热门标签
热门文章
- 1效率神器!ArcGIS模型构建器使用详解
- 2Windows安装Stable Diffusion WebUI及问题解决记录_no matching distribution found for torch==1.13.1+c
- 3Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: ...boot.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBean_caused by: java.lang.classnotfoundexception: org.s
- 4网络原理(6)——IP协议
- 5怎么用编程Python写一个圣诞树?_python圣诞树
- 6Android笔记:监听侧边音量键
- 7tick timer 间隔_adjtimex修改tick值用法举例
- 8python库安装:Could not build wheels for opencv-python_error: could not build wheels for pycrypto, which
- 9【HuggingFace】Transformers-BertAttention逐行代码解析_pruned_heads
- 10论文发表必备技能:空间数据(tif图像、shp边界)多子图可视化-基于cartopy与matplotlib的python包_matplotlib 绘制 tiff
当前位置: article > 正文
pytorch入门学习第二课词向量和语言模型
作者:你好赵伟 | 2024-04-02 16:56:52
赞
踩
pytorch入门学习第二课词向量和语言模型
01词向量
在计算机中表示一个词

离散表示: One-hot表示

离散表示:Bag of Words

离散表示:Bi-gram和N-gram

离散表示的问题

词编码需要保证词的相似性

简单 词/短语 翻译

词嵌入效果评估: 词类比任务

02语言模型
语言模型

语言模型的评价

基于神经网络的语言模型(Neural Language Model)

循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network)

h0一般就是一个全部为0的向量
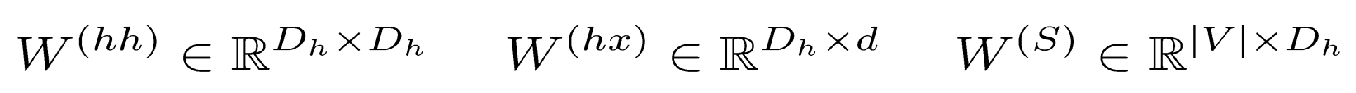

如何训练?Cross Entropy损失函数

随机梯度下降 SGD
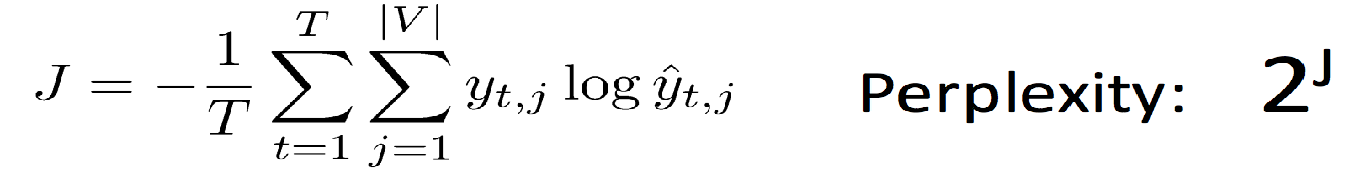
梯度消失和爆炸问题

根据反向传播(链式法则),梯度会不断相乘,很容易梯度消失或者爆炸
训练RNN
长短记忆网络(Long Short-term Memory)
LSTM是RNN的一种,大体结构几乎一样。区别是?
它的“记忆细胞”改造过。
该记的信息会一直传递,不该记的会被“门”截断。
RNN记忆细胞

