- 1python干货_ypeerror: save() takes exactly 1 argument (2 given
- 2pointpillar openpcd框架下实现_openpcd pointpillars 推理
- 306.分布式解决方案-canal解决mysql与redis数据一致性问题_canal双写一致
- 4Spring Boot中的跨域请求处理_springboot 跨域 预检请求
- 5Pytorch交叉熵损失函数CrossEntropyLoss及BCE_withlogistic_crossentropy和bce
- 6数据结构之内部排序总结_数据结构内部排序总结
- 7NLP快速入门_计算机nlp入门
- 8(计算机)末流211上岸国科大杭高院经验帖---考研的选择和努力同样重要_杭高院读研比得上211吗
- 9WebSocket connection to ‘ws://10.151.2.241:8080/ws‘ failed:_websocket connection to ws failed
- 107月5日,WAIC见!
[NLP]基于IMDB影评情感分析之BERT实战-测试集上92.24%_bert imdb
赞
踩
系列文章目录
深度学习NLP(一)之Attention Model;
深度学习NLP(二)之Self-attention, Muti-attention和Transformer;
深度学习NLP(三)之ELMO、BERT、GPT
深度学习NLP(四) 之IMDB影评情感分析之BERT实战
0. 前言
下面我用三种方法来训练Bert用IMDB影评数据集
1. 什么是WordPiece
现在基本性能好一些的NLP模型,例如OpenAI GPT,google的BERT,在数据预处理的时候都会有WordPiece的过程。WordPiece字面理解是把word拆成piece一片一片,其实就是这个意思。
WordPiece的一种主要的实现方式叫做BPE(Byte-Pair Encoding)双字节编码。
BPE的过程可以理解为把一个单词再拆分,使得我们的此表会变得精简,并且寓意更加清晰。
比如"loved",“loving”,"loves"这三个单词。其实本身的语义都是“爱”的意思,但是如果我们以单词为单位,那它们就算不一样的词,在英语中不同后缀的词非常的多,就会使得词表变的很大,训练速度变慢,训练的效果也不是太好。
BPE算法通过训练,能够把上面的3个单词拆分成"lov",“ed”,“ing”,"es"几部分,这样可以把词的本身的意思和时态分开,有效的减少了词表的数量。
在Bert 里做法其实是先查找这个单词是否存在在里,如果不存在,那么会尝试分成两个词。
例如"tokenizer" --> “token”,"##izer"
2. 第一种方法-利用Google-search在git-hub开源的代码训练Bert
2.1 所需环境
1.1.1 如果有GPU的话。
conda install python=3.6
conda install tensorflow-gpu=1.11.0
- 1
- 2
如果没有GPU, cpu版本的Tensorflow也可以。只是跑的慢而已
pip install tensorflow=1.11.0
- 1
1.1.2 在GitHub上下载google-search开源的bert代码

1.1.3 下载Bert的模型参数uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12, 解压
https://storage.googleapis.com/bert_models/2018_10_18/uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12.zip

2.2 代码修改与介绍
打开run_classifier.py 文件, 加入下面这个ImdbProcessor。
数据集imdb_train.npz,imdb_test.npz和imdb_val.npz可以看我下面这个博客
Imdb影评的数据集介绍与下载
class ImdbProcessor(DataProcessor): """Processor for the MRPC data set (GLUE version).""" def get_train_examples(self, data_dir): data = np.load('./data/imdb_train.npz') return self._create_examples(data, 'train') def get_dev_examples(self, data_dir): data = np.load('./data/imdb_val.npz') return self._create_examples(data, 'val') def get_test_examples(self, data_dir): data = np.load('./data/imdb_test.npz') return self._create_examples(data,'test') def get_labels(self): """See base class.""" return ["0", "1"] def _create_examples(self, train_data, set_type): """Creates examples for the training and dev sets.""" X = train_data['x'] Y = train_data['y'] examples = [] i = 0 for data, label in zip(X, Y): guid = "%s-%s" % (set_type, i) text_a = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(data) label1 = tokenization.convert_to_unicode(str(label)) examples.append(InputExample(guid=guid, text_a=text_a, label=label1)) i = i + 1 return examples
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
搜main()方法在run_classifier.py文件里,然后加一下你刚才写的ImdbProcessor类

运行run_classifier.py用命令行。
export BERT_BASE_DIR=.\data\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12 export DATASET=../data/ python run_classifier.py \ --data_dir=$DATASET \ --task_name=imdb \ --vocab_file=$BERT_BASE_DIR/vocab.txt \ --bert_config_file=$BERT_BASE_DIR/bert_config.json \ --output_dir=../output/ \ --do_train=true \ --do_eval=true \ --init_checkpoint=$BERT_BASE_DIR/bert_model.ckpt \ --max_seq_length=200 \ --train_batch_size=16 \ --learning_rate=5e-5\ --num_train_epochs=2.0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
或者用pycharm运行, 通过run菜单进去的然后输入下面的参数。
注意,你要修改两个目录的参数,第一个时数据集(我的时./data/),第二个是模型的目录(我的是D:\train_data\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12)
--data_dir=./data/ --task_name=imdb --vocab_file=D:\train_data\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\vocab.txt --bert_config_file=D:\train_data\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\bert_config.json --output_dir=../output/ --do_train=true --do_eval=true --init_checkpoint=D:\train_data\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\bert_model.ckpt --max_seq_length=200 --train_batch_size=16 --learning_rate=5e-5 --num_train_epochs=2.0
