热门标签
热门文章
- 1《ChatGPT实操应用大全》探索无限可能_chatgpt实操应用大全(全视频彩色) 电子书
- 22024人工智能与机器人系统国际学术会议(ICAIRS2024)_人工智能 会议
- 3Ubuntu10.04之grub2详解_grub set root='sd0
- 4Anaconda介绍与使用
- 5Http 416错误解决方案_错误 416
- 6论文AI率多少算高:深入剖析与应对策略
- 7启动uniapp小程序报错:Error:app.json:在项目根目录中未找到app.json_uniapp app.json: 在项目根目录未找到 app.json
- 8C++ 记录Windows程序崩溃时的dumpfile_电骡 cminidumper
- 9Invalid `Podfile` file: undefined method `exists?‘ for File:Class解决方案_invalid `podfile` file: undefined method `exists?'
- 10OpenHarmony 物联网设备开发环境搭建_openharmony devices
当前位置: article > 正文
【图论】计算图的n-hop邻居个数,并绘制频率分布直方图
作者:Monodyee | 2024-03-15 18:11:13
赞
踩
【图论】计算图的n-hop邻居个数,并绘制频率分布直方图
计算图的n-hop邻居个数,并绘制频率分布直方图
在图论中,n-hop邻居(或称为K-hop邻居)是指从某个顶点出发,通过最短路径(即最少的边数)可以到达的所有顶点的集合,其中n(或K)是这个最短路径的长度。换句话说,n-hop邻居就是在图中,从一个顶点出发,经过n步可以到达的所有顶点。
举个日常生活中的例子,我们的朋友是我们的1-hop邻居,我们的朋友的朋友是我们的2-hop邻居,以此类推。如果我们想找到所有与我们最多只有三层朋友关系的人(包括我们的朋友、我们的朋友的朋友、以及我们的朋友的朋友的朋友),那么这些人就是我们的3-hop邻居。
在下图中对于中间的红色节点,玫红色的就是1-hop邻居,橙色2,粉色3。

如何在networkx中计算n-hop邻居的数量?
由定义我们可以知道,只要找到某个节点通过最短路径为n的边就可以找到它的n-hop邻居了,那么我们就可以用nx.single_source_shortest_path_length。
代码如下:
import networkx as nx
def n_hop_neighbors(G, n_hop):
"""
Calculate n-hop neighbors for each node in the graph.
"""
n_hop_counts = {}
for node in G.nodes():
# n_hop_counts[node] = len(list(nx.single_source_shortest_path_length(G, node, cutoff=n_hop))) - 1
n_hop_counts[node] = len(list(nx.single_source_shortest_path_length(G, node, cutoff=n_hop).keys())) - 1
n_hop_array = list(n_hop_counts.values())
return n_hop_array
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
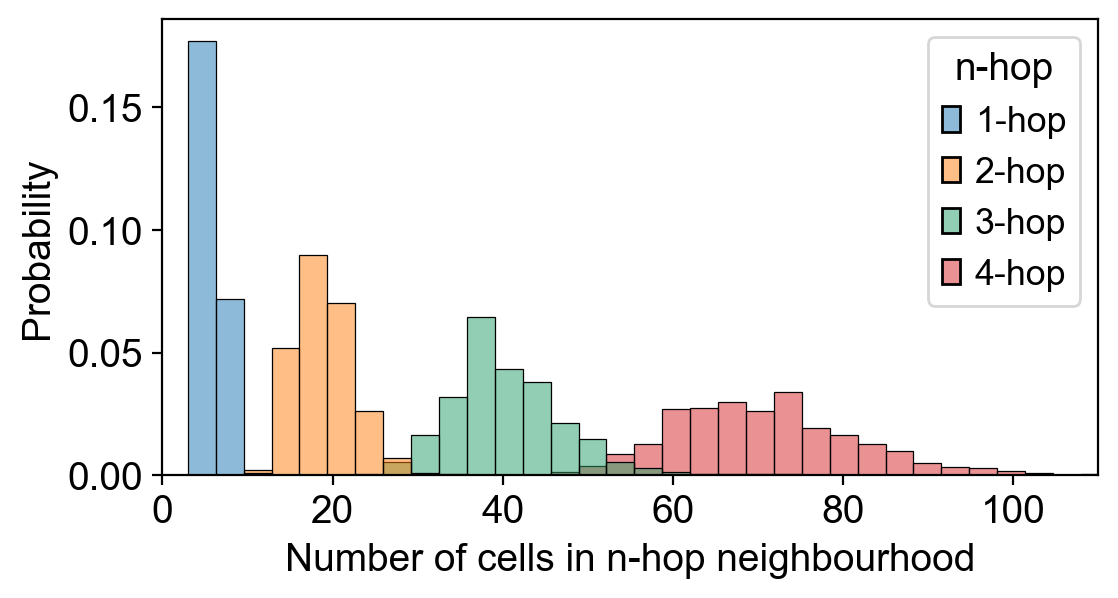
绘制分布直方图
我们使用seaborn的sns.histplot来进行绘制,代码如下:
import networkx as nx import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns # Assuming G is your NetworkX graph # Example graph # G = nx.Graph() # G.add_edges_from([('v1', 'v2'), ('v2', 'v4'), ('v1', 'v3')]) plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3)) # Calculate n-hop neighbors for n=1 # n_hop_counts = n_hop_neighbors(G, 3) # Step 1: Store n-hop counts in a dictionary n_hop_counts_dict = {} for i in range(1, 5): # Hop counts 1 through 4 n_hop_counts_dict[f'{i}-hop'] = n_hop_neighbors(G, i) # Step 2: Convert the dictionary to a DataFrame n_hop_counts_df = pd.DataFrame(n_hop_counts_dict) # Reshape the DataFrame to long format n_hop_counts_long = n_hop_counts_df.melt(var_name='n-hop', value_name='Number of cells in n-hop neighbourhood') # Plotting the histogram sns.histplot(data=n_hop_counts_long, x="Number of cells in n-hop neighbourhood", hue="n-hop", kde=False, log_scale=False, stat="probability") plt.xlim(0, 110) plt.grid(False) plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
结果如下:
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Monodyee/article/detail/243517
推荐阅读
相关标签



