- 1Vue-cli3从环境部署到打包上传到服务器_vue3 打包项目部署到服务器
- 2单节点的es添加另外一个节点组成主从集群
- 3Axure中继器案例:中继器的repeater属性,中继器的Item属性_axure 中继器 isfirst index
- 4PS故障风海报制作技术分享_学习故障风海报制作的心得
- 5三维点云重建 — open3d python_点云三维重建
- 6机器学习笔记(二):回归分析_通过分析不同的因素对研究生录取的影响来预测一个人是否会被录取。其中自变量入学
- 7WPF将Xml数据源序列化到 ObservableCollection
类型集合上_.net xml observalcollection - 8Systemverilog 第十课 随机化_verilog产生随机数互不相同
- 9基于SPH的流体仿真过程_csdn爱吃小笼包
- 10本地部署 ChatGLM3_chatglm3 github
ISAT制作YOLOv5实例分割数据集_isat with seg
赞
踩
1.软件安装与使用
ISAT为segment anything衍生的半自动分割标注软件,github地址:https://github.com/yatengLG/ISAT_with_segment_anything.git
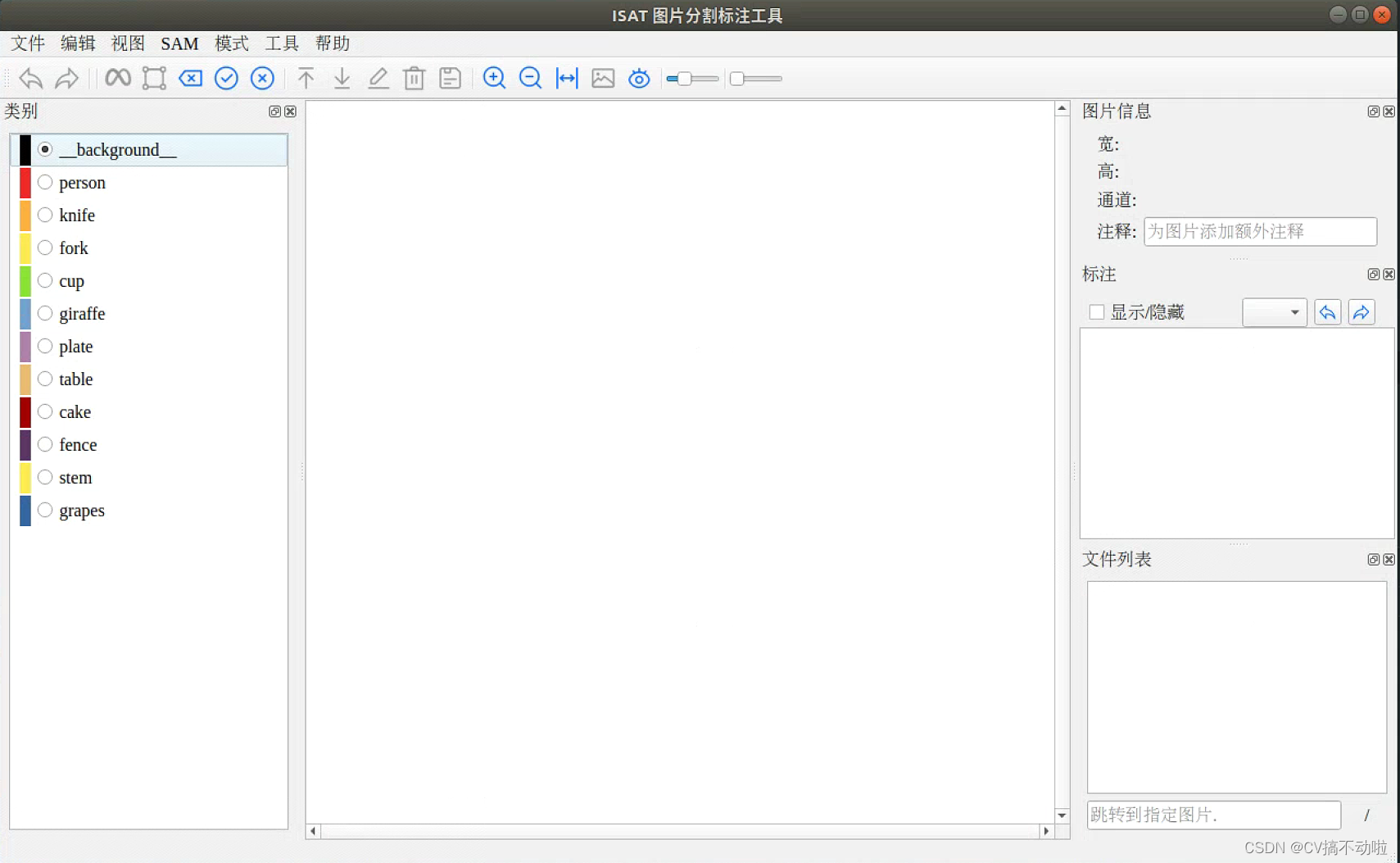
按照作者的readme安装好相应的依赖以及对应的权重,软件界面如下:
使用过程:
1.选取图片文件夹
2.确定标签保存文件夹
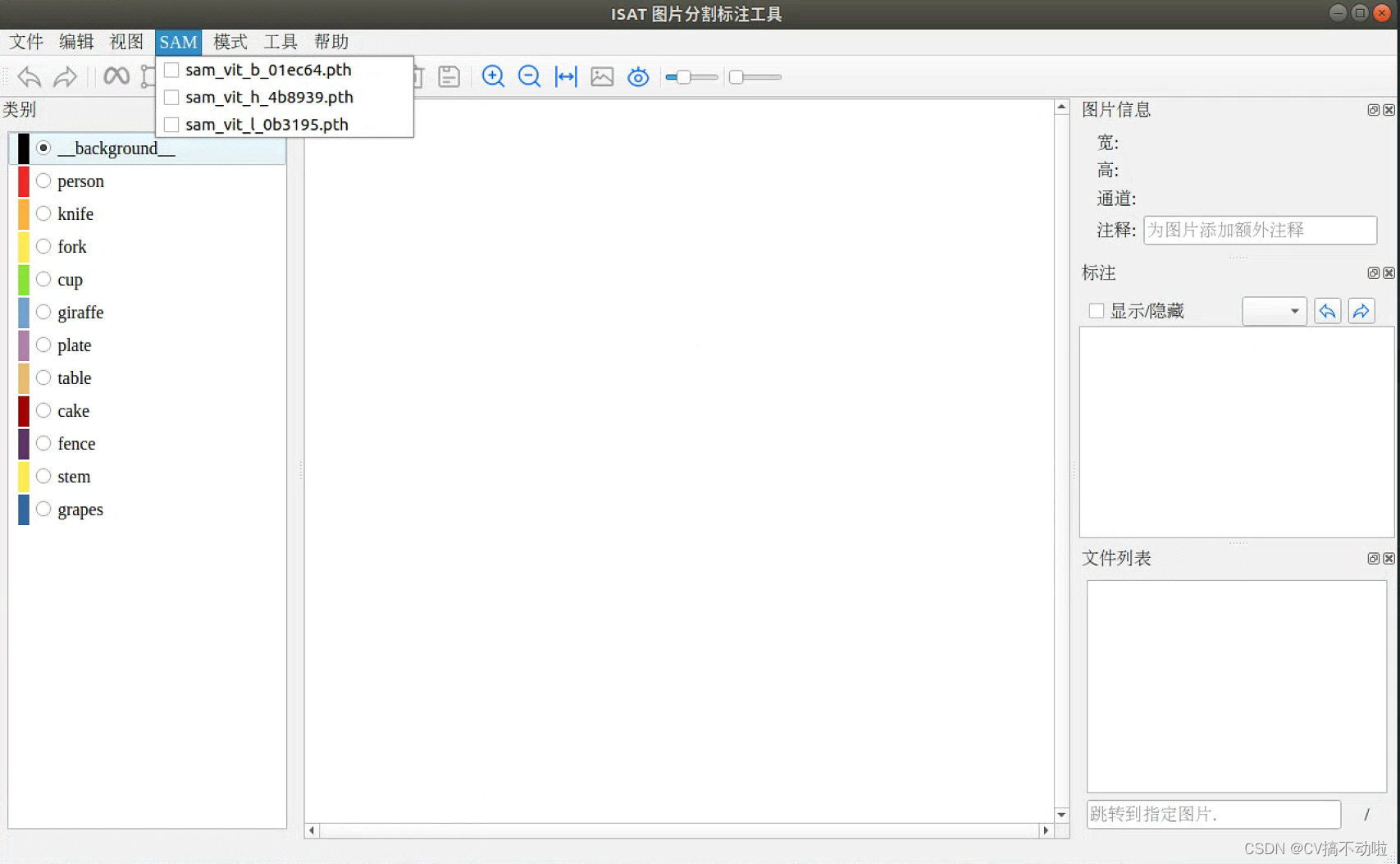
3.点击SAM,选择下载好的模型(完成标注前的准备工作)
快捷键:
Q:开始标注
E:完成标注
S:保存标签
Z:返回上一步
A:上一张图片
D:下一张图片
鼠标左键:选取感兴趣区域
鼠标右键:选取不感兴趣区域
标注实例:

选取对勾完成标注,按S保存标签,标签文件为json格式,但与COCO格式不相同,软件自带ISAT转成COCO格式,但有bug,没用;
2.数据类型转换
以下为另一个GitHub地址:GitHub - mushroom-x/SegConvert: 实例分割标注文件格式转换脚本工具集
针对ISAT转COCO格式,另外也包括直接转成YOLO格式。
将下面代码中的路径改成前面的图片路径和标签路径,将标签名和序号改为自己的类别名。
ISAT2COCO:
- import json
- import os
- import numpy as np
- from collections import defaultdict
-
- # ISAT标注数据路径
- ISAT_FOLDER = "./annotations"
- # 图像所在的路径
- IMAGE_FOLDER = "./images"
- # COCO格式的JSON文件存放路径
- # 可以自己指定,这里是直接定义在图像文件夹下
- COCO_PATH = os.path.join(IMAGE_FOLDER, "coco.json")
-
- # 定义类别名称与ID号的映射
- # 需要注意的是,不需要按照ISAT的classesition.txt里面的定义来
- # 可以选择部分自己需要的类别, ID序号也可以重新填写(从0开始)
- category_mapping = {"color_block": 0}
- # 定义COCO格式的字典
- # - "info"/"description" 里面写一下,你这个是什么的数据集
- coco = {
- "info": {
- "description": "Color Block Segmentation",
- "version": "1.0",
- "year": 2023,
- "contributor": "",
- "date_created": ""
- },
- "images": [],
- "annotations": [],
- "categories": []
- }
- # 填写annotations栏目