- 1
然后执行run_classifier.py
差不多2小时左右在GPU上就结果了。准确率92.24%

3. 第二种方法-利用 tensorflow_hub与bert-tensorflow训练Bert
所需环境
conda install python=3.6
conda install tensorflow-gpu=1.11.0
conda install tensorflow-hub
pip install bert-tensorflow
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
代码介绍
import pandas as pd import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow_hub as hub from datetime import datetime import bert from bert import run_classifier from bert import optimization from bert import tokenization import numpy as np OUTPUT_DIR = 'output1' def download_and_load_datasets(): train_data = np.load('./data/bert_train.npz') test_data = np.load('./data/bert_test.npz') train_df = pd.DataFrame({'sentence':train_data['x'], 'polarity':train_data['y']}) test_df = pd.DataFrame({'sentence':test_data['x'], 'polarity':test_data['y']}) return train_df, test_df # This is a path to an uncased (all lowercase) version of BERT BERT_MODEL_HUB = "D:/train_data/tf-hub/bert_uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12_1" def create_tokenizer_from_hub_module(): """Get the vocab file and casing info from the Hub module.""" with tf.Graph().as_default(): bert_module = hub.Module(BERT_MODEL_HUB) tokenization_info = bert_module(signature="tokenization_info", as_dict=True) with tf.Session() as sess: vocab_file, do_lower_case = sess.run([tokenization_info["vocab_file"], tokenization_info["do_lower_case"]]) return bert.tokenization.FullTokenizer( vocab_file=vocab_file, do_lower_case=do_lower_case) # We'll set sequences to be at most 128 tokens long. MAX_SEQ_LENGTH = 128 # label_list is the list of labels, i.e. True, False or 0, 1 or 'dog', 'cat' label_list = [0, 1] def getDataSet(): train, test = download_and_load_datasets() #train = train.sample(5000) #test = test.sample(5000) DATA_COLUMN = 'sentence' LABEL_COLUMN = 'polarity' # Use the InputExample class from BERT's run_classifier code to create examples from the data train_InputExamples = train.apply(lambda x: bert.run_classifier.InputExample(guid=None, # Globally unique ID for bookkeeping, unused in this example text_a=x[DATA_COLUMN], text_b=None, label=x[LABEL_COLUMN]), axis=1) test_InputExamples = test.apply(lambda x: bert.run_classifier.InputExample(guid=None, text_a=x[DATA_COLUMN], text_b=None, label=x[LABEL_COLUMN]), axis=1) tokenizer = create_tokenizer_from_hub_module() tokenizer.tokenize("This here's an example of using the BERT tokenizer") # Convert our train and test features to InputFeatures that BERT understands. train_features = bert.run_classifier.convert_examples_to_features(train_InputExamples, label_list, MAX_SEQ_LENGTH,tokenizer) test_features = bert.run_classifier.convert_examples_to_features(test_InputExamples, label_list, MAX_SEQ_LENGTH, tokenizer) return train_features, test_features def create_model(is_predicting, input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, labels, num_labels): """Creates a classification model.""" bert_module = hub.Module(BERT_MODEL_HUB,trainable=True) bert_inputs = dict(input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, segment_ids=segment_ids) bert_outputs = bert_module(inputs=bert_inputs, signature="tokens", as_dict=True) # Use "pooled_output" for classification tasks on an entire sentence. # Use "sequence_outputs" for token-level output. output_layer = bert_outputs["pooled_output"] hidden_size = output_layer.shape[-1].value print('hidden_size=',hidden_size) # Create our own layer to tune for politeness data. output_weights = tf.get_variable("output_weights", [num_labels, hidden_size], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02)) output_bias = tf.get_variable("output_bias", [num_labels], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()) with tf.variable_scope("loss"): # Dropout helps prevent overfitting output_layer = tf.nn.dropout(output_layer, keep_prob=0.9) logits = tf.matmul(output_layer, output_weights, transpose_b=True) logits = tf.nn.bias_add(logits, output_bias) log_probs = tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, axis=-1) # Convert labels into one-hot encoding one_hot_labels = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=num_labels, dtype=tf.float32) predicted_labels = tf.squeeze(tf.argmax(log_probs, axis=-1, output_type=tf.int32)) # If we're predicting, we want predicted labels and the probabiltiies. if is_predicting: return (predicted_labels, log_probs) # If we're train/eval, compute loss between predicted and actual label per_example_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(one_hot_labels * log_probs, axis=-1) loss = tf.reduce_mean(per_example_loss) return (loss, predicted_labels, log_probs) # model_fn_builder actually creates our model function # using the passed parameters for num_labels, learning_rate, etc. def model_fn_builder(num_labels, learning_rate, num_train_steps, num_warmup_steps): """Returns `model_fn` closure for TPUEstimator.""" def model_fn(features, labels, mode, params): # pylint: disable=unused-argument """The `model_fn` for TPUEstimator.""" input_ids = features["input_ids"] input_mask = features["input_mask"] segment_ids = features["segment_ids"] label_ids = features["label_ids"] is_predicting = (mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT) # TRAIN and EVAL if not is_predicting: (loss, predicted_labels, log_probs) = create_model(is_predicting, input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids, num_labels) train_op = bert.optimization.create_optimizer(loss, learning_rate, num_train_steps, num_warmup_steps, use_tpu=False) # Calculate evaluation metrics. def metric_fn(label_ids, predicted_labels): accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(label_ids, predicted_labels) f1_score = tf.contrib.metrics.f1_score( label_ids, predicted_labels) auc = tf.metrics.auc(label_ids,predicted_labels) recall = tf.metrics.recall( label_ids, predicted_labels) precision = tf.metrics.precision(label_ids,predicted_labels) true_pos = tf.metrics.true_positives(label_ids,predicted_labels) true_neg = tf.metrics.true_negatives(label_ids, predicted_labels) false_pos = tf.metrics.false_positives( label_ids, predicted_labels) false_neg = tf.metrics.false_negatives( label_ids,predicted_labels) return {"eval_accuracy": accuracy, "f1_score": f1_score,"auc": auc,"precision": precision,"recall": recall, "true_positives": true_pos,"true_negatives": true_neg, "false_positives": false_pos,"false_negatives": false_neg } eval_metrics = metric_fn(label_ids, predicted_labels) if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN: return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode=mode, loss=loss, train_op=train_op) else: return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode=mode,loss=loss,eval_metric_ops=eval_metrics) else: (predicted_labels, log_probs) = create_model(is_predicting, input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids, num_labels) predictions = {'probabilities': log_probs,'labels': predicted_labels} return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(mode, predictions=predictions) # Return the actual model function in the closure return model_fn # Compute train and warmup steps from batch size # These hyperparameters are copied from this colab notebook (https://colab.sandbox.google.com/github/tensorflow/tpu/blob/master/tools/colab/bert_finetuning_with_cloud_tpus.ipynb) BATCH_SIZE = 16 LEARNING_RATE = 2e-5 NUM_TRAIN_EPOCHS = 3.0 # Warmup is a period of time where hte learning rate # is small and gradually increases--usually helps training. WARMUP_PROPORTION = 0.1 # Model configs SAVE_CHECKPOINTS_STEPS = 500 SAVE_SUMMARY_STEPS = 100 def get_estimator(train_features): # Compute # train and warmup steps from batch size num_train_steps = int(len(train_features) / BATCH_SIZE * NUM_TRAIN_EPOCHS) num_warmup_steps = int(num_train_steps * WARMUP_PROPORTION) # Specify output directory and number of checkpoint steps to save run_config = tf.estimator.RunConfig(model_dir=OUTPUT_DIR,save_summary_steps=SAVE_SUMMARY_STEPS, save_checkpoints_steps=SAVE_CHECKPOINTS_STEPS) model_fn = model_fn_builder(num_labels=len(label_list),learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE, num_train_steps=num_train_steps,num_warmup_steps=num_warmup_steps) estimator = tf.estimator.Estimator(model_fn=model_fn, config=run_config, params={"batch_size": BATCH_SIZE}) return estimator def train_bert_model(train_features): num_train_steps = int(len(train_features) / BATCH_SIZE * NUM_TRAIN_EPOCHS) estimator = get_estimator(train_features) # Create an input function for training. drop_remainder = True for using TPUs. train_input_fn = bert.run_classifier.input_fn_builder(features=train_features, seq_length=MAX_SEQ_LENGTH, is_training=True, drop_remainder=False) print(f'Beginning Training!') current_time = datetime.now() estimator.train(input_fn=train_input_fn, max_steps=num_train_steps) print("Training took time ", datetime.now() - current_time) def test_bert_model(test_features): estimator = get_estimator(test_features) test_input_fn = run_classifier.input_fn_builder(features=test_features,seq_length=MAX_SEQ_LENGTH,is_training=False, drop_remainder=False) test_result = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=test_input_fn, steps=None) print(test_result) def getPrediction(in_sentences, train_features): estimator = get_estimator(train_features) labels = ["Negative", "Positive"] tokenizer = create_tokenizer_from_hub_module() input_examples = [run_classifier.InputExample(guid="", text_a = x, text_b = None, label = 0) for x in in_sentences] # here, "" is just a dummy label input_features = run_classifier.convert_examples_to_features(input_examples, label_list, MAX_SEQ_LENGTH, tokenizer) predict_input_fn = run_classifier.input_fn_builder(features=input_features, seq_length=MAX_SEQ_LENGTH, is_training=False, drop_remainder=False) predictions = estimator.predict(predict_input_fn) return [(sentence, prediction['probabilities'], labels[prediction['labels']]) for sentence, prediction in zip(in_sentences, predictions)] def predict(train_features): pred_sentences = [ "That movie was absolutely awful", "The acting was a bit lacking", "The film was creative and surprising", "Absolutely fantastic!" ] predictions = getPrediction(pred_sentences,train_features) print(predictions) def main(_): train_features, test_features = getDataSet() print(type(train_features), len(train_features)) print(type(test_features), len(test_features)) train_bert_model(train_features) test_bert_model(test_features) #predict(train_features) if __name__ == '__main__': tf.app.run()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
执行结果,准确率89.81%
{'auc': 0.89810693, 'eval_accuracy': 0.8981, 'f1_score': 0.897557, 'false_negatives': 501.0, 'false_positives': 518.0, 'loss': 0.52041256, 'precision': 0.8960257, 'recall': 0.8990936, 'true_negatives': 4517.0, 'true_positives': 4464.0, 'global_step': 6750}
- 1
- 2
4. 第三种方法-利用huggingFace的Transformer训练Bert
3.1. 所需环境
安装transformers
pip install transformers
- 1
下载Bert预训练数据集bert-base-uncased在HuggingFace的官网
注意bert-base-uncased-tf_model.h5或bert-base-uncased-pytorch_model.bin是二选择一
一个是pytorch的,一个是tensorflow的
https://cdn.huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased-tf_model.h5
https://cdn.huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased-pytorch_model.bin
https://cdn.huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased-vocab.txt
https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-uncased-config.json
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
下载后放在同一个文件夹下比如bert-base-uncased
对每一个文件改名
bert-base-uncased-tf_model.h5 --> tf_model.h5
bert-base-uncased-pytorch_model.bin - > pytorch_model.bin
bert-base-uncased-vocab.txt -->vocab.txt
bert-base-uncased-config.json --> config.json
4.2. 代码解释
imdb_train.npz与imdb_test.npz数据文件参数可以看下面博客
Imdb影评的数据集介绍与下载
Transformer包是HuggingFace公司基于Google开源的bert做了一个封装。使得用起来更方便
下面代码的功能和tokenizer.encode_plus()功能是一样的。
