热门标签
热门文章
- 1国内无法访问下载Docker镜像的多种解决方案, Docker 镜像 网络代理配置,推荐使用网络代理_国内无法拉取docker镜像
- 2使用Dom4j解析XML文件
- 3SpringCloud源码学习笔记之Eureka服务端——服务注册_no static resource eureka.
- 4自然语言生成(NLG)的好处是什么,它如何影响BI?_智能语音 nlg
- 5基于Big-Bang-Big-Crunch(BBBC)算法的目标函数最小值计算matlab仿真
- 6开源低代码平台,JeecgBoot v3.7.0 里程碑版本发布_检测到当前菜单表是 vue2版本 的,这将导致菜单加载异常,请更换成vue3版本的表!
- 7飞桨模型保存_重磅发布开源框架、生物计算平台螺旋桨,百度飞桨交了年终成绩单...
- 8svn提交提示服务器文件被锁,svn被锁定怎么解决-svn被锁定的解决方法 - 河东软件园...
- 9鸿蒙实战开发教程-注册登录页面_鸿蒙登录页面
- 10软考中级系统集成必备100题(91-100)真题精炼(1)
当前位置: article > 正文
基于OpenCV与Keras的停车场车位自动识别系统
作者:寸_铁 | 2024-07-19 17:08:30
赞
踩
基于OpenCV与Keras的停车场车位自动识别系统
本项目旨在利用计算机视觉技术和深度学习算法,实现对停车场车位状态的实时自动识别。通过摄像头监控停车场内部,系统能够高效准确地辨认车位是否被占用,为车主提供实时的空闲车位信息,同时为停车场管理者提供智能化的车位管理工具。该系统结合了OpenCV的强大图像处理能力与Keras的易用性,便于快速构建和部署。
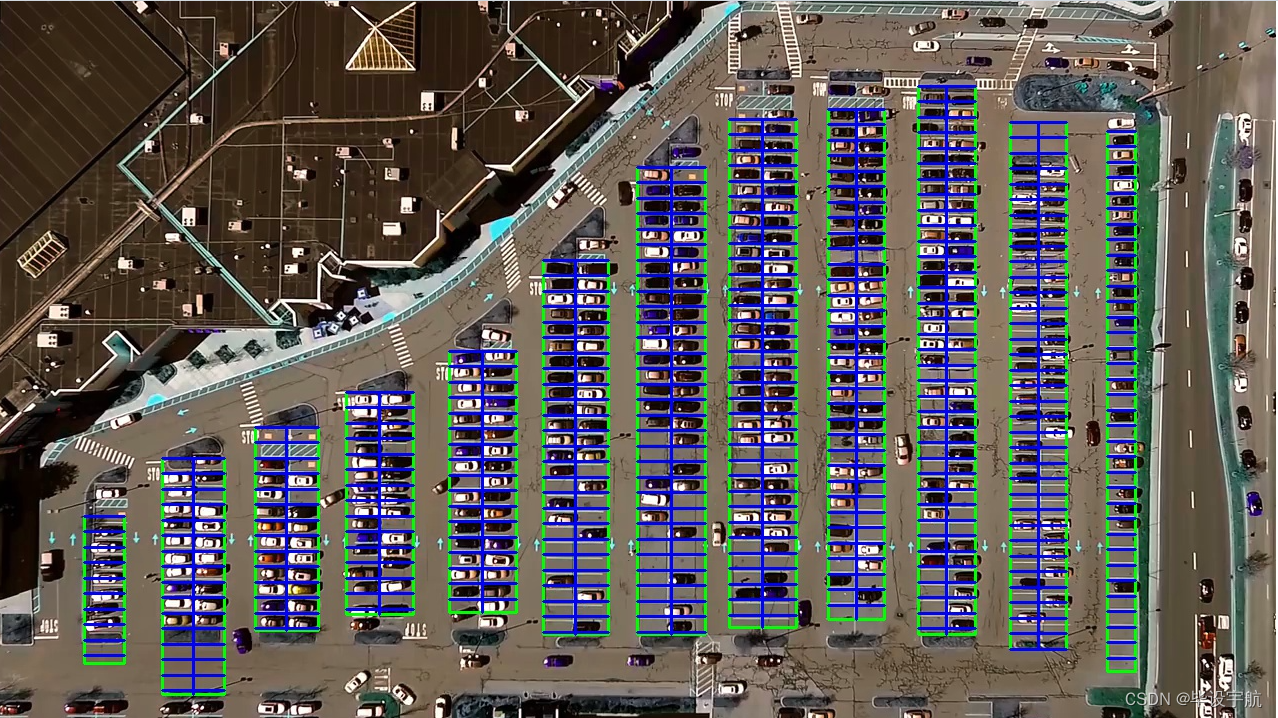
技术栈:
- OpenCV:用于图像的预处理,包括视频捕获、图像处理(如灰度转换、滤波、边缘检测等)以及ROI(感兴趣区域)的选取,为深度学习模型提供高质量的输入。
- Keras:基于TensorFlow的高级API,用于搭建和训练深度学习模型。项目中,可能采用预训练模型(如VGGNet、ResNet等)进行迁移学习,通过微调模型来适应车位识别任务,或者从零开始构建卷积神经网络(CNN)模型进行车位状态分类。
项目流程:
-
数据收集与预处理:首先,通过摄像头录制停车场视频,从中截取包含车位的画面,人工标注车位状态(如空闲或占用)。接着,对图像进行归一化、增强等预处理,创建训练和验证数据集。
-
模型训练:使用Keras构建深度学习模型,加载预处理后的数据集进行训练。训练过程中,可能涉及调整超参数、优化器选择、损失函数配置等,以达到理想的分类性能。
-
模型验证与优化:在验证集上评估模型性能,根据准确率、召回率等指标调整模型结构或参数,进行模型优化。
-
实时检测与应用:将训练好的模型集成到OpenCV中,实现实时视频流处理。系统不断捕获停车场的视频帧,进行图像处理后,通过模型预测车位状态。识别结果以可视化方式展示,如在视频流中标记车位为空闲或占用,并可进一步集成到停车场管理系统,实现车位引导、计费等功能。
特色与优势:
- 实时性:系统能够实时监控车位状态,及时更新信息,提高停车场的运营效率。
- 准确性:深度学习模型具有强大的特征学习能力,即使在复杂光照、遮挡等条件下也能保持较高识别准确率。
- 易部署与扩展:基于OpenCV和Keras的方案易于开发和调试,且模型可根据新数据持续优化,便于后续维护和功能升级。
- 智能化管理:为停车场管理者提供精准的车位占用情况,有助于优化停车资源分配,提升用户体验。
总结: 此项目通过融合OpenCV的图像处理能力和Keras构建的深度学习模型,实现了对停车场车位状态的自动识别,是智能交通系统和智慧城市应用中的一个重要组成部分,具有广泛的应用前景和社会价值。
- from __future__ import division # 改变 Python 2 中除法操作符 / 的默认行为,使其表现得像 Python 3 中的除法操作符,结果会保留小数部分
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 用于创建图表和可视化数据的 Python 库
- import cv2
- import os, glob # glob文件名匹配的模块
- import numpy as np
- from PIL import Image
- from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
- from keras.models import load_model
- from keras.preprocessing import image
- from Parking import Parking
- import pickle # 序列化和反序列化对象的标准模块
-
- cwd = os.getcwd() # 获取当前工作目录
-
- def img_process(test_images, park):
- # 过滤背景,低于lower_red和高于upper_red的部分分别编程0,lower_red~upper_red之间的值编程255
- # map 函数用于将一个函数应用到可迭代对象的每个元素,并返回结果
- # 通过 list 函数将其转换为列表
- white_yellow_images = list(map(park.select_rgb_white_yellow,test_images))
- park.show_images(white_yellow_images)
-
- # 转灰度图
- gray_images = list(map(park.convert_gray_scale, white_yellow_images))
- park.show_images(gray_images)
-
- # 进行边缘检测
- edge_images = list(map(lambda image: park.detect_edges(image),gray_images))
- park.show_images(edge_images)
