- 12023年12月CCF-GESP编程能力等级认证Python编程二级真题解析_gesp python 二级 2023年真题
- 2zk-smoketest: ZooKeeper健康检查工具
- 311 Java ArrayList遍历输出的会和添加的顺序不一致吗?_arrays.aslist字段顺序会乱吗
- 4Linux Centos 7 压缩和解压缩命令_centos7压缩文件夹命令
- 5手把手教你安装Python,2024最详细的安装教程来了(Pycharm+解释器安装)_phython工具包安装
- 6Python + MySQL(8)python中NaN的处理(往MySQL数据库插入数据时,报错 nan can‘t be used with mysql)_nan can not be used with mysql
- 7阿里云-签名文件直传_阿里云oss小程序直传 获取签名
- 8将你的STM32搞成Arduino(一)_stm32 arduino
- 9graalvm编译springboot3 native应用
- 10React前端框架学习 基础知识@stage3---week5--day2_react中@stage-space
Python常用操作_plistlib
赞
踩
在工作中偶尔会用python作为工具做进行一些文本处理或者打包脚本的工作。把用python作为工具使用的话,其逻辑也比较简单,只要找到合适的库函数就行了。这里记录的就是一些常用的操作。
python有2.x和3.x的版本,这两个跨度较大,所以电脑上最好装两个版本,我装的是2.7和3.5。如何设置多个python版本共存呢——把某一个版本的python.exe 和 pythonw.exe 重命名,后面加个数字,并且自行修改一下系统环境变量。
看到一般python文件,都会在开头写上下面这个,这是为了Python解释器会在解释文件的时候用,指定其编码方式
- #!/usr/bin/python
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
目录
2)类中的 __getitem__ , __setitem__,__init__
0.import 和 from import
1)import
import commands
引入commands模块,搜索commands.py,看看这个文件在哪
2)from import 导入某个部分
from mod_pbxproj import XcodeProject
要导入模块 mod_pbxproj 的 XcodeProject 类
搜索mod_pbxproj.py中肯定有XcodeProject。
3)模块搜索路径
当你导入一个模块,Python 解析器对模块位置的搜索顺序是:
- 1、当前目录
- 2、如果不在当前目录,Python 则搜索在 shell 变量 PYTHONPATH 下的每个目录。
- 3、如果都找不到,Python会察看默认路径。UNIX下,默认路径一般为/usr/local/lib/python/。
模块搜索路径存储在 system 模块的 sys.path 变量中。变量里包含当前目录,PYTHONPATH和由安装过程决定的默认目录。
https://www.runoob.com/python/python-modules.html
ps:自己写文件名不要和已经存在的模块名字取同一个,否则当导入此模块的时候自己的写的文件会被误当作模块导入的
1. 对文件和文件夹的操作
对文件和文件夹的操作是比较多,下面记录了:
复制文件,删除文件,删除文件夹,返回文件类型(是file还是dir)以及名字,合并文件夹,移动文件夹
- import os
- #1. 复制文件
- def copy_file(source_file, target_file):
-
- if os.path.isfile(source_file):
- # open函数返回file对象
- # open完整参数有7个,一般都写上第一第二参数,后面需要的参数就用命名参数来指定
- # 第一参数 文件名,第二参数 打开模式,后面比如命名参数encoding = '' 来指定编码格式。
- # file对象的write写入字符串
- # file对象的read读出字符串
- open(target_file, "wb").write(open(source_file, "rb").read())
-
-
- #2. 删除文件
- def delete_file(filePath):
- if os.path.isfile(filePath):
- os.remove(filePath)
-
- #3. 删除整个文件夹
- def delete_dir(path):
- if not os.path.exists(path):
- return
- if os.path.isfile(path):
- return
-
- for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path, topdown=False):
- for f in files:
- os.remove(os.path.join(root, f))
- for folder in dirs:
- os.rmdir(os.path.join(root, folder))
- # os.rmdir() 方法用于删除指定路径的目录。仅当这文件夹是空的才可以, 否则, 抛出OSError。
- os.rmdir(path)
-
- #4. 合并文件夹 把source目录下的文件 合并到 target目录下。
- def merge_dir(source_dir, target_dir):
- # 列表遍历
- for f in os.listdir(source_dir):
- # f 有可能是文件也有可能是目录
- # target_file 有可能存在,也有可能不存在
