热门标签
当前位置: article > 正文
自然语言处理前馈网络理论与实验
作者:木道寻08 | 2024-07-08 23:03:01
赞
踩
自然语言处理前馈网络理论与实验
目录
前言
近日在学习自然语言处理课程,以及自然语言处理实验课程,编辑此博客,以记录、梳理实验内容。各位同学也可以参考本文,共勉。
一、实验介绍
1、实验内容
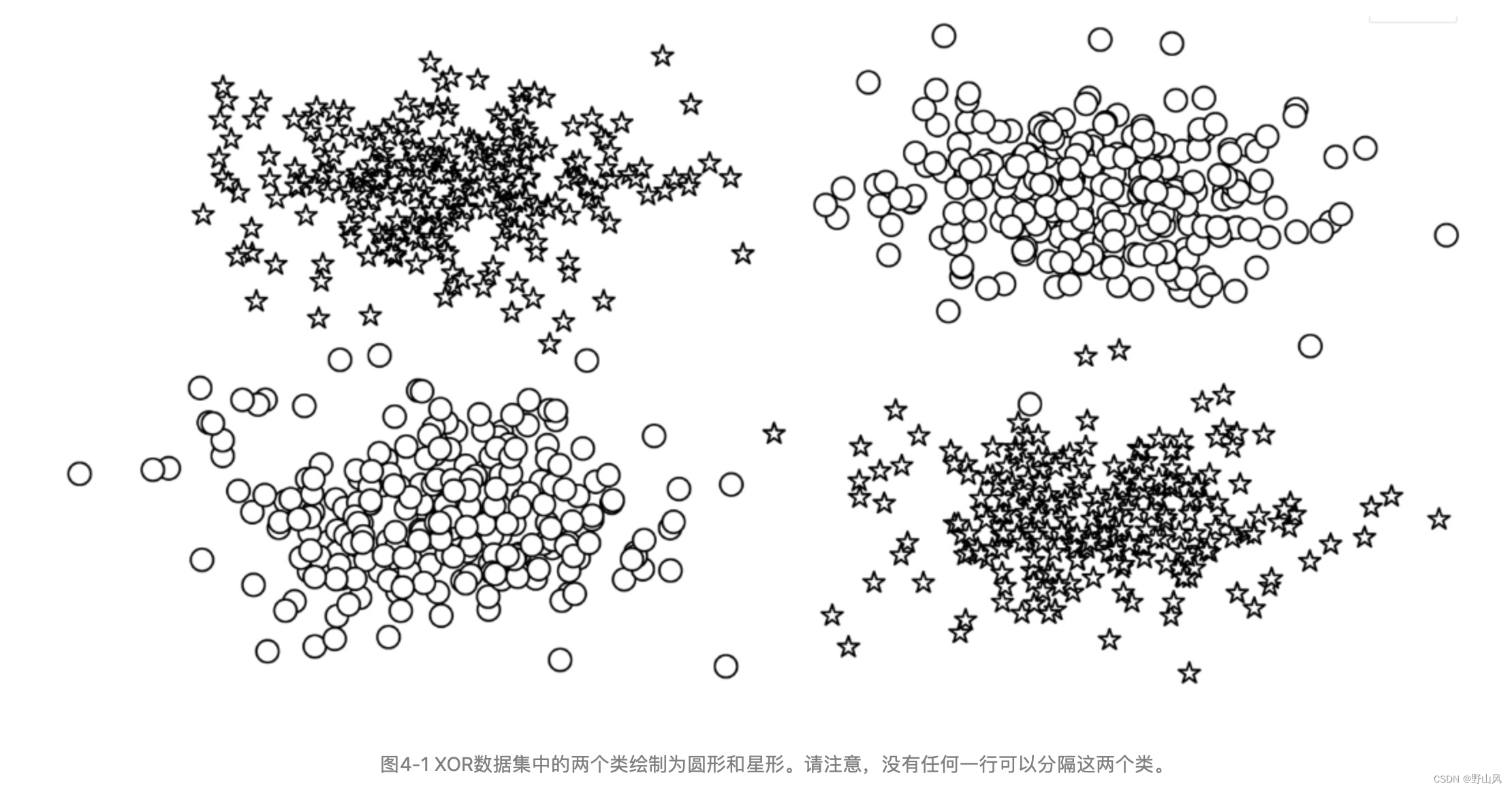
无法线性可分区别数据的时候,感知器无法成功起到作用,所以我们要学习前馈神经网络和多层感知器来解决问题。图4-1
分别通过“带有多层感知器的姓氏分类”和“使用CNN的姓氏分类”展示他们在多层分类中的作用,并理解其原理。

2、实验要点
*通过“示例:带有多层感知器的姓氏分类”,掌握多层感知器在多层分类中的应用2
*掌握每种类型的神经网络层对它所计算的数据张量的大小和形状的影响
3、实验环境
* Python 3.6.7
二、多层感知器
1、多层感知器原理
多层感知器(MLP)被认为是最基本的神经网络构建模块之一。图4-2解释多层感知器的处理过程和组成原理。
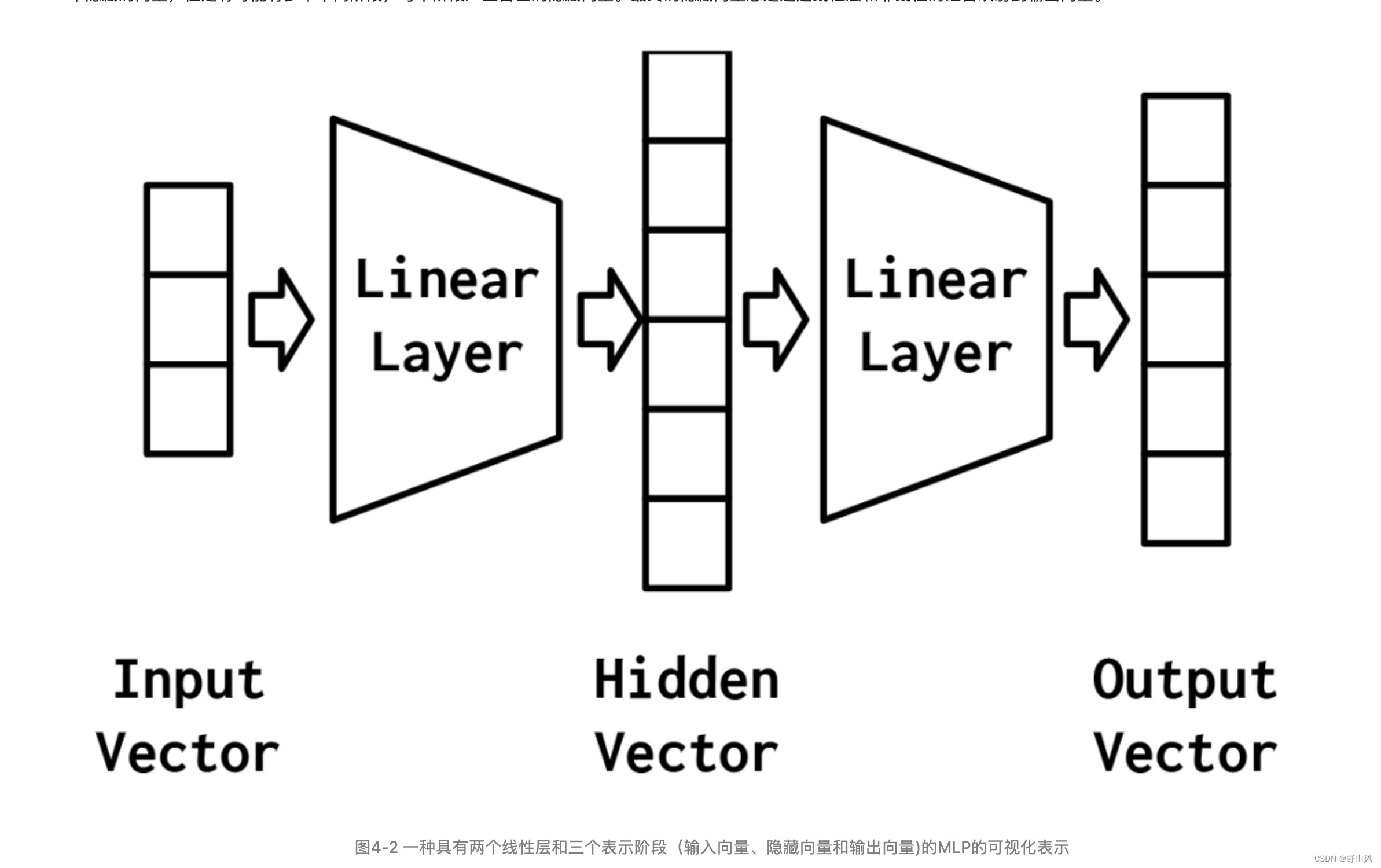
图4-3为感知器和MLP对XOR问题的解决方案效果区别
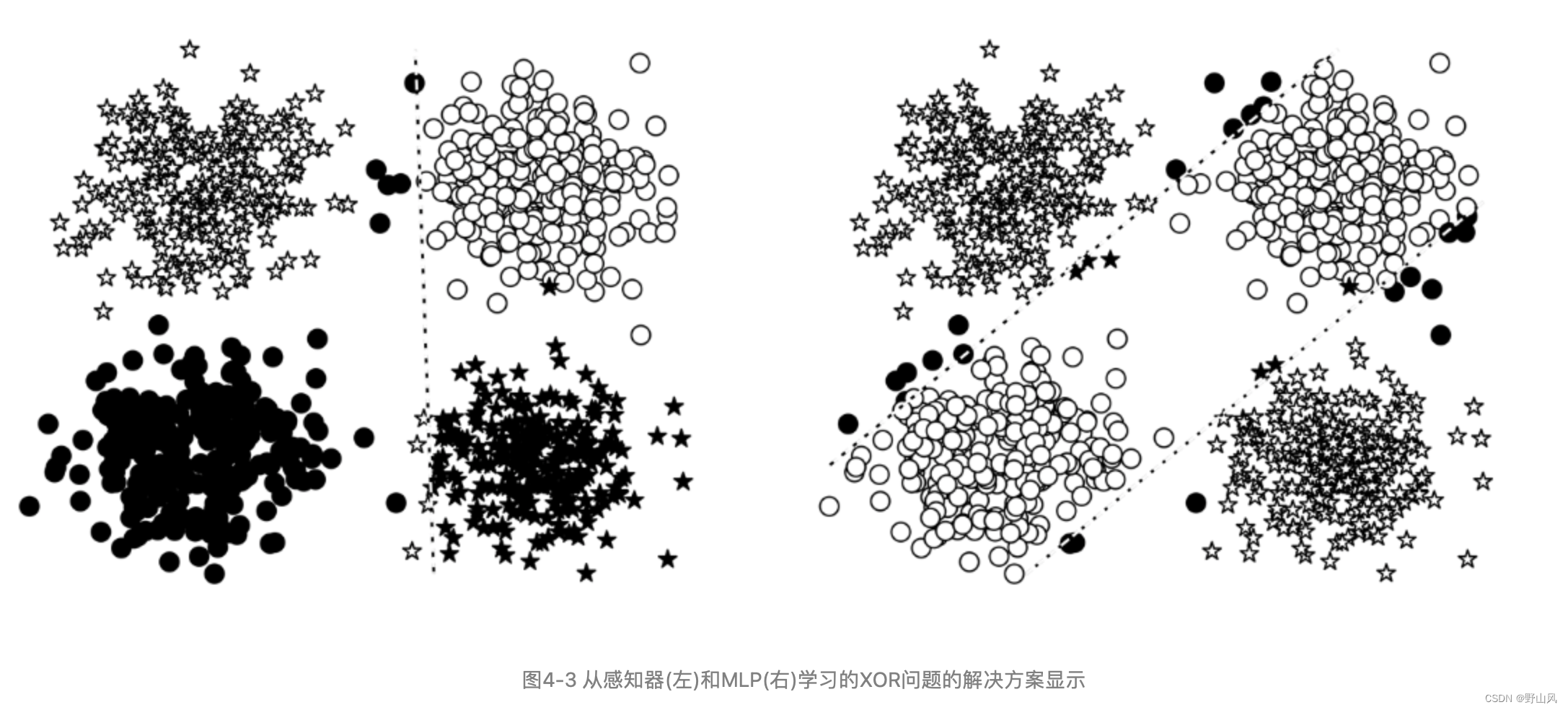
图4-4展示了MLP短语数据处理的可视化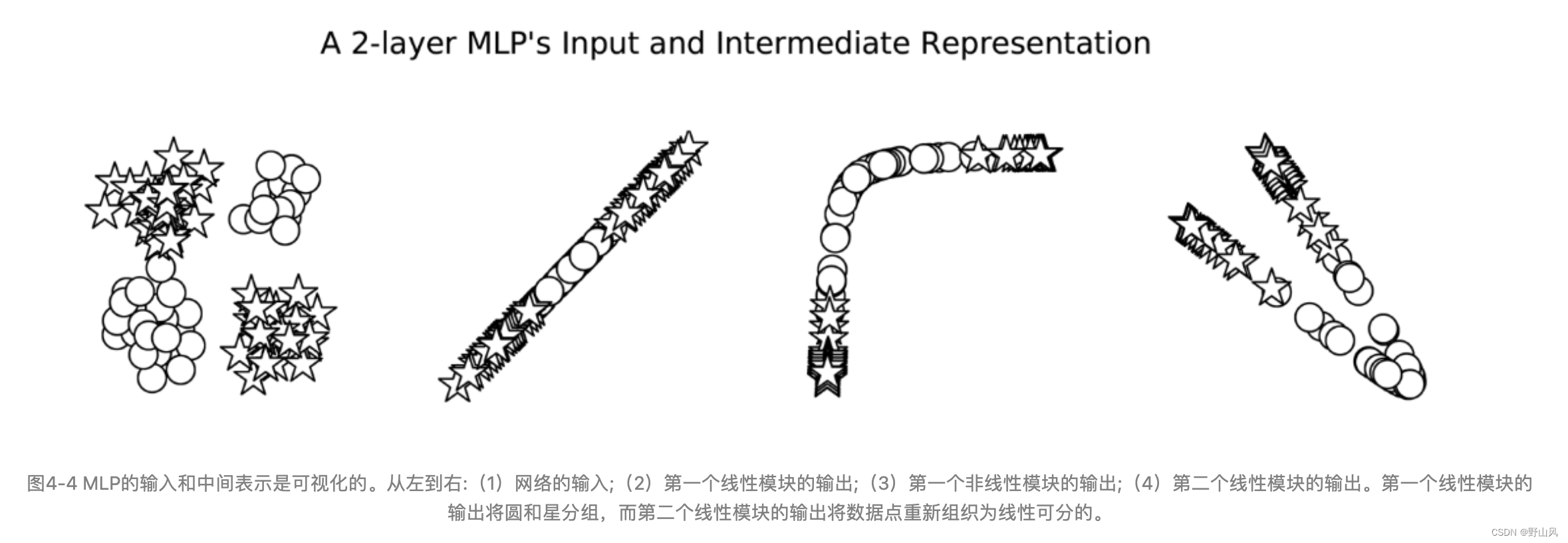
2、代码实现
MLP基础功能实现
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
-
- class MultilayerPerceptron(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
- """
- Args:
- input_dim (int): the size of the input vectors
- hidden_dim (int): the output size of the first Linear layer
- output_dim (int): the output size of the second Linear layer
- """
- #初始化函数,定义模型结构和参数。
- # Args:
- #input_dim (int): 输入向量的维度大小。
- #hidden_dim (int): 第一个线性层的输出维度大小。
- # output_dim (int): 第二个线性层的输出维度大小。
-
- super(MultilayerPerceptron, self).__init__()
- self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
- self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
-
- def forward(self, x_in, apply_softmax=False):
- """The forward pass of the MLP
- Args:
- x_in (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
- x_in.shape should be (batch, input_dim)
- apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
- should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
- Returns:
- the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, output_dim)
- """
- intermediate = F.relu(self.fc1(x_in))#第一个线性层输出
- output = self.fc2(intermediate)#第二个线性层输出
-
- if apply_softmax:
- output = F.softmax(output, dim=1)# 如果需要,应用softmax激活函数
- return output#返回输出张量

在例4-2中,我们实例化了MLP
- batch_size = 2 # 定义批次大小,表示一次输入的样本数量
- input_dim = 3
- hidden_dim = 100
- output_dim = 4
-
- # Initialize model
- mlp = MultilayerPerceptron(input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim)
- print(mlp)
三、实验步骤
1、MLP
创建数据集(one-hot方式)
- class SurnameDataset(Dataset):
- # Implementation is nearly identical to Section 3.5
-
- def __getitem__(self, index):
- # 获取指定索引的行数据
- row = self._target_df.iloc[index]
- # 将姓氏向量化
- surname_vector = \
- self._vectorizer.vectorize(row.surname)
- # 查找国籍在词汇表中的索引
- nationality_index = \
- self._vectorizer.nationality_vocab.lookup_token(row.nationality)
- # 返回包含姓氏向量和国籍索引的字典
- return {'x_surname': surname_vector,
- 'y_nationality': nationality_index}
使用梯度更新模型
- # the training routine is these 5 steps:
-
- # --------------------------------------
- # step 1. zero the gradients,梯度归零
- optimizer.zero_grad()
-
- # step 2. compute the output,计算模型输出
- y_pred = classifier(batch_dict['x_surname'])
-
- # step 3. compute the loss,计算损失
- # 使用损失函数loss_func计算模型预测y_pred与真实标签batch_dict【'y_nationality'】之间的损失值。
- # 将损失值转移到CPU并获取其标量值,以便后续处理。
- # 同时,使用运行平均的方式来更新running_loss,使其更平滑地反映损失的变化。
- loss = loss_func(y_pred, batch_dict['y_nationality'])
- loss_batch = loss.to("cpu").item()
- running_loss += (loss_batch - running_loss) / (batch_index + 1)
- # 步骤4. 使用损失来计算梯度
- # 对损失进行反向传播,计算模型中各参数的梯度。
- # 这些梯度将用于后续的参数更新
- # step 4. use loss to produce gradients
- loss.backward()
-
- # 步骤5. 使用优化器来更新参数(梯度下降)
- # 根据计算出的梯度,使用优化器(如SGD、Adam等)来更新模型的参数。
- # 这是训练过程中实际“学习”发生的步骤,模型通过不断迭代这个过程来逐渐优化其性能。
- # step 5. use optimizer to take gradient step
- optimizer.step()

采用drop-out训练数据
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
-
- class MultilayerPerceptron(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
- """
- Args:
- input_dim (int): the size of the input vectors
- hidden_dim (int): the output size of the first Linear layer
- output_dim (int): the output size of the second Linear layer
- """
- super(MultilayerPerceptron, self).__init__()
- self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim)
- self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim)
-
- def forward(self, x_in, apply_softmax=False):
- """The forward pass of the MLP
- Args:
- x_in (torch.Tensor): an input data tensor.
