热门标签
热门文章
- 12.3语料库NLTK数据包下载及安装
- 26款ai伪原创,手机上创作文章别错过_手机创作文章
- 3蓝桥杯Python A组国一经验分享(希望这篇文章可以给你一点点帮助)_蓝桥杯国赛一二三等奖比例
- 4bert 三种模型保存的方式以及调用方法总结(ckpt,单文件pb,tf_serving使用的pb)_bert.ckpt
- 5开源密码管理软件项目说明(附源代码)_统一密码服务平台的源代码
- 6- 概述 - 《设计模式(极简c++版)》
- 7基于matlab的指纹图像处理、脊线增强、脊线分割、脊线细化、细节点检测和细节点验证(毕设完整代码+报告)_脊线提取matlab
- 8SOC内部集成网络MAC外设+ PHY网络芯片方案:MII/RMII 接口与 MDIO 接口
- 9Java概念性问题7_哪一项的实现不可以添加为textfiled对象的监听器
- 10Transformer详解_transformer的输入
当前位置: article > 正文
决策树及matlab实现_决策树matlab代码
作者:weixin_40725706 | 2024-04-03 07:09:05
赞
踩
决策树matlab代码
决策树及matlab实现
- 决策树逻辑实现(参考机器学习实战,将python代码改成matlab)
代码结构
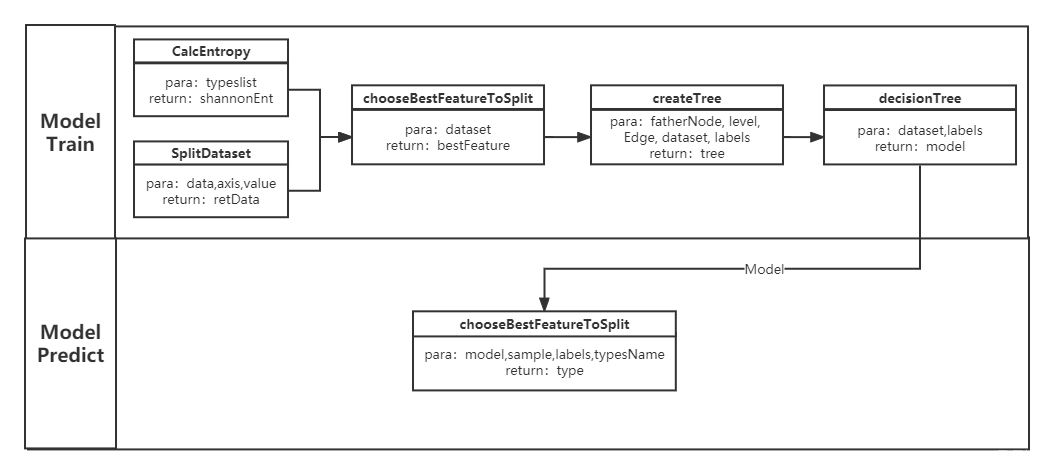
1.1. CalcEntropy
function shannonEnt=CalcEntropy(typeslist)
% 根据types列表,计算数据集的熵
% typeslist: 数据集的属性列表
% shannonEnt: 熵值计算
shannonEnt = 0;
Length = length(typeslist);
itemList = unique(typeslist); % 去重
pNum = length(itemList);
for i = 1:pNum
itemLength = length(find(typeslist==itemList(i)));
pItem = itemLength/Length;
shannonEnt = shannonEnt-pItem*log2(pItem);
end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
1.2. splitDataset
function retData=SplitDataset(data,axis,value)
% 按照给定的特征划分数据集
% data: 待划分数据集
% axis: 列数
% value: 特征的返回值
% retData: 划分后数据集
retData = [];
[m,n] = size(data);
for i = 1:m
if data(i,axis) == value
retData = [retData;data(i,:)];
end
end
retData(:,axis) = [];
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
1.3. chooseBestFeatureToSplit
function bestFeature=chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataset) % 找到最好的划分指标 % dataset: 数据集 % bestFeature: 最优指标 num数值 [m,n] = size(dataset); numFeatures = n-1; originEntropy = CalcEntropy(dataset(:,n)); % 初始熵 bestInfoGain = 0.0; % 熵变化最大值 bestFeature = -1; % 最佳特征 for i = 1:numFeatures uniqueVals = unique(dataset(:,i)); tmpEntropy = 0.0; for j = 1:length(uniqueVals) subDataset = SplitDataset(dataset,i,uniqueVals(j)); prob = length(subDataset(:,1))/m; tmpEntropy = tmpEntropy+prob*CalcEntropy(subDataset); end infoGain = originEntropy-tmpEntropy; if infoGain > bestInfoGain bestInfoGain = infoGain; bestFeature = i; end end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
1.4. createTree
function tree=createTree(fatherNode, level, Edge, dataset, labels) % 递归创建决策树 % fatherNode: 父节点 % level: 所属层次 % Edge: 边的属性 % dataset: 数据集 % labels: 特征属性 global tree; branch = struct('level',level+1,'fatherNode',fatherNode,'Edge',Edge,'Node',[]); [m,n] = size(dataset); typesList = dataset(:,n); % 第一种情况 数据集只剩一种type if length(unique(typesList)) == 1 branch.Node = typesList(1); tree = [tree branch]; return; end % 第二种情况 遍历完所有特征 if length(dataset(1,:)) == 1 branch.Node = mode(typeslist); % 取众数 tree = [tree branch]; return; end % 第三种情况 bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataset); bestFeatLabel = labels(bestFeat); branch.Node = bestFeatLabel; tree = [tree branch]; labels(strcmp(labels,bestFeatLabel)) = []; featVals = unique(dataset(:,bestFeat)); for i = 1:length(featVals) createTree(branch.Node, branch.level, featVals(i), SplitDataset(dataset,bestFeat,featVals(i)), labels); end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