- source_file = os.path.join(source_dir, f)
- target_file = os.path.join(target_dir, f)
- # 如果是文件,就拷贝
- if os.path.isfile(source_file):
- # 否定用not
- if not os.path.exists(target_dir):
- os.makedir(target_dir)
- open(target_file, "wb").write(open(source_file, "rb").read())
- # 如果是文件夹,继续递归
- if os.path.isdir(source_file):
- merge_dir(source_file, target_file)
-
- #5. 返回类型以及文件名
- def filetypeAndname(src):
- if os.path.isfile(src):
- index = src.rfind('\\')
- if index == -1:
- index = src.rfind('/')
- return 'FILE', src[index+1:]
- elif os.path.isdir(src):
- return 'DIR', ''
-
- #6. 移动文件 把source目录下以及子目录的文件 统一放到 target 根目录下。
- #import shutil
- def copy_files(source_dir, target_dir):
- # 列表遍历
- for f in os.listdir(source_dir):
- # f 有可能是文件也有可能是目录
- source_file = os.path.join(source_dir, f)
- # 如果是文件,就拷贝
- if os.path.isfile(source_file):
- # 否定用not
- if not os.path.exists(target_dir):
- os.makedir(target_dir)
- shutil.copy(source_file, target_dir)
- # 如果是文件夹,继续递归
- if os.path.isdir(source_file):
- copy_files(source_file, target_dir)

ps: 对目录下的每个文件进行操作的常用模式,递归操作:
- def dosomething_eachfile(dir):
- for f in os.listdir(dir):
- # f 有可能是文件也有可能是目录
- file = os.path.join(dir, f)
- # 如果是文件,就拷贝
- if os.path.isfile(file):
- #dosomething
- # 如果是文件夹,继续递归
- if os.path.isdir(file):
- dosomething_eachfile(file)
2. shell命令相关
在写工具的时候 经常用写shell命令,这里介绍的是execute库的使用,介绍了两个事例------调用unity静态函数 和 设置文件的一些权限。
<1> execute库
1)调用unity静态函数
- from execute import execute_command
- def build_unity_ios_assetBundle():
-
- cmd = unity_execute_Path + " -batchmode -quit -logfile /dev/stdout -projectPath "\
- + unity_project_path + " -executeMethod CommandBuild.BuildiOSAssetBundle"
-
- return execute_command(cmd, output_tag="Unity") == 0
-batchmode:命令行模式
-quit:关闭unityedtior当执行完命令
-logFile <pathname>:日志文件路径. If the path is ommitted, OSX and Linux will write output to the console. Windows uses the path %LOCALAPPDATA%\Unity\Editor\Editor.log as a default. (/dev/stdout 标准输出。shell中执行就是输出到shell窗口)
-projectPath <pathname>:unity工程路径
-executeMethod <ClassName.MethodName>:Editor文件夹下的静态函数,一打开Unity工程就执行
https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/CommandLineArguments.html
2)增加文件执行权限
- def update_xcode_other_file(path):
-
- cmd = "chmod +x "+ path+ "/MapFileParser.sh"
-
- if not execute_cmd(cmd):
- print "chmod +x MapFileParser.sh fail"
-
- cmd = "chmod +x "+ path+ "/MapFileParser"
-
- if not execute_cmd(cmd):
- print "chmod +x MapFileParser.sh fail"
权限对象 : 档案拥有者、群组、其他。u : 表示该档案的拥有者,g 表示与该档案的拥有者属于同一个群体(group)者,o 表示其他以外的人,a 表示这三者皆是。
权限种类: r读 w写 x执行
若要rwx属性则4+2+1=7;