from transformers import BertTokenizer bert_weight_folder = r'D:\train_data\bert\bert-base-uncased' tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(bert_weight_folder, do_lower_case=True) max_length_test = 20 test_sentence = 'Test tokenization sentence. Followed by another sentence' # add special tokens test_sentence_with_special_tokens = '[CLS]' + test_sentence + '[SEP]' tokenized = tokenizer.tokenize(test_sentence_with_special_tokens) print('tokenized', tokenized) # convert tokens to ids in WordPiece input_ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokenized) # precalculation of pad length, so that we can reuse it later on padding_length = max_length_test - len(input_ids) # map tokens to WordPiece dictionary and add pad token for those text shorter than our max length input_ids = input_ids + ([0] * padding_length) # attention should focus just on sequence with non padded tokens attention_mask = [1] * len(input_ids) # do not focus attention on padded tokens attention_mask = attention_mask + ([0] * padding_length) # token types, needed for example for question answering, for our purpose we will just set 0 as we have just one sequence token_type_ids = [0] * max_length_test bert_input = { "token_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids, "attention_mask": attention_mask } print(bert_input)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
tokenized ['[CLS]', 'test', 'token', '##ization', 'sentence', '.', 'followed', 'by', 'another', 'sentence', '[SEP]']
{
'token_ids': [101, 3231, 19204, 3989, 6251, 1012, 2628, 2011, 2178, 6251, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
完整的代码时如下:
import tensorflow as tf import os as os import numpy as np from transformers import BertTokenizer from transformers import TFBertForSequenceClassification import tensorflow as tf from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split max_length = 200 batch_size = 16 learning_rate = 2e-5 number_of_epochs = 10 bert_weight_folder = r'D:\train_data\bert\bert-base-uncased' tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(bert_weight_folder, do_lower_case=True) def convert_example_to_feature(review): return tokenizer.encode_plus(review, add_special_tokens=True, # add [CLS], [SEP] max_length=max_length, # max length of the text that can go to BERT pad_to_max_length=True, # add [PAD] tokens return_attention_mask=True, # add attention mask to not focus on pad tokens truncation=True ) # map to the expected input to TFBertForSequenceClassification, see here def map_example_to_dict(input_ids, attention_masks, token_type_ids, label): return {"input_ids": input_ids, "token_type_ids": token_type_ids, "attention_mask": attention_masks,}, label def encode_examples(x, y , limit=-1): # prepare list, so that we can build up final TensorFlow dataset from slices. input_ids_list = [] token_type_ids_list = [] attention_mask_list = [] label_list = [] for review, label in zip(x, y ): bert_input = convert_example_to_feature(review) input_ids_list.append(bert_input['input_ids']) token_type_ids_list.append(bert_input['token_type_ids']) attention_mask_list.append(bert_input['attention_mask']) label_list.append([label]) print('input_ids_list', input_ids_list) print('token_type_ids_list', token_type_ids_list) print('attention_mask_list', attention_mask_list) return tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices( (input_ids_list, attention_mask_list, token_type_ids_list, label_list)).map(map_example_to_dict) def get_raw_dataset(): train_data = np.load('./data/bert_train.npz') test_data = np.load('./data/bert_test.npz') val_data = np.load('./data/bert_val.npz') print("X_train:", train_data['x'].shape) print("y_train:", train_data['y'].shape) print("X_test:", test_data['x'].shape) print("y_test:", test_data['y'].shape) print("X_val:", val_data['x'].shape) print("y_val:", val_data['y'].shape) return train_data['x'], train_data['y'], test_data['x'], test_data['y'], val_data['x'], val_data['y'] def get_dataset(): x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test, x_val , y_val= get_raw_dataset() ds_train_encoded = encode_examples(x_train, y_train).shuffle(10000).batch(batch_size) # test dataset ds_test_encoded = encode_examples(x_test, y_test).batch(batch_size) ds_val_encoded = encode_examples(x_val, y_val).batch(batch_size) return ds_train_encoded, ds_test_encoded, ds_val_encoded def get_module(): # model initialization model = TFBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(bert_weight_folder) print(dir(model)) # classifier Adam recommended optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate, epsilon=1e-08) # we do not have one-hot vectors, we can use sparce categorical cross entropy and accuracy loss = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True) metric = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy('accuracy') model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss, metrics=[metric]) print(model.summary()) return model root_folder = r'.\bert' weight_dir = root_folder + '\weight.h5' def train_bert_module(model, ds_train_encoded, ds_val_encoded): if os.path.isfile(weight_dir): print('load weight') model.load_weights(weight_dir) current_max_loss = 9999 def save_weight(epoch, logs): global current_max_loss if (logs['val_loss'] is not None and logs['val_loss'] < current_max_loss): current_max_loss = logs['val_loss'] print('save_weight', epoch, current_max_loss) model.save_weights(weight_dir) # model.save(root_folder + '\module.h5', include_optimizer=False, save_format="tf") batch_print_callback = tf.keras.callbacks.LambdaCallback( on_epoch_end=save_weight ) callbacks = [ tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=4, monitor='loss'), batch_print_callback, # tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=root_folder + '\logs') ] print('start') bert_history = model.fit(ds_train_encoded, epochs=number_of_epochs, validation_data=ds_val_encoded, callbacks=callbacks) print('bert_history', bert_history) def test_bert_module(model, ds_test_encoded): if os.path.isfile(weight_dir): print('load weight') model.load_weights(weight_dir) scores = model.evaluate(ds_test_encoded) print(scores) if __name__ == '__main__': ds_train_encoded, ds_test_encoded, ds_val_encoded = get_dataset() bert_module = get_module() train_bert_module(bert_module,ds_train_encoded, ds_val_encoded) test_bert_module(bert_module, ds_test_encoded)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
结果 第一个epoch 测试集上准确率就已经是90.72%,
不够速度的很慢,大概1小时左右吧在GPU训练,如果是CPU那就得最少12小时了。
2186/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2793 - accuracy: 0.8811
2187/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.2793 - accuracy: 0.8811
2188/2188 [==============================] - 1023s 467ms/step - loss: 0.2793 - accuracy: 0.8811 - val_loss: 0.2340 - val_accuracy: 0.9072
- 1
- 2
- 3
第二个epoch 测试集上准确率是90.78%, 有点过拟合了
2186/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1526 - accuracy: 0.9438
2187/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1526 - accuracy: 0.9438
2188/2188 [==============================] - 1010s 462ms/step - loss: 0.1526 - accuracy: 0.9438 - val_loss: 0.2995 - val_accuracy: 0.9078
- 1
- 2
- 3
第三个epoch 测试集上准确率是91.46%
2186/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0758 - accuracy: 0.9747
2187/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0758 - accuracy: 0.9747
2188/2188 [==============================] - 1007s 460ms/step - loss: 0.0757 - accuracy: 0.9747 - val_loss: 0.2978 - val_accuracy: 0.9146
- 1
- 2
- 3
第四个epoch 测试集上准确率是91.35%
2185/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.0425 - accuracy: 0.9862
2186/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0425 - accuracy: 0.9861
2187/2188 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.0425 - accuracy: 0.9861
2188/2188 [==============================] - 999s 457ms/step - loss: 0.0425 - accuracy: 0.9861 - val_loss: 0.3121 - val_accuracy: 0.9135
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4.3. 可能遇到的问题
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘tools.nnwrap’
安装pytorch时遇到下面问题
解决方法是手动安装pytorch的相关whl.