- for class_id, class_name in category_mapping.items():
- coco["categories"].append({"id": class_id, "name": class_name, "supercategory": "object"})
- # 图像序号
- image_id = 1
- # 遍历所有的ISAT文件夹
- for filename in os.listdir(ISAT_FOLDER):
- # 判断是否为ISAT格式数据
- if not filename.endswith(".json"):
- continue
- # 载入ISAT数据
- with open(os.path.join(ISAT_FOLDER, filename), "r") as f:
- isat = json.load(f)
- # 获取图像名称
- image_filename = isat["info"]["name"]
-
- # 填写文件路径
- image_path = os.path.join(IMAGE_FOLDER, image_filename)
- image_info = {
- "id": image_id,
- "file_name": image_filename,
- "width": isat["info"]["width"],
- "height": isat["info"]["height"]
- }
- image_id += 1
- # 添加图像信息
- coco["images"].append(image_info)
- # 标注序号
- annotation_id = 1
- # 遍历标注信息
- for annotation in isat["objects"]:
- # 获取类别名称
- category_name = annotation["category"]
- # 位置类别名称(选择跳过)
- if category_name not in category_mapping:
- # print(f"未知类别名称: {category_name}")
- continue
- # 获取类别ID
- category_id = category_mapping[category_name]
- # 提取分割信息
- segmentation = annotation["segmentation"]
- segmentation = np.uint32(segmentation)
- # 转换为一行的形式 [[x1, y1, x2, y2, ..., xn, yn]]
- segmentation = [(segmentation.reshape(-1)).tolist()]
- # 提取面积信息
- area = annotation["area"]
- # 定义标注信息
- annotation_info = {
- "id": annotation_id,
- "image_id": image_id,
- "category_id": category_id,
- "segmentation": segmentation,
- "area": area,
- "iscrowd": 0
- }
- # 追加到annotations列表
- coco["annotations"].append(annotation_info)
- # 标注编号自增1
- annotation_id += 1
- # 保存coco格式
- with open(COCO_PATH, "w") as f:
- json.dump(coco, f)

运行结果是生成一个json文件。
ISAT2YOLO:
- import json
- import os
-
- # 定义类别名称与ID号的映射
- # 需要注意的是,不需要按照ISAT的classesition.txt里面的定义来
- # 可以选择部分自己需要的类别, ID序号也可以重新填写(从0开始)
- category_mapping = {"color_block": 0}