LSTM记忆细胞

Gated Recurrent Unit

第二课课后复习思维导图

代码
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.utils.data as tud from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter from collections import Counter import numpy as np import random import math import pandas as pd import scipy import sklearn from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity USE_CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available() # 为了保证实验结果可以复现,我们经常会把各种random seed固定在某一个值 random.seed(53113) np.random.seed(53113) torch.manual_seed(53113) if USE_CUDA: torch.cuda.manual_seed(53113) # 设定一些超参数 K = 100 # number of negative samples C = 3 # nearby words threshold NUM_EPOCHS = 2 # The number of epochs of training MAX_VOCAB_SIZE = 30000 # the vocabulary size BATCH_SIZE = 128 # the batch size LEARNING_RATE = 0.2 # the initial learning rate EMBEDDING_SIZE = 100 LOG_FILE = "word-embedding.log" # tokenize函数,把一篇文本转化成一个个单词 def word_tokenize(text): return text.split()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 从文本文件中读取所有的文字,通过这些文本创建一个vocabulary
- 由于单词数量可能太大,我们只选取最常见的MAX_VOCAB_SIZE个单词
- 我们添加一个UNK单词表示所有不常见的单词
- 我们需要记录单词到index的mapping,以及index到单词的mapping,单词的count,单词的(normalized)
frequency,以及单词总数。
with open("text8.train.txt", "r") as fin:
text = fin.read()
text = [w for w in word_tokenize(text.lower())]
vocab = dict(Counter(text).most_common(MAX_VOCAB_SIZE-1))
vocab["<unk>"] = len(text) - np.sum(list(vocab.values()))
idx_to_word = [word for word in vocab.keys()]
word_to_idx = {word:i for i, word in enumerate(idx_to_word)}
word_counts = np.array([count for count in vocab.values()], dtype=np.float32)
word_freqs = word_counts / np.sum(word_counts)
word_freqs = word_freqs ** (3./4.)
word_freqs = word_freqs / np.sum(word_freqs) # 用来做 negative sampling
VOCAB_SIZE = len(idx_to_word)
VOCAB_SIZE
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
output:30000
- 1
实现Dataloader
一个dataloader需要以下内容:
- 把所有text编码成数字,然后用subsampling预处理这些文字。
- 保存vocabulary,单词count,normalized word frequency
- 每个iteration sample一个中心词
- 根据当前的中心词返回context单词
- 根据中心词sample一些negative单词
- 返回单词的counts
- 这里有一个好的tutorial介绍如何使用PyTorch dataloader.
为了使用dataloader,我们需要定义以下两个function: - len function需要返回整个数据集中有多少个item
- get 根据给定的index返回一个item
有了dataloader之后,我们可以轻松随机打乱整个数据集,拿到一个batch的数据等等。
class WordEmbeddingDataset(tud.Dataset): def __init__(self, text, word_to_idx, idx_to_word, word_freqs, word_counts): ''' text: a list of words, all text from the training dataset word_to_idx: the dictionary from word to idx idx_to_word: idx to word mapping word_freq: the frequency of each word word_counts: the word counts ''' super(WordEmbeddingDataset, self).__init__() self.text_encoded = [word_to_idx.get(t, VOCAB_SIZE-1) for t in text] self.text_encoded = torch.Tensor(self.text_encoded).long() self.word_to_idx = word_to_idx self.idx_to_word = idx_to_word self.word_freqs = torch.Tensor(word_freqs) self.word_counts = torch.Tensor(word_counts) def __len__(self): ''' 返回整个数据集(所有单词)的长度 ''' return len(self.text_encoded) def __getitem__(self, idx): ''' 这个function返回以下数据用于训练 - 中心词 - 这个单词附近的(positive)单词 - 随机采样的K个单词作为negative sample ''' center_word = self.text_encoded[idx] pos_indices = list(range(idx-C, idx)) + list(range(idx+1, idx+C+1)) pos_indices = [i%len(self.text_encoded) for i in pos_indices] pos_words = self.text_encoded[pos_indices] neg_words = torch.multinomial(self.word_freqs, K * pos_words.shape[0], True) return center_word, pos_words, neg_words
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
创建dataset和dataloader
