热门标签
热门文章
- 1NodeJS用作后端服务的优点、缺点分析_nodejs写后端优缺点
- 2ReLU6_layer aten::relu6_ not exists or registered
- 3【Linux】vi/vim编辑器
- 4Linux 中的$* $@特殊变量介绍_linux $@
- 5Cocos Creator 坐标转换_cocos creator 世界坐标转局部坐标
- 6基于YOLO的自动驾驶目标检测研究综述
- 7多模态大模型总结2(主要2023年)_improved baselines with visual instruction tuning
- 8【React-Native开发3D应用】React Native加载GLB格式3D模型并打包至Android手机端_react native glwallpaper
- 9linux基础学习笔记6_linux设置test1其注释为this is a test user创建用户test2,创建目录/
- 10根据某列的值N复制 Pandas DataFrame 上的N行_dataframe 复制一行
当前位置: article > 正文
HarmonyOS鸿蒙应用开发——HTTP网络访问与封装_harmonyos http封装
作者:IT小白 | 2024-02-19 18:54:07
赞
踩
harmonyos http封装
网络基础
基本使用
鸿蒙应用发起HTTP请求的基本使用,如下:
- 导入http模块
- 创建httpRequest对象
- 发起http请求,并处理响应结果
第一、导入http模块:
import http from '@ohos.net.http'
- 1
第二、创建httpRequest对象,注意的是每一个httpRequest对象对应一个http请求任务,不可复用。
const httpRequest = http.createHttp()
- 1
第三、发起请求,比如POST请求
httpRequest.request( // 请求url地址 url, { // 请求方式 method: http.RequestMethod.POST, // 请求的额外数据。 extraData: { "param1": "value1", "param2": "value2", }, // 可选,默认为60s connectTimeout: 60000, // 可选,默认为60s readTimeout: 60000, // 开发者根据自身业务需要添加header字段 header: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } }) .then((data) => { if (data.responseCode === http.ResponseCode.OK) { // 处理响应结果 // data.result为服务器返回的业务数据 console.info('Result:' + data.result); console.info('code:' + data.responseCode); } }).catch((err) => { console.info('error:' + JSON.stringify(err)); });
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
最后需要声明网络权限,在module.josn5文件中声明:
{
"module" : {
"requestPermissions":[
{
"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"
}
]
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
上面就是网络请求的简单使用,接下来通过Promise来封装一个网络请求库,统一管理请求参数、响应数据、日志的输出等,对外屏蔽了细节,使用者只需定义业务数据的实体类以及调用即可。
封装
以**玩Android**开放接口为测试用例
定义业务数据的实体类,通过泛型来接收不同的数据类型:
export class ResponseResult<T> {
errorCode: number;
errorMsg: string;
data?: T | Object | string;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
把各种请求方式用枚举声明RequestMethod
export enum RequestMethod {
OPTIONS,
GET,
HEAD,
POST ,
PUT,
DELETE,
TRACE,
CONNECT
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
其实在http模块中已经有对应的枚举,之所以再用一个新枚举来声明,是简化使用,同时也是将http模块相关细节屏蔽掉不对外开放,这样就可以灵活替换网络库,也具有扩展性。
定义一个HttpUtils类实现:
export class HttpUtils{ public static readonly SUCCESS_CODE: number = 0 public static readonly READ_TIME_OUT = 60 * 1000 public static readonly CONNECT_TIME_OUT = 60 * 1000 private baseUrl: string = "" constructor(baseUrl: string) { this.baseUrl = baseUrl } private methodName(method: RequestMethod): http.RequestMethod { switch (method){ case RequestMethod.OPTIONS:{ return http.RequestMethod.OPTIONS } case RequestMethod.GET:{ return http.RequestMethod.GET } case RequestMethod.HEAD:{ return http.RequestMethod.HEAD } case RequestMethod.POST:{ return http.RequestMethod.POST } case RequestMethod.PUT:{ return http.RequestMethod.PUT } case RequestMethod.DELETE:{ return http.RequestMethod.DELETE } case RequestMethod.TRACE:{ return http.RequestMethod.TRACE } case RequestMethod.CONNECT:{ return http.RequestMethod.CONNECT } } } private tag(n: string): string { return `${TAG}/${n}` } request<T>(path: string, reqMethod: RequestMethod, parameter: Map<string, Object> = null): Promise<T | null> { // 注意的是每一个httpRequest对象对应一个http请求任务,不可复用。 const httpRequest = http.createHttp() const method = this.methodName(reqMethod) let extraData = {} let url = `${this.baseUrl}/${path}` if (parameter != null) { switch (reqMethod) { case RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.PUT: { extraData = Object.fromEntries(parameter) break; } case RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.DELETE: { const urlParams = Object.keys(parameter).map(key => `${key}=${parameter[key]}`).join('&') if (url.includes("?")) { url = `${url}${urlParams}` } else { url = `${url}?