- 1python学习 字符串_len("python\n编程\t很\t容易\t学会")
- 2新闻分类任务实战(自然语言处理经典案例实战)_自然语言处理案例代码
- 3【RabbitMQ】之高可用集群搭建
- 4Git 详细安装教程【图文讲解】_git安装教程图文详解
- 5向上管理(中高层核心能力的表现)_向上管理能力
- 6防护墙概述以及USG6000基础应用实验配置_usg6000e旁挂三层配置
- 7GQA数据集介绍
- 8在一台电脑上管理多个github、gitlab账号_一个电脑多个git账号 如何控制提交代码的git账号
- 9linux 安装 nacos 使用命令sh startup.sh -m standalone启动报错:
- 10智能零售柜商品识别从零开始使用YOLOv5+PyQt5+OpenCV实现(支持图片、视频、摄像头实时检测)_零售柜ai动态识别算法
四叉树 相关内容
赞
踩
/
四叉树索引的基本思想是将地理空间递归划分为不同层次的树结构。它将已知范围的空间等分成四个相等的子空间,如此递归下去,直至树的层次达到一定深度或者满足某种要求后停止分割。四叉树的结构比较简单,并且当空间数据对象分布比较均匀时,具有比较高的空间数据插入和查询效率,因此四叉树是GIS中常用的空间索引之一。常规四叉树的结构如图所示,地理空间对象都存储在叶子节点上,中间节点以及根节点不存储地理空间对象。

四叉树对于区域查询,效率比较高。但如果空间对象分布不均匀,随着地理空间对象的不断插入,四叉树的层次会不断地加深,将形成一棵严重不平衡的四叉树,那么每次查询的深度将大大的增多,从而导致查询效率的急剧下降。
本节将介绍一种改进的四叉树索引结构。四叉树结构是自顶向下逐步划分的一种树状的层次结构。传统的四叉树索引存在着以下几个缺点:
(1)空间实体只能存储在叶子节点中,中间节点以及根节点不能存储空间实体信息,随着空间对象的不断插入,最终会导致四叉树树的层次比较深,在进行空间数据窗口查询的时候效率会比较低下。
(2)同一个地理实体在四叉树的分裂过程中极有可能存储在多个节点中,这样就导致了索引存储空间的浪费。
(3)由于地理空间对象可能分布不均衡,这样会导致常规四叉树生成一棵极为不平衡的树,这样也会造成树结构的不平衡以及存储空间的浪费。
相应的改进方法,将地理实体信息存储在完全包含它的最小矩形节点中,不存储在它的父节点中,每个地理实体只在树中存储一次,避免存储空间的浪费。首先生成满四叉树,避免在地理实体插入时需要重新分配内存,加快插入的速度,最后将空的节点所占内存空间释放掉。改进后的四叉树结构如下图所示。四叉树的深度一般取经验值4-7之间为最佳。

为了维护空间索引与对存储在文件或数据库中的空间数据的一致性,作者设计了如下的数据结构支持四叉树的操作。
(1)四分区域标识
分别定义了一个平面区域的四个子区域索引号,右上为第一象限0,左上为第二象限1,左下为第三象限2,右下为第四象限3。
typedef enum
{
UR = 0,// UR第一象限
UL = 1, // UL为第二象限
LL = 2, // LL为第三象限
LR = 3 // LR为第四象限
}QuadrantEnum;
(2)空间对象数据结构
空间对象数据结构是对地理空间对象的近似,在空间索引中,相当一部分都是采用MBR作为近似。
/*空间对象MBR信息*/
typedef struct SHPMBRInfo
{
int nID; //空间对象ID号
MapRect Box; //空间对象MBR范围坐标
}SHPMBRInfo;
nID是空间对象的标识号,Box是空间对象的最小外包矩形(MBR)。
(3)四叉树节点数据结构
四叉树节点是四叉树结构的主要组成部分,主要用于存储空间对象的标识号和MBR,也是四叉树算法操作的主要部分。
/*四叉树节点类型结构*/
typedef struct QuadNode
{
MapRect Box; //节点所代表的矩形区域
int nShpCount; //节点所包含的所有空间对象个数
SHPMBRInfo* pShapeObj; //空间对象指针数组
int nChildCount; //子节点个数
QuadNode *children[4]; //指向节点的四个孩子
}QuadNode;
Box是代表四叉树对应区域的最小外包矩形,上一层的节点的最小外包矩形包含下一层最小外包矩形区域;nShpCount代表本节点包含的空间对象的个数;pShapeObj代表指向空间对象存储地址的首地址,同一个节点的空间对象在内存中连续存储;nChildCount代表节点拥有的子节点的数目;children是指向孩子节点指针的数组。
上述理论部分都都讲的差不多了,下面就贴上我的C语言实现版本代码。
头文件如下:
#ifndef __QUADTREE_H_59CAE94A_E937_42AD_AA27_794E467715BB__
#define __QUADTREE_H_59CAE94A_E937_42AD_AA27_794E467715BB__
/* 一个矩形区域的象限划分::
UL(1) | UR(0)
----------|-----------
LL(2) | LR(3)
以下对该象限类型的枚举
*/
typedef enum
{
UR = 0,
UL = 1,
LL = 2,
LR = 3
}QuadrantEnum;
/*空间对象MBR信息*/
typedef struct SHPMBRInfo
{
int nID; //空间对象ID号
MapRect Box; //空间对象MBR范围坐标
}SHPMBRInfo;
/* 四叉树节点类型结构 */
typedef struct QuadNode
{
MapRect Box; //节点所代表的矩形区域
int nShpCount; //节点所包含的所有空间对象个数