dataset = WordEmbeddingDataset(text, word_to_idx, idx_to_word, word_freqs, word_counts)
dataloader = tud.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
- 1
- 2
定义PyTorch模型
class EmbeddingModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size): ''' 初始化输出和输出embedding ''' super(EmbeddingModel, self).__init__() self.vocab_size = vocab_size self.embed_size = embed_size initrange = 0.5 / self.embed_size self.out_embed = nn.Embedding(self.vocab_size, self.embed_size, sparse=False) self.out_embed.weight.data.uniform_(-initrange, initrange) self.in_embed = nn.Embedding(self.vocab_size, self.embed_size, sparse=False) self.in_embed.weight.data.uniform_(-initrange, initrange) def forward(self, input_labels, pos_labels, neg_labels): ''' input_labels: 中心词, [batch_size] pos_labels: 中心词周围 context window 出现过的单词 [batch_size * (window_size * 2)] neg_labelss: 中心词周围没有出现过的单词,从 negative sampling 得到 [batch_size, (window_size * 2 * K)] return: loss, [batch_size] ''' batch_size = input_labels.size(0) input_embedding = self.in_embed(input_labels) # B * embed_size pos_embedding = self.out_embed(pos_labels) # B * (2*C) * embed_size neg_embedding = self.out_embed(neg_labels) # B * (2*C * K) * embed_size log_pos = torch.bmm(pos_embedding, input_embedding.unsqueeze(2)).squeeze() # B * (2*C) log_neg = torch.bmm(neg_embedding, -input_embedding.unsqueeze(2)).squeeze() # B * (2*C*K) log_pos = F.logsigmoid(log_pos).sum(1) log_neg = F.logsigmoid(log_neg).sum(1) # batch_size loss = log_pos + log_neg return -loss def input_embeddings(self): return self.in_embed.weight.data.cpu().numpy()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
定义一个模型以及把模型移动到GPU
model = EmbeddingModel(VOCAB_SIZE, EMBEDDING_SIZE)
if USE_CUDA:
model = model.cuda()
- 1
- 2
- 3
下面是评估模型的代码,以及训练模型的代码
def evaluate(filename, embedding_weights): if filename.endswith(".csv"): data = pd.read_csv(filename, sep=",") else: data = pd.read_csv(filename, sep="\t") human_similarity = [] model_similarity = [] for i in data.iloc[:, 0:2].index: word1, word2 = data.iloc[i, 0], data.iloc[i, 1] if word1 not in word_to_idx or word2 not in word_to_idx: continue else: word1_idx, word2_idx = word_to_idx[word1], word_to_idx[word2] word1_embed, word2_embed = embedding_weights[[word1_idx]], embedding_weights[[word2_idx]] model_similarity.append(float(sklearn.metrics.pairwise.cosine_similarity(word1_embed, word2_embed))) human_similarity.append(float(data.iloc[i, 2])) return scipy.stats.spearmanr(human_similarity, model_similarity)# , model_similarity def find_nearest(word): index = word_to_idx[word] embedding = embedding_weights[index] cos_dis = np.array([scipy.spatial.distance.cosine(e, embedding) for e in embedding_weights]) return [idx_to_word[i] for i in cos_dis.argsort()[:10]]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
训练模型:
模型一般需要训练若干个epoch
每个epoch我们都把所有的数据分成若干个batch
把每个batch的输入和输出都包装成cuda tensor
forward pass,通过输入的句子预测每个单词的下一个单词
用模型的预测和正确的下一个单词计算cross entropy loss
清空模型当前gradient
backward pass
更新模型参数
每隔一定的iteration输出模型在当前iteration的loss,以及在验证数据集上做模型的评估
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=LEARNING_RATE) for e in range(NUM_EPOCHS): for i, (input_labels, pos_labels, neg_labels) in enumerate(dataloader): # TODO input_labels = input_labels.long() pos_labels = pos_labels.long() neg_labels = neg_labels.long() if USE_CUDA: input_labels = input_labels.cuda() pos_labels = pos_labels.cuda() neg_labels = neg_labels.cuda() optimizer.zero_grad() loss = model(input_labels, pos_labels, neg_labels).mean() loss.backward() optimizer.step() if i % 100 == 0: with open(LOG_FILE, "a") as fout: fout.write("epoch: {}, iter: {}, loss: {}\n".format(e, i, loss.item())) print("epoch: {}, iter: {}, loss: {}".format(e, i, loss.item())) if i % 2000 == 0: embedding_weights = model.input_embeddings() sim_simlex = evaluate("simlex-999.txt", embedding_weights) sim_men = evaluate("men.txt", embedding_weights) sim_353 = evaluate("wordsim353.csv", embedding_weights) with open(LOG_FILE, "a") as fout: print("epoch: {}, iteration: {}, simlex-999: {}, men: {}, sim353: {}, nearest to monster: {}\n".format( e, i, sim_simlex, sim_men, sim_353, find_nearest("monster"))) fout.write("epoch: {}, iteration: {}, simlex-999: {}, men: {}, sim353: {}, nearest to monster: {}\n".format( e, i, sim_simlex, sim_men, sim_353, find_nearest("monster"))) embedding_weights = model.input_embeddings() np.save("embedding-{}".format(EMBEDDING_SIZE), embedding_weights) torch.save(model.state_dict(), "embedding-{}.th".format(EMBEDDING_SIZE))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
在 MEN 和 Simplex-999 数据集上做评估
embedding_weights = model.input_embeddings()
print("simlex-999", evaluate("simlex-999.txt", embedding_weights))
print("men", evaluate("men.txt", embedding_weights))
print("wordsim353", evaluate("wordsim353.csv", embedding_weights))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
simlex-999 SpearmanrResult(correlation=0.17251697429101504, pvalue=7.863946056740345e-08)
men SpearmanrResult(correlation=0.1778096817088841, pvalue=7.565661657312768e-20)
wordsim353 SpearmanrResult(correlation=0.27153702278146635, pvalue=8.842165885381714e-07)
- 1
- 2
- 3
寻找nearest neighbors
for word in ["good", "fresh", "monster", "green", "like", "america", "chicago", "work", "computer", "language"]:
print(word, find_nearest(word))
- 1
- 2
good ['good', 'bad', 'perfect', 'hard', 'questions', 'alone', 'money', 'false', 'truth', 'experience']
fresh ['fresh', 'grain', 'waste', 'cooling', 'lighter', 'dense', 'mild', 'sized', 'warm', 'steel']
monster ['monster', 'giant', 'robot', 'hammer', 'clown', 'bull', 'demon', 'triangle', 'storyline', 'slogan']
green ['green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'white', 'cross', 'orange', 'black', 'red', 'mountain', 'gold']
like ['like', 'unlike', 'etc', 'whereas', 'animals', 'soft', 'amongst', 'similarly', 'bear', 'drink']
america ['america', 'africa', 'korea', 'india', 'australia', 'turkey', 'pakistan', 'mexico', 'argentina', 'carolina']
chicago ['chicago', 'boston', 'illinois', 'texas', 'london', 'indiana', 'massachusetts', 'florida', 'berkeley', 'michigan']
work ['work', 'writing', 'job', 'marx', 'solo', 'label', 'recording', 'nietzsche', 'appearance', 'stage']
computer ['computer', 'digital', 'electronic', 'audio', 'video', 'graphics', 'hardware', 'software', 'computers', 'program']
language ['language', 'languages', 'alphabet', 'arabic', 'grammar', 'pronunciation', 'dialect', 'programming', 'chinese', 'spelling']
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
单词之间的关系
man_idx = word_to_idx["man"]
king_idx = word_to_idx["king"]
woman_idx = word_to_idx["woman"]
embedding = embedding_weights[woman_idx] - embedding_weights[man_idx] + embedding_weights[king_idx]
cos_dis = np.array([scipy.spatial.distance.cosine(e, embedding) for e in embedding_weights])
for i in cos_dis.argsort()[:20]:
print(idx_to_word[i])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
king henry charles pope queen iii prince elizabeth alexander constantine edward son iv louis emperor mary james joseph frederick francis
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/你好赵伟/article/detail/353106
推荐阅读
相关标签