访问这个网站,https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
下载torch-1.1.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl和torchvision-0.3.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
然后安装
pip install yourfolder\torch-1.1.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
pip install yourfolder\torchvision-0.3.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
或者直接根据pytorch官网命令直接安装。但是我的没有成功,可能是因为我的网络的问题
https://pytorch.org/
5. 其它补充
tokens --> { input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids}
Bert 模型的输入参数 {guid,input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids}
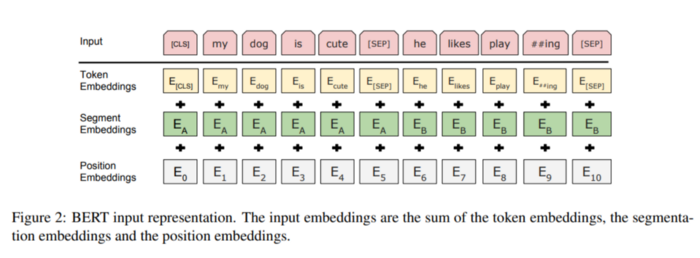
一段tensorflow的日志
I0818 00:30:55.294839 4156 run_classifier.py:465] guid: None
INFO:tensorflow:tokens: [CLS] this here ' s an example of using the bert token ##izer [SEP] fuck you [SEP]
I0818 00:30:55.294839 4156 run_classifier.py:467] tokens: [CLS] this here ' s an example of using the bert token ##izer [SEP] fuck you [SEP]
INFO:tensorflow:input_ids: 101 2023 2182 1005 1055 2019 2742 1997 2478 1996 14324 19204 17629 102 6616 2017 102 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
I0818 00:30:55.294839 4156 run_classifier.py:468] input_ids: 101 2023 2182 1005 1055 2019 2742 1997 2478 1996 14324 19204 17629 102 6616 2017 102 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
INFO:tensorflow:input_mask: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
I0818 00:30:55.294839 4156 run_classifier.py:469] input_mask: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
INFO:tensorflow:segment_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
I0818 00:30:55.294839 4156 run_classifier.py:470] segment_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
INFO:tensorflow:label: 0 (id = 0)
I0818 00:30:55.294839 4156 run_classifier.py:471] label: 0 (id = 0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
6. 总结
Bert 这个模型特别吃内存和CPU, 训练的时候特别的慢。最好用GPU吧。不然一个epoch一天都跑不完啊。
一个epoch测试集上准确率就已经是90.72%,很高了,但是第二个epoch准确没怎么提高,应该是过拟合。
7. 参考资料
[1] https://github.com/atherosai/python-graphql-nlp-transformers/tree/master/notebooks/BERT%20fine-tunning%20in%20Tensorflow%202%20with%20Keras%20API
[2] https://medium.com/atheros/text-classification-with-transformers-in-tensorflow-2-bert-2f4f16eff5ad
[3] HuggingFace的官网
[4] google-search的Bert开源代码在gitbub上的链接