-
- # 根据需要设定屏蔽区域
- roi_images = list(map(park.select_region, edge_images))
- park.show_images(roi_images)
-
- # 霍夫变换,得出直线
- list_of_lines= list(map(park.hough_line, roi_images))
-
- # zip 函数来同时迭代 test_images 和 list_of_lines 中的元素
- line_images = []
- for image,lines in zip(test_images,list_of_lines):
- line_images.append(park.draw_lines(image,lines))
- park.show_images(line_images)
-
- rect_images = []
- rect_coords = [] # 列矩形
- for image,lines in zip(test_images, list_of_lines):
- # 过滤部分直线,对直线进行排序,得出每一列的起始点和终止点,并将列矩形画出来
- new_image,rects = park.identify_blocks(image,lines)
- rect_images.append(new_image)
- rect_coords.append(rects)
-
- park.show_images(rect_images)
-
- delineated = []
- spot_pos = []
- for image,rects in zip(test_images, rect_coords):
- # 在图上将停车位画出来,并返回字典{坐标:车位序号}
- new_image,spot_dict = park.draw_parking(image,rects)
- delineated.append(new_image)
- spot_pos.append(spot_dict)
-
- park.show_images(delineated)
- final_spot_dict = spot_pos[1]
-
- print(len(final_spot_dict))
-
- with open('spot_dict.pickle','wb') as handle:
- pickle.dump(final_spot_dict,handle,property==pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
-
- park.save_images_for_cnn(test_images[0],final_spot_dict)
-
- return final_spot_dict
-
- def keras_model(weights_path):
- model = load_model(weights_path)
- return model
-
- def img_test(test_image,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary):
- for i in range (len(test_images)):
- predicted_images = park.predict_on_image(test_images[i],final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary)
-
- def video_test(video_name,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary):
- name = video_name
- cap = cv2.VideoCapture(name)
- park.predict_on_video(name,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary,ret=True)
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- test_images = [plt.imread(path) for path in glob.glob('test_images/*.jpg')]
- weights_path = 'car1.h5'
- video_name = 'parking_video.mp4'
- class_dictionary = {}
- class_dictionary[0] = 'empty'
- class_dictionary[1] = 'occupied'
- park = Parking()
- park.show_image(test_images)
- final_spot_dict = img_process(test_images, park)
- model = keras_model(weights_path)
- img_test(test_images,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary)
- video_test(video_name,final_spot_dict,model,class_dictionary)
parking py
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import cv2
- import os,glob
- import numpy as np
-
- class Parking:
-
- def show_images(self, images, cmap=None):
- cols = 2
- rows = (len(images) + 1)//cols # //为整除运算符
-
- plt.figure(figsize=(15,12)) # 创建一个图形窗口,并指定其大小为 15x12 英寸
