- 1java.sql.SQLException No suitable driver 的解决办法_java.sql.sqlexception: no suitable driver
- 2交叉注意力融合时域、频域特征的FFT + CNN-Transformer-CrossAttention轴承故障识别模型_时域频域 transformer
- 3Java实现Excel多表头动态数据导出_java导出excel多级表头
- 4MVVM设计模式时什么?浅谈MVVM设计模式_wpf之mvvm模式描述错误的是
- 5用Eclipse创建一个JavaWeb项目,把资源添加到Tomcat服务器,并运行jsp文件详细过程(附图片)_eclipse创建web项目
- 6云计算实战系列四(Linux文件权限I)
- 7Docker入门指南:从基础到实践_ubuntu docker 入门
- 8vue+vite项目打包生成可以后端修改url ip的相关配置与使用方式_vite 设置后端ip
- 9牛客网-刷题解析2
- 10数学计算机教学课题,《现代信息技术与小学数学教学整合的实践研究》顺利结题...
鲁棒线性回归问题,使用MindOpt也可优化_鲁棒回归
赞
踩
回归分析是一种预测技术,目的是建立 自变量x(向量)和 相关变量y(标量)之间的关系。目前有七种常见的回归分析:Linear Regression线性回归(本篇)、Logistic Regression逻辑回归、Polynomial Regression多项式回归、Stepwise Regression逐步回归、Ridge Regression岭回归、Lasso Regression套索回归、ElasticNet回归。
本篇我们讲述的是**Linear Regression线性回归中的鲁棒线性回归。**鲁棒回归又称为稳健回归,是统计学稳健估计的方法之一,主要思路是对离群点十分敏感的最小二乘回归中的的函数进行修改。
下文我们将讲述一个例子,来展示MindOpt优化鲁棒线性回归问题(含源代码)。
问题描述
学生的行为习惯和测试成绩之间的关系。线性回归使用线性函数 $y = <\boldsymbol a,\boldsymbol x> + b $ 来描述这种关系(更准确地说法是仿射函数)。向量 a \boldsymbol a a 表示“梯度”,标量 b b b 表示“截距”。通过 m m m 次观测 ( x 1 , y 1 ) . . . ( x m , y m ) (\boldsymbol x_1, y_1) ... (\boldsymbol x_m, y_m) (x1,y1)...(xm,ym) ,我们可以估计出 a \boldsymbol a a 和 b b b 的值。
普通的最小二乘回归(least-squares regression)对“离群观测”很敏感。仅一个离群观测就会影响对 a \boldsymbol a a 和 b b b 的估计。而鲁棒回归则不受少数离群观测的影响。
假设“离群观测”的数量相对 m m m 而言很少,其他正常观测又很准确。则我们应该使用鲁棒线性回归去恢复真实的 a \boldsymbol a a 和 b b b :
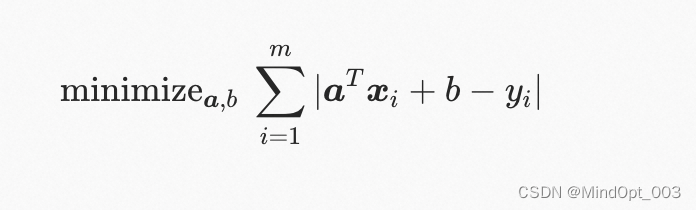
相比最小二乘回归,鲁棒回归可以更好地抵御(但不也能完全消除)离群观测的影响。
通过变换和引入变量 c \boldsymbol c c ,我们可以把这个问题转化为线性规划:
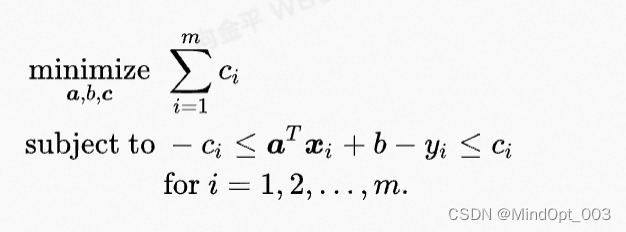
为了编程方便,我们将变量放在不等式一侧,非变量参数放在另一侧:
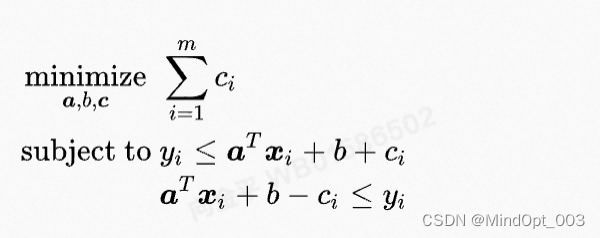
等价的矩阵形式
将 x_1, …, x_m 作为行放入矩阵 X,将 y_1, …, y_m 作为元素放在列向量 y 中。令 1 为元素为1的向量。原始鲁棒线性回归问题可以简写为
m
i
n
i
m
i
z
e
a
,
b
∥
X
a
+
1
b
−
y
∥
1
\mathop{\mathrm{minimize}}_{\boldsymbol a,b} ~\|X\boldsymbol a + \boldsymbol 1 b - \boldsymbol y\|_1
minimizea,b ∥Xa+1b−y∥1.