若要rw-属性则4+2=6;
若要r-x属性则4+1=7。
权限设置符号:+ : 表示增加权限、- 表示取消权限、= 表示唯一设定权限。
chmod a=rwx file 相当于 chmod 777 file
chmod +x file 相当于 chmod a+x file
3.Python的一些特性
1)入口函数
- def main():
- #balabala
- #balabala
- #balabala
- return True
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- main()
2)类中的 __getitem__ , __setitem__,__init__
- __init__ 构造函数
- class MyTime:
- # 外面调用MyTime() 即调用这个函数
- def __init__(self):
- self.year = -1
- self.month= -1
- self.day = -1
- self.hour = -1
- def initWithList(self, list):
- if len(list) == 4:
- # 判断是不是int型
- if type(list[0]) == type(1):
- self.year = list[0]
- self.month= list[1]
- self.day = list[2]
- self.hour = list[3]
- def timeStamp(self):
- timestr = [self.year,self.month,self.day,self.hour]
- # 分隔符.join(列表) 把列表元素用分隔符连成字符串
- return '-'.join(timestr)

- __getitem__
- __setitem__
4.关于编码方式
在读取文本的时候会出现解码方式错误,下面是遇到过的一些问题
1)判断是不是带BOM的utf-8格式
- def IsUTF8WithBOM(file):
- isWithBOM = false
- BOM = b'\xef\xbb\xbf'
- existBOM = lambda s: True if s == BOM else False
- f = open(file, 'rb')
- if existBOM (f.read(3)):
- isWithBOM = true
- f.close()
- return isWithBOM
2)使用不同的编码方式打开文件
知道编码方式大部分都是utf16,个别文件是gbk。
如果想知道 提示的编码错误说某个位置,某个字节,用某种编码方式具体是个什么字符,可以用16进制编辑器打开文本查看。
- def FileLines(file):
- file_lines = []
- try:
- # file对象 readlines 返回列表
- # 同理写入 file.writelines[列表]
- file_lines = open(file, encoding = 'utf16').readlines()
- except UnicodeDecodeError:
- file_lines = open(file, encoding = 'gbk').readlines()
- except:
- file_lines = []
- return file_lines
ps:try ....except...else 语句,当没有异常发生时,else中的语句将会被执行。
5. 关于文本处理
1)去除空行和注释——s.strip('ab') 对s 去除a和b字符
- def RemoveComment(file_lines, filename):
- f = open(filename, 'w')
- for line in file_lines
- # str.strip()去除前后的空格
- line_tmp = line.strip()
- # 1.len(str)字符串长度 2. str.startswith(ss)
- # str.find(ss) 查找ss子串在不在str中,返回索引,找不到返回-1
- if line_tmp.startswith('//') or not len(line_tmp)
- continue
- f.write(line)
- f.close()
6.正则匹配Re模块
正则匹配是python在处理文本的时候很重要的一个功能,用到的是Re模块,下面是一些常用函数:
1)常用的函数介绍:
1.match( rule , targetString [,flag] ) 和 search( rule , targetString [,flag] ),返回一个MatchObject (如果匹配成功的话),如果匹配不成功,它们则返回一个NoneType。匹配到一个成功的,就不继续匹配了。所以在对匹配完的结果进行操作之前,你必需先判断一下是否匹配成功了。match从字符串的开头开始匹配,如果开头位置没有匹配成功,就算失败了;而search会跳过开头,继续向后寻找是否有匹配的字符串。
- def findFirstSubName(filename):
- file = open(filename).read()
- # 1.不能是注释的 2.可以是GotoSub("XXX") 也可以是 Sub("XXX")
- # 1.(?<!)前向非界定 2.*? 尽可能少的重复 3.使用括号()表示组
- pattern1 = '(?<!\/\/)\s*?GotoSub\("(.*?)"\)'
- pattern2 = '(?<!\/\/)\s*?Sub\("(.*?)"\)'
- hasFound = re.search(pattern1, file)
- # 判断是不是 NoneType 有没有找到
- if hasFound:
- # 用数字来取第一组 这里也只有一组