SHPMBRInfo* pShapeObj; //空间对象指针数组
int nChildCount; //子节点个数
QuadNode *children[4]; //指向节点的四个孩子
}QuadNode;
/* 四叉树类型结构 */
typedef struct quadtree_t
{
QuadNode *root;
int depth; // 四叉树的深度
}QuadTree;
//初始化四叉树节点
QuadNode *InitQuadNode();
//层次创建四叉树方法(满四叉树)
void CreateQuadTree(int depth,GeoLayer *poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree);
//创建各个分支
void CreateQuadBranch(int depth,MapRect &rect,QuadNode** node);
//构建四叉树空间索引
void BuildQuadTree(GeoLayer*poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree);
//四叉树索引查询(矩形查询)
void SearchQuadTree(QuadNode* node,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched);
//四叉树索引查询(矩形查询)并行查询
void SearchQuadTreePara(vector<QuadNode*> resNodes,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched);
//四叉树的查询(点查询)
void PtSearchQTree(QuadNode* node,double cx,double cy,vector<int>& ItemSearched);
//将指定的空间对象插入到四叉树中
void Insert(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode);
//将指定的空间对象插入到四叉树中
void InsertQuad(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode);
//将指定的空间对象插入到四叉树中
void InsertQuad2(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode);
//判断一个节点是否是叶子节点
bool IsQuadLeaf(QuadNode* node);
//删除多余的节点
bool DelFalseNode(QuadNode* node);
//四叉树遍历(所有要素)
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<int>& resVec);
//四叉树遍历(所有节点)
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<QuadNode*>& arrNode);
//释放树的内存空间
void ReleaseQuadTree(QuadNode** quadTree);
//计算四叉树所占的字节的大小
long CalByteQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,long& nSize);
#endif
源文件如下:
#include "QuadTree.h"
QuadNode *InitQuadNode()
{
QuadNode *node = new QuadNode;
node->Box.maxX = 0;
node->Box.maxY = 0;
node->Box.minX = 0;
node->Box.minY = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
node->children[i] = NULL;
}
node->nChildCount = 0;
node->nShpCount = 0;
node->pShapeObj = NULL;
return node;
}
void CreateQuadTree(int depth,GeoLayer *poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree)
{
pQuadTree->depth = depth;
GeoEnvelope env; //整个图层的MBR
poLayer->GetExtent(&env);
MapRect rect;
rect.minX = env.MinX;
rect.minY = env.MinY;
rect.maxX = env.MaxX;
rect.maxY = env.MaxY;
//创建各个分支
CreateQuadBranch(depth,rect,&(pQuadTree->root));
int nCount = poLayer->GetFeatureCount();
GeoFeature **pFeatureClass = new GeoFeature*[nCount];
for (int i = 0; i < poLayer->GetFeatureCount(); i ++)
{
pFeatureClass[i] = poLayer->GetFeature(i);
}
//插入各个要素
GeoEnvelope envObj; //空间对象的MBR
//#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < nCount; i ++)