通过变换,我们可以把这个问题转化为线性规划:
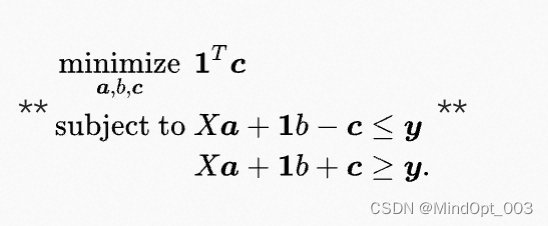
产生数据
我们通过生成随机数据,验证鲁棒线性回归的有效性。现在随机产生真正的 a \boldsymbol a a 和b :
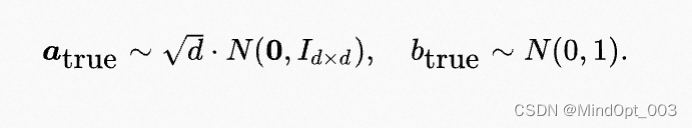
再使用它们产生 0.9 ∗ m 0.9*m 0.9∗m 次正确观测:
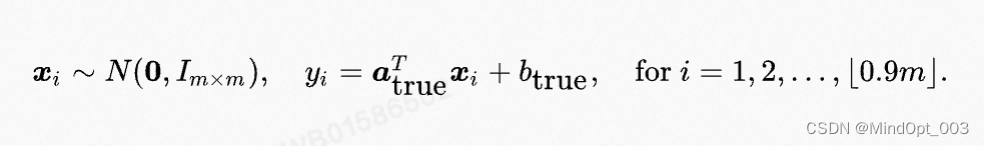
外加 0.1 ∗ m 0.1*m 0.1∗m 次离群观测:
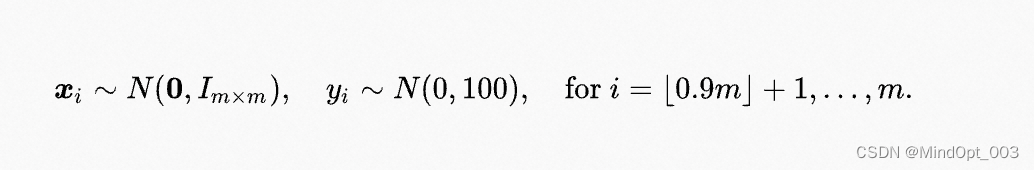
因为观测的次序对鲁棒线性回归没有任何影响,所以不失一般性,我们将离群观测放在最后。
我们在下面的代码里面会实现数据生成的过程。
使用MindOpt求解器的API
直接采用求解器的API,需要查阅API文档来理解API的意思,没有建模语言可读性高。请参阅https://solver.damo.alibaba.com/doc/html/API%20reference/API-python/index.html来查看PythonAPI的使用说明。
关于Python的例子,在文档的5.建模与优化求解章节有Python的示例。这里是个LP的问题,我们可以参考:https://solver.damo.alibaba.com/doc/html/model/lp/linear%20optimization-python.html
下面我们分两种方式描述在本平台环境中的运行方法:
方法1:cell中直接输入代码运行
请运行下面cell中的代码,点击本窗口上面的播放△运行,或者摁shift+enter键运行:
# LP_5_RobustRegression.py from mindoptpy import * import numpy as np import random def simulateData(dimension=4,m_observations=15,is_write_data = False,output_dir = ""): # use time to seed the random number generator random.seed(time.time()) # randomly generate vector a and scalar b d = dimension true_a = np.random.randn(d) * np.sqrt([d]) true_b = np.random.randn(1)[0] # randomly generate observations (x[i],y[i]), i = 1,...,m with 10% outliers m = m_observations X = np.zeros((m,d)) y = np.zeros((m,1)) for i in range(m): X[i,] = np.random.randn(d) if i < np.floor(0.9*m): y[i] = np.inner(true_a,X[i,]) + true_b else: y[i] = np.random.randn(1) #print("true_a:\n",true_a) #print("true_b:\n",true_b) #print("X:\n",X) #print("y:\n",y) if is_write_data: f_true_a = open(output_dir+"true_a.txt", "w") L = ["{}\n".format(true_a[i]) for i in range(len(true_a))] f_true_a.writelines(L) f_true_b = open(output_dir+"true_b.txt", "w") L = ["{}\n".format(true_b)] f_true_b.writelines(L) f_X = open(output_dir+"X.txt", "w") L = ["{}\n".format(X[i]) for i in range(len(X))] f_X.writelines(L) f_y = open(output_dir+"y.txt", "w") L = ["{}\n".format(y[i]) for i in range(len(y))] f_y.writelines(L) return true_a,true_b,X,y if __name__ == "__main__": # --- Create simulation data --------------- d = 4 m = 15 true_a,true_b,X,y = simulateData(d,m) #--- MindOpt Step 1. Initialize an empty optimization model --- model = MdoModel() try: #--- MindOpt Step 2. Set model inputs --- # Change to minimization problem. model.set_int_attr("MinSense", 1) # add variables, specify their low bounds, upper bounds, and cost coefficients # set objective: minimize_{a,b,c} 0'a + 0b + 1'c INF = MdoModel.get_infinity() var_a = [] for j in range(d): var_a.append(model.add_var(-INF, INF, 0.0)) # low bnd, upr bnd, 0 cost coeff var_b = model.add_var(-INF, INF, 0) # low bnd, upr bnd, 0 cost coeff var_c = [] for i in range(m): var_c.append(model.add_var(-INF, INF, 1.0)) # low bnd, upr bnd, cost coeff = 1.0 # Add constraints row by row for i in range(m): # compute a'x[i,] expr = MdoExprLinear() for j in range(d): expr += X[i,j]*var_a[j] # add: y[i] <= a'x[i,] + b + c[i] model.add_cons(y[i], INF, expr + var_b + var_c[i]) # add: a'x[i,] + b - c[i] <= y[i] model.add_cons(-INF, y[i], expr + var_b - var_c[i]) #--- MindOpt Step 3. Set solver parameters --- model.set_int_param("Method", 2) # as an example, set to run the interior-point method model.set_int_param("NumThreads", 2) # as an example, set to run 2 threads # ------Step3. Solve the problem and populate the result.------- model.solve_prob() model.display_results() time.sleep(0.01) #for print status_code, status_msg = model.get_status() if status_msg == "OPTIMAL": print("----\n") print("The solver terminated with an OPTIMAL status (code {0}).".format(status_code)) print("目标函数总收益是: {0}".format(model.get_real_attr("PrimalObjVal"))) print("\n----------------\nCompare var_a to true_a, and var_b to true_b:\n----------------") # Compare var_a to true_a, and var_b to true_b; Display residuals # Display solutions a[0],...,a[d-1] print('\n{0:<5} {1:>9} {2:>9}'.format('Entry','True','Soln')) for j in range(d): print('{0:>5} {1:>9f} {2:>9f}'.format('a['+'%s'%j+']', true_a[j], var_a[j].get_real_attr('PrimalSoln'))) # Display solution b print('\n{0:<5} {1:>9} {2:>9}'.format(' ','True','Soln')) print('{0:>5} {1:>9f} {2:>9f}'.format('b', true_b, var_b.get_real_attr('PrimalSoln'))) print("\n----------------\nShow Residual(c value):\n----------------") # Display solutions c[0],...,c[m] print('\n{0:>11} {1:>9}'.format('Observation','Residual')) for i in range(m): print('{0:>11d} {1:>9f}'.format(i, var_c[i].get_real_attr('PrimalSoln'))) else: print("Optimizer terminated with a(n) {0} status (code {1}).".format(status_msg, status_code)) except MdoError as e: print("Received Mindopt exception.") print(" - Code : {}".format(e.code)) print(" - Reason : {}".format(e.message)) except Exception as e: print("Received exception.") print(" - Reason : {}".format(e)) finally: # MindOpt Step 5. Free the model. model.free_mdl()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
运行后得到如下结果:
Start license validation (current time : 01-MAR-2023 20:59:47). License validation terminated. Time : 0.002s Model summary. - Num. variables : 20 - Num. constraints : 30 - Num. nonzeros : 180 - Bound range : [5.6e-01,9.6e+00] - Objective range : [1.0e+00,1.0e+00] - Matrix range : [3.5e-02,2.3e+00] Presolver started. Presolver terminated. Time : 0.000s Interior point method started. Iter PrimObj DualObj PrimFea DualFea GapFea Mu Time 0 +0.00000000e+00 -3.05311332e-15 2.2e+00 3.7e-02 3.6e+02 1.2e+01 0.01s 1 +3.87012911e+01 +1.10363647e+01 7.4e-02 1.0e-04 2.5e+00 1.2e+00 0.01s 2 +2.30985411e+01 +1.91163774e+01 2.0e-04 5.5e-06 2.1e-01 1.3e-01 0.01s 3 +1.98974978e+01 +1.98777823e+01 5.6e-07 1.5e-08 1.0e-03 6.6e-04 0.01s 4 +1.98802551e+01 +1.98802008e+01 