- for i,image in enumerate(images):
- plt.subplot(rows, cols, i+1) # 在当前图形窗口中创建一个子图,i+1 是因为子图的编号是从 1 开始的
- # 检查图像的维度,如果图像是二维的(灰度图像),则将颜色映射设置为灰度,否则保持传入的 cmap 参数不变
- cmap = 'gray' if len(image.shape)==2 else cmap
- plt.imshow(image, cmap=cmap)
- plt.xticks([]) # 去除 x 轴和 y 轴的刻度标签
- plt.yticks([])
- plt.tight_layout(pad=0,h_pad=0,w_pad=0) # 调整子图之间的间距
- plt.show()
-
- def cv_show(self, name, img):
- cv2.imshow(name, img)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
-
- def select_rgb_white_yellow(self,image):
- # 过滤掉背景
- lower = np.uint8([120,120,120])
- upper = np.uint8([255,255,255])
-
- # 低于lower_red和高于upper_red的部分分别编程0,lower_red~upper_red之间的值编程255,相当于过滤背景
- white_mask = cv2.inRange(image,lower,upper)
- self.cv_show('white_mask',white_mask)
-
- # 与操作
- masked = cv2.bitwise_and(image, image, mask=white_mask)
- self.cv_show('masked',masked)
- return masked
-
- def convert_gray_scale(selfself,image):
- return cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
-
- # 提取图像中的边缘信息
- # 返回的是一个二值图像,其中边缘点被标记为白色(255),而非边缘点被标记为黑色(0)
- def detect_edges(self, image, low_threshole=50, high_threshold=200):
- return cv2.Canny(image, low_threshole, high_threshold)
-
- def filter_region(self, image, vertices):
- # 剔除掉不需要的地方
- mask = np.zeros_like(image) # 创建和原图一样大的图,置零
- if len(mask.shape)==2: # 是否为一张灰度图
- cv2.fillPoly(mask, vertices, 255) # 使用顶点vertices在mask上填充多边形,并置为255白色
- self.cv_show('mask',mask)
- return cv2.bitwise_and(image,mask)
-
- def select_region(self, image):
- # 手动选择区域
- # 首先,通过顶点定义多边形。
- rows, cols = image.shape[:2] # h和w
- pt_1 = [cols*0.05, rows*0.09]
- pt_2 = [cols*0.05, rows*0.70]
- pt_3 = [cols*0.30, rows*0.55]
- pt_4 = [cols*0.6, rows*0.15]
- pt_5 = [cols*0.90, rows*0.15]
- pt_6 = [cols*0.90, rows*0.90]
-
- vertices = np.array([[pt_1, pt_2, pt_3, pt_4, pt_5, pt_6]],dtype=np.int32)
- point_img = image.copy()
- point_img = cv2.cvtColor(point_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- for point in vertices[0]:
- cv2.circle(point_img,(point[0], point[1]), 10, (0,0,255), 4)
- self.cv_show('point_img',point_img)
-
- return self.filter_region(image, vertices)
-
- # 霍夫变换,得出直线
- def hough_line(self,image):
- # 检测输入图像中的直线,并返回检测到的直线的端点坐标
- # 输入的图像需要是边缘检测后的结果
- # minLineLength(线的最短长度,比这个短的都被忽略)和MaxLineCap(两条直线之间的最大间隔,小于辞职,认为是一条直线)
- # rho以像素为单位的距离分辨率,通常设置为 1 像素
- # thrta角度精度
- # threshod直线交点数量阈值。只有累加器中某个点的投票数高于此阈值,才被认为是一条直线。
- return cv2.HoughLinesP(image, rho=0.1, thrta=np.pi/10, threshold=15,minLineLength=9,maxLineGap=4)
-
- # 过滤霍夫变换检测到的直线
- def draw_lines(self, image, lines, color=[255,0,0], thickness=2, make_copy=True):
- if make_copy:
- image = np.copy(image)
- cleaned = []
