- 1Unity3D RPG实现 2 —— 背包系统_unity背包系统
- 2(一)UDP基本编程步骤_pb udp编程
- 3[Emuelec]在gamelist.xml中,为中文游戏名生成拼音字母
- 4时序预测 | Python基于Multihead-Attention-TCN-LSTM的时间序列预测_multiheadattention 时序预测
- 5Pytorch ----- 卷积神经网络 CNN --基础部分(卷积层,池化层 下采样) 附代码解读+实现~~学习笔记_pytorch下采样
- 6python|gdal实现按掩膜提取影像/裁剪影像_gdal 掩膜 shp
- 7直方图均衡化C++实现_直方图均衡化 c++
- 8【Docker系列】4.docker-compose文件如何传递参数_docker-compose 传参
- 9python启动后台程序_Windows 下后台运行 Python 程序
- 10iOS:详解MJRefresh刷新加载更多数据的第三方库_ios 无痕加载更多数据
【记录】定时器ScheduledExecutorService
赞
踩
ScheduledExecutorService
ScheduledExecutorService是一个定时器,可以用来将任务安排在指定的时间后执行,或者周期性的执行一个任务。
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService
- 1
可以看到该类是一个抽象类,并且继承了ExecutorService接口。
该类的主要方法:
| 方法名 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) | 该方法用于创建并执行给定的delay时间后的command任务,只执行一次 |
| schedule(Callable callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit) | 同上,该方法用于创建并执行给定的delay时间后的callable任务,只执行一次 |
| scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit) | 周期执行任务的方法。会在给定的初始的initialDelay时间后执行第一次任务,之后根据period时间周期执行任务 |
| scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay,TimeUnit unit) | 同上,周期执行任务的方法。会在给定的初始的initialDelay时间后执行第一次任务,之后根据delay时间周期执行任务 |
主要区别就是scheduleAtFixedRate与scheduleWithFixedDelay方法,它们都会根据任务的执行时间以其周期执行时间delay|period来取决下一次何时执行,后面也主要讨论这两个方法。
该类的继承树:
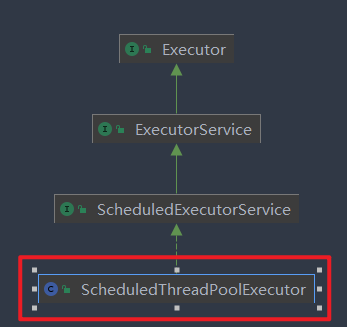
可以看到,我们常用的定时任务线程池ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor就实现了该类。
scheduleAtFixedRate
如果任务的执行时间与给定的周期执行时间period相同,scheduleAtFixedRate与scheduleWithFixedDelay方法是没有区别的,都会在给定的周期执行时间到了后执行任务。现在主要讨论两者时间大小不一样的情况。
- 测试1,当任务的执行时间大于周期执行时间period
public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); TimerTask run = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { try { // 让线程睡眠 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String date = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()); System.out.println("当前运行时间为:" + date); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(run, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:46:12
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:46:17
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:46:22
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:46:27
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:46:32
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以看到,当任务的执行时间大于周期执行时间period,线程会在当前任务执行完后立即执行下一次任务。
- 测试2,当任务的执行时间小于周期执行时间period
public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); TimerTask run = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { try { // 让线程睡眠 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String date = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()); System.out.println("当前运行时间为:" + date); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(run, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:55:14
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:55:19
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:55:24
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:55:29
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:55:34
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以看到,当任务的执行时间小于周期执行时间period,线程会在给定的周期执行时间5秒后执行下一次任务。
scheduleWithFixedDelay
- 测试1,当任务的执行时间大于周期执行时间delay
public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); TimerTask run = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { try { // 让线程睡眠 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String date = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()); System.out.println("当前运行时间为:" + date); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(run, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:57:52
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:58:00
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:58:08
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:58:16
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 10:58:24
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以看到,当任务的执行时间大于周期执行时间delay,线程会在当前任务执行完成后,才开始用周期执行时间delay计算下一次的任务执行时间。
- 测试1,当任务的执行时间小于周期执行时间delay
public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); TimerTask run = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { try { // 让线程睡眠 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String date = simpleDateFormat.format(new Date()); System.out.println("当前运行时间为:" + date); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }; scheduledExecutorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(run, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 11:01:08
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 11:01:16
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 11:01:24
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 11:01:32
当前运行时间为:2023-02-23 11:01:40
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以看到,当任务的执行时间小于周期执行时间delay,与当任务的执行时间大于周期执行时间delay的结果一样,线程会在当前任务执行完成后,才开始用周期执行时间delay计算下一次的任务执行时间。
所以,scheduleWithFixedDelay会在一个任务执行的终止和下一个任务执行的开始之间使用给定的延迟delay。