- # ISAT格式的实例分割标注文件
- ISAT_FOLDER = "./annotations/"
- # YOLO格式的实例分割标注文件
- YOLO_FOLDER = "./labels"
-
- # 创建YoloV8标注的文件夹
- if not os.path.exists(YOLO_FOLDER):
- os.makedirs(YOLO_FOLDER)
-
- # 载入所有的ISAT的JSON文件
- for filename in os.listdir(ISAT_FOLDER):
- if not filename.endswith(".json"):
- # 不是json格式, 跳过
- continue
- # 载入ISAT的JSON文件
- with open(os.path.join(ISAT_FOLDER, filename), "r") as f:
- isat = json.load(f)
- # 提取文件名(不带文件后缀)
- image_name = filename.split(".")[0]
- # Yolo格式的标注文件名, 后缀是txt
- yolo_filename = f"{image_name}.txt"
- # 写入信息
- with open(os.path.join(YOLO_FOLDER, yolo_filename), "w") as f:
- # 获取图像信息
- # - 图像宽度
- image_width = isat["info"]["width"]
- # - 图像高度
- image_height = isat["info"]["height"]
- # 获取实例标注数据
- for annotation in isat["objects"]:
- # 获取类别名称
- category_name = annotation["category"]
- # 如果不在类别名称字典里面,跳过
- if category_name not in category_mapping:
- continue
- # 从字典里面查询类别ID
- category_id = category_mapping[category_name]
- # 提取分割信息
- segmentation = annotation["segmentation"]
- segmentation_yolo = []
- # 遍历所有的轮廓点
- for segment in segmentation:
- # 提取轮廓点的像素坐标 x, y
- x, y = segment
- # 归一化处理
- x_center = x/image_width
- y_center = y/image_height
- # 添加到segmentation_yolo里面
- segmentation_yolo.append(f"{x_center:.4f} {y_center:.4f}")
- segmentation_yolo_str = " ".join(segmentation_yolo)
- # 添加一行Yolo格式的实例分割数据
- # 格式如下: class_id x1 y1 x2 y2 ... xn yn\n
- f.write(f"{category_id} {segmentation_yolo_str}\n")

运行结果是所有标签对应的txt文件

第一个为标签编号,后面的数为标签点的归一化坐标。
3.训练集、验证集、测试集划分
代码:main函数的default内填入对应的自定义路径
- # 将图片和标注数据按比例切分为 训练集和测试集
- import shutil
- import random
- import os
- import argparse
-
- # 检查文件夹是否存在
- def mkdir(path):
- if not os.path.exists(path):
- os.makedirs(path)
-
-
- def main(image_dir, txt_dir, save_dir):
- # 创建文件夹