{
pFeatureClass[i]->GetGeometry()->getEnvelope(&envObj);
rect.minX = envObj.MinX;
rect.minY = envObj.MinY;
rect.maxX = envObj.MaxX;
rect.maxY = envObj.MaxY;
InsertQuad(i,rect,pQuadTree->root);
}
//DelFalseNode(pQuadTree->root);
}
void CreateQuadBranch(int depth,MapRect &rect,QuadNode** node)
{
if (depth != 0)
{
*node = InitQuadNode(); //创建树根
QuadNode *pNode = *node;
pNode->Box = rect;
pNode->nChildCount = 4;
MapRect boxs[4];
pNode->Box.Split(boxs,boxs+1,boxs+2,boxs+3);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//创建四个节点并插入相应的MBR
pNode->children[i] = InitQuadNode();
pNode->children[i]->Box = boxs[i];
CreateQuadBranch(depth-1,boxs[i],&(pNode->children[i]));
}
}
}
void BuildQuadTree(GeoLayer *poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree)
{
assert(poLayer);
GeoEnvelope env; //整个图层的MBR
poLayer->GetExtent(&env);
pQuadTree->root = InitQuadNode();
QuadNode* rootNode = pQuadTree->root;
rootNode->Box.minX = env.MinX;
rootNode->Box.minY = env.MinY;
rootNode->Box.maxX = env.MaxX;
rootNode->Box.maxY = env.MaxY;
//设置树的深度( 根据等比数列的求和公式)
//pQuadTree->depth = log(poLayer->GetFeatureCount()*3/8.0+1)/log(4.0);
int nCount = poLayer->GetFeatureCount();
MapRect rect;
GeoEnvelope envObj; //空间对象的MBR
for (int i = 0; i < nCount; i ++)
{
poLayer->GetFeature(i)->GetGeometry()->getEnvelope(&envObj);
rect.minX = envObj.MinX;
rect.minY = envObj.MinY;
rect.maxX = envObj.MaxX;
rect.maxY = envObj.MaxY;
InsertQuad2(i,rect,rootNode);
}
DelFalseNode(pQuadTree->root);
}
void SearchQuadTree(QuadNode* node,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched)
{
assert(node);
//int coreNum = omp_get_num_procs();
//vector<int> * pResArr = new vector<int>[coreNum];
if (NULL != node)
{
for (int i = 0; i < node->nShpCount; i ++)
{
if (queryRect.Contains(node->pShapeObj[i].Box)
|| queryRect.Intersects(node->pShapeObj[i].Box))
{
ItemSearched.push_back(node->pShapeObj[i].nID);
}
}
//并行搜索四个孩子节点
/*#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[0] != NULL) &&
(node->children[0]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[0]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[0],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[1] != NULL) &&
(node->children[1]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[1]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[1],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[2] != NULL) &&