- # group(0)代表整个匹配的子串;不填写参数时,返回group(0)
- subname = hasFound.group(1)
- else:
- hasFound = re.search(pattern2, file)
- if hasFound:
- subname = hasFound.group(1)
- else:
- subname = None
- return subname

2.split( rule , target [,maxsplit] ),切片函数。使用指定的正则规则在目标字符串中查找匹配的字符串,使用匹配字符串用作为分界,把字符串切片。
- # 把文本内容解析成 subname 和 subcontent的字典 {subname:内容}
- def BuildSubDict(filename):
- file = open(filename).read()
- # 按规则先切分内容(没有注释的文件了)
- list_subcontent_raw = re.split('(?<!Goto)Sub\("(.*?)"\)\s*;\s*', file)
- if len(list_subcontent_raw) <= 1:
- return {}
- # 列表从0开始索引,[1:]排除第0个 [-1]列表的最后一个元素
- list_subcontent = list_subcontent_raw[1:]
-
- # 找到所有的subname
- pattern_subname = '(?<!Goto)Sub\("(.*?)"\)\s*;'
- list_subname = re.findall(pattern_subname, file)
-
- # 组成元组
- subpair = zip(list_subname, list_subcontent )
-
- # 组成字典
- subdict = {name : content for(name,content) in subpair}
- return subdict

findall(rule , target [,flag] ),返回一个列表,中间存放的是符合规则的字符串。如果没有符合规则的字符串被找到,就返回一个空列表。
- # {subname:内容中的其他sub名字的列表}
- def BuildSubNameDict(subdict):
- subnamedict = {}
- # 遍历字典 subname是key
- for subname in subdict
- # str.split(seprate) 用seprate切分字符串
- list_old = subdict[subname].split('\n')
- list_new = []
-
- list_pattern = ['GotoSub\(\s*"(.*?)"\s*\)',\
- 'SetSelectDlg\(\s*&.*?&\s*,\s*(.*?)\s*\)',\
- 'SetSelectDlgEx\(\s*&.*?&\s*,\s*(.*?)\s*,',\
- 'foreach\(.*?,\s*(.*?)\s*\)',\
- 'foreach_new\(.*?,\s*(.*?)\s*,']
- # 遍历列表 line是列表元素
- for line in list_old:
- for pattern in list_pattern:
- matched = re.findall(pattern, line)
- # 空列表[] 空字典{} 都是False
- if matched:
- if matched [0] not in list_new:
- list_new.append(matched [0])
- break
- subnamedict[subname] = list_new

在字符串找到第一组数字
- def ReturnNumStr(source):
- found = re.search('\d+', source)
- if found:
- numstr = found.group()
- else:
- numstr = ""
- return numstr
2)正则字符介绍:
| 功能字符 | ‘.’ ‘*’ ‘+’ ‘|’ ‘?’ ‘^’ ‘$’ ‘/’ 等 | 它们有特殊的功能含义。特别是’\’字符,它是转义引导符号,跟在它后面的字符一般有特殊的含义。 |
| 规则分界符 | ‘[‘ ‘]’ ‘(’ ‘)’ ‘{‘ ‘}’ 等 | ‘[‘ ‘]’ 字符集合设定符号,匹配包含在其中的任意一个字符 |
| 预定义转义字符集 | “\d” 数字 “\w”英文字母和数字 “\s”间隔符 等等 | 它们是以字符’\’开头,后面接一个特定字符的形式,用来指示一个预定义好的含义。一般大写就是小写的补集。
ps: \s = [ \r\n\t\v\f] 最前面有个空格。 \r : 回车CR (0D)。 \n:换行LF(0A)。
主流的操作系统一般使用CRLF或者LF作为其文本的换行符。其中,Windows 系统使用的是 CRLF, Unix系统(包括Linux, MacOS近些年的版本) 使用的是LF。 |
| 其它特殊功能字符 | ’#’ ‘!’ ‘:’ ‘-‘ 等 | 它们只在特定的情况下表示特殊的含义,比如(?# …)就表示一个注释,里面的内容会被忽略。 |
功能字符
| | |
如果想限定它的有效范围,必需使用一个无捕获组 ‘(?: )’包起来。比如要匹配 ‘I have a dog’或’I have a cat’,需要写成r’I have a (?:dog|cat)’ ,而不能写成 r’I have a dog|cat’ |
| * | 0或多次匹配:表示匹配前面的规则0次或多次。 |
| + | 1次或多次匹配:表示匹配前面的规则至少1次,可以多次匹配 |