- x_in.shape should be (batch, input_dim)
- apply_softmax (bool): a flag for the softmax activation
- should be false if used with the Cross Entropy losses
- Returns:
- the resulting tensor. tensor.shape should be (batch, output_dim)
- """
- intermediate = F.relu(self.fc1(x_in))
- output = self.fc2(F.dropout(intermediate, p=0.5))
- #dropout
- if apply_softmax:
- output = F.softmax(output, dim=1)
- return output

2、CNN
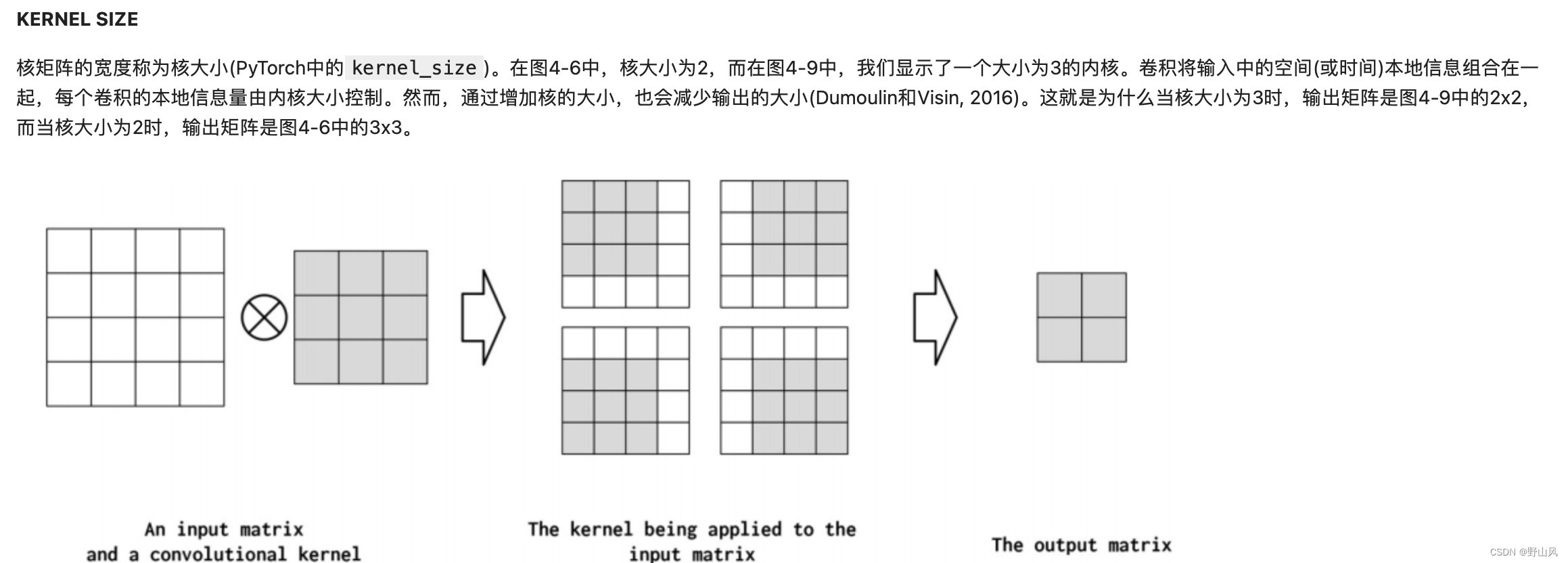
核矩阵
pooling操作
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】
推荐阅读
相关标签


