减AI的研究。 - 1973-1974,美国DARPA削减了一般性AI学术研究经费。t
Jokes about English-Russian translation
(1) The spirit is willing but the flesh is week. (心有余而力不足)
The vodka is strong but meat is rotten. (伏特加酒虽然很浓,但肉是腐烂的)
The reason for this error :Spirit:1)精神 2) liquor (烈性酒)
(2) Out of sight, out of mind (blind and insane)
“眼不见,心不烦”vs.“又瞎又疯”
(3) Time flies like an arrow.
“光阴似箭” vs. “苍蝇喜欢箭”
Conclusion:
Only if the machine can understand , it can translate correctly.
and understanding requires knowledge.
结论:必须理解才能翻译,而理解需要知识.
The mistake lies in the literal translation and not understanding.
错误在于仅字面翻译,并非理解了。
1980–1987, AI Boom
- In 1977, Feigenbaum proposed the concept of “knowledge
engineering” at the 5th IJCAI, which promoted knowledge centered research.
1977年,费根鲍姆在第五届国际人工智能联合会议上提出了“知识工程”概念,推动了知识为中心的研究。 - Knowledge is power–-Bacon;
- In the Knowledge lies the power–-Feigenbaum
-The world entered the era of knowledge engineering. Knowledge
representation and reasoning have made a breakthrough.
进入知识工程时代,知识表示与推理取得了突破。 - Since 1978, China has taken “intelligent simulation” as the main
research topic of national science and technology development
planning.
我国自1978年开始把“智能模拟”作为国家科学技术发展规划的主要研究课题。 - In 1981, the Chinese Society of Artificial Intelligence (CSAI) was
established. 1981年成立了中国人工智能学会。 - Nowadays, AI has become a key technology in many fields such as computer, aerospace, military equipment, and industry.
现在,人工智能已经成为计算机、航空航天、军事装备、工业等众多领域的关键技术。 - 1980, First National Conference of the American Association for
Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) held at Stanford.
1980年,美国人工智能学会(AAAI)在斯坦福大学召开了第一届全国大会。 - 1982, Japan started Fifth Generation Computer System (FGCS)
project for knowledge processing.
1982年,日本启动了第五代计算机系统(FGCS)项目,用于知识处理。
- In mid-1980s, the machine learning came, when the decision tree model was invented and distributed as software. The model is visualized and is easy to explain.
1985年,机器学习出现了,当时发明了决策树模型并且以软件形式推出。该模型具有可视化、易说明的特点。
机器学习算法分类:监督学习、无监督学习、强化学习
监督学习算法 (Supervised Algorithms):在监督学习训练过程中,可以由训练数据集学到或建立一个模式(函数 / learning model),并依此模式推测新的实例。该算法要求特定的输入/输出,首先需要决定使用哪种数据作为范例。例如,文字识别应用中一个手写的字符,或一行手写文字。主要算法包括神经网络、支持向量机、最近邻居法、朴素贝叶斯法、决策树等。
无监督学习算法 (Unsupervised Algorithms):这类算法没有特定的目标输出,算法将数据集分为不同的组。
强化学习算法 (Reinforcement Algorithms):没有数据集,强化学习普适性强,主要基于决策进行训练,算法根据输出结果(决策)的成功或错误来训练自己,通过大量经验训练优化后的算法将能够给出较好的预测。类似有机体在环境给予的奖励或惩罚的刺激下,逐步形成对刺激的预期,产生能获得最大利益的习惯性行为。在运筹学和控制论的语境下,强化学习被称作“近似动态规划”(approximate dynamic programming,ADP)。(骑自行车例子)
基本的机器学习算法:线性回归、支持向量机(SVM)、最近邻居(KNN)、逻辑回归、决策树、k平均、随机森林、朴素贝叶斯、降维、梯度增强
- Also in mid-1980s, multilayer Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) was invented. With enough hidden layers, a ANN can express any function, thus overcoming the limitation of perceptron.
1985年,还发明了多层人工神经元网络(ANN)。具有足够多的隐藏层,一个ANN可以表达任意的功能,因此突破了感知的局限性。
1987–1997, The Second AI Winter
- 1987, the LISP machine market collapsed.