- for line in lines:
- for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:
- if abs(y2-y1) <= 1 and abs(x2-x1) >= 25 and abs(x2-x1) <= 55:
- cleaned.append((x1,y1,x2,y2))
- cv2.line(image, (x1,y1), (x2,y2), color, thickness)
- print(" No lines detected: ", len(cleaned))
- return image
-
- # 过滤部分直线,对直线进行排序,得出每一列的起始点和终止点,并将列矩形画出来
- def identify_blocks(self, image, lines, make_copy=True):
- if make_copy:
- new_image = np.copy(image)
-
- # step1: 过滤部分直线
- cleaned = []
- for line in lines:
- for x1,y1,x2,y2 in line:
- if abs(y2-y1) <= 1 and abs(x2-x1) >= 25 and abs(x2-x1)<= 55:
- cleaned.append((x1,y1,x2,y2))
-
- # step2: 对直线按照 起始点的x和y坐标 进行排序
- import operator # 可以使用其中的各种函数来进行操作,例如比较、算术
- list1 = sorted(cleaned, key=operator.itemgetter(0,1)) # 从列表的每个元素中获取索引为0和1的值,然后将这些值用作排序的依据
-
- # step3: 找到多个列,相当于每列是一排车
- clusters = {} # 列数:对应该列有哪些车位线
- dIndex = 0
- clus_dist = 10
-
- for i in range(len(list1) - 1):
- distance = abs(list1[i+1][0] - list1[i][0]) # 根据前后两组车位线的x1距离
- if distance <= clus_dist:
- if not dIndex in clusters.keys(): clusters[dIndex] = []
- clusters[dIndex].append(list1[i])
- clusters[dIndex].append(list1[i + 1])
- else:
- dIndex += 1
-
- # step4: 得到每一列的四个坐标
- rects = {} # 每一列的四个角的坐标
- i = 0
- for key in clusters:
- all_list = clusters[key]
- # 将列表 all_list 转换为一个集合set,去重
- # {(10, 20, 30, 40), (20, 30, 40, 50)} 转为 [(10, 20, 30, 40), (20, 30, 40, 50)]
- cleaned = list(set(all_list))
- if len(cleaned) > 5:
- cleaned = sorted(cleaned, key=lambda tup: tup[1]) # 按y1进行排序
- avg_y1 = cleaned[0][1] # 第一条线段的起始点 y 坐标
- avg_y2 = cleaned[-1][1] # 最后一条线段的起始点 y 坐标,即整个区域的上下边界
- avg_x1 = 0
- avg_x2 = 0
- for tup in cleaned: # 累加起始点和结束点的 x 坐标
- avg_x1 += tup[0]
- avg_x2 += tup[2]
- avg_x1 = avg_x1/len(cleaned) # 取平均起始点和结束点x坐标值
- avg_x2 = avg_x2/len(cleaned)
- rects[i] = (avg_x1, avg_y1,avg_x2,avg_y2)
- i += 1
- print("Num Parking Lanes:", len(rects))
-
- # step5: 把列矩形画出来
- buff = 7
- for key in rects:
- tup_topLeft = (int(rects[key][0] - buff), int(rects[key][1])) # x1-buff, y1
- tup_botRight = (int(rects[key][2] + buff), int(rects[key][3])) # x2+buff, y2
- cv2.rectangle(new_image, tup_topLeft, tup_botRight,(0,255,0),3)
- return new_image,rects
-
- # 在图上将停车位画出来,并返回字典{坐标:车位序号}
- def draw_parking(self, image, rects, make_copy=True, color=[255,0,0], thickness=2, save=True):
- if make_copy:
- new_image = np.copy(image)
- gap = 15.5 # 一个车位大致高度
- spot_dict = {} # 字典:一个车位对应一个位置
- tot_spots = 0 # 总车位
-
- # 微调
- adj_y1 = {0: 20, 1: -10, 2: 0, 3: -11, 4: 28, 5: 5, 6: -15, 7: -15, 8: -10, 9: -30, 10: 9, 11: -32}
- adj_y2 = {0: 30, 1: 50, 2: 15, 3: 10, 4: -15, 5: 15, 6: 15, 7: -20, 8: 15, 9: 15, 10: 0, 11: 30}
-