(node->children[2]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[2]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[2],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[3] != NULL) &&
(node->children[3]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[3]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[3],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
}*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if ((node->children[i] != NULL) &&
(node->children[i]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
SearchQuadTree(node->children[i],queryRect,ItemSearched);
//node = node->children[i]; //非递归
}
}
}
/*for (int i = 0 ; i < coreNum; i ++)
{
ItemSearched.insert(ItemSearched.end(),pResArr[i].begin(),pResArr[i].end());
}*/
}
void SearchQuadTreePara(vector<QuadNode*> resNodes,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched)
{
int coreNum = omp_get_num_procs();
omp_set_num_threads(coreNum);
vector<int>* searchArrs = new vector<int>[coreNum];
for (int i = 0; i < coreNum; i ++)
{
searchArrs[i].clear();
}
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < resNodes.size(); i ++)
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
for (int j = 0; j < resNodes[i]->nShpCount; j ++)
{
if (queryRect.Contains(resNodes[i]->pShapeObj[j].Box)
|| queryRect.Intersects(resNodes[i]->pShapeObj[j].Box))
{
searchArrs[tid].push_back(resNodes[i]->pShapeObj[j].nID);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < coreNum; i ++)
{
ItemSearched.insert(ItemSearched.end(),
searchArrs[i].begin(),searchArrs[i].end());
}
delete [] searchArrs;
searchArrs = NULL;
}
void PtSearchQTree(QuadNode* node,double cx,double cy,vector<int>& ItemSearched)
{
assert(node);
if (node->nShpCount >0) //节点
{
for (int i = 0; i < node->nShpCount; i ++)
{
if (node->pShapeObj[i].Box.IsPointInRect(cx,cy))
{
ItemSearched.push_back(node->pShapeObj[i].nID);
}
}
}
else if (node->nChildCount >0) //节点
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (node->children[i]->Box.IsPointInRect(cx,cy))
{
PtSearchQTree(node->children[i],cx,cy,ItemSearched);
}
}
}
//找出重复元素的位置
sort(ItemSearched.begin(),ItemSearched.end()); //先排序,默认升序
vector<int>::iterator unique_iter =
unique(ItemSearched.begin(),ItemSearched.end());
ItemSearched.erase(unique_iter,ItemSearched.end());
}
void Insert(long key, MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode)
{
QuadNode *node = pNode; //保留根节点副本
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
//节点有孩子
if (0 < node->nChildCount)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(itemRect))
{
//node = node->children[i];