1987年,LISP 机(专家系统)的市场崩溃。(符号主义的代表) - 1988, new funding on AI were cancelled by the United States government‘s Strategic Computing Initiative.
1988年,美国政府的战略计算促进会取消了新的AI经费。 - 1993, expert systems slowly slipped to the valley bottom.
1993年,专家系统缓慢滑向低谷。 - 1990s, the fifth-generation computer project disappeared quietly because it did not achieve its original goals. (1982提出)
1990年代,日本第五代计算机项目未能达到其初始目标,悄然退场。
1997–Present, Breakthrough
- In 1997-5-12, Deep Blue beat a reigning world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, and became the first computer chess-playing system. This event set off AI boom.
1997年,深蓝战胜了卫冕国际象棋冠军加里·卡斯帕罗夫,成为第一台计算机国际象棋系统。这一事件又掀起了AI热潮。 - It marks the successful application of AI in game.
它标志着AI在博弈中的成功应用。
(AI战胜人类的要素:DP算法、算力、大数据,游戏行业满足)
-
In 1956, Samuel developed the checkers program, which can learn from the checker games, but also from the practice of checkers.
1956年,塞缪尔研制出了跳棋程序,这个程序能从棋谱中学习,也能从下棋实践中提供棋艺。 -
In 1959 it defeated Samuel himself; in 1962 it defeated a state champion.
1959年,它击败了塞缪尔本人;1962年它击败了一个州的冠军。 -
In August 1991, IBM‘s Deep Thought computer system and Australian chess champion Johansson held a human-computer confrontation, which ended at a draw of 1:1.
1991年8月,IBM的“深思”计算机系统与澳大利亚象棋冠军约翰森举行了人机对抗赛,以1:1平局告终。 -
In 1996, IBM invited the chess champion Kasparov to fight with Deep Blue developed by IBM and Kasparov won at 4:2.
1996年,IBM邀请国际象棋棋王卡斯帕罗夫与IBM研制的“深蓝”计算机系统进行了六局的人机大战,最终,卡斯帕罗夫以4:2获胜。 -
In 1997, Deep Blue beat Kasparov at 3.5:2.5.
1997年,深蓝终于以3.5:2.5打败了Kasparov (1胜2负3平)。 -
In 1957, Simon predicted that the computer could beat the world champion in 10 years, but 40 years later Deep Blue beat Kasparov, 30 years later than the prediction.
1957年,西蒙曾预测:10年内计算机可以击败人类世界冠军,虽然未成功,但40年后“深蓝”击败了国际象棋棋王卡斯帕罗夫,比预测晚了30年。
- In 2005, a Stanford’s Stanley, an autonomous robotic vehicle, won the DARPA Grand Challenge.
2005年,斯坦福的自主机器人车辆Stanley,赢得了DARPA无人驾驶汽车挑战赛。 - In 2006, the term “deep learning” gained attention after a publication by Geoffrey Hinton and Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
2006年,在杰弗里·辛顿和鲁斯兰·萨拉赫丁诺夫在科学杂志上发表了有关“深度学习”的论文之后,该术语成了热门。 - Watson, the computer was specifically developed by IBM to answer questions on the quiz show Jeopardy!
沃森,是IBM专门开发的、在智力竞赛Jeopardy!回答问题的计算机。 - In 2011, Watson competed on Jeopardy! against former winners Brad Rutter and Ken Jennings.
2011年,沃森在Jeopardy!上战胜了上届冠军布拉德·路特和肯恩·詹宁斯。 - Watson received the first prize of $1 million.
沃森获得了1百万美元大奖。
Note:Jeopardy! is an American television game show created by Merv Griffin. The show features a quiz competition in which contestants are presented with general knowledge clues in
the form of answers, and must phrase their responses in the form of questions. The original daytime version debuted on NBC on March 30, 1964, and aired until January 3, 1975.
危险!是 Merv Griffin创作的美国电视游戏节目。该节目以竞赛为特色,竞赛者以答案的形式呈现一般知识线索,并且必须以问题的形式表达他们的回答。最初的白天版本于1964年3月30日在 NBC上首次亮相,播出时间直到1975年1月3日。
- In 2011, Google started Deep Learning project, Google Brain, as one of the Google X projects.
