热门标签
热门文章
- 1MS Access 教程之如何将 MDB 文件转换为 SQLite 数据库_mdb转sqlite
- 2《花雕学AI》ChatGPT Shortcut Chrome 扩展:让生产力和创造力加倍的 ChatGPT 快捷指令库
- 3用通俗易懂的方式讲解:决策树模型及案例(Python 代码)
- 4ubuntu下使用ollama来运行gemma_ubuntu ollama
- 5Bert几个数据集的概念Cola、MRPC、XNLI、MNLI等_mrpc数据集
- 6小程序实现卡片式设计(又叫原子化设计)_小程序css卡片效果
- 7【Pytorch(七)】基于 PyTorch 实现残差神经网络 ResNet_resnet18.pt
- 8【氮化镓】同质GaN垂直PiN二极管的SEB
- 9oracle镜像装载不到软盘中,Oracle ASM无法识别扩展分区的磁盘设备
- 10Bert基础(一)--自注意力机制_bert中transformer编码器
当前位置: article > 正文
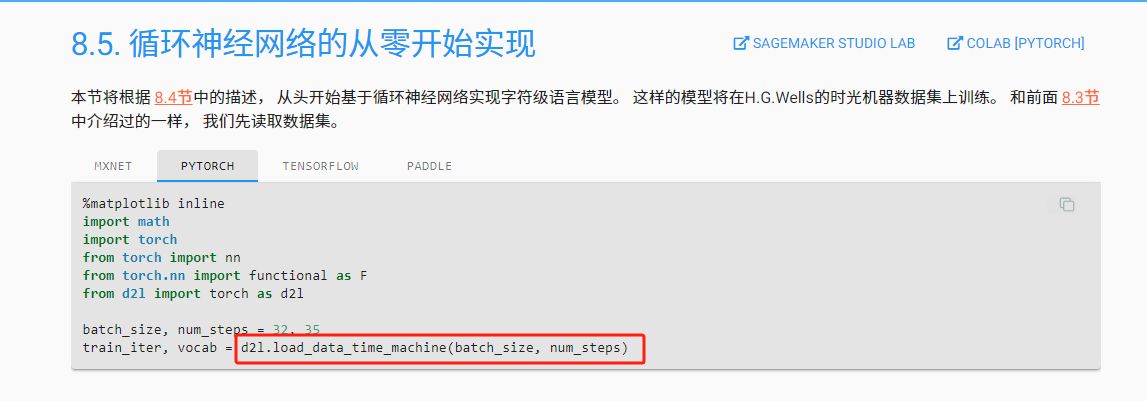
【动手学深度学习-pytorch】8.5 循环神经网络的从零开始实现
作者:盐析白兔 | 2024-03-31 00:10:01
赞
踩
【动手学深度学习-pytorch】8.5 循环神经网络的从零开始实现
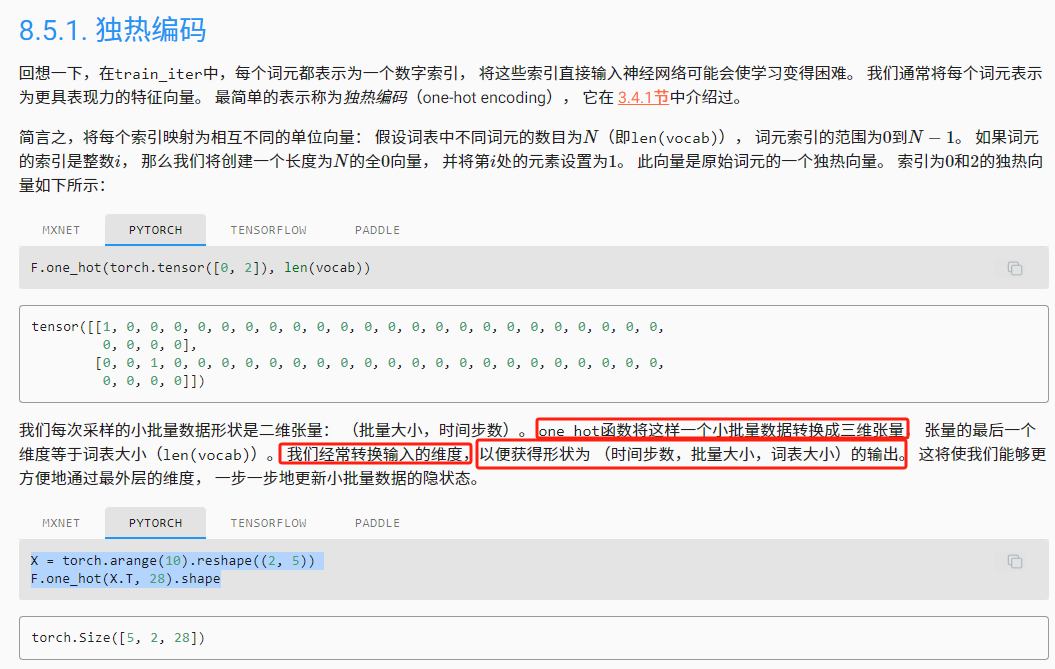
转换输入的维度, 以获得形状为(时间步数,批量大小,词表大小)的输出,这将使我们能够更方便地通过最外层的维度, 一步一步地更新小批量数据的隐状态。
