- 1网格布局中 justify-self align-self 和 place-self
- 2GDB调试之多进程/线程_detach的线程怎么gdb
- 3通过fail2ban服务监控frps日志实现禁止非法IP
- 4Harmony随笔-资源引用_color.json位置
- 5云打码实现验证码识别_云打码官网登录
- 6Android RecyclerView 使用完全解析 体验艺术般的控件
- 7解决HarmonyOS Device has not been authorized. Error while Deploying HAP_! device a7j5t16112002616 is not authorized.
- 8jupyter中python3如何导入文件_python之jupyter安装与使用
- 9Qt5.14.2-Linux平台配置Qt Creator的ARM体系结构Linux交叉编译器_qt 5.14.2 arm
- 10数据资产管理活动职能_一方面以新建系统或重构系统为契机,实施数据标准的“强管控”,基于数据建模工具打
Java小白必备之异常详解(try-catch、throws)_java 中try h和throw
赞
踩
1、异常概述
什么是异常?java提供的异常处理机制有什么用?
程序运行发生不正常的情况,而这种不正常的情况叫做:异常。java语言是很完善的语言,提供了异常的处理方式,以下程序执行过程中出现了不正常的情况,java把该异常信息打印1输出到控制台,供程序员参考。程序员看到异常信息之后,可以对程序进行修改,让程序更加健壮。
以下程序执行控制太打印的信息被称为异常信息,这个信息是JVM打印的。

2、异常分类
Throwable 是 Java 语言中所有错误或异常的超类,在 Java 中只有 Throwable 类型的实例才可以被抛出(throw)或者捕获(catch),它是异常处理机制的基本组成类型。
实例分为 Error 和 Exception 两种。
2.1、Error
Error表示编译时和系统错误,表示系统在运行期间出现了严重的错误,属于不可恢复的错误,应用程序不会抛出该类对象。如果出现了这样的错误,除了告知用户,剩下的就是尽力使程序安全的终止。
2.2、Exception
Exception又分为编译时异常和运行时异常,而按照编译器检查方式划分,异常又可以分为检查型异常(CheckedException)和非检查型异常 (UncheckedException)。
常见的RuntimeException(运行时异常)包括
- NullPointerException(空指针异常)
- ClassCastException(类型转换异常)
- IndexOutOfBoundsException(越界异常),
- IllegalArgumentException(非法参数异常)
- ArrayStoreException(数组存储异常)
- AruthmeticException(算术异常)
- BufferOverflowException(缓冲区溢出异常)
常见的非运行时异常有 :
- IOException (IO异常),
- SQLException(SQL异常),
- InterruptedException(中断异常),
- ParseException(解析异常).
3、异常处理
Java采用的异常处理机制,是将异常处理的程序代码集中在一起,与正常代码分开,使程序简洁、优雅、并易于维护。
异常处理的两种方式:
- 在方法声明的位置上,使用throws关键字,抛给上一级。
- 使用try…catch语句进行异常捕捉。
3.1、try…catch方式处理
try…catch整体格式
finally不一定要写

使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
try {
int c = a/b;
System.out.println(c);
}catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("出现数学运算异常");
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

如果catch填写的异常类型不匹配,就不会进入

常用的异常对象处理的方式
1.getMessage()

2.printStackTrace()

在try结构中声明的变量,在try’结构之外无法调用

解决

1. 使用try-catch将可能出现的异常代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,就会生成一个对应异常类得对象,根据此对象得类型,去catch中匹配。
2. 一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中处理。一旦处理完成,就跳出当前的try-catch结构(没有finally的情况下)。
3. catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类关系,则谁声明在上,在下无所谓,catch中的异常类型如果有子父类关系,则要求子类一定声明在父类上面。否则报错。
finally
finally中的代码是最后执行的,有保障,并且是一定会执行的,即使try语句块中的代码出现了异常。
finally必须和try一起出现,不能单独编写。
public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("hello.txt"); String str = null; //一定出现空指针异常 str.toString(); System.out.println("hello"); fileInputStream.close(); }catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (NullPointerException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("hello皮皮虾"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
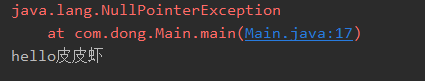
问题:str.toString();报异常,System.out.println(“hello”);和fileInputStream.close();都不会执行,流不会关闭,这非常危险。
解决方式——>使用finally
public static void main(String[] args) { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("hello.txt"); String str = null; //一定出现空指针异常 str.toString(); System.out.println("hello"); }catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (NullPointerException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (fileInputStream != null) { //避免空指针异常 try { fileInputStream.close(); System.out.println("流关闭了"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println("hello皮皮虾"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
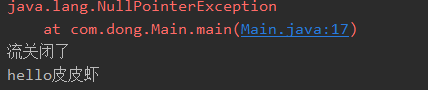
3.2、throws方式处理
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ try { test(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void test() throws IOException { FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("hello.txt"); String str = null; //一定出现空指针异常 str.toString(); System.out.println("hello"); fileInputStream.close(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
throws + 异常类型 写在方法的声明处。指明此方法执行时,可能会抛出的异常类型。一旦方法体执行时,出现异常,仍会在异常代码处生成一个异常类的对象,此对象满足thorws后异常类型时,就会被抛出。异常代码后续的代码就不执行。
throws()的方式只是将异常抛给了方法的调用者。并没有真正将异常处理掉,而try-catch-finally才是真正的将异常给处理掉了。
4、自定义异常
如何自定义异常类?
1. 继承于现有的异常结构:RuntimeException、Exception
2. 提供全局变量:serialVersionUID
3. 提供重载的构造器
public class MyException extends RuntimeException{
static final long serialVersionUID = -70348923766939L;
public MyException() {
}
public MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
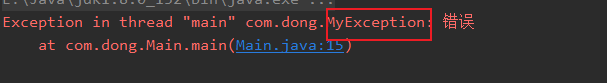
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
int id = -1;
if (id > 0) {
System.out.println("正确");
}else {
throw new MyException("错误");
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
觉得博主写的不错的读者大大们,可以点赞关注和收藏哦,谢谢各位!