1.5. decisionTree
function decisionTreeModel=decisionTree(dataset,labels)
% 决策树模型训练主函数
% dataset: 数据集
% labels: 特征属性
% decisionTreeModel: 保存模型数据的struct数组
global tree;
tree=struct('level',-1,'fatherNode',[],'Edge',[],'Node',[]);
createTree('root',-1,-1,dataset,labels);
tree(1) = [];
tree(1) = [];
model.Node = tree;
decisionTreeModel = model;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
1.6. modelPredict
function type=modelPredict(model,sample,labels,typesName) % 训练好的模型进行预测 % model: 训练好的模型 % sample: 待预测样本 % typesName: 类别名称 % type: 输出类别 Nodes = model.Node; rootNode = Nodes(1); head = rootNode.fatherNode; level = 1; for i = 1:length(Nodes) if Nodes(i).level == level if Nodes(i).Edge == sample(find(labels==head)) if length(find(typesName==double(Nodes(i).Node))) == 1 type = Nodes(i).Node; break; else head = Nodes(i).Node; level = level+1; end end end end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-
Matlab自带函数实现
2.1. dataPreprocess
function [xtrain,ytrain,xtest,ytest] = dataPreprocess() % 数据预处理 % xtrain,ytrain,xtest,ytest:x训练集,测试集,y训练集,测试集 load fisheriris x = meas; y = species; % 数据划分 train_index = randsample(150,120,false); test_index = randsample(150,30,false); xtrain = x(train_index,:); xtest = x(test_index,:); ytrain = y(train_index,:); ytest = y(test_index,:); % 数据归一化 % Flattened1 = xtrain'; % MappedFlattened1 = mapminmax(Flattened1); % 默认行归一 % xtrain = MappedFlattened1'; % Flattened2 = xtest'; % MappedFlattened2 = mapminmax(Flattened2); % 默认行归一 % xtest = MappedFlattened2';
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
2.2. modelTrain
function model = modelTrain(xtrain,ytrain)
% 模型训练
model = fitctree(xtrain,ytrain);
view(model, 'Mode', 'graph');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.3. modelTrainOpt
function model = modelTrainOpt(xtrain,ytrain)
% 模型训练 Optimize Classification Tree
model = fitctree(xtrain,ytrain,'OptimizeHyperparameters','auto');
view(model, 'Mode', 'graph');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2.4. modelPredict
function [train_acc,test_acc]=modelPredict(model,xtrain,ytrain,xtest,ytest) % xtrain,ytrain,xtest,ytest train_pre = predict(model,xtrain); test_pre = predict(model,xtest); train_right = 0; for i = 1:length(train_pre) if isequal(train_pre(i),ytrain(i)) train_right = train_right + 1; end end test_right = 0; for i = 1:length(test_pre) if isequal(test_pre(i),ytest(i)) test_right = test_right + 1; end end train_acc = train_right/length(ytrain); test_acc = test_right/length(ytest);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
本博客为个人笔记,欢迎交流!!!!
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/weixin_40725706/article/detail/354706?site
推荐阅读
相关标签