2011,谷歌启动了深度学习项目,谷歌大脑,作为 Google X (research lab) 项目之一。
Google brain is a cluster of 16,000 computers dedicated to mimicking some aspects of human brain activity.
谷歌大脑是由1万6千台计算机连成的一个集群,致力于模仿人类大脑活动的某些方面。
It had successfully recognized a cat based on 10 million digital images.
通过1千万张数字图片的学习,已成功地学会识别一只猫。 - In 2012, Siri (Speech Interpretation & Recognition Interface ) was introduced by Apple as an integral part of iOS since iOS 5, running from iPhone 4S.
2012年苹果公司引进了Siri,从iPhone 4S上运行的iOS5开始,已作为iOS的一个组成部分。 - 2012年,计算机视觉界顶级比赛ILSVRC中,多伦多大学Hinton团队所提出的深度卷积神经网络结构AlexNet(8层)一鸣惊人(图像分类错误率降低11%),同时也拉开了深度卷积神经网络在计算机视觉领域广泛应用的序幕。
- Siri is an intelligent personal assistant and knowledge
navigator. Siri 是一种智能个人助理和知识导航软件。
Use a natural language user interface to answer questions, make recommendations, and perform actions.
使用自然语言用户接口来回答问题、做出建议和执行动作。
Available in: English, French, German, Japanese, Chinese, Korean, Italian, Spanish. 支持英语、法语、德语、日语、中文、韩文、意大利语、西班牙语。 - In 2012, Rick Rashid, Microsoft’s Chief Research Officer, demonstrated a real-time English-to-Chinese universal translator that keeps your voice and accent.
2012年,瑞克·拉希德,微软首席研究官,演示了一款实时的英文-中文通用翻译系统,可以保持你的声音和口音。
Not only is the translation very accurate, but the software also preserves the user’s accent and intonation.
该软件不仅翻译非常准确,而且能够保持讲者的口音和语调。 - Apr. 2014,Microsoft demonstrated “Cortana”, an intelligent personal assistant on Windows Phone.
2014年4月,微软演示了“Cortana”,一款运行在Windows Phone上的智能个人助理。 - Jun. 2014, Microsoft China released chatbot “XiaoIce(小冰)” which allowed WeChat users to have conversations with it.
2014年6月,微软中国推出了聊天机器人小冰,微信用户可与她交谈。 - On Sept. 8, 2015, Baidu launched a robot assistant — Duer at the
2015 Baidu World Congress, which provides a secretarial search service for users.
2015年9月8日,百度在2015百度世界大会上推出了一款机器人助理—度秘,可以为用户提供秘书化搜索服务。 - Jun. 2014, chatbot Eugene Goostman, at a contest marking the 60th anniversary of Turing‘s death, 33% of the event’s judges thought that Goostman was human, so that the event’s organizer considered it to have passed Turing’s test.
2014年6月,聊天机器人尤金·古斯特曼,在纪念图灵逝世60周年的一个比赛上,被该活动33%的评委认为古斯特曼是人类,因此组织者认为它已经通过了图灵测试。
Eugene Goostman is developed in Saint Petersburg in 2001 by a group of three programmers.
尤金·古斯特曼是由三个程序员小组于2001年在圣·彼得堡开发的。 - Aug. 2014, IBM announced “TrueNorth”chip to work like human brain.
2014年8月,IBM发表了类人脑工作的TrueNorth芯片。
TrueNorth is a neuromorphic CMOS chip, consists of 4096 hardware cores, each one simulating 256 programmable silicon “neurons” for a total of just over a million neurons. TrueNorth是一款神经形态的CMOS芯片,由4096个硬件核组成,每个仿真256个可编程的硅神经元,总计刚好超过百万个神经元。 (4096*256=1,048,576) - On April 9th, 2016, “I am a singer” came to a close in the fourth season finals. Li Wen won the championship. According to reports, before the final result was announced, Ali Cloud xiao Ai predicted that Li Wen won the championship.