| ? | 0或1次匹配:只匹配前面的规则0次或1次。 +? *? 尽可能少的重复匹配 >>> s= 'abbbaa' >>> re.findall( r'a.*?a' , s) ['abbba', 'aa'] >>> re.findall( r'a.*a' , s) ['abbbaa'] |
| . | 匹配任意字符,除了换行符。 >>> s=’1 \n4 \n7’ >>> re.findall(r‘.’,s) ['1',' ','4',' ','7'] |
| ‘^’和’$’ | 匹配字符串开头和结尾,多行模式下匹配每行的开头和结尾。 >>> s= '12 34\n56 78\n90' >>> re.findall( r'^\d+' , s , re.M ) #匹配每行位于行首的数字,re.M多行模式 ['12', '56', '90'] >>> re.findall( r'\d+$' , s , re.M ) #匹配位于行尾的数字 ['34', '78', '90'] |
|
|
规则分界符以及其它特殊功能字符
| (?<!) | 前向非界定:希望前面的字符串不是... 的内容时候才匹配。 |
| (?:) | 无捕获组:当你要将一部分规则作为一个整体对它进行某些操作,比如指定其重复次数时,你需要将这部分规则用’(?:’ ‘)’把它包围起来。 |
| {m,n} | 匹配最少m次,最多n次。{m} 精确匹配m次 ,{m,} 大于等于m次{,n}, 小于等于n次 >>> s= ‘ 1 22 333 4444 55555 666666 ‘ >>> re.findall( r’\b\d{3}\b’ , s ) # a:3位数 ['333'] |
|
() | 分组 () 无命名组,只返回了包含在’()’中的内容。 (?P<name>…)’命名组,(?P=name) 通过名字调用已匹配的命名组 。 (/number) 通过序号调用已匹配的组。
>>> s='aaa111aaa,bbb222,333ccc,444ddd444,555eee666,fff777ggg' >>> re.findall( r'([a-z]+)\d+([a-z]+)' , s ) #无命名组,列表元素为元组 [('aaa', 'aaa'), ('fff', 'ggg')] >>> re.findall( r '(?P<g1>[a-z]+)/d+(?P=g1)' , s ) #找出被中间夹有数字的前后同样的字母 ['aaa'] |
| {} |
预定义转义字符集
| ‘\A’和’\Z’ | 匹配字符串开头和结尾,在’M’模式下,它也不会匹配其它行的首尾。 |
| \b (\B匹配非边界) | 它匹配一个单词的边界,比如空格等,不过它是一个‘0’长度字符,它匹配完的字符串不会包括那个分界的字符。 >>> s = 'abc abcde bc bcd' >>> re.findall( r’\bbc\b’ , s ) #匹配一个单独的单词 ‘bc’ ,而当它是其它单词的一部分的时候不匹配 ['bc'] #只找到了那个单独的’bc’ >>> re.findall( r’\sbc\s’ , s ) #匹配一个单独的单词 ‘bc’ [' bc '] # 只找到那个单独的’bc’,不过注意前后有两个空格,可能有点看不清楚 |
https://blog.csdn.net/smilelance/article/details/6529950
9.算法
1)图搜索 ps:判断是否包含某字符串 if substr in str
图用字典存,key为某个node,value为这个node可以到达的其他node。
给出一个起始点node,和指定另外一个node,判断这个指定的那个node,能不能通过起始点node达到,如果能的话,给出路径即可,不需要最短。
- def find_path(graphdict, extrance, target, path[]):
- # 1.+:两个列表相加合并 2.[]字符串变列表
- path = path + [extrance]
- if extrance == target:
- return path
- # 判断key在不在字典中 判断子串在不在字符串中也可以用in, if substr in str
- if target not in graphdict:
- return None
- # 遍历列表中的元素
- for node in graphdict[extrance]:
- if path and node not in path:
- newpath = find_path(graphdict, node, target, path)
- if newpath:
- return newpath
- return None
10. 重定向
1)输出到文件
输出到文件中,后面使用print打印就都是输出到文件中了
- # a是追加
- f_handler = open(filename, 'w')
- sys.stdout = f_handler
ps: windows console把标准输出重定向到一个文件中 command > filename
11.读取配置
如何读取命令行参数以及如果读取配置文件
1.sys库——命令行参数
- import sys
- #命令行输入: python 文件名 argv1 argv2 argv3
- # 输入参数有4个,第0个参数是文件名
- print('参数个数为:' + len(sys.argv) + '个参数。')
- print('参数列表:' + str(sys.argv))
ps:读入的最后一个参数可能带有回车换行符号,所以在进行读取对比的时候进行strip()转换一下。
2.configparser库——配置文件
test.conf文件
- [para1]
- key1 = value1
- key2 = value2
- key3 = value3
-
- [para2]
- key1 = value1
- key2 = value2
- key3 = value3
读取文件
- import configparser