Insert(key,itemRect,node->children[i]);
}
}
}
//如果当前节点存在一个子节点时
else if (1 == node->nShpCount)
{
MapRect boxs[4];
node->Box.Split(boxs,boxs+1,boxs+2,boxs+3);
//创建四个节点并插入相应的MBR
node->children[UR] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[UL] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[LL] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[LR] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[UR]->Box = boxs[0];
node->children[UL]->Box = boxs[1];
node->children[LL]->Box = boxs[2];
node->children[LR]->Box = boxs[3];
node->nChildCount = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//将当前节点中的要素移动到相应的子节点中
for (int j = 0; j < node->nShpCount; j ++)
{
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(node->pShapeObj[j].Box)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(node->pShapeObj[j].Box))
{
node->children[i]->nShpCount += 1;
node->children[i]->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(node->children[i]->nShpCount*sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
memcpy(node->children[i]->pShapeObj,&(node->pShapeObj[j]),sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
free(node->pShapeObj);
node->pShapeObj = NULL;
node->nShpCount = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(itemRect))
{
if (node->children[i]->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
node->children[i]->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->children[i]->nShpCount);
}
else if (node->children[i]->nShpCount > 0)
{
node->children[i]->nShpCount += 1;
node->children[i]->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(node->children[i]->pShapeObj,
sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->children[i]->nShpCount);
}
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->children[i]->pShapeObj,
&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
}
//当前节点没有空间对象
else if (0 == node->nShpCount)
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->pShapeObj,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
void InsertQuad(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode)
{
assert(pNode != NULL);
if (!IsQuadLeaf(pNode)) //非叶子节点
{
int nCorver = 0; //跨越的子节点个数
int iIndex = -1; //被哪个子节点完全包含的索引号
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (pNode->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
&& pNode->Box.Contains(itemRect))
{
nCorver += 1;
iIndex = i;
}
}
//如果被某一个子节点包含,则进入该子节点
if (/*pNode->Box.Contains(itemRect) ||
pNode->Box.Intersects(itemRect)*/1 <= nCorver)
