- 1用Python开发了一个一建、一造、二建等职考拍照搜题神器_拍照搜题代码
- 2C语言文件操作入门_什么语言可以在文档中使用
- 3信号处理(二)——每比特6dB的信噪比是怎么来的_量化样本每增加一位,信噪比提高6db
- 4使用自己的数据基于SWIFT微调Qwen-Audio-Chat模型_swfit 微调过的模型怎么用
- 5五一国际劳动节快乐
- 6阿里通义千问:本地部署Qwen1.5开源大模型
- 7SQL优化之EXPLAIN执行计划(转载)_sql执行计划 explain
- 8完美解决AndroidStudio错误:Installed Build Tools revision xxx is corrupted. Remove and install again_installed build tools revision 34.0.0 is corrupted
- 9Elasticsearch Pipeline 详解_es pipeline
- 10java设计并完成一个数据驱动的管理系统_用java和数据库做一个管理系统
spring 静态方法使用bean实例_spring 静态方法中引用bean
赞
踩
与第三方做交互时,封装了一个HttpUtil,由于开发和测试的地址不一样,所以准备将对应的一些属性写在配置文件里, 但是 Util 嘛,还是想通过静态方法调用,那么我们能不能将配置文件的属性读取到工具类的静态方法呢?
spring 生命周期
Bean的完整生命周期经历了各种方法调用,这些方法可以划分为以下几类:
Bean自身的方法:包括Bean本身调用的方法和通过配置文件中< bean>的init-method和destroy-method指定的方法。
Bean级生命周期接口方法: 包括BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware,也包括InitializingBean和DiposableBean这些接口的方法(可以被@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解替代)。
容器级生命周期接口方法: 包括InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 BeanPostProcessor 两个接口实现,一般称它们的实现类为“后处理器”。
工厂后处理器接口方法: 包括AspectJWeavingEnabler, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, CustomAutowireConfigurer等非常有用的工厂后处理器接口的方法。工厂后处理器也是容器级的。在应用上下文装配配置文件之后立即调用。
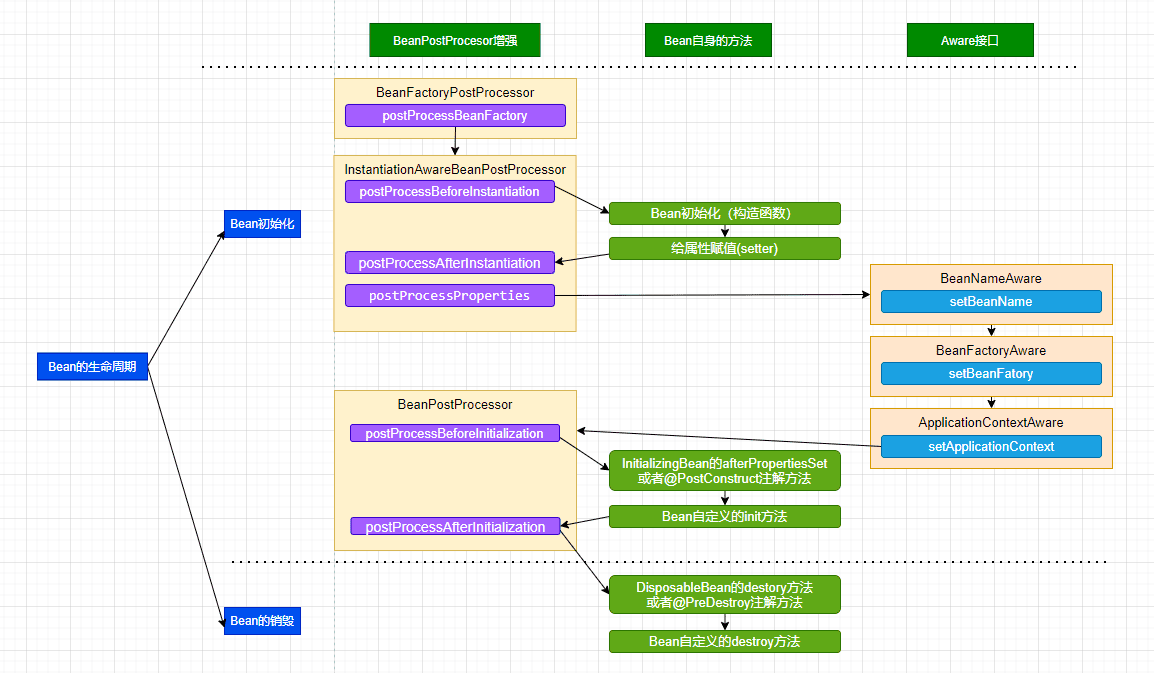
具体流程如下:
-
如果 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联, 则调用postProcessBeanFactory方法.(即首先尝试从Bean工厂中获取Bean)
-
如果 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
-
根据配置情况调用 Bean 构造方法实例化 Bean。
-
利用依赖注入完成 Bean 中所有属性值的配置注入。
-
如果 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则调用postProcessAfterInstantiation方法和postProcessProperties
-
调用xxxAware接口 (上图只是给了几个例子)
- 第一类Aware接口
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 Bean 的 setBeanName() 方法传入当前 Bean 的 id 值。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanClassLoaderAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setBeanClassLoader() 方法传入classLoader的引用。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setBeanFactory() 方法传入当前工厂实例的引用。
- 第二类Aware接口
- 如果 Bean 实现了 EnvironmentAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setEnvironment() 方法传入当前 Environment 实例的引用。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 EmbeddedValueResolverAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setEmbeddedValueResolver() 方法传入当前 StringValueResolver 实例的引用。
- 如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口,则 Spring 调用 setApplicationContext() 方法传入当前 ApplicationContext 实例的引用。
- 第一类Aware接口
-
如果 BeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则 Spring 将调用该接口的预初始化方法 postProcessBeforeInitialzation() 对 Bean 进行加工操作,此处非常重要,Spring 的 AOP 就是利用它实现的。
-