1.5e-09 4.2e-11 2.7e-06 1.8e-06 0.01s 5 +1.98802076e+01 +1.98802075e+01 4.3e-12 1.2e-13 7.5e-09 5.0e-09 0.02s Terminated. - Method : Interior point method. - Primal objective : 1.9880207641660E+01 - Dual objective : 1.9880207492544E+01 - Num. threads : 2 - Num. iterations : 5 - Solver details : Solver terminated with a primal/dual optimal status. Iteration Objective Dual Inf. Primal Inf. Time 0 1.98802e+01 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 0.02s pushes: P(0) D(8) 8 1.98802e+01 0.0000e+00 0.0000e+00 0.02s Interior point method terminated. Time : 0.027s Optimizer summary. - Optimizer used : Interior point method - Optimizer status : OPTIMAL - Total time : 0.028s Solution summary. Primal solution - Objective : 1.9880207511e+01 ---- The solver terminated with an OPTIMAL status (code 1). 目标函数总收益是: 19.880207510885242 ---------------- Compare var_a to true_a, and var_b to true_b: ---------------- Entry True Soln a[0] 3.381614 3.381614 a[1] 2.077166 2.077166 a[2] 1.788548 1.788548 a[3] 1.662762 1.662762 True Soln b -2.102494 -2.102494 ---------------- Show Residual(c value): ---------------- Observation Residual 0 0.000000 1 0.000000 2 0.000000 3 0.000000 4 0.000000 5 0.000000 6 0.000000 7 0.000000 8 0.000000 9 0.000000 10 0.000000 11 0.000000 12 0.000000 13 11.513372 14 8.366835 OpenBLAS WARNING - could not determine the L2 cache size on this system, assuming 256k
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
方法2:命令行直接运行.py文件
上面是直接在cell中运行所有的脚本,我们也可以建立个新文档,将Python代码存在 src/python_src文件夹的LP_5_RobustRegression.py文件。然后在Launcher中打开Terminal,执行 python xx.py文件来运行。
您也可以下载本.py文件,在自己的电脑上安装MindOpt求解器,然后在自己电脑的环境运行。
Luancher可以点击左上角的+打方块打开,Terminal在最下方,如截图示意。打开的窗口可以拖动调整位置。

然后在Terminal命令行里运行如下指令:
cd src/python_src
python LP_5_RobustRegression.py
- 1
- 2
运行得到的结果,特性类似算法1,由于每次数据随机生成的,所以数据不一样:

求解结果
本案例的数据是随机生成的,因此每次结果会不一样,但是从结果的True原值和鲁棒线性回归的结果Soln几乎一样,拟合度很好。
如下面是一个示例的结果打印。
Optimizer summary. - Optimizer used : Interior point method - Optimizer status : OPTIMAL - Total time : 0.013s Solution summary. Primal solution - Objective : 9.7151651023e+00 ---- The solver terminated with an OPTIMAL status (code 1). 目标函数总收益是: 9.715165102347509 ---------------- Compare var_a to true_a, and var_b to true_b: ---------------- Entry True Soln a[0] 2.710648 2.710648 a[1] 0.477721 0.477721 a[2] 1.164849 1.164849 a[3] 0.251547 0.251547 True Soln b 0.878660 0.878660 ---------------- Show Residual(c value): ---------------- Observation Residual 0 0.000000 1 0.000000 2 0.000000 3 0.000000 4 0.000000 5 0.000000 6 0.000000 7 0.000000 8 0.000000 9 0.000000 10 0.000000 11 0.000000 12 0.000000 13 6.173857 14 3.541308
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
联系我们
钉钉答疑群:32451444
钉钉活动群:18890022111
邮箱地址:solver.damo@list.alibaba-inc.com
更多更新通知:https://solver.damo.alibaba.com