2016年4月9日,《我是歌手》第四季总决赛落下帷幕,李玟夺得总冠军。据报道,在决赛结果宣布之前,阿里云小Ai 就预测到了李玟夺冠。
Xiao Ai is an AI program developed by Alibaba Cloud. It is based on the principles of neural network, social computing, and emotional perception. It is good at understanding the essence and real-time prediction, and can understand human emotions. It can continuously evolve itself through powerful computing and machine learning capabilities.
小Ai 是阿里云研发的人工智能程序,主要基于神经网络、社会计算、情绪感知等原理工作,善于洞察本质和实时预测,并能理解人类情感,可以通过强大的计算和机器学习能力不断自我进化。 - In 2010, AI programmer and neuroscientist Demis Hassabis et al. co-founded DeepMind, a cutting-edge artificial intelligence company, located in London.
2010年,人工智能程序师兼神经科学家戴密斯·哈萨比斯(Demis Hassabis)等人联合创立了DeepMind,是前沿的人工智能企业,位于英国伦敦。
The company combines state-of-the-art technology in machine learning and system neuroscience to establish a powerful general-purpose learning algorithm.
该公司结合机器学习和系统神经科学的最先进技术,建立了强大的通用学习算法。
In January 2014, Google bought DeepMind. for $400m
2014年1月,谷歌斥资4亿美元收购DeepMind。
Feb. 2015, Google DeepMind published Deep Q-Network, the human-level control through deep reinforcement learning.
2015年2月,谷歌DeepMind公司在Nature杂志上发表了Deep Q-Network,通过深度强化学习达到人类水平的操控。
- Dec. 2015, program AlphaGo developed by Google DeepMind beat Fan Hui, the European Go champion. Five battles, five victories.
2015年12月,谷歌DeepMind公司的程序AlphaGo打败了欧洲围棋冠军樊麾,成绩5战5胜。 - Jan. 27 2016, the announcement of the news was delayed until this day, to coincide with the publication of a paper in the journal Nature describing the algorithms used.
这个消息直到2016年1月27日才宣布,目的是与描述所用算法的论文在《自然》杂志发表的时间同步。 - Deep-learning software defeats human professional for the first time.
深度学习软件第一次击败了人类职业棋手。
- Mar. 9-15 2016, AlphaGo played South Korean professional Go player Lee Sedol, ranked 9-dan, in Seoul, South Korea. AlphaGo won all but the fourth game.
2016年3月8日至15日,AlphaGo在韩国首尔对垒韩国九段职业棋手李世石。AlphaGo以5战4胜赢得了比赛。
1997.5 Deep Blue beat Kasparov, 3.5:2.5(chess)
2017.5.27 AlphaGo beat 柯洁, 3:0
2016.3 AlphaGo beat 李世石, 4 :1
AlphaGo Zero Vs AlphaGo
- AlphaGo learned about human’s 30 million chess games before it defeat humanity;阿尔法狗学习人类三千万棋局,才打败人类;(监督学习)
- AlphaGo Zero was self-taught from scratch, relying on reinforcement learning without any human game and priori knowledge;
AlphaGo Zero,译为阿尔法元,, 从零开始自学,没有任何人类棋谱和先验知识,完全依靠强化学习;
It played around 4.9 million chess games with itself within three days, using 4 TPU (Tensor Processing Unit);
阿尔法元仅用4个TPU,用三天时间自己左右互博490万棋局;
In 2017, AlphaGo Zero beat AlphaGo with a score of 100:0.
2017年,阿尔法元以100:0的成绩完胜阿尔法狗。
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature24270
- Demis Hassabis (born 27 July 1976) is a British AI researcher, neuroscientist, video game designer, entrepreneur, and world-class games player.
Demis Hassabis (1976年7月27日出生)是英国人工智能研究员,神经科学家,视频游戏设计师,企业家和世界级游戏玩.
Professor David Silver (dob c.1976) leads the reinforcement learning research group at DeepMind and was lead researcher on AlphaGo .
David Silver 教授(dob c.1976)领导DeepMind的强化学习研究小组,并担任AlphaGo的首席研究员。
人工智能简明趣史
三起两落( Three ups and two falls )
推荐阅读:AI研究内容及应用