{
InsertQuad(key,itemRect,pNode->children[iIndex]);
}
//如果跨越了多个子节点,直接放在这个节点中
else if (nCorver == 0)
{
if (pNode->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
else
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(pNode->pShapeObj,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(pNode->pShapeObj+pNode->nShpCount-1,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
//如果是叶子节点,直接放进去
else if (IsQuadLeaf(pNode))
{
if (pNode->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
else
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(pNode->pShapeObj,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(pNode->pShapeObj+pNode->nShpCount-1,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
void InsertQuad2(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode)
{
QuadNode *node = pNode; //保留根节点副本
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
//节点有孩子
if (0 < node->nChildCount)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(itemRect))
{
//node = node->children[i];
Insert(key,itemRect,node->children[i]);
}
}
}
//如果当前节点存在一个子节点时
else if (0 == node->nChildCount)
{
MapRect boxs[4];
node->Box.Split(boxs,boxs+1,boxs+2,boxs+3);
int cnt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (boxs[i].Contains(itemRect))
{
cnt = i;
}
}
//如果有一个矩形包含此对象,则创建四个孩子节点
if (cnt > -1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//创建四个节点并插入相应的MBR
node->children[i] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[i]->Box = boxs[i];
}
node->nChildCount = 4;
InsertQuad2(key,itemRect,node->children[cnt]); //递归
}
//如果都不包含,则直接将对象插入此节点
if (cnt == -1)
{
if (node->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
}
else if (node->nShpCount > 0)
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(node->pShapeObj,
sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
}
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->pShapeObj,
&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
//当前节点没有空间对象
/*else if (0 == node->nShpCount)
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->pShapeObj,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}*/
}
bool IsQuadLeaf(QuadNode* node)
{
if (NULL == node)
{
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (node->children[i] != NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
bool DelFalseNode(QuadNode* node)
{
//如果没有子节点且没有要素
if (node->nChildCount ==0 && node->nShpCount == 0)
{
ReleaseQuadTree(&node);
}
//如果有子节点
else if (node->nChildCount > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