-
- cf = configparser.ConfigParser()
- cf.read("test.conf")
-
- var1 = cf.get("para1", "key1")
3.plistlib库——配置文件
test.plist文件
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
- <plist version="1.0">
- <dict>
- <key>ChannelList</key>
- <array>
- <string>IOSAppstore-dev-test</string>
- <string>IOSAppstore-dev-official</string>
- </array>
- <key>ChannelConfig</key>
- <dict>
- <key>IOSAppstore-dev-test</key>
- <dict>
- <key>SettingFlags</key>
- <dict>
- <key>GCC_ENABLE_OBJC_EXCEPTIONS</key>
- <string>YES</string>
- </dict>
- <key>BuildFlags</key>
- <dict>
- <key>ENABLE_BITCODE</key>
- <string>NO</string>
- <key>ASSETCATALOG_COMPILER_LAUNCHIMAGE_NAME</key>
- <string>LaunchImage_dj</string>
- </dict>
- <key>OtherLDFlags</key>
- <array>
- <string>-ObjC</string>
- <string>-lc++.1</string>
- <string>-liconv</string>
- <string>-lz</string>
- </array>
- <key>dylibs</key>
- <array>
- <string>libz</string>
- <string>libstdc++.6.0.9</string>
- <string>libsqlite3.0</string>
- </array>
- <key>Frameworks</key>
- <array>
- <string>Security</string>
- <string>SystemConfiguration</string>
- <string>JavaScriptCore</string>
- <string>MobileCoreServices</string>
- <string>CoreTelephony</string>
- <string>CoreAudio</string>
- <string>WebKit</string>
- </array>
- </dict>
- <key>IOSAppstore-dev-official</key>
- <dict>
- <key>DependenceChannel</key>
- <string>IOSAppstore-dev-test</string>
- </dict>
- </dict>
- </dict>
- </plist>

读取文件
- global plistConfig
- global dic_channel_config
- global unity_build_lasttype
- global current_channel_name
-
-
- def read_plistConfig():
- #读取配置文件
-
- global plistConfig
- global dic_channel_config
- # 返回的是一个字典
- plistConfig = plistlib.readPlist('test.plist')
-
- return len(plistConfig) > 0
-
-
-
- def build_channel():
- # for element in list列表,plist中是array类型
- for current_buildchannel in plistConfig["ChannelList"]:
- global dic_channel_config
- global current_channel_name
- current_channel_name = current_buildchannel
- # 可以返回多个参数
- isFindChannel, dic_channel_config = getBuildingChannelConfig(current_buildchannel, {})
-
- # buildchannelDic 不一定是空
- # 因为有"DependenceChannel"这一项 如果找不到也算是没有找到
- def getBuildingChannelConfig(buildchannel, buildchannelDic):
- if buildchannel in plistConfig["ChannelConfig"]:
- dic_channel_config = plistConfig["ChannelConfig"][current_channel]
- if len(dic_channel_config) > 0:
- for currentItem in dic_channel_config:
- if currentItem not in buildchannelDic:
- buildchannelDic[currentItem] = dic_channel_config[currentItem]
-
- if "DependenceChannel" in dic_channel_config:
- if dic_channel_config["DependenceChannel"] == buildchannel:
- break;
-
- return getBuildingChannelConfig(dic_channel_config["DependenceChannel"], buildchannelDic)
- else:
- return True, buildchannelDic
- else:
- break
- return False, buildchannelDic

ps:
如果函数内需要修改全局变量var,需要在函数内先申明一下 global var。否则就是创建了一个 内部的局部变量var了。
python如果想使用作用域之外的全局变量,可以不加global,修改一定要先声明一下是 global。
12.一些内置函数:
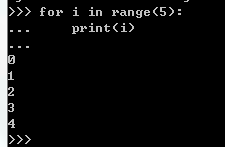
1)range生成一个数值序列
13.一些常用库
一些比较杂比较常用的库。
0.os库
os.system(),返回值为十进制数(分别对应一个16位的二进制数)。
该函数的返回值与 linux命令返回值两者的转换关系为:
转化成16二进制数,截取其高八位,然后转乘十进制数即为 linux命令返回值。(如果低位数是0的情况下,有关操作系统的错误码共 131个,所以低位都是零)
- #jenkins调用脚本时需要先解锁钥匙串,此处为钥匙串密码
- os.system("security unlock-keychain -p cc.com")
1.时间库 time
- import time
- def get_timestamp():
- # time.localtime返回struct_time对象
- # %Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999)
- # %m 月份(01-12)
- # %d 月内中的一天(0-31)
- # %H 24小时制小时数(0-23)
- # %M 分钟数(00-59)
- # %S 秒(00-59)
- return time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S', time.localtime(time.time()))
2.压缩库 zipfile——大文件 allowZip64=True
>python common_file.py zip C:\Users\ivy0709\Desktop\99999 911.zip
- import zipfile
- import sys
- import os
-
- def zip_dir(dirname, zipfilename):
- filelist = []
- if os.path.isfile(dirname):
- filelist.append(dirname)
- else :
- for root, dirs, files in os.walk(dirname):
- for name in files:
- filelist.append(os.path.join(root, name))
- zf = zipfile.ZipFile(zipfilename, "w", zipfile.zlib.DEFLATED, allowZip64=True)
- for tar in filelist:
- arcname = tar[len(dirname):]
- zf.write(tar,arcname)
- zf.close()
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- if sys.argv[1] == "zip":
- zip_dir(sys.argv[2], sys.argv[3])

3.ftp库 ftplib
- class Xfer(object):
- def __init__(self):
- self.ftp = None
-
- def __del__(self):
- pass
- #self.ftp.close()
-
- def setFtpParams(self, ip, uname, pwd, port, timeout):
- self.ip = ip
- self.uname = uname
- self.pwd = pwd
- self.port = port
- self.timeout = timeout
-
- def initEnv(self):
- if self.ftp is None:
- self.ftp = FTP()
- print '### connect ftp server: %s ...'%self.ip
- self.ftp.connect(self.ip, self.port, self.timeout)
- self.ftp.login(self.uname, self.pwd)
- print self.ftp.getwelcome()
-
- def clearEnv(self):
- if self.ftp:
- self.ftp.close()
- print '### disconnect ftp server: %s!'%self.ip
- self.ftp = None
-
- def creatdir(self,dirname,remotepath):
- self.initEnv()
- dirpath=remotepath+'/'+dirname
- print dirpath
- try:
- self.ftp.cwd(dirpath)
- except:
- try:
- self.ftp.cwd(remotepath)
- self.ftp.mkd(dirname)
- except:
- print "Creat directory failed!"