- adj_x1 = {0: -8, 1: -15, 2: -15, 3: -15, 4: -15, 5: -15, 6: -15, 7: -15, 8: -10, 9: -10, 10: -10, 11: 0}
- adj_x2 = {0: 0, 1: 15, 2: 15, 3: 15, 4: 15, 5: 15, 6: 15, 7: 15, 8: 10, 9: 10, 10: 10, 11: 0}
-
- for key in rects:
- tup = rects[key]
- x1 = int(tup[0] + adj_x1[key])
- x2 = int(tup[2] + adj_x2[key])
- y1 = int(tup[1] + adj_y1[key])
- y2 = int(tup[3] + adj_y2[key])
- cv2.rectangle(new_image,(x1,y1), (x2,y2), (0,255,0), 2)
- num_splits = int(abs(y2-y1)//gap) # 一列总共有多少个车位
- for i in range (0,num_splits+1): # 画车位框
- y = int(y1 + i*gap)
- cv2.rectangle(new_image, (x1,y), (x2,y2), (0,255,0), 2)
- if key > 0 and key < len(rects)-1:
- # 竖直线
- x = int((x1+x2)/2)
- cv2.line(new_image,(x,y1),(x,y2),color,thickness)
-
- # 计算数量
- if key == 0 or key == (len(rects) - 1): # 对于第一列和最后一列(只有一排车位)
- tot_spots += num_splits + 1
- else:
- tot_spots += 2*(num_splits + 1) # 一列有两排车位
-
- # 字典对应好
- if key == 0 or key == (len(rects) - 1): # 对于第一列和最后一列(只有一排车位)
- for i in range(0, num_splits+1):
- cur_len = len(spot_dict)
- y = int(y1 + i*gap)
- spot_dict[(x1,y,x2,y+gap)] = cur_len + 1
- else:
- for i in range(0, num_splits+1):
- cur_len = len(spot_dict)
- y = int(y1 + i*gap)
- x = int((x1+x2)/2)
- spot_dict[(x1,y,x,y+gap)] = cur_len + 1
- spot_dict[(x,y,x2,y+gap)] = cur_len + 2
-
- print("total parking spaces: ", tot_spots, cur_len)
- if save:
- filename = 'with_parking.jpg'
- cv2.imwrite(filename, new_image)
- return new_image, spot_dict
-
- # 根据传入的起始点和终止点坐标列表画框
- def assign_spots_map(self, image, spot_dict, make_copy= True, color=[255,0,0], thickness=2):
- if make_copy:
- new_image = np.copy(image)
- for spot in spot_dict.keys():
- (x1,y1,x2,y2) = spot
- cv2.rectangle(new_image,(int(x1),int(y1)), (int(x2),int(y2)), color, thickness)
- return new_image
-
- # 遍历字典{坐标,车位号}在图片中截取对应坐标的图像,按车位号保存下来
- def save_images_for_cnn(self, image, spot_dict, folder_name= 'cnn_data'):
- for spot in spot_dict.keys():
- (x1,y1,x2,y2) = spot
- (x1,y1,x2,y2) = (int(x1),int(y1),int(x2),int(y2))
-
- # 裁剪
- spot_img= image[y1:y2, x1:x2]
- spot_img = cv2.resize(spot_img, (0,0), fx=2.0, fy=2.0)
- spot_id = spot_dict[spot]
-
- filename = 'spot' + str(spot_id) + '.jpg'
- print(spot_img.shape, filename, (x1,x2,y1,y2))
-
- cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(folder_name, filename), spot_img)
-
- # 将图像进行归一化,并将其转换成一个符合深度学习模型输入要求的四维张量,进行训练
- def make_prediction(self, image, model, class_dictionary):
- # 预处理
- img = image/255. # 将图像的像素值归一化到 [0, 1] 的范围内
-
- # 将图像转换成一个四维张量
- image = np.expend_dims(img, axis = 0)
-
- # 将图片调用keras算法进行预测
- class_predicted = model.predict(image) # 得出预测结果
- inID = np.argmax(class_predicted[0]) # 找到数组中最大值所在的索引
- label = class_dictionary[inID]