DelFalseNode(node->children[i]);
}
}
return 1;
}
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<int>& resVec)
{
QuadNode *node = quadTree;
int i = 0;
if (NULL != node)
{
//将本节点中的空间对象存储数组中
for (i = 0; i < node->nShpCount; i ++)
{
resVec.push_back((node->pShapeObj+i)->nID);
}
//遍历孩子节点
for (i = 0; i < node->nChildCount; i ++)
{
if (node->children[i] != NULL)
{
TraversalQuadTree(node->children[i],resVec);
}
}
}
}
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<QuadNode*>& arrNode)
{
deque<QuadNode*> nodeQueue;
if (quadTree != NULL)
{
nodeQueue.push_back(quadTree);
while (!nodeQueue.empty())
{
QuadNode* queueHead = nodeQueue.at(0); //取队列头结点
arrNode.push_back(queueHead);
nodeQueue.pop_front();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (queueHead->children[i] != NULL)
{
nodeQueue.push_back(queueHead->children[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
void ReleaseQuadTree(QuadNode** quadTree)
{
int i = 0;
QuadNode* node = *quadTree;
if (NULL == node)
{
return;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
ReleaseQuadTree(&node->children[i]);
}
free(node);
node = NULL;
}
node = NULL;
}
long CalByteQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,long& nSize)
{
if (quadTree != NULL)
{
nSize += sizeof(QuadNode)+quadTree->nChildCount*sizeof(SHPMBRInfo);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (quadTree->children[i] != NULL)
{
nSize += CalByteQuadTree(quadTree->children[i],nSize);
}
}
}
return 1;
}
///
四叉树
介绍
四元树又称四叉树是一种树状数据结构,在每一个节点上会有四个子区块。四元树常应用于二维空间数据的分析与分类。它将数据区分成为四个象限。
今天要介绍的四叉树可以认为是二叉查找树的高维变体,它适合对有二维属性的数据进行存储和查询,当然四叉树存储的也不一定是二维数据,而是有着二维属性的数据,如有着 x,y 信息的点,用它还可以用来存储线和面数据。它有四个叉,在数据插入时,我们通过其二维属性(一般是 x,y)选择四个叉之一继续向下,直至叶子结点,同样使用“四分法”来迅速查找数据。四叉树的一般图形结构如下:
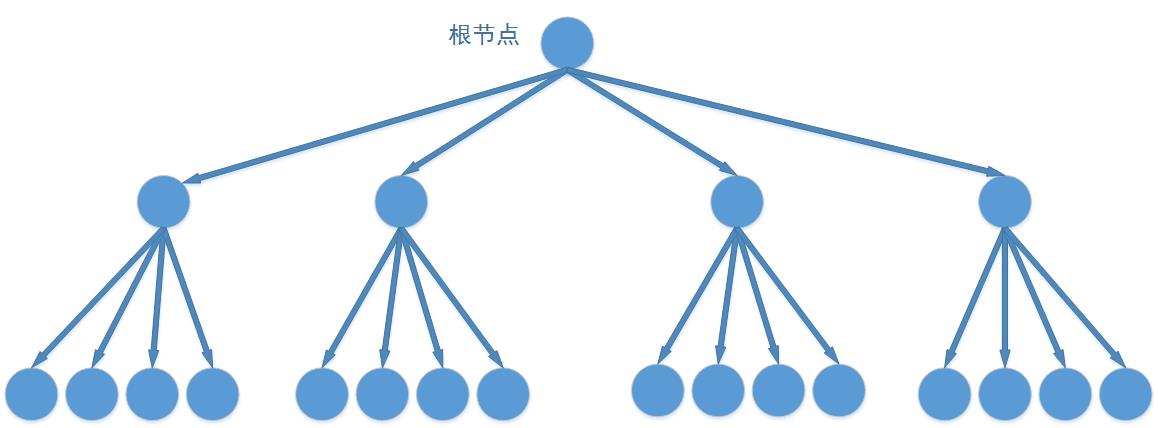
聪明的小伙伴一定想到了适合存储和查询三维数据的八叉树,它们原理是一致的,不过我们暂不讨论。
分类
四叉树常见的应用有图像处理、空间数据索引、2D中的快速碰撞检测、稀疏数据等,今天我们很纯粹地只介绍它在空间索引方面的应用。
根据其存储内容,四叉树可以分为点四叉树、边四叉树和块四叉树,今天我们实现的是点四叉树。
根据其结构,四叉树分为满四叉树和非满四叉树。
对于满四叉树,每个节点都有四个子结点,它有着固定的深度,数据全都存在最底层的子结点中,进行数据插入时不需要分裂。
满四叉树在确定好深度后,进行插入操作很快,可是如果用它来存储下图所示数据,我们会发现,四叉树的好多叉都是空的,当然它们会造成内存空间的大量浪费。

非满四叉树解决了此问题,它为每个结点添加一个“容量”的属性,在四叉树初始化时只有一个根结点,在插入数据时,如果一个结点内的数据量大于了结点“容量”,再将结点进行分裂。如此,可以保证每个结点内都存储着数据,避免了内存空间的浪费。
在查询时,只有找到了位置对应的结点,那么结点下的所有点都会是此位置的附近点,更小的“容量”意味着每个结点内点越少,也就意味着查询的精度会越高。
以下是一个非满点四叉树的实现:
附上 GitHub 仓库地址:枕边书-空间索引
代码实现
首先是数据结构的定义:
树结点:
- struct QuadTreeNode {
- int depth; // 结点深度
- int is_leaf; // 是否是叶子结点
- struct Region region; // 区域范围
- struct QuadTreeNode *LU; // 左上子结点指针
- struct QuadTreeNode *LB; // 左下子结点指针