${urlParams}` } break; } } } let n = Math.random().toString(10).slice(2) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "==================Request====================") LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "url: " + url) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "method: " + method.toString()) if (reqMethod == RequestMethod.POST || reqMethod == RequestMethod.PUT) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "extraData: " + JSON.stringify(parameter, null, 2)) return new Promise( async (resolve, reject) => { let beginTime = await systemDateTime.getCurrentTime(false) httpRequest.request(url, { method, readTimeout: HttpUtils.READ_TIME_OUT, connectTimeout: HttpUtils.CONNECT_TIME_OUT, header: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }, extraData } ).then( async (value) => { let endTime = await systemDateTime.getCurrentTime(false) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "==================Response====================") LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "url: " + url + " "+ (endTime - beginTime)+"ms") LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "method: " + method.toString()) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "header: " + JSON.stringify(value.header, null, 2)) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "responseCode: " + value.responseCode) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "resultType: " + value.resultType) if (value.responseCode == http.ResponseCode.OK) { let result: ResponseResult<T> = JSON.parse(value.result.toString()) LogUtils.debug(this.tag(n), "body: " + JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)) if (result.errorCode == HttpUtils.SUCCESS_CODE) { resolve(result.data as T) } else { reject(result.errorMsg) } } else { reject("请求失败") } }).catch((reason) => { reject(reason) }) }) } get<T>(path: string, parameter: Map<string, Object> = null): Promise<T | null> { return this.request<T>(path, RequestMethod.GET, parameter) } post<T>(path: string, parameter: Map<string, Object> = null): Promise<T | null> { return this.request<T>(path, RequestMethod.POST, parameter) } delete<T>(path: string, parameter: Map<string, Object> = null): Promise<T | null> { return this.request<T>(path, RequestMethod.DELETE, parameter) } put<T>(path: string, parameter: Map<string, Object> = null): Promise<T | null> { return this.request<T>(path, RequestMethod.PUT, parameter) } } const YiNet = new HttpUtils(BASE_URL) export default YiNet
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
使用发起网络请求:
aboutToAppear() { let map = new Map<string,string>() map["cid"] = 294 YiNet.get<ArticleList>("project/list/1/json",map).then((data)=>{ this.data = JSON.stringify(data, null, 2) }) let map2 = new Map<string,string>() map2["username"] = "123" map2["password"] = "123456" YiNet.post<User>("user/login",map2).then((data)=>{ this.data = JSON.stringify(data, null, 2) }).catch((err)=>{ Prompt.showToast({message:err}) }) }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
日志输出效果:
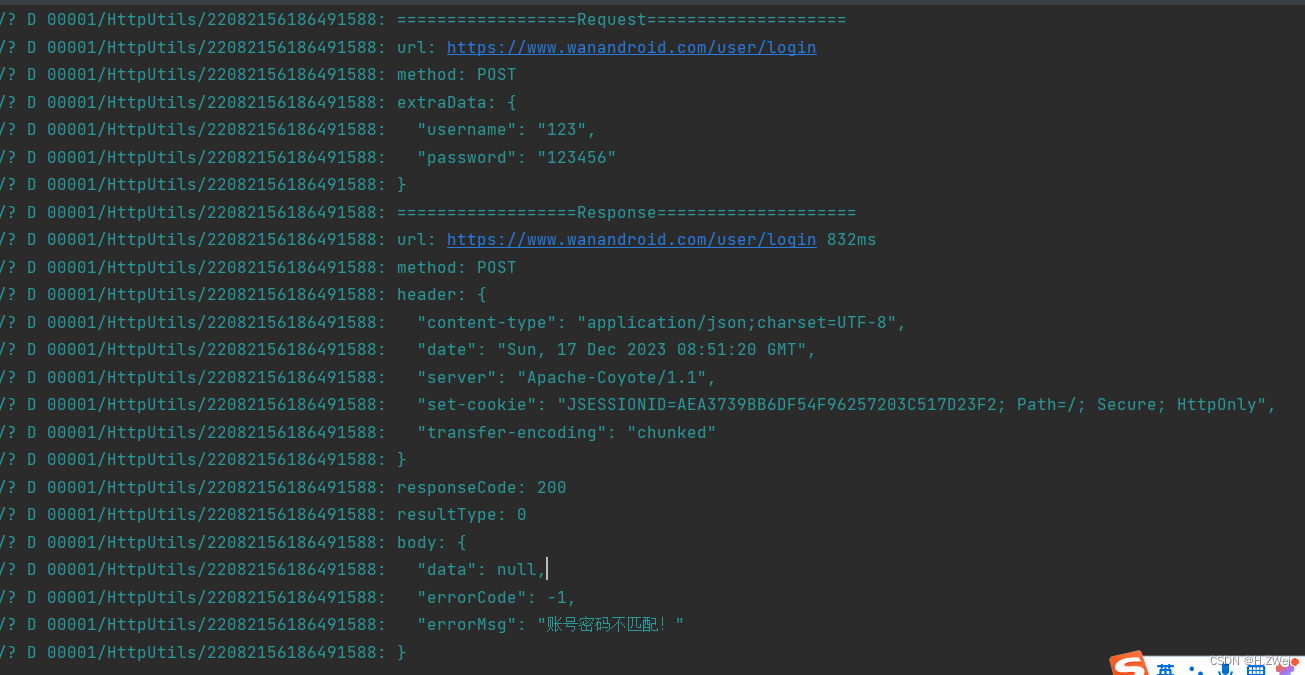
如果有多个请求,日志可能会混合交叉不利于查看,可以通过HttpUtils/xxxxxx来查看具体某一个请求日志,其中xxxx是一个随机数大部分情况下是具有唯一性。
上面就是官方的http模块的基本封装,在此基础上可以设计一套拦截器来辅助业务需求。
参考
- https://developer.huawei.com/consumer/cn/training/course/slightMooc/C101667364948559963?ha_linker=eyJ0cyI6MTcwMjE3NzI3OTYyMywiaWQiOiI4MmM3ZTI1MmFmMDJlMDZiODBmOGU1ZDM5ZTI5YmMyOCJ9
- https://www.wanandroid.com/blog/show/2
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/IT小白/article/detail/116327
推荐阅读
相关标签