- self.clearEnv()
-
- def get_filename(self, line):
- pos = line.rfind(':')
- while(line[pos] != ' '):
- pos += 1
- while(line[pos] == ' '):
- pos += 1
- file_arr = [line[0], line[pos:]]
- return file_arr
-
- def get_file_list(self, line):
- ret_arr = []
- file_arr = self.get_filename(line)
- if file_arr[1] not in ['.', '..']:
- self.file_list.append(file_arr)
-
- def downloadDir(self, localdir='./', remotedir='./'):
- try:
- #print '--------%s' %(remotedir)
- self.ftp.cwd(remotedir)
- except:
- return
- if not os.path.isdir(localdir):
- os.makedirs(localdir)
-
- self.file_list = []
- self.ftp.dir(self.get_file_list)
- remotenames = self.file_list
-
- for item in remotenames:
- filetype = item[0]
- filename = item[1]
- local = os.path.join(localdir, filename)
- if filetype == 'd':
- self.download_files(local, filename)
- elif filetype == '-':
- self.download_file(local, filename)
-
- self.ftp.cwd('..')
-
- def downloadFile(self, localfile, remotefile):
- #return
- file_handler = open(localfile, 'wb')
- self.ftp.retrbinary('RETR %s'%(remotefile), file_handler.write)
- file_handler.close()
-
- def download(self,localfile, remotefile):
- self.initEnv()
- try:
- self.ftp.cwd(remotefile)
- except:
- #
- print 'It is a file:------%s' %(remotefile)
- self.downloadFile(localfile, remotefile)
- else:
- print "It is a dir:------"
- self.downloadDir(localfile, remotefile)
- finally:
- self.clearEnv()
-
- def __filetype(self, src):
- if os.path.isfile(src):
- index = src.rfind('\\')
- if index == -1:
- index = src.rfind('/')
- return 'FILE', src[index+1:]
- elif os.path.isdir(src):
- return 'DIR', ''
-
- def uploadDir(self, localdir='./', remotedir='./'):
- if not os.path.isdir(localdir):
- return
- self.ftp.cwd(remotedir)
- for file in os.listdir(localdir):
- src = os.path.join(localdir, file)
- if os.path.isfile(src):
- self.uploadFile(src, file)
- elif os.path.isdir(src):
- try:
- self.ftp.mkd(file)
- except:
- sys.stderr.write('the dir is exists %s'%file)
- self.uploadDir(src, file)
- self.ftp.cwd('..')
-
- def uploadFile(self, localpath, remotepath='./'):
- if not os.path.isfile(localpath):
- return
- print '+++ upload %s to %s:%s'%(localpath, self.ip, remotepath)
- self.ftp.storbinary('STOR ' + remotepath, open(localpath, 'rb'))
-
- def upload(self, src,remotepath):
- if (os.path.isfile(src) or os.path.isdir(src)):
- filetype, filename = self.__filetype(src)
- self.initEnv()
- self.ftp.cwd(remotepath)
- if filetype == 'DIR':
- self.srcDir = src
- self.uploadDir(self.srcDir)
- elif filetype == 'FILE':
- self.uploadFile(src, filename)
- self.clearEnv()
- else:
- print '+++file not find %s'%src
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- xfer = Xfer()
- if sys.argv[1] == "10.12.20.197":
- xfer.setFtpParams(ip = sys.argv[1], uname = "dddd", pwd = "dddd", port = 21, timeout = 60)
- elif sys.argv[1] == "10.2.4.29":
- xfer.setFtpParams(ip = sys.argv[1], uname = "eeeee", pwd = "eeeee", port = 888, timeout = 60)
- elif sys.argv[1] == "10.1.9.50":
- xfer.setFtpParams(ip = sys.argv[1], uname = "fffff", pwd = "fffff", port = 999, timeout = 60)
-
- if sys.argv[2] == "upload":
- xfer.upload(sys.argv[3],sys.argv[4])
- elif sys.argv[2]== "creatdir":
- xfer.creatdir(sys.argv[3],sys.argv[4])
- elif sys.argv[2]== "download":
- xfer.download(sys.argv[3],sys.argv[4])