- struct QuadTreeNode *RU; // 右上子结点指针
- struct QuadTreeNode *RB; // 右下子结点指针
- int ele_num; // 位置点数
- struct ElePoint *ele_list[MAX_ELE_NUM]; // 位置点列表
- };
为了加快插入和查询速度,数据结构设计稍微冗余了一些;
四叉树位置点的插入流程如下图所示:

结点的分裂是重点,这里介绍一下:
- void splitNode(struct QuadTreeNode *node) {
- // 获取xy方向上的中间点,用来初始化子结点的范围
- double mid_vertical = (node->region.up + node->region.bottom) / 2;
- double mid_horizontal = (node->region.left + node->region.right) / 2;
-
- node->is_leaf = 0; // 将是否为叶子结点置为否
- // 填充四个子结点
- node->RU = createChildNode(node, mid_vertical, node->region.up, mid_horizontal, node->region.right);
- node->LU = createChildNode(node, mid_vertical, node->region.up, node->region.left, mid_horizontal);
- node->RB = createChildNode(node, node->region.bottom, mid_vertical, mid_horizontal, node->region.right);
- node->LB = createChildNode(node, node->region.bottom, mid_vertical, node->region.left, mid_horizontal);
-
- // 遍历结点下的位置点,将其插入到子结点中
- for (int i = 0; i < node->ele_num; i++) {
- insertEle(node, *node->ele_list[i]);
- free(node->ele_list[i]);
- node->ele_num--;
- }
- }

更具体的代码见 GitHub 吧,我觉得我代码质量还看得过去,另外方法上面还有详细些的注释。
问题和优化
边界点问题
四叉树还是面临着边界点问题,每个结点内的点必然是相邻的,但相邻的点越不一定在同一个结点内,如下图,A点和B点相邻的很近,如果A点是我们查找的目标点,那么仅仅取出A点所在结点内的所有位置点是不够的,我们还需要查找它的周边结点。
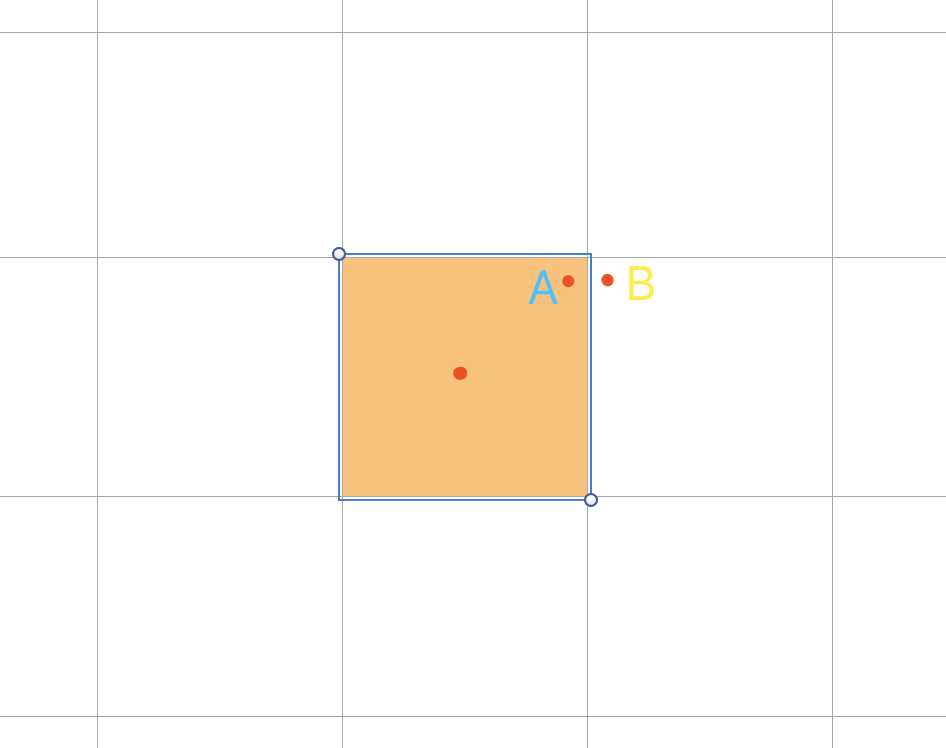
这里我们要介绍四叉树的另一个特性。
字典树
字典树,又称前缀树或trie树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。
我们可以类比字典的特性:我们在字典里通过拼音查找晃(huang)这个字的时候,我们会发现它的附近都是读音为huang的,可能是声调有区别,再往前翻,我们会看到读音前缀为huan的字,再往前,是读音前缀为hua的字... 取它们的读音前缀分别为 h qu hua huan huang。我们在查找时,根据 abc...xyz 的顺序找到h前缀的部分,再根据 ha he hu 找到 hu 前缀的部分...最后找到 huang,我们会发现,越往后其读音前缀越长,查找也越精确,这种类似于字典的树结构就是字典树,也是前缀树。
四叉树也有此特性,我们给每一个子结点都编号,那么每个子结点会继承父结点的编号为前缀,并在此基础上有相对其兄弟结点的独特编号。
与 GeoHash 的相似之处
如果我们给右上、左上、左下、右下四个子结点分别编号为00 01 10 11,那么生成的四叉树就会像:
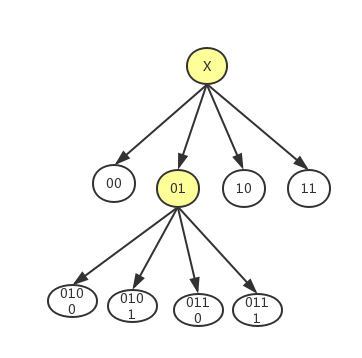
我们在查找到目标结点时,根据其编码获取到其周边八个结点的编码,再获取各个周边结点内的位置点。
看过我上一篇空间索引(详见:空间索引 - GeoHash算法及其实现优化)文章的小伙伴可能会说,这不就是 GeoHash 么?
嗯,这种通过编码来确定周边格子的方式确实跟 GeoHash 是相同的,但不要混淆了他们查找原理上的截然不同:
- GeoHash 本质上是通过格子编码将二维信息用一维来表示,其查找原理从根本上来说是二叉树(B树),在查找时会根据格子编码选择两个方向之一继续精确,查询效率准确来说是
log2N; - 四叉树保留了其二维查找的特性,其查找会根据其 x,y 选择四个方向之一继续查找,忽略方向选择时的计算,其查询效率应该是
log4N;
我们可以使用此方法来继续优化四叉树,给结点添加一个“编号”属性即可,由于时(bo)间(zhu)关(fan)系(lan),这里不再实现了。
小结
由于 C 语言的高效率,由它实现的四叉树效率极高。 进行十万数据的插入和一次查询总操作为 7毫秒。在数据量更大的插入时,因为要进行结点的多次分裂,效率会有所下降,进行了8百万数据的测试插入需要两分钟多一些(16年的 mac pro),至于查询,都是一些内存寻址操作,时间可以忽略不计了。 更大量级的测试就不跑了,跑的时候散热风扇速转系统温度迅速上升。。。
不过这么高的效率是因为这些都是内存操作,真正的数据库中数据肯定是要落地的,那时候更多的就是些磁盘和 IO 操作了,效率也会有所下降,但最终的效率和结点数据的扩展能力,与 GeoHash 相比,还是四叉树更好一些。