- mkdir(save_dir)
- images_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'images')
- labels_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'labels')
-
- img_train_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'train')
- img_test_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'test')
- img_val_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'val')
-
- label_train_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'train')
- label_test_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'test')
- label_val_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'val')
-
- mkdir(images_dir);mkdir(labels_dir);mkdir(img_train_path);mkdir(img_test_path);mkdir(img_val_path);mkdir(label_train_path);mkdir(label_test_path);mkdir(label_val_path);
-
-
- # 数据集划分比例,训练集75%,验证集15%,测试集15%,按需修改
- train_percent = 0.8
- val_percent = 0.1
- test_percent = 0.1
-
-
- total_txt = os.listdir(txt_dir)
- num_txt = len(total_txt)
- list_all_txt = range(num_txt) # 范围 range(0, num)
-
- num_train = int(num_txt * train_percent)
- num_val = int(num_txt * val_percent)
- num_test = num_txt - num_train - num_val
-
- train = random.sample(list_all_txt, num_train)
- # 在全部数据集中取出train
- val_test = [i for i in list_all_txt if not i in train]
- # 再从val_test取出num_val个元素,val_test剩下的元素就是test
- val = random.sample(val_test, num_val)
-
- print("训练集数目:{}, 验证集数目:{},测试集数目:{}".format(len(train), len(val), len(val_test) - len(val)))
- for i in list_all_txt:
- name = total_txt[i][:-4]
-
- srcImage = os.path.join(image_dir, name+'.jpg')
- srcLabel = os.path.join(txt_dir, name + '.txt')
-
- if i in train:
- dst_train_Image = os.path.join(img_train_path, name + '.jpg')
- dst_train_Label = os.path.join(label_train_path, name + '.txt')
- shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_train_Image)
- shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_train_Label)
- elif i in val:
- dst_val_Image = os.path.join(img_val_path, name + '.jpg')
- dst_val_Label = os.path.join(label_val_path, name + '.txt')
- shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_val_Image)
- shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_val_Label)
- else:
- dst_test_Image = os.path.join(img_test_path, name + '.jpg')
- dst_test_Label = os.path.join(label_test_path, name + '.txt')
- shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_test_Image)
- shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_test_Label)
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- """
- python split_datasets.py --image-dir my_datasets/color_rings/imgs --txt-dir my_datasets/color_rings/txts --save-dir my_datasets/color_rings/train_data
- """
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='split datasets to train,val,test params')
- parser.add_argument('--image-dir', default = '', type=str, help='image path dir')
- parser.add_argument('--txt-dir', default = '', type=str, help='txt path dir')
- parser.add_argument('--save-dir', default = '', type=str, help='save dir')
- args = parser.parse_args()
- image_dir = args.image_dir
- txt_dir = args.txt_dir
- save_dir = args.save_dir
-
- main(image_dir, txt_dir, save_dir)

完成数据集划分
4.yolov5模型训练
data文件夹里面有yaml文件,下面图片是data/coco128-seg.yaml的内容。
path:是上面--save-dir切分图片存放的路径;
train、val、test分别对于images里面的文件夹,按实际填入;
names:是类别名称和赋予的下标,跟上面转txt顺序相同

完成数据集的创建
训练:
python segment/train.py --epochs 300 --data coco128-seg.yaml --weights yolov5m-seg.pt --img 640 --cfg models/segment/yolov5m-seg.yaml --batch-size 16 --device 2参考链接:YOLOv5-7.0实例分割训练自己的数据,切分mask图并摆正_yolov5图像分割_jin__9981的博客-CSDN博客