- return label
-
- def predict_on_image(self, image, spot_dict, model, class_dictionary,
- make_copy=True, color=[0,255,0], alpha=0.5):
- if make_copy:
- new_image = np.copy(image)
- overlay = np.copy(image)
- self.cv_show('new_image',new_image)
- cnt_empty = 0
- all_spots = 0
- for spot in spot_dict.keys():
- all_spots += 1
- (x1, y1, x2, y2) = spot
- (x1, y1, x2, y2) = (int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2))
- spot_img = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]
- spot_img = cv2.resize(spot_img, (48,48))
-
- label = self.make_prediction(spot_img, model, class_dictionary)
- if label== 'empty':
- cv2.rectangle(overlay, (int(x1), int(y1)), (int(x2), int(y2)), color, -1)
- cnt_empty += 1
- cv2.addWeighted(overlay, alpha, new_image, 1-alpha, 0, new_image)
-
- cv2.putText(new_image, "Available: %d spots" %cnt_empty, (30,95),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(255,255,255),2)
-
- cv2.putText(new_image, "Total: %d spots" %all_spots, (30,125),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7,(255,255,255),2)
- save = False
-
- if save:
- filename = 'with_parking.jpg'
- cv2.imwrite(filename, new_image)
- self.cv_show('new_image',new_image)
-
- return new_image
-
- def predict_on_video(self, video_name, final_spot_dict, model, class_dictionary, ret=True):
- cap= cv2.VideoCapture(video_name)
- count = 0
- while ret:
- ret, image = cap.read()
- count += 1
- if count == 5:
- count == 0
-
- new_image = np.copy(image)
- overlay = np.copy(image)
- cnt_empty = 0
- all_spots = 0
- color = [0,255,0]
- alpha = 0.5
- for spot in final_spot_dict.keys():
- all_spots += 1
- (x1,y1,x2,y2) = spot
- (x1,y1,x2,y2) = (int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2))
- spot_img = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]
- spot_img = cv2.resize(spot_img, (48,48))
-
- label = self.make_prediction(spot_img, model, class_dictionary)
- if label == 'empty':
- cv2.rectangle(overlay, (int(x1),int(y1)), (int(x2),int(y2)), color, -1)
- cnt_empty += 1
- cv2.addWeighted(overlay, alpha, new_image, 1-alpha, 0, new_image)
-
- cv2.putText(new_image,"Available: %d spots" % cnt_empty,(30,95),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (255,255,255),2)
-
- cv2.putText(new_image, "Total: %d spots" %all_spots, (30,125),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (255,255,255), 2)
- cv2.imshow('frame',new_image)
- # 检测用户是否按下了 'q' 键
- if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'): # 通过 & 0xFF 操作,可以确保只获取ASCII码的最后一个字节
- break
- cv2.destroyWindow()
- cap.release()
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/寸_铁/article/detail/852598
推荐阅读
相关标签