>当训练语言模型时,输入和输出来自相同的词表
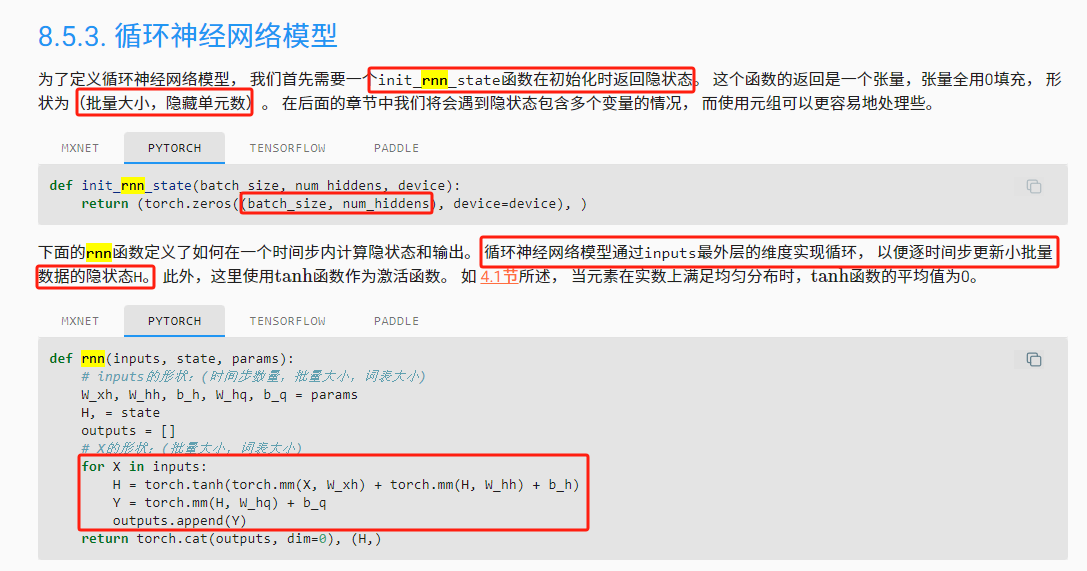
循环神经网络模型通过inputs最外层的维度实现循环, 以便逐时间步更新小批量数据的隐状态H
最外层为时间步,与上面的转置相关
输出 output 和隐状态
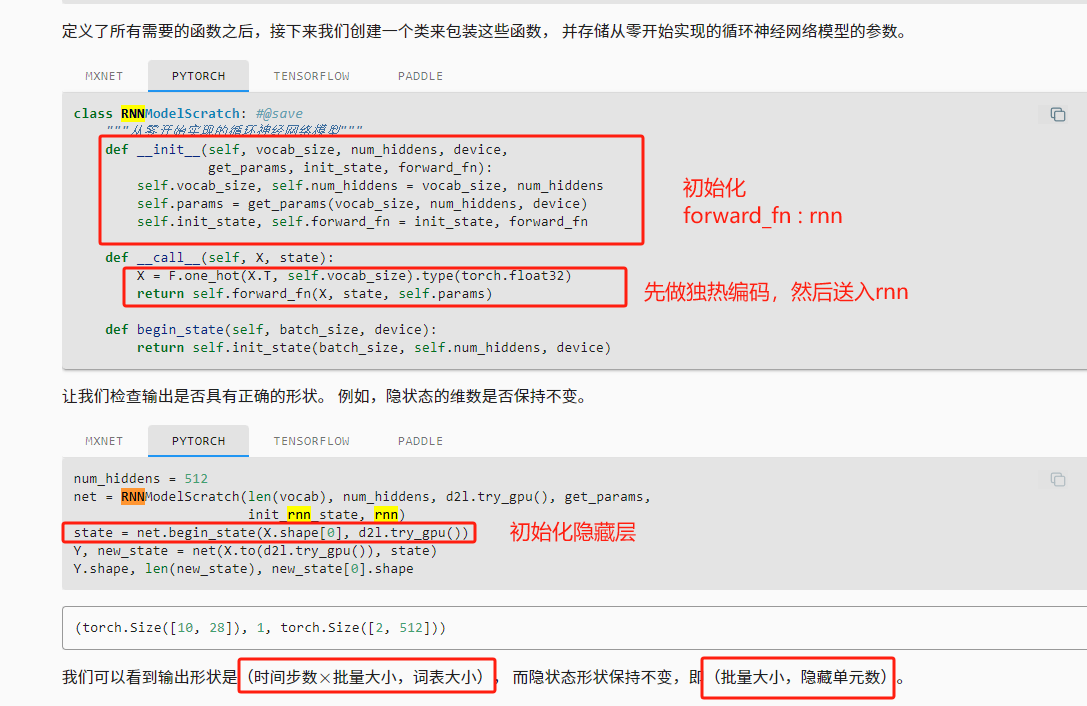
我们可以看到输出形状是(时间步数
批量大小,词表大小), 而隐状态形状保持不变,即(批量大小,隐藏单元数)。
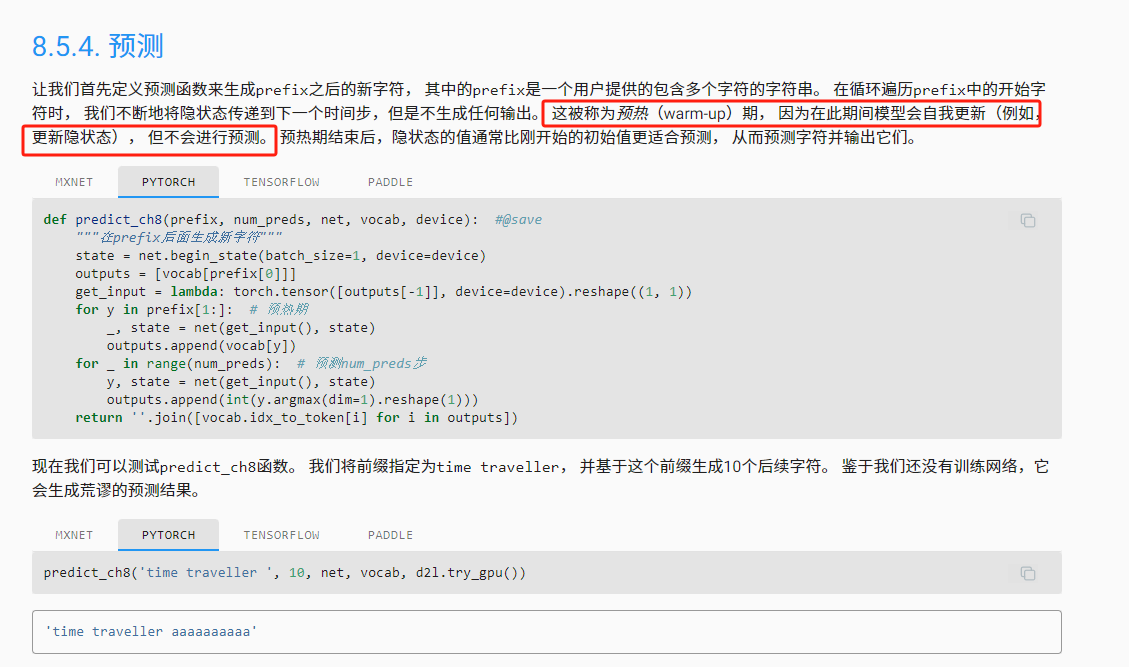
预热(warm-up)期
问题:不用把预测值加到末尾再预测下一个吗?