如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,则 Spring 将调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。(或者有执行@PostConstruct注解的方法), 在此处可以进行静态类的属性配置
-
如果在配置文件中通过 init-method 属性指定了初始化方法,则调用该初始化方法。
-
如果 BeanPostProcessor 和 Bean 关联,则 Spring 将调用该接口的初始化方法 postProcessAfterInitialization()。此时,Bean 已经可以被应用系统使用
-
如果在 < bean> 中指定了该 Bean 的作用范围为 scope=“singleton”,则将该 Bean 放入 Spring IoC 的缓存池中,将触发 Spring 对该 Bean 的生命周期管理;如果在 < bean> 中指定了该 Bean 的作用范围为 scope=“prototype”,则将该 Bean 交给调用者,调用者管理该 Bean 的生命周期,Spring 不再管理该 Bean。
-
如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,则 Spring 会调用 destory() 方法将 Spring 中的 Bean 销毁;(或者有执行@PreDestroy注解的方法)
-
如果在配置文件中通过 destory-method 属性指定了 Bean 的销毁方法,则 Spring 将调用该方法对 Bean 进行销毁。
了解了spring生命周期后,开始进行实践,以如下配置为例,在静态类中打印配置文件的属性。
server:
port: 36321
servlet:
context-path: /
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
属性类,进行配置文件属性的注入
import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Data @Component public class RequestProperty { @Value("${server.port}") public String port; @Value("${server.servlet.context-path}") public String contextPath; public static String NAME = "name"; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
静态类实现InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware接口,进行属性的初始化(实例注入)
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class PropertiesUtil implements InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext; private static RequestProperty perporty; @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() { perporty = applicationContext.getBean(RequestProperty.class); } @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public static void printProperty() { System.out.println("*********打印配置属性开始*******"); System.out.println(perporty.getPort()); System.out.println(perporty.getContextPath()); System.out.println(RequestProperty.NAME); System.out.println("*********打印配置属性结束*******"); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
测试类,调用静态类的静态方法
方式一:定时任务调用
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@EnableScheduling
@Component
public class SpringBeanTask {
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 10000)
public void excute() {
PropertiesUtil.printProperty();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
方式二: 监听 spring 容器启动
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments; import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 监听Spring容器启动完成,完成后执行属性打印 **/ @Component public class ProertiesUtilListener implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { PropertiesUtil.printProperty(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18