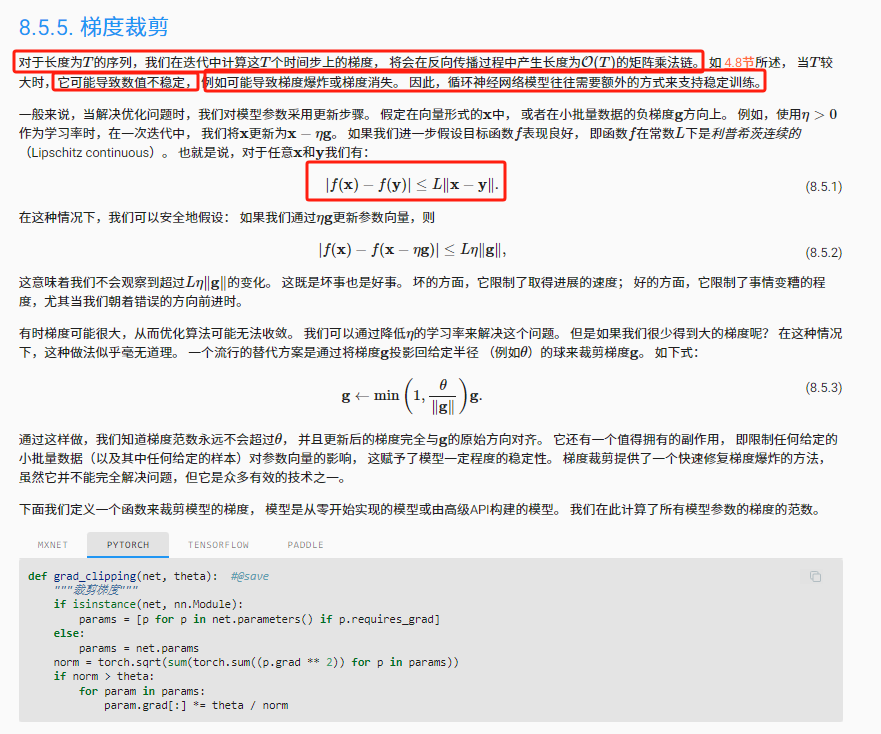
梯度裁剪
为了防止梯度爆炸或者消失,进行梯度剪裁
@save def train_epoch_ch8(net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter): """训练网络一个迭代周期(定义见第8章)""" state, timer = None, d2l.Timer() metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 训练损失之和,词元数量 for X, Y in train_iter: if state is None or use_random_iter: # 在第一次迭代或使用随机抽样时初始化state state = net.begin_state(batch_size=X.shape[0], device=device) else: if isinstance(net, nn.Module) and not isinstance(state, tuple): # state对于nn.GRU是个张量 state.detach_() else: # state对于nn.LSTM或对于我们从零开始实现的模型是个张量 for s in state: s.detach_() y = Y.T.reshape(-1) X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device) y_hat, state = net(X, state) l = loss(y_hat, y.long()).mean() if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer): updater.zero_grad() l.backward() grad_clipping(net, 1) updater.step() else: l.backward() grad_clipping(net, 1) # 因为已经调用了mean函数 updater(batch_size=1) metric.add(l * y.numel(), y.numel()) return math.exp(metric[0] / metric[1]), metric[1] / timer.stop()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
#@save def train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device, use_random_iter=False): """训练模型(定义见第8章)""" loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='perplexity', legend=['train'], xlim=[10, num_epochs]) # 初始化 if isinstance(net, nn.Module): updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr) else: updater = lambda batch_size: d2l.sgd(net.params, lr, batch_size) predict = lambda prefix: predict_ch8(prefix, 50, net, vocab, device) # 训练和预测 for epoch in range(num_epochs): ppl, speed = train_epoch_ch8( net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter) if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0: print(predict('time traveller')) animator.add(epoch + 1, [ppl]) print(f'困惑度 {ppl:.1f}, {speed:.1f} 词元/秒 {str(device)}') print(predict('time traveller')) print(predict('traveller'))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, d2l.try_gpu())
- 1
- 2
小结
-
我们可以训练一个基于循环神经网络的字符级语言模型,根据用户提供的文本的前缀生成后续文本。
-
一个简单的循环神经网络语言模型包括输入编码、循环神经网络模型和输出生成。
-
循环神经网络模型在训练以前需要初始化状态,不过随机抽样和顺序划分使用初始化方法不同。
-
当使用顺序划分时,我们需要分离梯度以减少计算量。
-
在进行任何预测之前,模型通过预热期进行自我更新(例如,获得比初始值更好的隐状态)。
-
梯度裁剪可以防止梯度爆炸,但不能应对梯度消失。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/盐析白兔/article/detail/342429
推荐阅读
相关标签



